Abstract
Background
Helminths are among the most widespread infectious agents prevalent in tropical and sub-tropical regions of the developing world defined by inadequate sanitation, poverty and unsafe water sources. This study was carried out to describe the distribution of helminth and malaria parasite infections in the middle-belt of Ghana in sub-Saharan Africa where disease burden, including anaemia is rife and helminths are perceived to be significant contributors of the burden.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey involving 1826 residents located in the middle belt of Ghana where no or very little previous community-based helminth work had been carried out. The participants randomly recruited at household level provided biological samples collected over a 12-month period following a rigorous consenting process and these were analysed to describe the different types and seasonal distribution of helminths.
Findings
Overall, 19.3% intestinal helminth infection prevalence was documented. Also based on parasites targeted for elimination, 12.1% Hookworm, 4.0% Hymenolepis nana/Hymenolepis dimunita, 1.5% Ascaris lumbricoides, 1.5% Taenia species, 0.9% Strongyloides stercoralis and 0.8% Trichuris trichiura, with about 1.0% polyphelminthiasis were recorded in the survey. About 55.4% and 44.4% of the participants had heavy hookworm and Trichuris infections respectively. Most of the Ascariasis (83.3%) infections were light in intensity. Hookworm infection was identified with significant odds considering decreasing age (OR = 2.09, p = 0.03), inappropriate footwear use (OR = 1.88, p = 0.021), malaria parasite co-infection (OR = 1.62, p = 0.018), not scrubbing nails during hand washing (OR = 0.68, p = 0.048), source of drinking water (OR = 2.51, p = 0.027) and religion (OR = 4.36, p = 0.002).
Conclusions
Hookworm infection was significantly higher in younger age groups and among those who did not have safe drinking water. Proper sanitation, protective footwear, religion and good personal hygiene practices were found to influence helminth and hookworm prevalence in the area. Malaria parasite coinfection with helminths, especially hookworm infections increased 2-fold.
Keywords: Helminth, Malaria, Environmental and personal hygiene
1. Author summary
Helminth infections, which are common in the tropical climates such as the middle belt of Ghana are strongly associated with sources of poor drinking water, lack of sanitation, poor hygiene and poor nutritional status. In an observational cross-sectional community-based survey involving samples from 1569 residents, a crude prevalence of 19.3% intestinal helminth infection with the highest contribution from hookworm (12.1%) was recorded in the survey. Personal hygiene, sanitation, safe drinking water and other factors were assessed and found to relate to helminth infection in the middle-belt of Ghana. Malaria parasite co-infection was also found to contribute to higher helminth infection.
2. Introduction
Humans are hosts to nearly 300 species of helminths who are among the most widespread infectious agents that have co-evolved over hundred million years (Ridley, 2012; Voeks and Sercombe, 2000; Zaiss et al., 2015) affecting more than a third of the world's population (Salazar-Castañon et al., 2014) and mostly prevalent in tropical and sub-tropical regions of the developing world where adequate water, hygiene and sanitation are lacking (Knopp et al., 2012). Despite their complexity, helminths usually cause asymptomatic and chronic infections (Salazar-Castañon et al., 2014). An estimated 1.2 billion, 800 million and 740 million people worldwide are specifically infected by three species of helminths; namely Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, and hookworm, respectively (Keiser and Utzinger, 2008; Knopp et al., 2012). In sub-Saharan Africa, hookworm (Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus) prevalence is approximately 30% to 50% (De Silva et al., 2003); prevalence in the middle belt of Ghana is very similar, 45%. The prevalence of other intestinal parasites' infection including Hymenolepis nana, Taenia solium, and Trichuris trichiura is 3% (Humphries et al., 2011). The effects of helminth infection especially among children and in pregnancy include growth delay, anaemia and poor birth outcomes (Hotez, 2008). Helminth infection control efforts have traditionally focused on community-based treatment of high-risk populations (for instance, school-age children) through the use of anti-helminths (Bentwich, 2000; Humphries et al., 2011). Periodic deworming has been shown to increase growth in some populations (Taylor-Robinson et al., 2012). It is important to assess the impact that environmental factors have on the spread of helminth infection and the effect on available control strategies. To describe the epidemiology of soil transmitted helminths infections and factors that influence their distribution among a population with known demographic characteristics in the middle-belt of Ghana, Africa, we sampled participants using the Kintampo Health and Demographic Surveillance System (KHDSS).
3. Materials and methods
3.1. Ethical approval and consent statement
Ethical and Scientific approvals were sought from the Kintampo Health Research Centre (KHRC), Ghana and Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research, Accra, Ghana. The study processes were implemented in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration and the principles of Good Clinical Practice (GCP). Permission was sought from the community opinion leaders before entry for study processes. All scientific and ethical approvals were obtained before recruitment, enrolment and data collection commenced. Individuals selected from the HDSS database were contacted by field supervisors in the community to seek their informed consent to participate in the study after explaining to them the benefits, risks, confidentiality, voluntary participation and what would be required of them. Participants who voluntarily agreed to be part of the study were taken through the study procedures for the necessary samples and data collection. Care-takers were invited to give their consent on behalf of participating minors. Children at 10 to 17 years were invited to give their assent. Data handling protection of the identity of participants were carried out according to what the ethics committees approved.
3.2. Study design
A randomly selected cohort of residents at household level in the study area were enrolled as part of a cross-sectional community-based survey using the Health Demographic Surveillance (HDS) database as the sampling frame. The survey spanned from September 2015 to August 2016. Participants identified with infections after screening were treated using a single dose of albendazole (400 mg); the medicine routinely used to treat both suspected and confirmed STH infections (Ministry of Health/Ghana Health Service, 2010).
3.3. Study site
The survey was carried out in Kintampo North Municipality and Kintampo South District located within the forest-savannah transitional ecological zone in the middle part of Ghana, an area covering a total of 7162 km2 with a resident population of approximately 140,000 in 32,329 households (KHRC, 2010; Owusu-Agyei et al., 2012). Community members are predominantly subsistent farmers including various animal farming which contribute to the risk of acquiring helminths infections (Agrawal, 2012; David and William Jr., 2006). About 40% of the population use open fields to defecate and Pit latrine remains the most available toilet facility (57.5%) in the study area (KHRC, 2010). KHRC has a HOBOware weather station installed onsite to monitor temperature, rainfall, relative humidity and wind speed for the study area. The routine laboratory examination of stool is based on wet film preparation with normal saline and of urine samples based on examination of urine deposits in health facilities. Periodic deworming in Mass Drug Administration (MDA) with benzimidazole anti-helminths of school children in targeted communities as part of the hookworm control efforts have to a large extent been beneficial to the populations (Humphries et al., 2011). Two of such deworming exercise offered to school aged children (SAC) from seven (7) years to sixteen (16) years occurred in the study area in November 2014 and November 2015. The exercises administered albendazole (400 mg) and praziquantel (600 mg). In each round of dosing, there was 74.1% and 77.1% coverage in the respective years as reported by the district assemblies.
3.4. Sampling of study participants
Kintampo Health Research Centre (KHRC) maintains an HDSS database of the population in the study area. A list of household heads was randomly generated from the database using a computer software. From the list, the study team enrolled all participants above 6 months of age within the selected households after informed consent was sought. All individuals enrolled within a selected household provided samples that were analysed in order to achieve the study objectives(Owusu-Agyei et al., 2012). Participants who refused consenting were excluded from being part of the study.
