Graphical abstract
Keywords: Neonicotinoid, Tea, Japan, Sri Lanka, Dinotefuran
Highlights
-
•
A method for 7 neonicotinoids and 20 metabolites in tea was developed by LC–MS/MS.
-
•
All seven neonicotinoids and ten of the metabolites were detected in Japanese tea.
-
•
Dinotefuran and dinotefuran-urea were most abundant neonicotinoid and metabolite.
-
•
The estimated MDIs of neonicotinoid insecticides were lower than the ADIs.
Abstract
Tea is one of the world’s most popular beverages due to health promoting effects. Despite these, there have been concerns about the adverse effects of tea contamination by neonicotinoid insecticides. Only a handful of studies on neonicotinoid insecticides in tea have been carried out and this study was therefore performed to determine the concentrations of seven neonicotinoid insecticides and 20 metabolites in Japanese green tea leaves, and black tea leaves from Sri Lanka; and assess the Maximum Daily Intake (MDI) of neonicotinoid insecticides. From the results, the seven parent compounds were detected in Japanese tea leaves and beverages. Dinotefuran (3004 ng/g) was found at the highest level in green tea leaves. Ten of the 20 metabolites were detected in Japanese tea products. Dinotefuran-urea (92%) and thiacloprid-amide (89%) were most frequently detected in Japanese tea leaves. Clothianidin-urea (100 ng/g) was found at the highest level in green tea leaves. Neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites were not detected in Sri Lankan black tea leaves. The concentrations and MDI of neonicotinoid insecticides in tea leaves were below the Maximum Residual Levels (MRLs) and Acceptable Daily Intakes (ADIs), respectively.
1. Introduction
Neonicotinoid insecticides are among the most rapidly adopted insecticides introduced to the market since the introduction of pyrethroid insecticides. The current market share of neonicotinoid insecticides in the world is over £600 million per year [1]. Imidacloprid was the biggest selling insecticide worldwide, followed by acetamiprid, nitenpyram, thiacloprid, thiamethoxam, clothianidin, and dinotefuran, and the former six are chlorinated compounds [1]. Neonicotinoid insecticides are used at various stages of cultivation and post-harvest storage. Since 1993, many tons have entered the Japanese market, and they have been widely used on a variety of crops. In 2015, large quantities of various neonicotinoid insecticides, including acetamiprid (51.5 t), thiamethoxam (49.2 t), clothianidin (75.6 t), imidacloprid (66.0 t), thiacloprid (12.7 t), nitenpyram (6.5 t), and dinotefuran (167 t), were shipped to Japan [2].
Tea is one of the most widely consumed non-alcoholic beverages globally [3] and it contains multiple health-promoting compounds, including vitamins, caffeine, catechin, and other polyphenols [4]. Unfermented green tea and semi-fermented tea are commonly consumed in East Asian countries, while fermented black tea is common in the West [5]. Epidemiological studies have shown the beneficial health effects of tea consumption [6]. However, the consumption of tea may represent a potential source of human exposure to toxicants, because of the high levels of insecticides in tea cultivation [7]. For example, neonicotinoid insecticides, such as imidacloprid, thiamethoxam, and acetamiprid, are regularly used in tea cultivation to control pests, such as Empoasca vitis (false-eye leafhopper) [[8], [9], [10], [11]].
Neonicotinoid insecticides act as modulators at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) for mammals and insects [12]. In addition, some metabolites of neonicotinoid insecticides, especially N-unsubstituted imines, i.e., desnitro- or descyano-metabolites, have greater IC50 values on mammalian α4β2 nAChR than Drosophila nAChR, e.g., 4.6 nM and 2600 nM for imidacloprid and 1500 nM and 8.2 nM for N-desnitro-imidacloprid, respectively [13]. These results indicated that it is necessary to screen for neonicotinoid metabolites as well as their parent compounds. Several studies in Japan have suggested that tea is one of the major sources of human exposure to neonicotinoid insecticides in the Japanese population [[14], [15], [16], [17], [18]]. However, there have been limited studies to assess the levels of parent compounds and metabolites in tea leaves and tea beverages, with the exception of one monitoring survey that indicated residual levels of approximately 0.5 ppm of clothianidin, imidacloprid, and thiamethoxam in domestic tea leaves in 2012 [19].
