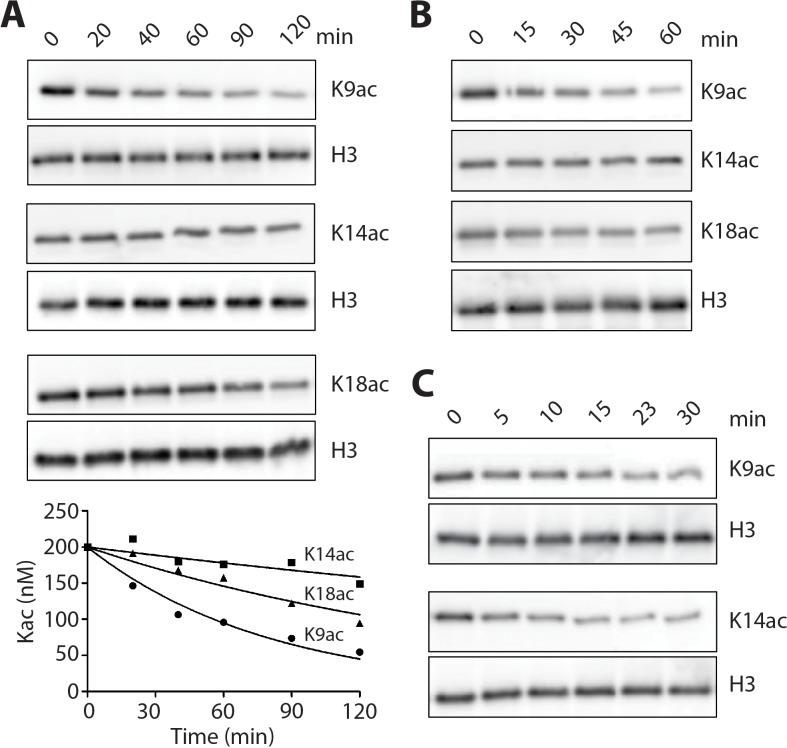
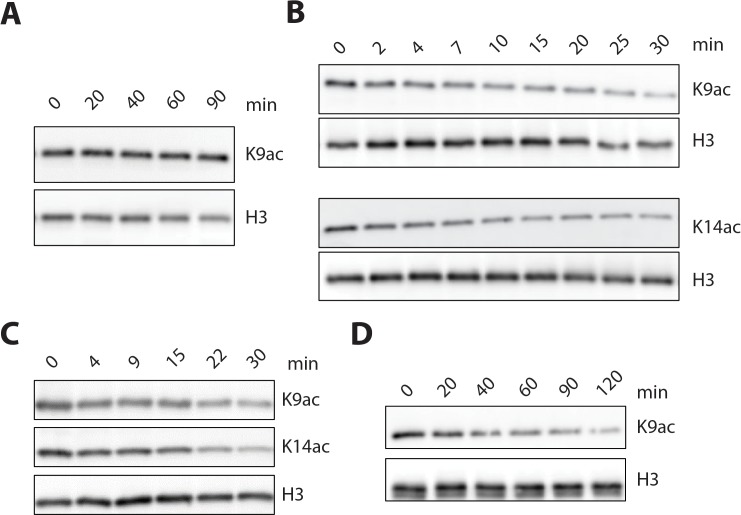
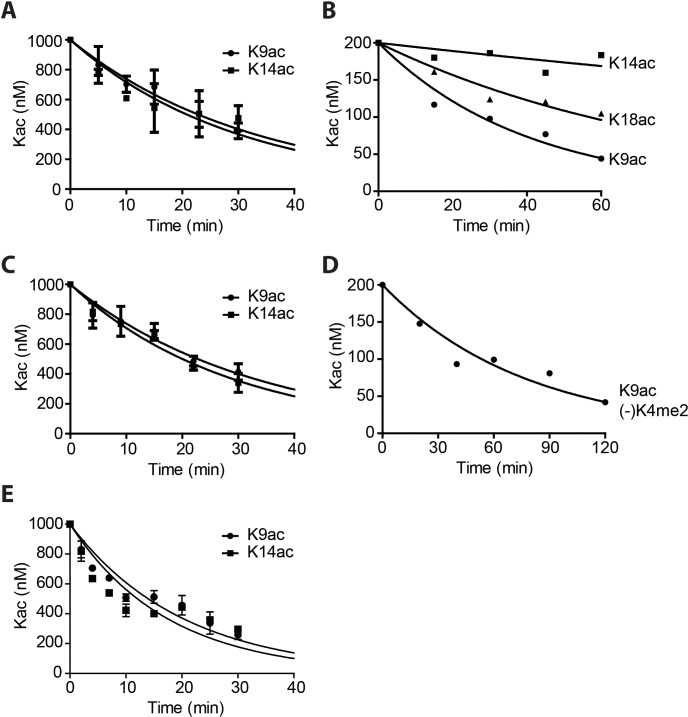
Figure 6. LHC deacetylation of nucleosomes and isolated histone H3 containing Kac.
(A) The deacetylation of 100 nM monoacetylated nucleosomes by 20 nM LHC. The quantified bands of Kac are measured in the plot below. (B) Deacetylation of 200 nM triacetylated H3K9acK14acK18ac nucleosomes by 40 nM LHC. (C) The deacetylation of 1 μM monoacetylated semisynthetic histone H3s possessing either K9ac or K14ac by 1 nM LHC. These assays were performed at three times (n = 3) in A and B and twice (n = 2) in C on separate occasions.