3.5. Field and laboratory procedures
The field team contacted and enrolled members of each selected household, gave guide on how appropriate stool (at least 50 g) and urine (10 ml) samples be collected in appropriate containers that were provided. They administered study questionnaire, collected required demographic and socio-economic data. The team returned the following day to collect all samples including, blood (5 ml) by venipuncture, stool and urine. The samples were transported to the KHRC laboratory for processing, examination and parasite identification within four (4) hours. Stool samples were processed using routine wet preparation (Cheesbrough, 2009), Kato-Katz (Magalhães et al., 2011) and Formol Ether-based Concentration methods (Cheesbrough, 2009; David and William Jr., 2006; Xu et al., 2012) to screen for parasitic infection. Urine samples collected were processed and routine urine chemistry analysis and examination of urine sediments by microscopy (×400 magnification) were carried out (Cheesbrough, 2006; Cheesbrough, 2009). For the blood samples, Full Blood Counts (FBC) analysis using the ABX Micros Pentra 60 (Horiba ABX, Montpellier, France) was performed and also screening for malaria and other blood borne parasites for each participant's sample was performed with adequate quality control measures (Adu-Gyasi et al., 2015) in all. All participants with any helminth infection, except pregnant women in the first trimester and children less than one year of age, were treated with observed single dose of albendazole (400 mg) (Ministry of Health/Ghana Health Service, 2010). Participants with any other infections were referred to the nearest health facilities for treatment and management. The geographical position of houses and other facilities within the communities were recorded with global positioning system (GPS) to aid in mapping infections in the study area.
3.6. Sample size calculation
At 95% confidence level and with 90% power, using a population size of 140,000 with expected frequency of 41% of hookworm infection (Humphries et al., 2011). Assuming a worst acceptable frequency of 33.2% of helminth infection among the population in this study, we calculated a minimum sample size of 1660 (using Stata software version 13). Considering a 10% refusal rate to obtain samples and incomplete data gave a total sample size of 1826 individual participants. Using an average of 6 members in a household in the study area, a total of 304 households from the HDS database was selected at random to recruit participants for this survey.
3.7. Data management and statistical analysis
All data collected from the field or laboratory were checked by supervisors for completeness and logged for traceability. Forms were then batched for double data entry by two independent data clerks and verified using Microsoft Access software. StataCorp Stata statistical software version 13 and R software were used for data analyses. Basic descriptive analyses were done, proportions and means were compared using the Chi squared (χ2) where necessary (Campbell et al., 2016). All reported p-values were at 95% confidence level. Presentation of spatial distribution and analyses of the data were carried out using the ArcMap Desktop 10.0 software. Purely Spatial analysis using the Discrete Poisson model was done with software for the Spatial and Space-Time scan statistics (SaTScan version 9.4.4, Harvard, USA) to explore to identify clusters of the infections in the study area.
3.8. Quality control
The field team was trained on the study tools, they piloted the study procedures and all processes were reviewed according to the protocol. Before the survey, clinical laboratory staff were trained with at least 10 slides prepared using samples with common and known eggs and larvae of the STH that could be obtained. Competency was assessed in consistency of sample preparation, parasite detection, egg counting and results reporting among laboratory staff. During the training, a discrepancy of up to 10% for egg counts was considered normal (Knopp et al., 2011). Reasons with each staff that were identified with larger discrepancies were identified and corrected with refresher training. In the study, 10% of the slides were selected for double reading across all the diagnostic methods used in this survey. This was carried out by double reading every tenth sample during sample processing and examination. All quality control and assurance measures needed with each of the study processes were strictly adhered.
4. Results
4.1. Population and site description
A total of 1826 participants were enrolled into the survey over the 12-month period. Out of this, the study team successfully obtained the complete set of samples from 85.9% (1569/1826) of participants to determine the prevalence of STH in the study area. The demographic characteristics of the population are presented in Table 1A, Table 1B. The mean age of the population was 24.1 years and ranged from 1 year to 96 years. Of the total participants recruited and provided all expected samples, 50.0% (785/1569) were in the target age group for mass drug administration of anti-helminth and praziquantel (either 16 years old or less). More than half of the population was educated (57%), with most of them Unemployed (60%) and also Christians (68%). The highest level of education was largely Elementary (High/Middle/Ordinary Level/Advance Level school certificate). Only 7.8% (121/1560) of the population had taken anti-helminths within three months prior to our visit. Among children aged up to 16 years, a previous deworming was reported in 8.4% (66/790) compared to 7.3% (57/776) among those aged 16 years and above. The difference between the two proportions was not significant (p = 0.458). The mean (standard deviation) of weight and height were 42.3 (19.7) kg and 143 (30.9) cm for males and 43.2 (19.0) kg and 141 (27.2) cm for females respectively. Considering means of defecation among those that did not have toilet facilities at home, 60.3% (806/1336) used Open Fields, 22.1% (295/1336) used Pit Latrine and 17.1% used Ventilated Improved Pit (KVIP).
Table 1A.
Demographic characteristics of the population.
| Age group | Males, n(%) | Females, n(%) |
|---|---|---|
| <8 | 160(50.2) | 159(49.8) |
| 8–16 | 239(50.7) | 232(49.3) |
| 17–30 | 121(41.6) | 170(58.4) |
| 31–60 | 149(39.2) | 231(60.8) |
| 61–100 | 52(49.5) | 53(50.5) |
| BMI | Males, n(%) | Females, n(%) |
| Underweight | 340(50.1) | 339(49.9) |
| Normal weight | 338(47.5) | 373(52.5) |
| Over weight | 42(24.1) | 132(75.9) |
| Education | No education, n(%) | 568(36.3) |
| Elementary, n(%) | 898(57.3) | |
| Higher education, n(%) | 100(6.4) | |
| Occupation | Professional, n(%) | 20(1.3) |
| Trader, n(%) | 125(8) | |
| Farmer, n(%) | 480(30.9) | |
| Unemployed, n(%) | 931(59.8) | |
| Religion | Muslim, n(%) | 372(23.8) |
| Christian, n(%) | 1065(68) | |
| Traditional, n(%) | 36(2.3) | |
| None | 93(5.9) | |
| Bed share | Yes, n(%) | 1297(82.9) |
| No, n(%) | 268(17.1) | |
| Actual season | Nov15-Apr16, n(%) | 604(48.5) |
| Jun16-Oct16, n(%) | 642(51.5) |
Table 1B.
Characteristics of the population and environment.