The present study was performed to quantify neonicotinoid insecticides, i.e., acetamiprid, clothianidin, dinotefuran, imidacloprid, nitenpyram, thiacloprid, and thiamethoxam, and 20 neonicotinoid metabolites (Table 1) in tea leaves and tea beverages. As there are only a few standards available for neonicotinoid metabolites, we synthesized most of the neonicotinoid metabolites and developed a quantitative method using solid-phase extraction (SPE) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI/MS/MS). In addition, we compared the intakes of neonicotinoid insecticides through Japanese green tea with the current Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) in Japan.
Table 1.
Target neonicotinoids and their metabolites.
| Neonicotinoids | Recovery rate (%) | LOQ (ng/ml-bottled tea beverage) | LOQ (ng/g-tea leaves) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetamiprid | 80.2 ± 2.9 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| N-desmethyl-Acetamiprid | 87.6 ± 5.4 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| N-acetyl-Acetamiprid | 33.2 ± 23.4 | 0.125 | 3.33 | |
| N-acetyl-desmethyl-Acetamiprid | 78.2 ± 16.8 | 1.25 | 33.33 | |
| N-descyano-Acetamiprid | 81.0 ± 3.7 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| Clothianidin | 91.8 ± 3.7 | 0.125 | 3.33 | |
| N-desmethyl-Clothianidin | 79.7 ± 5.2 | 0.5 | 13.33 | |
| N-desmethyl-Clothianidin urea | 73.6 ± 3.2 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| N-desnitro-Clothianidin | 54.1 ± 2.7 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| Clothianidin urea | 84.0 ± 3.1 | 0.125 | 3.33 | |
| N-desmethyl-desnitro-Clothianidin | 41.7 ± 2.5 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| Dinotefuran | 92.6 ± 2.8 | 0.125 | 3.33 | |
| N-desmethyl-Dinotefuran | 87.1 ± 6.1 | 0.125 | 3.33 | |
| Dinotefuran-urea | 75.2 ± 9.3 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| Imidacloprid | 87.0 ± 2.7 | 0.5 | 13.33 | |
| Hydroxy-Imidacloprid | 78.2 ± 9.7 | 1.25 | 33.33 | |
| N-desnitro-Imidacloprid | 85.7 ± 5.5 | 1.25 | 33.33 | |
| Nitenpyram | 88.6 ± 4.6 | 0.5 | 13.33 | |
| N-desmethyl-Nitenpyram | 100.6 ± 31.3 | 0.5 | 13.33 | |
| CPMA | 47.9 ± 10.2 | 0.5 | 13.33 | |
| CPMF | 84.8 ± 10.3 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| CPF | 32.9 ± 20.3 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| Thiacloprid | 92.9 ± 1.8 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| Thiacloprid-amide | 94.0 ± 5.6 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| N-descyano-dehydro-Thiacloprid | 66.7 ± 11.7 | 0.05 | 1.33 | |
| Thiamethoxam | 116.7 ± 7.9 | 0.125 | 3.33 | |
| N-desmethyl-Thiamethoxam | 70.2 ± 10.3 | 0.5 | 13.33 | |
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemicals
Acetamiprid, dinotefuran, imidacloprid, and thiacloprid were purchased from Kanto Chemical (Tokyo, Japan). Clothianidin and N-desmethyl-thiamethoxam were purchased from Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland). Nitenpyram, CPMA, CPMF, and CPF were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries (Osaka, Japan). Clothianidin-d3, dinotefuran-d3, imidacloprid-d4, thiacloprid-d4, thiamethoxam-d4, N-desmethyl-acetamiprid and N-desnitro-imidacloprid were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Hydroxy-imidacloprid was purchased from Hypha Discovery (Uxbridge, UK). Acetamiprid-d6 and nitenpyram-d3 were purchased from Hayashi Junyaku (Osaka, Japan). Thiamethoxam was purchased from Dr. Ehrenstorfer (Augsburg, Germany). Other metabolites (N-acetyl-acetamiprid, N-acetyl-desmethyl-acetamiprid, N-descyano-acetamiprid, N-desmethyl-clothianidin, N-desmethyl-clothianidin urea, N-desnitro-clothianidin, clothianidin urea, N-desmethyl-desnitro-clothianidin, N-desmethyl-dinotefuran, dinotefuran-urea, N-desmethyl-nitenpyram, thiacloprid-amide, N-descyano-dehydro-thiacloprid) were synthesized at Toho University (Supplement).