| Footwear | Slippers (“Chalewate”), n(%) | 1030(65.8) |
| Sandals, n(%) | 191(12.2) | |
| Wellingtonboot, n(%) | 99(6.3) | |
| Shoe & “Cambuu”, n(%) | 129(8.2) | |
| None, n(%) | 117(7.5) | |
| Toilet | Yes, n(%) | 224(14.3) |
| No, n(%) | 1340(85.7) | |
| Dewormer (last 3-months) | Yes, n(%) | 123(7.9) |
| No, n(%) | 1443(92.1) | |
| Scrub nails before eating | Yes, n(%) | 1043(66.6) |
| No, n(%) | 523(33.4) | |
| Wash hands with soap | Yes, n(%) | 1063(67.9) |
| No, n(%) | 503(32.1) | |
| Water source in house | Yes, n(%) | 207(13.2) |
| No, n(%) | 1359(86.8) | |
| Drinking water source close to house | Pipe-borne, n(%) | 232(14.8) |
| Well, n(%) | 256(16.4) | |
| River/Stream, n(%) | 290(18.5) | |
| Bore-hole, n(%) | 710(45.3) | |
| Other, n(%) | 78(5.0) | |
| Use refuse site | Yes, n(%) | 1078(68.8) |
| No, n(%) | 488(31.2) | |
| Animal reared by tenant of compound | Yes, n(%) | 1182(75.5) |
| No, n(%) | 384(24.5) | |
| Animal reared within compound | Yes, n(%) | 1174(75.0) |
| No, n(%) | 392(25.0) | |
| Participants directly involved in animal rearing | Yes, n(%) | 828(52.9) |
| No, n(%) | 738(47.1) |
4.2. Climate and environmental factors in study area
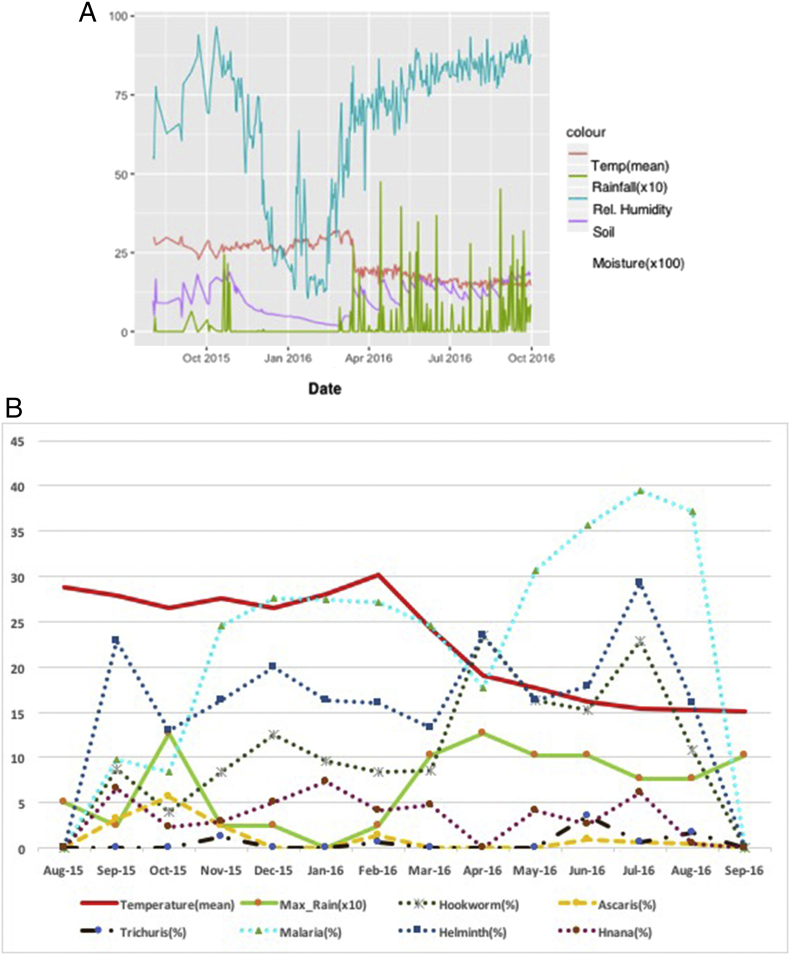
Over the period, a mean temperature of 21.6 °C was recorded with a minimum of 9.4 °C occurring in September 2016 and a maximum of 41.2 °C, occurring in February 2016. Maximum rainfall of 1.27 mm was recorded in the months of October 2015 and April 2016. The mean relative humidity over the period was 65.7% with a minimum of 6% recorded in August 2015 and the maximum of 100% recorded in September 2016. A mean soil moisture of 0.11m3/m3 with a minimum of zero (0) recorded in August 2015 and a maximum of 0.28 m3/m3 were recorded in April 2016 (see also Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Presentation of the climatic conditions (A) and identified infections in the middle belt of Ghana over a 12 month period (B).
4.3. Distribution and prevalence of parasitic infections
The study reports of an overall intestinal helminth infection (mono- and polyparasitic) prevalence of 19.3% (305/1569) over the 12 months period for the middle–belt of Ghana, Africa. With particular interest to helminths targeted for elimination using MDA, the prevalences of Hookworm, Ascaris lumbricoides, Hymenolepis nana/Hymenolepis dimunita, Strongyloides stercoralis, Trichuris trichiura, Taenia species have been presented in Table 2 and other infections. Considering polyphelminthiasis, 1.0% of the participants were infected with Hookworm and Hymenolepis nana/Hymenolepis dimunita while 4% had Hookworm infection with either of A. lumbricoides, H. nana/H. dimunita, S. stercoralis, T. species or Trichuris trichiura (Hookworm with each species was 0.8%).
Table 2.
Prevalence of soil transmitted helminth and other parasitic infections among participants.
| Parasite | Infected with intestinal and malaria parasite |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total population |
≤16 years |
>16 years |
||||
| No. of examined | No. of infected (%) | No. of examined | No. of infected (%) | No. of examined | No. of infected (%) | |
| Helminth | 1569 | 302(19.3) | 790 | 140(17.7) | 162(20.8) | |
| Hookworm (Ancylostoma duodenale/Necator Americana) | 1569 | 190(12.1) | 790 | 84(10.6) | 779 | 106(13.6) |
| Ascaris lumbricoides | 1569 | 23(1.5) | 790 | 9(1.1) | 779 | 14(1.8) |
| Taenia spp. | 1569 | 23(1.5) | 790 | 12(1.5) | 779 | 11(1.4) |
| Trichuris trichiura | 1569 | 13(0.8) | 790 | 5(0.6) | 779 | 8(1.0) |
| Hymenolepis nana/dimunita | 1569 | 62(4.0) | 790 | 38(4.8) | 779 | 24(3.1) |
| Strongyloide stercoralis | 1569 | 14(0.9) | 790 | 4(0.5) | 779 | 10(1.3) |
| Trichostrongyloides | 1569 | 4(0.3) | 790 | 2(0.3) | 779 | 2(0.3) |
| Dicrocoelium spp. | 1569 | 11(0.7) | 790 | 6(0.8) | 779 | 5(0.6) |
| Schistosoma mansoni | 1569 | 3(0.2) | 790 | 0 | 779 | 3(0.4) |
| Enterobius vermicularis | 1569 | 2(0.1) | 790 | 0 | 779 | 2(0.3) |
| Schistosoma haematobium | 1569 | 1(0.1) | 790 | 0 | 779 | 1(0.1) |
| Hookworm + Strongyloide stercoralis | 1369 | 2(0.2) | 704 | 1(0.1) | 665 | 1(0.2) |
| Hookworm + Ascaris lumbricoides | 1360 | 2(0.2) | 697 | 0 | 663 | 0 |
| Hookworm + Taenia spp. | 1362 | 3(0.2) | 698 | 2(0.3) | 664 | 1(0.2) |
| Hookworm + Trichuris trichiura | 1370 | 2(0.2) | 701 | 0 | 669 | 2(0.3) |
| Hookworm + Hymenolepis nana/dimunita | 1343 | 13(1.0) | 684 | 8(1.2) | 659 | 5(0.8) |
| Malaria and helminth | ||||||
| Hookworm + malaria | 1094 | 78(7.1) | 484 | 53(11.0) | 610 | 25(4.1) |
| Ascaris + malaria | 1117 | 6(0.5) | 463 | 5(1.1) | 654 | 1(0.2) |
| Trichuris trichiura + malaria | 1125 | 5(0.4) | 461 | 2(0.4) | 664 | 3(0.5) |
| Strongyloides stercoralis + malaria | 1120 | 3(0.3) | 464 | 3(0.7) | 656 | 0 |
| Hymenolepis nana/dimunita + malaria | 1122 | 28(2.5) | 468 | 22(4.7) | 654 | 6(0.9) |
| Taenia spp. + malaria | 1125 | 10(0.9) | 468 | 9(1.9) | 657 | 1(0.2) |
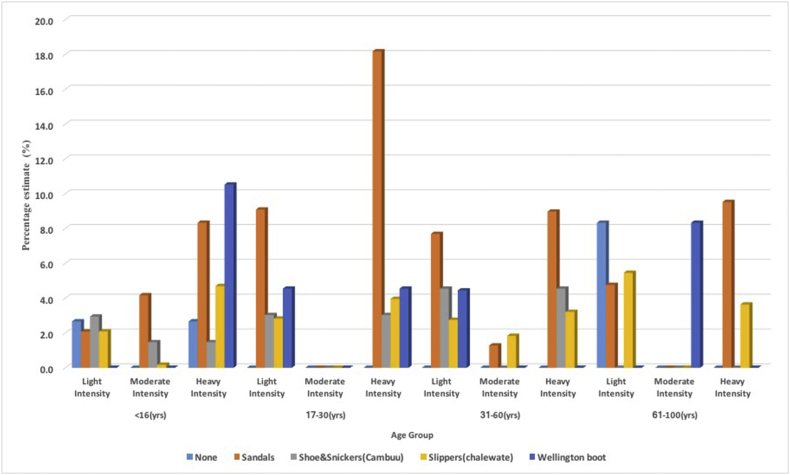
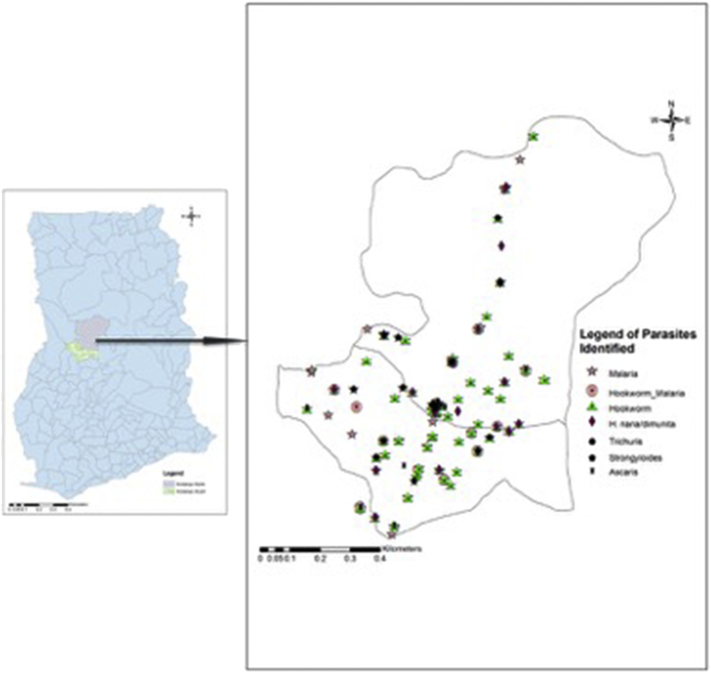
For infection intensity, 36.9% of those who had Hookworm infections had light infection, whiles 7.7% had moderate infection and 55.4% had heavy infection.2 Intensity among the various age groups and the participants who used footwear are presented in Fig. 2. For Ascariasis, 83.3% had light infection, 16.7% had moderate infection and none were heavily infected.3 Trichuriasis, 33.3% had light infections, 22.2% had moderate infections and 44.4% had heavy infectio.4 Using the hookworm egg intensity criteria, with Hymenolepis nana/Hymenolepis diminuta, 30% had light infection, 7.5% had moderate infection and 62.5% had heavy infection. Twenty percent (20%) of those infected with Taenia spp. had light infection while 80% were classified as having heavy infection. The geometric mean count of Strongyloides stercoralis larvae in infected individuals was 29 per gram of stool. Comparing means of egg or larvae count among children with ages less or equal 16 years and those >16 years old, difference in hookworm egg count (p = 0.505), Ascaris egg count (p = 0.118), Trichuris trichiura egg count (p = 0.281), Hymenolepis nana/Hymenolepis diminuta egg count (p = 0.404), Taenia spp. egg count (p = 0.208), Strongyloides steroralis larval count (p = 0.734) was not significant. The parasites identified in the study are geospatially plotted and the distributions are presented in Fig. 3. From Fig. 3, parasites are more identified in the southern part than the northern part of the study area.
Fig. 2.
Plot of Hookworm egg intensity and type of footwear used compared among age groups of the population.
Fig. 3.
The map of the study area in Ghana showing Kintampo North and South districts with the distributions of the soil transmitted helminths and malaria parasites identified among the study population.
4.4. Seasonal influence on helminth infection
The crude prevalence with at least one intestinal helminth infection was 17.7% in the Dry Season (November 2015 to April 2016) and 25.1% in the Rainy Season (May 2016 to October 2016). The difference in prevalence for the two seasons was significantly different (p = 0.002). Considering prevalence of coinfection of hookworm and at least one of the other helminths, the difference in the prevalence in the rainy (8.4%) and dry (7.4%) seasons was not significant (p value = 0.553).
4.5. Prevalence of malaria and other parasites
Crude asymptomatic malaria parasite prevalence of 28.1% (441/1569) was recorded in the study with 17.1% in children <2 years, 40.5% in those 2 years to <8 years and 44.0% among participants aged 8 years to 16 years old. The difference in crude prevalence in the two seasons (p < 0.001) and across the various age groups (p < 0.001) was significantly different for malaria parasite infection. The crude prevalence of infection with intestinal flagellates was 7.4% and 4.4% prevalence of microfilaria present in the blood films of participants within the 12 months period of study. With microfilaria, the highest prevalence not in respective order, of 55.6% occurred among the 31–60 year old group, followed by 18.5% prevalence among the 17–30 year old group and the least of 3.7% among children <7 years old (p = 0.002). Considering infections with intestinal flagellates, the prevalence was similar across the various age groups (p = 0.186).
4.6. Haematological profile of participants
The mean (Std. Err.) and 95% CI (Lower, Upper)) for White Blood Cells (WBC) concentration was 6.6 (0.14) and 95% CI (6.3, 6.7)) × 10(9)g/L and 12.2 (0.05) and 95% CI (12.1, 12.3)) g/dL for haemoglobin (Hb). Anaemia in the studied population 15.8% (247/1567) (Ministry of Health/Ghana Health Service, 2010). Comparing helminth parasitic infection to those without infection, anaemia was found not to be significantly different.
4.6.1. Factors associated with Hookworm infections
Univariate logistic associations between hookworm infection and factors of interest revealed no significant differences (Table 3). Using a multivariate logistic regression model, however, age, footwear use, malaria parasite coinfection, scrubbing nails during hand washing, type of drinking water close to house, and religion had significant associations with hookworm infection (Table 3).
Table 3.
Hookworm distribution and the effects of risk factors assessed in the study area.