2.1.2. Tea leaves and beverages
From January to May 2016, green tea leaves labeled “domestically grown” of different brands and manufacturers were purchased from randomly selected grocery stores in Japan (n = 39), and black tea leaves were purchased from grocery stores in Sri Lanka (n = 30). In addition, bottled green tea beverages (these are ready-to-drink green teas stored in bottles) were purchased from convenience stores in Japan (n = 9). The tea leaves and bottled tea were all produced from the respective countries, but the samples were of different brands and manufacturers, and were produced between 2015 and May 2016. All were stored in a refrigerator keep under 5 centigrade until analysis was performed.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Extraction of neonicotinoids from tea leaves
Tea leaves were ground using a mortar and pestle, and 1.5 g of finely ground tea leaves were placed in 50-mL centrifuge tubes (Corning Inc., Corning, NY). After adding the internal standards to the leaves (50 μL of 100 ppb solution), water (40 mL) at 25 °C was added. The content was vortex-mixed for 10 min and centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min. Samples of 5 mL of the supernatant were separated and used for the next extraction and purification step. Tea was loaded onto a pre-conditioned (2 mL each of methanol and distilled water) Presep RPP 60 mg cartridge (Wako Pure Chemical Industries). Conditioning of ENVIcarb/PSA (500 mg/300 mg) (Sigma-Aldrich) was then carried out with 10 mL of acetone. The Presep RPP and ENVIcarb/PSA cartridges were connected in series, and analytes were eluted with 8 mL of dichloromethane:acetonitrile (2:8 v:v) solution. After concentrating analytes with a centrifugal concentrator (CVE-200D with UT-2000; EYELA, Tokyo, Japan) at 60 °C for 1 h, the samples were reconstituted with 100 μL of 3% ethanol aqueous solution and transferred into vials for analysis. Seven neonicotinoid insecticides and 20 metabolites (Table 1) were analyzed simultaneously in each sample. Results of neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites in tea leaves were expressed in ng/g w/w.
2.2.2. Extraction of neonicotinoids from bottled green tea beverages
Samples of 25 mL of bottled tea beverages were spiked with 5 ng (50 μL of 100 ppb solution) of internal standards; and the mixture were loaded onto pre-conditioned (2 mL each of methanol and distilled water) Presep RPP 60 mg cartridges (Wako Pure Chemical Industries). Conditioning of ENVIcarb/PSA (500 mg/300 mg) (Sigma-Aldrich) was then performed with 10 mL of acetone. The Presep RPP and ENVIcarb/PSA cartridges were connected in series, and analytes were eluted with 8 mL of dichloromethane:acetonitrile (2:8 v:v) solution. After concentrating analytes with a centrifugal concentrator (CVE-200D with UT-2000; EYELA) at 60 °C for 1 h, the samples were reconstituted with 100 μL of 3% methanol aqueous solution and transferred into vials for analysis. The levels of neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites in bottled tea beverages were expressed in ng/mL.
LC-ESI/MS/MS (Shimadzu 20 A series with LCMS8040; Shimadzu Co., Kyoto, Japan) equipped with RSpak DE-213 (2 mm ID × 150 mm) (Showa Denko, Tokyo, Japan) was used for quantitative analysis of samples. Mobile phases for HPLC analysis were 0.1% formic acid + 10 mM acetic acid water solution (A) and 0.1% formic acid + 10 mM acetic acid methanol solution (B). The gradient was programmed as follows: t = 0–2 minutes: 20% B, t = 11 min: 95% B, t = 11–13 minutes: 95% B. The column oven temperature and the flow rate were 45 °C and 0.4 mL/min, respectively. Detection of target compounds was performed by multiple-reaction monitoring (MRM) in positive ionization mode.
2.3. Quality control and quality assurance
Samples were spiked with a mixture of six deuterium-labeled neonicotinoids as internal standards prior to sample preparation and extraction. Quantification was performed using the internal standard method. Calibration points were set at 5 points and average coefficients of determination ( r2) for the calibration curves were ≥0.995. The analytical methods were checked for precision and accuracy. Limits of quantification (LOQs) were calculated based on 10 × SD/S, where SD is the standard deviation of the response of seven replicate standard solution measurements and S is the slope of the calibration curve. Recovery efficiencies and LOQs (ng/mL) of the analytes are listed in Table 1.
2.4. Maximum daily intake of neonicotinoids through green tea leaves
The maximum daily intake of neonicotinoid insecticides through consumption of green tea leaves (MDIgt) was calculated based on the following equation:
where Cmax is the maximum concentration of neonicotinoid insecticides in tea leaves in this study (mg/g w/w); LP is the 97.5th percentile of daily consumption of tea leaves among Japanese adults and children (1–6 years old), 35.7 g and 15.3 g were assumed, respectively (Japanese government data); and Bw is the average body weight (kg), 57.0 kg (adults) and 16.2 kg (children) were assumed (Japanese government data) in this study.
2.5. Data analysis
Data analysis was performed using JMP statistical software v. 10 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). Concentrations of neonicotinoid insecticides and their metabolites below their respective LOQs were replaced with a value of LOQ/2. Student’s t test was used to compare the concentrations of neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites in Japanese green tea leaves, and the differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Quantification method for neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites in tea leaves and bottled green tea beverages
A method to quantify seven neonicotinoid insecticides and 20 metabolites simultaneously in tea leaves was developed by LC-ESI/MS/MS and SPE. The LOQs were satisfactory and ranged from 1.33 to 33.3 ng/g in tea leaves (Table 1). Recovery efficiencies were satisfactory and greater than 80% for all parent compounds examined. Water at room temperature was used as the extraction solvent in this study because neonicotinoid insecticides have considerable water solubility. We also attempted hot water extraction at 90 °C, but this led to high background signals caused by the wax components in tea leaves and higher LOQs for most of the analytes (data not shown). The high recovery and low LOQs confirmed that water is a good solvent for neonicotinoid insecticide extraction. Recovery efficiencies were greater than 50% for all metabolites except N-acetyl-acetamiprid, N-desmethyl-desnitro-clothianidin, CPMA, and CPF. The low recovery rates for these compounds could be due to low retention of metabolites in the stationary phase during SPE or the degraded during the extraction and purification process. Despite the low recovery rates of some metabolites, N-acetyl-acetamiprid and CPMA were found in Japanese green tea leaves, suggesting that the developed method was robust and applicable for determination of neonicotinoid metabolites.
3.1.1. Neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites in green tea leaves
All seven neonicotinoid insecticides and nine of the 20 neonicotinoid metabolites examined were detected in Japanese tea leaves (Table 2, Table 3). The detection frequency and maximum concentration of neonicotinoid insecticides were highest for dinotefuran (100%, 3004 ng/g) with dinotefuran-urea (87%, 77.1 ng/g) and N-dm-dinotefuran (10%, 9.4 ng/g), followed by imidacloprid (92%, 139 ng/g); thiacloprid (79%, 910 ng/g) with thiacloprid-amide (82%, 2.4 ng/g) and N-dc-dh-thiacloprid (3%, 6.1 ng/g); thiamethoxam (79%, 650 ng/g); clothianidin (74%, 233 ng/g) with N-dm-clothianidin-urea (56%, 6.1 ng/g), clothianidin-urea (51%, 6.1 ng/g), N-dn-clothianidin (21%, 7.3 ng/g); acetamiprid (67%, 472 ng/g) with N-dm-acetamiprid (39%, 52.6 ng/g) and N-acetyl-acetamiprid (8%, 4.8 ng/g); and nitenpyram (3%, 54 ng/g).
Table 2.