| Hookworm |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Cases | No. Controls | Univariate |
Multivariate |
|||||
| OR(SE) | 95% CI(L,U) | P-value | OR(SE) | 95% CI(L,U) | P-value | |||
| Age group | ||||||||
| <8 | 23 | 295 | 1 | 0.0511a,0.0298b | 1 | |||
| 8-16 | 61 | 406 | 1.93 | 1.16,3.19 | 2.32 | 1.24,4.34 | 0.008* | |
| 17–30 | 40 | 251 | 2.04 | 1.19,3.52 | 2.73 | 1.23,6.07 | 0.014* | |
| 31–60 | 53 | 326 | 2.09 | 1.24,3.50 | 2.21 | 0.87,5.60 | 0.095 | |
| 61–100 | 13 | 92 | 1.81 | 0.88,3.73 | 1.73 | 0.60,5.04 | 0.311 | |
| Actual season | ||||||||
| Nov15-Apr16 | 57 | 545 | 1 | 0.0001a, b | (omitted) | |||
| Jun16-Oct16 | 110 | 531 | 1.98 | 1.40,2.79 | ||||
| BMI | ||||||||
| Underweight | 75 | 598 | 1 | 0.032a,0.990b | 1 | |||
| Normal | 102 | 606 | 1.34 | 0.97,1.85 | 0.91 | 0.55,1.48 | 0.692 | |
| Over-weight | 13 | 154 | 0.67 | 0.36,1.25 | 0.70 | 0.31,1.57 | 0.383 | |
| Footwear | ||||||||
| Slippers (“Chalewate”) | 113 | 912 | 1 | <0.000a, 0.2489b | 1 | |||
| Sandals | 46 | 145 | 2.56 | 1.74,3.78 | 1.88 | 1.10,3.21 | 0.021* | |
| Wellingtonboot | 12 | 86 | 1.13 | 0.60,2.13 | 1.09 | 0.49,2.43 | 0.838 | |
| Shoe & “Cambuu” | 11 | 117 | 0.76 | 0.40,1.45 | 0.79 | 0.37,1.71 | 0.552 | |
| None | 8 | 109 | 0.59 | 0.28,1.25 | 1.62 | 0.66,3.98 | 0.292 | |
| Malaria parasite | ||||||||
| No | 112 | 1016 | 1 | <0.000a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 78 | 361 | 1.96 | 1.43,2.69 | 1.62 | 1.09,2.40 | 0.018* | |
| Education | ||||||||
| None | 79 | 488 | 1 | 0.072a,0.033b | 1 | |||
| Elementary/primary | 105 | 789 | 0.82 | 0.60,1.12 | 1.07 | 0.69,1.67 | 0.763 | |
| Higher school | 6 | 93 | 0.40 | 0.17,0.94 | 0.59 | 0.20,1.74 | 0.336 | |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male | 108 | 609 | 1 | 0.0013a, b | 1 | |||
| Female | 82 | 761 | 0.61 | 0.45,0.83 | 0.72 | 0.47,1.10 | 0.124 | |
| Toilet | ||||||||
| No | 171 | 1165 | 1 | 0.0738a, b | ||||
| Yes | 19 | 203 | 0.64 | 0.39,1.05 | ||||
| Dewormer (last 3-months) | ||||||||
| No | 184 | 1255 | 1 | 0.0115a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 6 | 115 | 0.36 | 0.15,0.82 | 0.46 | 0.17,1.26 | 0.129 | |
| Scrub nails before eating | ||||||||
| No | 78 | 443 | 1 | 0.0173a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 112 | 926 | 0.69 | 0.50,0.94 | 0.68 | 0.47,1.00 | 0.048* | |
| Wash hands with soap | ||||||||
| No | 82 | 420 | 1 | 0.0006a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 108 | 949 | 0.58 | 0.43,0.80 | 0.90 | 0.39,2.08 | 0.809 | |
| Water source in house | ||||||||
| No | 177 | 1176 | 1 | 0.0053a, b | (omitted) | |||
| Yes | 13 | 194 | 0.45 | 0.25,0.80 | ||||
| Drinking water source close to house | ||||||||
| Pipe-borne | 11 | 162 | 1 | 0.0012a,0.0003b | 1 | |||
| Well | 11 | 144 | 1.13 | 0.47,2.68 | 1.98 | 0.69,5.71 | 0.207 | |
| River/stream | 40 | 251 | 2.35 | 1.16,4.73 | 2.05 | 0.88,4.73 | 0.094 | |
| Bore-hole | 113 | 593 | 2.81 | 1.47,5.36 | 2.51 | 1.11,5.68 | 0.027* | |
| Other | 2 | 27 | 1.09 | 0.23,5.22 | 0.66 | 0.07,6.06 | 0.717 | |
| Use refuse site | ||||||||
| No | 75 | 411 | 1 | 0.0089a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 115 | 955 | 0.66 | 0.48,0.90 | 1.02 | 0.68,1.51 | 0.939 | |
| Share bed | ||||||||
| No | 39 | 226 | 1 | 0.1672a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 151 | 1143 | 0.77 | 0.52,1.12 | 0.84 | 0.52,1.34 | 0.458 | |
| Occupation | ||||||||
| Unemployed | 98 | 829 | 1 | 0.0003a,0.700b | 1 | |||
| Farmer | 82 | 398 | 1.74 | 1.27,2.40 | 1.33 | 0.66,2.71 | 0.427 | |
| Trader | 7 | 117 | 0.51 | 0.23,1.12 | 0.55 | 0.15,2.03 | 0.366 | |
| Professional | 1 | 19 | 0.45 | 0.06,3.37 | 2.25 | 0.21,24.00 | 0.501 | |
| Religion | ||||||||
| Muslim | 39 | 329 | 1 | 0.0001a,0.0027b | 1 | |||
| Christianity | 121 | 943 | 1.08 | 0.74,1.59 | 1.00 | 0.63,1.58 | 0.996 | |
| Traditional | 12 | 24 | 4.21 | 1.92,9.24 | 4.36 | 1.74,10.95 | 0.002* | |
| None | 18 | 74 | 2.05 | 1.11,3.80 | 0.98 | 0.47,2.04 | 0.956 | |
| Animal reared by tenant of compound | ||||||||
| No | 34 | 350 | 1 | 0.0218a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 156 | 1020 | 1.57 | 1.06,2.33 | 0.81 | 0.48,1.36 | 0.430 | |
| Animal reared within compound | ||||||||
| No | 36 | 356 | 1 | 0.0361a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 154 | 1014 | 1.50 | 1.02,2.20 | 0.37 | 0.07,1.96 | 0.244 | |
| Participants directly involved in animal rearing | ||||||||
| No | 72 | 664 | 1 | 0.0074a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 117 | 706 | 1.53 | 1.12,2.09 | 3.16 | 0.58,17.12 | 0.182 | |
*Variables in the multivariate analysis significant at P-value < 0.05.
Test of homogeneity (equal odds).
Score test for trend of odds.
4.6.2. Factors associated with Helminth infections
Considering univariate associations between helminth infections and same factors of interest, there were no significant differences in the odds of being infected with helminth parasite (Table 4). Using multivariate logistic regression model, however, significant associations in the odds ratio were identified considering helminth infection with factors such as season, footwear use, malaria parasite co-infection, occupation, and religion (Table 4).
Table 4.
Helminth distribution and the effects of risk factors assessed in the middle belt of Ghana.