Concentrations (ng/g ww) and the % frequencies of detection of neonicotinoids in Japanese tea leaves and Japanese bottled green tea beverage.
| Japanese tea leaves |
Japanese bottled green tea beverage# |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freq (%) | Min | 25th | 50th | 75th | Max | Freq (%) | 25th | 50th | 75th | Max | |
| Acetamiprid | 67 | <LOQ | <LOD | 2 | 4 | 472 | 78 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 2.01 |
| Clothianidin | 74 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 233 | 100 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 1.01 | 2.08 | |
| Dinotefuran | 100 | 52 | 274 | 581 | 3004 | 100 | 3.09 | 17.51 | 23.30 | 59.00 | |
| Imidacloprid | 92 | 4 | 6 | 13 | 139 | 78 | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 1.91 | |
| Nitenpyram | 3 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 54 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| Thiacloprid | 79 | 2 | 7 | 15 | 910 | 100 | 0.22 | 0.65 | 0.81 | 2.35 | |
| Thiamethoxam | 79 | 5 | 13 | 27 | 650 | 100 | 1.45 | 1.71 | 2.50 | 5.53 | |
Freq (%): Frequency (%); Max: Maximum; <LOQ: below detection quantification;#: indicates concentrations expressed in ng/mL.
Table 3.
Concentrations (ng/g ww) of neonicotinoids metabolites in tea from Japan.
| Japanese tea leaves |
Japanese bottled tea# |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freq(%) | 25th | 50th | 75th | Max | Freq(%) | 25th | 50th | 75th | Max | |
| N-dm-Acetamiprid | 38.5 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 1.5 | 52.6 | 11.1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.5 |
| N-acetyl-Acetamiprid | 7.7 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 4.8 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| N-acetyl-dm-Acetamiprid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| N'-dc-Acetamiprid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| N-dm-Clothianidin | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| N-dm-Clothianidin urea | 56.4 | <LOQ | 2.5 | 3.2 | 6.1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| N'-dn-Clothianidin | 20.5 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 7.3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| Clothianidin urea | 51.3 | <LOQ | 0.6 | 6.4 | 100.0 | 66.7 | <LOQ | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.7 |
| dm-dn-Clothianidin | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| dm-Dinotefuran | 10.3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 9.4 | 11.1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.1 |
| Dinotefuran-urea | 87.2 | 1.5 | 4.3 | 14.4 | 77.1 | 77.8 | <LOQ | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| Hydroxy-Imidacloprid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| dn-Imidacloprid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| dm-Nitenpyram | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| CPMA | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 11.1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.2 |
| CPMF | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| CPF | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| Thiacloprid-amide | 82.1 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 42.6 | 88.9 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| dc-dh-Thiacloprid | 2.6 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 6.1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| dm-Thiamethoxam | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
More than one type of neonicotinoid insecticide and metabolites were simultaneously detected in Japanese tea leaves. In addition to the 100% detection of dinotefuran, imidacloprid, thiamethoxam/clothianidin, thiacloprid, and acetamiprid are also commonly used, as well as nitenpyram. Concentrations of neonicotinoid insecticides in tea leaves from Japan were below the Maximum Residual Levels (MRL) recommended by Japan (Table 4). However, there could be health concerns due to the high intake of tea in the Japanese population because human health risk assessment does not only depend on the concentration of the target chemical in food, but also on the consumption rate [20]. The MRL set in Japan for fruits, tea leaves were higher than recommended levels from other countries (Table 4).
Table 4.
Maximum Residual Limits (MRLs) (mg/kg) of neonicotinoids in tea leaves.
| Neonicotinoids | Japan | US | CODEX | EU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetamiprid | 30 | 50** | - | 0.1* |
| Clothianidin | 50 | 70**** | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Dinotefuran | 25 | - | - | - |
| Imidacloprid | 10 | - | - | 0.05* |
| Nitenpyram | 10 | - | - | - |
| Thiacloprid | 30 | - | - | 10 |
| Thiamethoxam | 20 | 20*** | 20 | 20 |
indicates lower limit of analytical determination.
There are no US regulations as of February 10, 2010, for the use of acetamiprid on dried tea leaves.
There are no US regulations as of March 27, 2013.
No US regulations.