| Helminth |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Cases | No. Controls | Univariate |
Multivariate |
|||||
| OR(SE) | 95% CI(L,U) | p-value | OR(SE) | 95% CI(L,U) | p-value | |||
| Age group | ||||||||
| <8 | 48 | 270 | 1 | 0.0803a,0.2027b | ||||
| 8-16 | 92 | 375 | 1.38 | 0.94,2.02 | ||||
| 17–30 | 64 | 227 | 1.59 | 1.05,2.40 | ||||
| 31–60 | 83 | 296 | 1.58 | 1.06,2.33 | ||||
| 61–100 | 15 | 90 | 0.94 | 0.50,1.76 | ||||
| Actual season | ||||||||
| Nov15–Apr16 | 94 | 508 | 1 | 0.0003a, b | (omitted) | |||
| Jun16–Oct16 | 153 | 488 | 1.69 | 1.27,2.26 | ||||
| Footwear | ||||||||
| Slippers (“Chalewate”) | 185 | 840 | 1 | 0.0019a,0.7747b | 1 | |||
| Sandals | 56 | 135 | 1.88 | 1.32,2.68 | 1.60 | 1.01,2.52 | 0.044* | |
| Wellingtonboot | 23 | 75 | 1.39 | 0.85,2.28 | 1.36 | 0.73,2.54 | 0.330 | |
| Shoe & “Cambuu” | 18 | 110 | 0.74 | 0.44,1.25 | 0.93 | 0.50,1.73 | 0.817 | |
| None | 20 | 97 | 0.94 | 0.56,1.55 | 1.72 | 0.93,3.18 | 0.086 | |
| Malaria parasite | ||||||||
| No | 185 | 943 | 1 | 0.0000a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 117 | 322 | 1.85 | 1.42,2.42 | 1.94 | 1.41,2.67 | 0.000* | |
| Education | ||||||||
| None | 119 | 448 | 1 | 0.3917a,0.1712b | ||||
| Elementary/primary | 167 | 727 | 0.86 | 0.66,1.13 | ||||
| Higher school | 16 | 83 | 0.73 | 0.41,1.29 | ||||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male | 160 | 557 | 1 | 0.0064a, b | 1 | |||
| Female | 142 | 701 | 0.71 | 0.55,0.91 | 0.76 | 0.54,1.06 | 0.107 | |
| Toilet | ||||||||
| No | 264 | 1072 | 1 | 0.2798a, b | ||||
| Yes | 37 | 185 | 0.81 | 0.55,1.19 | ||||
| Dewormer (last 3-months) | ||||||||
| No | 287 | 1152 | 1 | 0.0436a, b | 1 | |||
| Yes | 15 | 106 | 0.57 | 0.33,0.99 | 0.55 | 0.26,1.15 | 0.111 | |
| Scrub nails before eating | ||||||||
| No | 109 | 412 | 1 | 0.2728a, b | ||||
| Yes | 193 | 845 | 0.86 | 0.66,1.12 | ||||
| Wash hands with soap | ||||||||
| No | 110 | 392 | 1 | 0.0803a, b | ||||
| Yes | 192 | 865 | 0.79 | 0.61,1.03 | ||||
| Water source in house | ||||||||
| No | 272 | 1081 | 1 | 0.0572a, b | ||||
| Yes | 30 | 177 | 0.67 | 0.44,1.01 | ||||
| Drinking water source close to house | ||||||||
| Pipe-borne | 28 | 145 | 1 | 0.1362a,0.1735b | ||||
| Well | 25 | 130 | 1.00 | 0.55,1.80 | ||||
| River/stream | 67 | 224 | 1.55 | 0.95,2.53 | ||||
| Bore-hole | 150 | 556 | 1.40 | 0.90,2.18 | ||||
| Other | 3 | 26 | 0.60 | 0.17,2.12 | ||||
| Use refuse site | ||||||||
| No | 105 | 381 | 1 | 0.1400a, b | ||||
| Yes | 197 | 873 | 0.82 | 0.63,1.07 | ||||
| Share bed | ||||||||
| No | 58 | 207 | 1 | 0.2556a, b | ||||
| Yes | 244 | 1050 | 0.83 | 0.60,1.15 | ||||
| Occupation | ||||||||
| Unemployed | 163 | 764 | 1 | 0.0499a,0.3756b | 1 | |||
| Farmer | 112 | 368 | 1.43 | 1.09,1.87 | 1.43 | 1.00,2.04 | 0.048* | |
| Trader | 20 | 104 | 0.90 | 0.54,1.50 | 0.67 | 0.28,1.62 | 0.375 | |
| Professional | 3 | 17 | 0.83 | 0.24,2.86 | 0.69 | 0.08,5.79 | 0.731 | |
| Religion | ||||||||
| Muslim | 64 | 304 | 1 | 0.0181a,0.0865b | 1 | |||
| Christianity | 204 | 860 | 1.13 | 0.83,1.54 | 1.03 | 0.72,1.48 | 0.872 | |
| Traditional | 14 | 22 | 3.02 | 1.45,6.29 | 3.02 | 1.35,6.78 | 0.007* | |
| None | 20 | 72 | 1.32 | 0.75,2.32 | 0.83 | 0.44,1.59 | 0.574 | |
| Animal reared by tenant of compound | ||||||||
| No | 73 | 311 | 1 | 0.8422a, b | ||||
| Yes | 229 | 947 | 1.03 | 0.77,1.38 | ||||
| Animal reared within compound | ||||||||
| No | 75 | 317 | 1 | 0.8958a, b | ||||
| Yes | 227 | 941 | 1.02 | 0.76,1.36 | ||||
| Participants directly involved in animal rearing | ||||||||
| No | 130 | 606 | 1 | 0.1200a, b | ||||
| Yes | 171 | 652 | 1.22 | 0.95,1.58 | ||||
*Variables in the multivariate analysis significant at P-value < 0.05.
Test of homogeneity (equal odds).
Score test for trend of odds.
4.6.3. Cluster identification of parasitic infection in the study area
Within the study period and considering helminth infections, a total of 281 cases were identified in 71 communities with a total population of 130,262. The annual cases were 107.8/100000. In the Purely Spatial analysis, 9 clusters were identified of which HM1 (RR = 7.96, p < 0.001, radius = 7.76 km) – located with a centroid (7.946841 N, 1.625205 W), HM3 (RR = 2.56, p < 0.001, radius = 24.24 km) – located with a centroid (8.134854 N, 1.945655 W), HM4 (RR = 16.31, p < 0.001, radius = 0 km) – located (8.470169 N, 1.575561 W), HM6 (RR = 13.58, p = 0.002, radius = 0 km) – located (8.170988 N, 1.694296 W) and HM7 (RR = 7.03, p < 0.003, radius = 1.73 km) – located with a centroid (8.144346 N, 1.645723 W) had significantly high relative risks (Fig. 4).
5. Discussion
A total prevalence of 19.3% of intestinal helminth infection estimated in our survey can be classified as low for the middle-belt of Ghana compared to other findings reported (Campbell et al., 2016; De Silva et al., 2003; Humphries et al., 2011; Mangali et al., 1994; Toma et al., 1999; Yelifari et al., 2005). This can be explained by the fact that two successive Mass Drug Administration (MDA) exercises with anti-helminths (albendazole and praziquantel) have been carried out before our survey. A prevalence of 12.1% for hookworm compared to 45% in earlier reports by (Humphries et al., 2011) attest to our results being lower. A reduction from the report of 45% Hookworm prevalence could be suggestive of the success in control measures embarked on in the intervening periods (Salam et al., 2015). Interestingly, the team reports 1.5% Ascaris lumbricoides, 0.9% Strongyloides stercoralis and 0.8% Trichuris trichiura as prevalences for the study area; these are lower compared to what has been documented elsewhere with similar climatic conditions (Kounnavong et al., 2011). It is interesting noting the increased prevalence of 4.0% Hymenolepis nana/Hymenolepis dimunita and 1.5% Taenia species (Humphries et al., 2011) infections despite the high MDA with albendazole coverage given by the Municipal Health Directorate within the period used for this study. With polyhelminthiasis, the estimate of 1.0% prevalence of Hookworm and Hymenolepis nana/Hymenolepis dimunita was the first reported (Kounnavong et al., 2011). Evidence of improved sanitation (increased use of community refuse dumping site), personal hygiene (washing of hands with soap, scrubbing nails during handwashing) and available good sources of drinking water recorded in this study could have contributed to the reduction in helminth infection documented in the study area (Campbell et al., 2016; Efunshile et al., 2015; Kounnavong et al., 2011). Homes with toilet facilities (14%) were few and that increased “Open Field” defecation among participants (Kounnavong et al., 2011). Rearing of animals within compounds and direct animal keeping by study participants were high and are known to contribute largely to helminth transmission and infection (Campbell et al., 2016; Yelifari et al., 2005). Fortunately, these were not found to have significantly increased the prevalence of helminth infections, probably because of the positive mitigating factors mentioned earlier. Our finding is not different from what was observed by Toma et al. (1999). This presupposes that an improvement in the provision of toilet facilities across the study area could add up to an effective helminth control measure.