This is the first report in which various neonicotinoid metabolites were detected in agricultural products purchased from the market. The metabolism of neonicotinoid insecticides in tea leaves involves oxidation (e.g., N-demethylation), reduction (e.g., conversion from N-nitro to imine), hydrolysis (e.g., conversion from cyano to amide), dehydrogenation, and N-acetylation. The detection of clothianidin was accompanied by that of thiamethoxam in all cases, and the detection of clothianidin-urea was significantly correlated with those of clothianidin and thiamethoxam (p < 0.0001). The significant correlations (p < 0.0001) of clothianidin, clothianidin-urea, and thiamethoxam supported the metabolic conversion of thiamethoxam to clothianidin in tea leaves. Additionally, the relatively high level of detection of clothianidin-urea may be attributable to direct metabolic transformation of thiamethoxam, which is hydrolyzed to clothianidin.
Among the metabolites detected in this study, N-dm-acetamiprid has nicotinic properties on nAChRs, and is toxic for humans (Marfo 2016). N-desnitro-clothianidin and N-descyano-dehydro-thiacloprid are also toxicologically relevant because this compound might have nicotinic properties on nAChRs, and is more toxic to mammalian nAChRs than those of insects. The toxicological evaluation of these metabolites has not been fully investigated.
In addition, thiacloprid-amide does not have nicotinic properties, but can undergo hydrolysis to yield N-descyano-thiacloprid, which also has nicotinic properties and is extremely toxic for mammals, its oral LD50 for mice is 1.1 mg/kg BW [21]. The fate of thiacloprid-amide after consumption of tea beverages is unknown. Further comprehensive studies are required to determine the effects of these metabolites on human health.
3.1.2. Neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites in bottled green tea beverages
Six of seven neonicotinoid insecticides were detected in Japanese bottled tea beverages (Table 2). Nitenpyram was not detected, but its metabolite, CPMA, was detected in these samples. More than one type of neonicotinoid insecticide and their metabolites were simultaneously detected in Japanese tea leaves. The order of detection frequency and maximum concentration of neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites were dinotefuran (100%, 59.0 ng/mL) with dinotefuran-urea (77.8%, 0.6 ng/mL) and N-dm-dinotefuran (11.1%, 0.1 ng/mL); thiacloprid (100%, 2.35 ng/mL) with thiacloprid-amide (88.9%, 0.2 ng/mL); thiamethoxam (100%, 5.53 ng/mL) with clothianidin (100%, 2.08 ng/mL), clothianidin-urea (66.7%, 1.7 ng/mL); followed by imidacloprid (78%, 1.91 ng/mL); acetamiprid (78%, 2.01 ng/mL) with N-dm-acetamiprid (11%, 0.5 ng/mL); and CPMA (11.1%, 0.2 ng/mL) (Table 2, Table 3).
The 50th percentile concentrations were highest for dinotefuran (17.5 ng/mL), followed by thiamethoxam (1.71 ng/mL), thiacloprid (0.65 ng/mL), clothianidin (0.59 ng/mL), imidacloprid (0.43 ng/mL), and acetamiprid (0.04 ng/mL) (Table 2).
3.1.3. Neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites in tea leaves in Sri Lanka
The levels of all neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites in tea leaves from Sri Lanka were below the respective LOQs (data not shown). The higher concentrations of neonicotinoids detected in Japanese green tea leaves compared to those from Sri Lanka could be due to high and widespread use of neonicotinoid insecticides on crops in Japan.
3.2. Assessment of maximum dietary intake of neonicotinoid insecticides through green tea leaves in the Japanese population
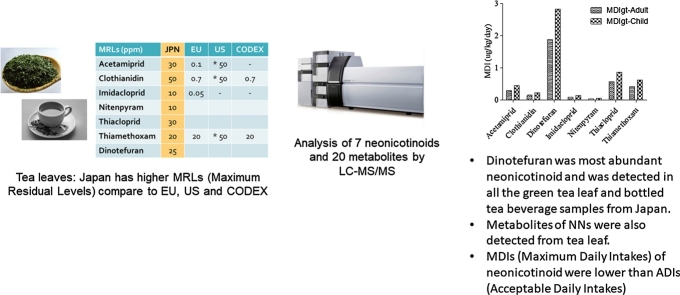
The MDIgts of neonicotinoids obtained from this study were compared with the current Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) proposed by the Food Safety Commission of Japan (Table 5). The MDIgt rates in adults and children were highest for thiacloprid (4.75%, 7.16%, respectively), followed by thiamethoxam (2.26%, 3.41%, respectively), dinotefuran (0.86, 1.29%, respectively), and acetamiprid (0.42, 0.63, respectively) (Table 5). Children are most vulnerable to the health effects of neonicotinoid insecticides as they could be exposed more to contaminated soil while playing on the ground and they also have higher dietary consumption rates than adults. Moreover, the developmental neurotoxicities of neonicotinoid insecticides and their metabolites have not been established.
Table 5.
: Daily intakes (μg/kg/day) of neonicotinoid through consumption of Japanese tea leaves.
| ADI | MDIgt-Adult |
MDIgt-Child |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neonicotinoids | μg/kg/day | μg/kg/day | %ADI | μg/kg/day | %ADI |
| Acetamiprid | 71 | 0.296 | 0.42 | 0.446 | 0.63 |
| Clothianidin | 97 | 0.146 | 0.15 | 0.220 | 0.23 |
| Dinotefuran | 220 | 1.88 | 0.86 | 2.84 | 1.29 |
| Imidacloprid | 57 | 0.087 | 0.15 | 0.131 | 0.23 |
| Nitenpyram | 530 | 0.034 | 0.05 | 0.051 | 0.07 |
| Thiacloprid | 12 | 0.570 | 4.75 | 0.859 | 7.16 |
| Thiamethoxam | 18 | 0.407 | 2.26 | 0.614 | 3.41 |
ADI: Acceptable Daily Intake in mg/kg/day; MDIgt: Maximum Daily Intake from green tea.
The toxicological properties of some neonicotinoid metabolites are unknown and the effects of prolonged exposure to neonicotinoid insecticides on human health and neurodevelopment are still not clear. Therefore, to clarify the risks and safety of neonicotinoid insecticide use for food production as well as other uses, toxicological studies of unknown neonicotinoid metabolites, and epidemiological studies of environmental exposure to neonicotinoid insecticides and metabolites in large populations are required.
4. Conclusions
Seven neonicotinoid insecticides and 10 of 20 metabolites were detected in Japanese green tea leaves and tea beverages, while none was detected in Sri Lankan black tea leaves. The concentration ranges of neonicotinoid insecticides and their metabolites were comparable in bottled green tea beverages and in brewed green tea leaves from Japan. Dinotefuran was the most abundant neonicotinoid insecticide and was detected in all of the green tea leaf and bottled tea beverage samples from Japan. Dinotefuran-urea was the most abundant metabolite detected in Japanese green tea leaves, while thiacloprid-amide was most abundant in bottled tea beverages. Although the estimated MDIs of neonicotinoid insecticides were lower than the ADIs, there may be concerns regarding their health effects upon prolonged and excessive consumption.
Transparency document
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan awarded to M. Ishizuka (No. 16H0177906, 16K1503406) and Y. Ikenaka (No. 15H0282505, 15K1221305 and 17K2003807), S.M.M. Nakayama (16K16197), H. Mizukawa (15K1613205), K. Taira (15K0055915), and T. Kawakami (15H0512017). We are also grateful to The Soroptimist Japan Foundation, The Sumitomo foundation, and Yamada research grant for financial support. We thank Ms. Mio Yagihashi and Ms. Nagisa Hirano for technical assistance.