The highest Hookworm prevalence of about 30% was found in the 8 to 16-year group with the least occurring in the 61 to 100-year group. Children in lower age groups have increased odds of contracting hookworm infection (Table 3). This is due to the fact that they have inadequate immune response compared to adults who naturally might have prolonged exposure and reinfection to antigens of the parasites (Humphries et al., 2013). Again, hookworm transmission and infection are known to be associated with poor sanitation and personal hygiene (Campbell et al., 2016; Kounnavong et al., 2011; Toma et al., 1999). Since generally adults keep better personal hygiene and sanitized environment compared to children, children are highly expected to contract hookworm infection than adults. It is worth noting that prevalence >10% each of Hookworm, Ascaris l., Trichuris trichiura, H. nana/dimunita, Taenia spp. and Strongyloides stercoralis infections were recorded among children in the <8-year age group. This suggests that policy makers should review the MDA programme to target children within this age group. The continuous target of only school going age groups (mostly 8 to 16 years) might reserve and maintain helminth transmission in the lower age group making the control and elimination of the parasites difficult. The study reports of 26.6% and 46.9% helminth and malaria parasite coinfections and 19.2% and 48.7% hookworm and malaria parasite coinfections in the age groups <8 years and 8–16 years respectively, a situation that was found to be significantly associated with decreasing age. This also suggests why parasitic control measures should focus on children. Particularly, for hookworm, about 49% of the coinfections with malaria occurred among children in the 8–16 year old group, followed by 19% among those in the <8 year old group. Since the two parasitic infections occur endemic in most developing and poor countries (Adegnika and Kremsner, 2012; Bethony et al., 2006; Brooker et al., 2006; Campbell et al., 2016; Degarege et al., 2010; Humphries et al., 2011; Kounnavong et al., 2011; Ojurongbe et al., 2011; Phongluxa et al., 2013; Toma et al., 1999), a more targeted approach to reduce their burden would be a step in the right direction and appropriate. A combination of the morbidity associated with hookworm infection and mortality from malaria parasite infections in children in the school going age would be burdensome if not curbed.
Helminth infections have been strongly linked to the nutritional status and anaemia of affected victim (Crompton et al., 1990; Humphries et al., 2013). Among those who had helminth infection compared to those who did not, anaemia and body weight were not significantly different (Humphries et al., 2013).
Provision of good drinking water is known to reduce the risk of helminth transmission and infection (Campbell et al., 2016; Humphries et al., 2013; Salam et al., 2015). When we assessed the contribution of drinking water commonly used by those who did not have source of water in their compounds, majority used Well and then Bore-hole. These sources of water compared to pipe-borne water increased the odds of hookworm infection though only bore-hole (OR = 2.51, p = 0.027) remained significant in the multivariate model. Bore-holes are considered safe drinking water and one would wonder its contribution to increasing hookworm infection. Individuals who go and fetch from the bore-holes could contaminate the water and make it unsafe and possible source to transmit hookworm infection. It would be advisable to educate individuals who collect water from other sources out of their houses to at least boil to make the water safe before use.
Animal rearing increases the risk of helminth infection particularly hookworm (Campbell et al., 2016; Humphries et al., 2011; Humphries et al., 2013) but this was not the case in this study. Though 75% of the population had animals reared in their compounds with 70% directly involved in keeping the animals, the odds recorded for helminth, hookworm, Trichuris trichiura, Ascaris lumbricoides, and H. nana/H. dimunita infections indicate no risk as there was no significance in association.
Helminth infections were found to cluster with significant relative risks in places within the study area in the middle-belt of Ghana (Fig. 4). These are location that are largely surrounded by water bodies which might be contributing factor to helminth infection transmission in such zones. Interesting to note and suggestive of places to target in case of specific control measures, malaria parasite infection clusters with significant relative risks were found intersecting some of the helminth infection risk zones. This exploratory analysis provides a target of communities that could be used for piloting helminth and malaria control programmes in the middle-belt of Ghana.
6. Conclusions
Hookworm infection was found to be significantly higher among younger age groups, which covered the school going age and among those who did not have safe drinking water. Proper sanitation, protective footwear, religion and good personal hygiene practices were found to influence helminth and hookworm infection in the area. Appropriate hand washing while scrubbing the fingernails was a protective attitude that needs to be encouraged when hookworm infection and transmission is considered. Individuals who were traditionalists had significant increase in the odds of contracting hookworm infection.
Malaria infection still remains about a 2-fold contributor of contracting helminth infection and for that matter, the two infections must be targeted together in control measures in places where the parasites are endemic.
List of abbreviations
Consent for publication.
The study team accepts the terms of the journal publishing the work.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during the current study and for this manuscript are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Funding
This study was locally supported by the management of Kintampo Health Research Centre, Ghana.
Authors' contributions
DAG, KPA, MTF, BG, and SOA conceived and designed the study and wrote the manuscript. DAG, DKG, LFI, LA and DD performed the experiments and helped in writing the manuscript. EA, OA, SG and SAE contributed to the study design, performance of experiments, data management and statistical analysis and help wrote the manuscript. KPA, MTF, BG, and SOA supervised the study. All authors contributed to the development of the manuscript, read and approved the final version.
Acknowledgments
Our utmost appreciation goes to the community members and participants who were involved in this study. We thank KHRC for the funding of the project and staff particularly, Mr. Jacob Saah and Elvis Amedeka for their kind contribution in the management of the project. Greatest appreciation goes to Mr. Augustine Nii O. Sowah of Parasitology Unit of Korle-Bu Teaching Hospital who gave preserved stool samples with known parasites to train researchers for this study. Again, The Parasitology Department of Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research, University of Ghana for the training in the use of the Kato Katz stool test kit.
Footnotes
Hookworm/Taenia spp./H. nana/dimunita: light infection ((<2000 eggs per gram [epg] of feces), moderate infection (2000–3999 epg) and heavy infection (>3999 epg).
Ascaris l.: light infection (<5000 epg), moderate infection (5000–49,999 epg) and heavy infection (>49,999 epg).
Trichuriasis: light infection (<1000 epg), moderate infection (1000–9999 epg) and heavy infection (>9999 epg).
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found in the online version, at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parepi.2018.e00071. These data include the Google map of the most important areas described in this article.
Contributor Information
Dennis Adu-Gyasi, Email: dennis.adu-gyasi@kintampo-hrc.org.
Kwaku Poku Asante, Email: kwakupoku.asante@kintampo-hrc.org.
Dennis Konadu Gyasi, Email: dennis.konadu@kintampo-hrc.org.
Louisa Fatahiya Iddrisu, Email: louisa.iddrisu@kintampo-hrc.org.
Love Ankrah, Email: love.ankrah@kintampo-hrc.org.
David Dosoo, Email: david.dosoo@kintampo-hrc.org.
Elisha Adeniji, Email: elisha.adeniji@kintampo-hrc.org.
Oscar Agyei, Email: oscar.agyei@kintampo-hrc.org.
Stephaney Gyaase, Email: stephaney.gyaase@kintampo-hrc.org.
Seeba Amenga-Etego, Email: seeba.ae@kintampo-hrc.org.
Ben Gyan, Email: BGyan@noguchi.ug.edu.gh.
Seth Owusu-Agyei, Email: sowusuagyei@uhas.edu.gh.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following KML file contains the Google map of the most important areas described in this article.
Exploration to identify helminth and malaria infection clusters in the study area in the middle belt of Ghana.
References
- Adegnika A., Kremsner P. Epidemiology of malaria and helminth interaction: a review from 2001 to 2011. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS. 2012;7:221–224. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e3283524d90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adu-Gyasi D., Asante K., Newton S., Dosoo D., Amoako S., Adjei G., Amoako N., Ankrah L., Tchum S., Mahama E., Agyemang V., Kayan K., Owusu-Agyei S. Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of CareStart G6PD deficiency rapid diagnostic test (RDT) in a malaria endemic area in Ghana, Africa. PLoS One. 2015;10 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal M. Schistosomes and Schistosomiasis in South Asia. Springer; 2012. Parasitological Diagnosis; pp. 187–213. [Google Scholar]
- Bentwich Z. Good worms or bad worms: do worm infections affect the epidemiological patterns of other diseases? Parasitol. Today. 2000;16:312. doi: 10.1016/s0169-4758(00)01693-8. (Personal ed.) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethony J., Brooker S., Albonico M., Geiger S., Loukas A., Diemert D., Hotez P. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm. Lancet. 2006;367:1521–1532. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68653-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker S., Clements A., Bundy D. Global epidemiology, ecology and control of soil-transmitted helminth infections. Adv. Parasitol. 2006;62:221–261. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(05)62007-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S., Nery S., D'Este C., Gray D., McCarthy J., Traub R., Andrews R., Llewellyn S., Vallely A., Williams G. Water, sanitation and hygiene related risk factors for soil-transmitted helminth and giardia duodenalis infections in rural communities in Timor-Leste. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016;46:771–779. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheesbrough M. Second Edition. Cambridge University Press; UK: 2006. District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Country. Part 2. [Google Scholar]
- Cheesbrough M. Second Edition. Cambridge University Press; UK. Cambridge: 2009. District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries. Part 1. [Google Scholar]
- Crompton D., Stephenson L., Schad G., Warren K. Hookworm Disease-current Status and New Directions. 1990. Hookworm infection, nutritional status and productivity; pp. 231–264. [Google Scholar]
- David T.J., William A.P., Jr. Saunders Elsevier; 2006. Markell and Voge's Medical Parasitology. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva N.R., Brooker S., Hotez P.J., Montresor A., Engels D., Savioli L. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: updating the global picture. Trends Parasitol. 2003;19:547–551. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2003.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degarege A., Animut A., Legesse M., Erko B. Malaria and helminth co-infections in outpatients of Alaba Kulito Health Center, southern Ethiopia: a cross sectional study. BMC. Res. Notes. 2010;3:143. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-3-143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efunshile A.M., Olawale T., Stensvold C.R., Kurtzhals J.A., Konig B. Epidemiological study of the association between malaria and helminth infections in Nigeria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015;92:578–582. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotez P. Hookworm and poverty. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008;1136:38–44. doi: 10.1196/annals.1425.000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries D., Mosites E., Otchere J., Twum W.A., Woo L., Jones-Sanpei H., Harrison L.M., Bungiro R.D., Benham-Pyle B., Bimi L. Epidemiology of hookworm infection in Kintampo North Municipality, Ghana: patterns of malaria coinfection, anemia, and albendazole treatment failure. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011;84:792–800. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2011.11-0003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries D., Simms B.T., Davey D., Otchere J., Quagraine J., Terryah S., Newton S., Berg E., Harrison L.M., Boakye D., Wilson M., Cappello M. Hookworm infection among school age children in Kintampo north municipality, Ghana: nutritional risk factors and response to albendazole treatment. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013;89:540–548. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.12-0605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser J., Utzinger J. Efficacy of current drugs against soil-transmitted helminth infections: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2008;299:1937–1948. doi: 10.1001/jama.299.16.1937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KHRC . 2010. Kintampo Health Research Centre Annual Report. [Google Scholar]
- Knopp S., Speich B., Hattendorf J., Rinaldi L., Mohammed K.A., Khamis I.S., Mohammed A.S., Albonico M., Rollinson D., Marti H., Cringoli G., Utzinger J. Diagnostic accuracy of Kato-Katz and FLOTAC for assessing anthelmintic drug efficacy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011;5 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopp S., Steinmann P., Keiser J., Utzinger J. Nematode infections: soil-transmitted helminths and Trichinella. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012;26:341–358. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2012.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kounnavong S., Vonglokham M., Houamboun K., Odermatt P., Boupha B. Soil-transmitted helminth infections and risk factors in preschool children in southern rural Lao People's Democratic Republic. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011;105:160–166. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2010.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães R.J.S., Biritwum N.-K., Gyapong J.O., Brooker S., Zhang Y., Blair L., Fenwick A., Clements A.C. Mapping helminth co-infection and co-intensity: geostatistical prediction in Ghana. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011;5 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangali A., Sasabone P., Syafruddin, Abadi K., Hasegawa H., Toma T., Kamimura K., Hasan M., Miyagi I., Mogi M. Prevalence of intestinal helminthic infections in Kao District, north Halmahera, Indonesia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health. 1994;25:737–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health/Ghana Health Service, G . 6th Edition. 2010. Standard Treatment Guidelines:Introduction; pp. 376–378. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ojurongbe O., Adegbayi A.M., Bolaji O.S., Akindele A.A., Adefioye O.A., Adeyeba O.A. Asymptomatic falciparum malaria and intestinal helminths co-infection among school children in Osogbo, Nigeria. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2011;16:680. the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owusu-Agyei S., Nettey O.E.A., Zandoh C., Sulemana A., Adda R., Amenga-Etego S., Mbacke C. Demographic patterns and trends in Central Ghana: baseline indicators from the Kintampo health and demographic surveillance system. Glob. Health Action. 2012;5 doi: 10.3402/gha.v5i0.19033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phongluxa K., Xayaseng V., Vonghachack Y., Akkhavong K., van Eeuwijk P., Odermatt P. Helminth infection in southern Laos: high prevalence and low awareness. Parasit. Vectors. 2013;6:328. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley J.W. DELMAR CENGAGE Learning; USA: 2012. Parasitology for Medical and Clinical Laboratory Professionals. [Google Scholar]
- Salam R., Haider B., Humayun Q., Bhutta Z. Effect of administration of antihelminthics for soil-transmitted helminths during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015:Cd005547. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005547.pub3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar-Castañon V., Legorreta-Herrera M., Rodriguez-Sosa M. Helminth parasites alter protection against plasmodium infection. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014;2014 doi: 10.1155/2014/913696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Maayan N., Soares-Weiser K., Donegan S., Garner P. The Cochrane Library; 2012. Deworming Drugs for Soil-Transmitted Intestinal Worms in Children: Effects on Nutritional Indicators, Haemoglobin and School Performance (Review) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma A., Miyagi I., Kamimura K., Tokuyama Y., Hasegawa H., Selomo M., Dahlan D., Majid I., Hasanuddi I., Ngatimin R., Mogi M., Kuwabara N. Questionnaire survey and prevalence of intestinal helminthic infections in Barru, Sulawesi, Indonesia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health. 1999;30:68–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voeks R.A., Sercombe P. The scope of hunter–gatherer ethnomedicine. Soc. Sci. Med. 2000;51:679–690. doi: 10.1016/s0277-9536(00)00012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu B., Gordon C., Hu W., McManus D., Chen H.-G., Gray D., Ju C., Zeng X.-J., Gobert G., Ge J. A novel procedure for precise quantification of Schistosoma japonicum eggs in bovine feces. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012;6 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelifari L., Bloch P., Magnussen P., Lieshout L.v., Dery G., Anemana S., Agongo E., Polderman A. Distribution of human Oesophagostomum bifurcum, hookworm and Strongyloides stercoralis infections in northern Ghana. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005;99:32–38. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2004.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaiss M., Rapin A., Lebon L., Dubey L., Mosconi I., Sarter K., Piersigilli A., Menin L., Walker A., Rougemont J., Paerewijck O., Geldhof P., McCoy K., Macpherson A., Croese J., Giacomin P., Loukas A., Junt T., Marsland B., Harris N. The intestinal microbiota contributes to the ability of helminths to modulate allergic inflammation. Immunity. 2015;43:998–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Exploration to identify helminth and malaria infection clusters in the study area in the middle belt of Ghana.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study and for this manuscript are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.