References
- 1.Di Muccio A., Fidente P., Barbini D.A., Dommarco R., Seccia S., Morrica P. Application of solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry to the determination of neonicotinoid pesticide residues in fruit and vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A. 2006;1108:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2005.12.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.PPSD&PPD . Japan Plant Protection Association; Tokyo: 2013. . Plant Products Safety Division & Plant Protection Division. Food Safety and Consumer Affairs Bureau, Ministry of Agriculture, Firestry and Fisheries. Noyaku Yoran 2012. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wang L., Gong L.-H., Chen C.-J., Han H.-B., Li H.-H. Column-chromatographic extraction and separation of polyphenols, caffeine and theanine from green tea. Food Chem. 2012;131:1539–1545. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Carloni P., Tiano L., Padella L., Bacchetti T., Customu C., Kay A., Damiani E. Antioxidant activity of white, green and black tea obtained from the same tea cultivar. Food Res. Int. 2013;53:900–908. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hamer M. The beneficial effects of tea on immune function and inflammation: a review of evidence from in vitro, animal, and human research. Nutr. Res. 2007;27:373–379. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Saito E., Inoue M., Sawada N., Shimazu T., Yamaji T., Iwasaki M., Sasazuki S., Noda M., Iso H., Tsugane S. Association of green tea consumption with mortality due to all causes and major causes of death in a Japanese population: the Japan public health center-based prospective study (JPHC study) Ann. Epidemiol. 2015;25:512–518. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.03.007. e513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Deng Z., Tao B., Li X. Effect of tea on the living time of musca domesticas and the anti-stress of KM rats. J. Nanchang Univ. 1997;2:69–72. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen Z. EU’S new MRLS standards of pesticides in tea. Chin. Tea. 2009;7:17–18. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gupta M., Shanker A. Bioefficacy of imidacloprid and acetamiprid against Nippaecoccus vastator and Toxoptera aurantii in tea. Appl. Entomol. 2007;21:75–78. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shanker A., Sood C., Kumar V., Ravindranath S. Insect and mite pests attacking tea plantation of kangra Valley and their management. Indian J. Entomol. 2002;64:53–57. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tomizawa M., Casida J.E. Selective toxicity of neonicotinoids attributable to specificity of insect and mammalian nicotinic receptors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003;48:339–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.48.091801.112731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ihara M., Matsuda K., Otake M., Kuwamura M., Shimomura M., Komai K., Akamatsu M., Raymond V., Sattelle D.B. Diverse actions of neonicotinoids on chicken α7, α4β2 and Drosophila–chicken SADβ2 and ALSβ2 hybrid nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Neuropharmacology. 2003;45:133–144. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(03)00134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sheets L.P., Li A.A., Minnema D.J., Collier R.H., Creek M.R., Peffer R.C. A critical review of neonicotinoid insecticides for developmental neurotoxicity. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016;46:153–190. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2015.1090948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Marfo J.T., Fujioka K., Ikenaka Y., Nakayama S.M., Mizukawa H., Aoyama Y., Ishizuka M., Taira K. Relationship between urinary N-desmethyl-acetamiprid and typical symptoms including neurological findings: a prevalence case-control study. PLoS One. 2015;10 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Taira K. Health effects of neonicotinoid insecticides-Part1: physicochemical characteristics and case reports. Jpn. J. Clin. Ecol. 2012;21:24–34. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Taira K. Human neonicotinoids exposure in Japan. Jpn. J. Clin. Ecol. 2014;23:14–24. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Taira K., Aoyama Y., Kawakami T., Kamata M., Aoi T. Detection of chloropyridinyl neonicotinoid insecticide metabolite 6-chloronicotinic acid in the urine: six cases with subacute nicotinic symptoms. Chudoku Kenkyu: Chudoku kenkyukai jun kikanshi= Jpn. J. Toxicol. 2011;24:222–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Taira K., Fujioka K., Aoyama Y. Qualitative profiling and quantification of neonicotinoid metabolites in human urine by liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. PLoS One. 2013;8 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nakanishi R., Hamada S., Ohfuji M., Owaki S., Kobayashi S., Higuchi Y. Vol. 58. Kyoto Prefectural Institute of Public Health and Environment; Kyoto: 2013. pp. 29–33. (Annual Report of Kyoto Prefectural Institute of Public Health and Environment 2013). e.a., [in Japanese] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wongsasuluk P., Chotpantarat S., Siriwong W., Robson M. Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province. Thail. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2014;36:169–182. doi: 10.1007/s10653-013-9537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tomizawa M. Neonicotinoids and derivatives: effects in mammalian cells and mice. J. Pest. Sci. 2004;29:177–183. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.