Preface 2011
We deeply appreciate the great contributions of many physicians in the registry of esophageal cancer cases. The Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan, 2011, was published here, despite some delay. The registry complies with the Act for the Protection of Personal Information. The encryption with an HASH function is used for anonymity in an unlinkable fashion.
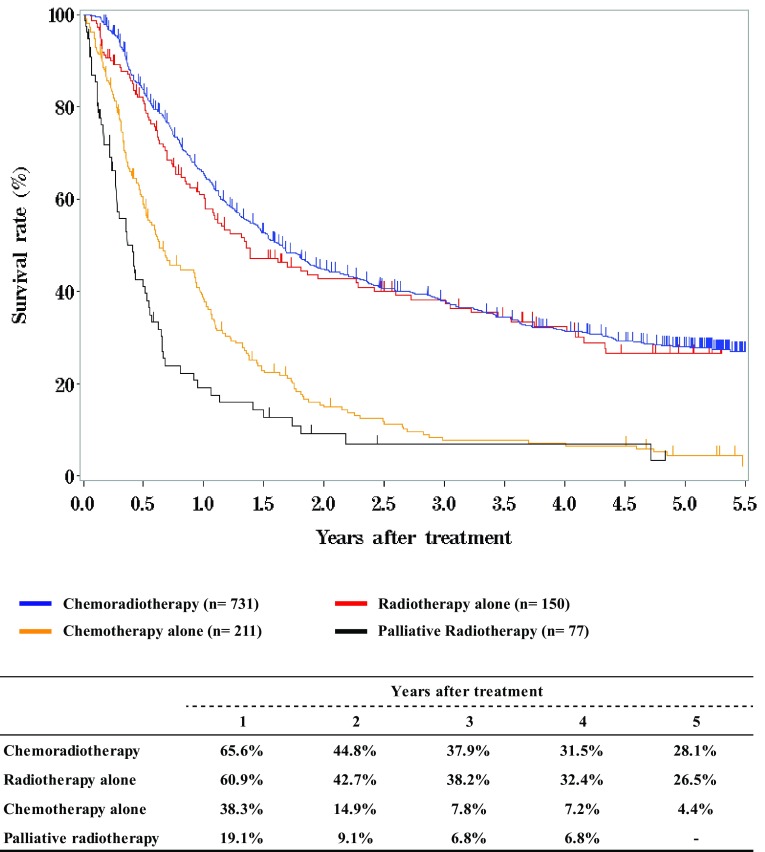
We briefly summarized the Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan, 2011. Japanese Classification of Esophageal Cancer 10th and UICC TNM Classification 7th were used for cancer staging according to the subjected year. A total of 6993 cases were registered from 300 institutions in Japan. Tumor locations were cervical: 4.5%, upper thoracic: 13.0%, middle thoracic: 47.8%, lower thoracic: 27.2%, and EG junction: 7.1%. Superficial carcinomas (Tis, T1a, and T1b) were 36.4%. For the histologic type of biopsy specimens, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma accounted for 88.3 and 5.3%, respectively. Regarding clinical results, the 5-year survival rates of patients treated using endoscopic resection, concurrent chemoradiotherapy, radiotherapy alone, or esophagectomy were 86.0, 28.1, 26.5, and 54.5%, respectively. The endoscopic submucosal dissection accounted for 78.1% of endoscopic resection. Esophagectomy was performed in 4147 cases. Concerning the approach used for esophagectomy, 33.5% of the cases were treated thoracoscopically. The operative mortality (within 30 days after surgery) was 0.65% and the hospital mortality was 3.76%. The 5-year survival rate of patients with pStage IV in UICC classification (including patients with supraclavicular node metastasis) was better than that of patients with pStage IVb in JES classification (not including patients with supraclavicular node metastasis).
We hope that this Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan for 2011 will help to improve all aspects of the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer in Japan.
Contents
-
I.Clinical factors of esophageal cancer patients treated in 2011
- Institution-registered cases in 2011
- Patient background
- Table 1 Age and gender
- Table 2 Primary treatment
- Table 3 Tumor location
- Table 4 Histologic types of biopsy specimens
- Table 5 Depth of tumor invasion, cT (UICC TNM 7th)
- Table 6 Lymph node metastasis, cN (UICC TNM 7th)
- Table 7 Distant metastasis, cM (UICC TNM 7th)
- Table 8 Clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
-
II.Results of endoscopically treated patients in 2011
- Table 9 Details of endoscopic treatment for curative intent
- Table 10 Complications of EMR/ESD
- Table 11 Pathological depth of tumor invasion of EMR/ESD specimens
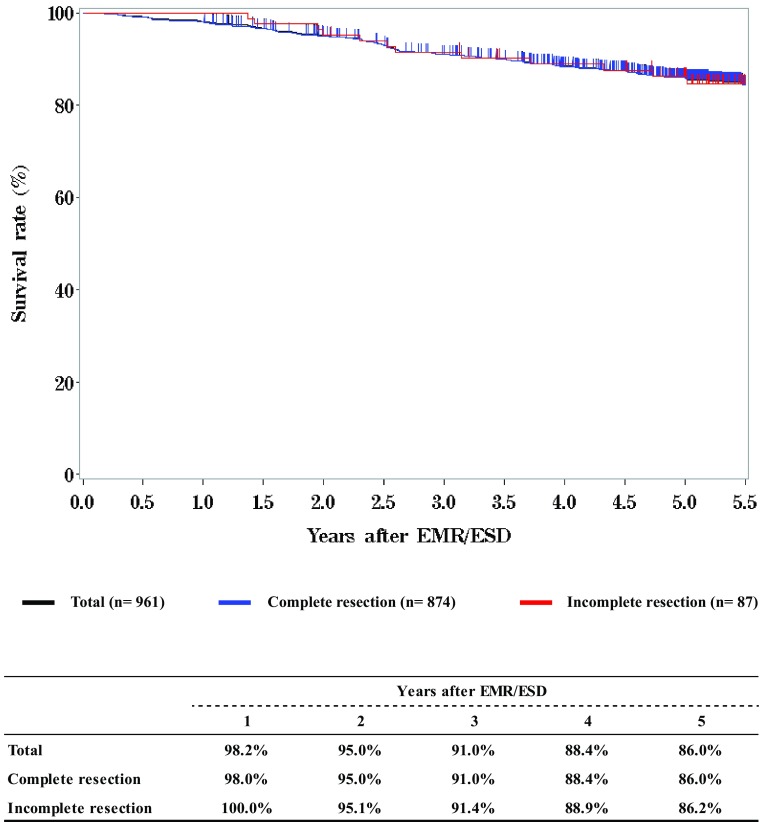
- Figure 1 Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD
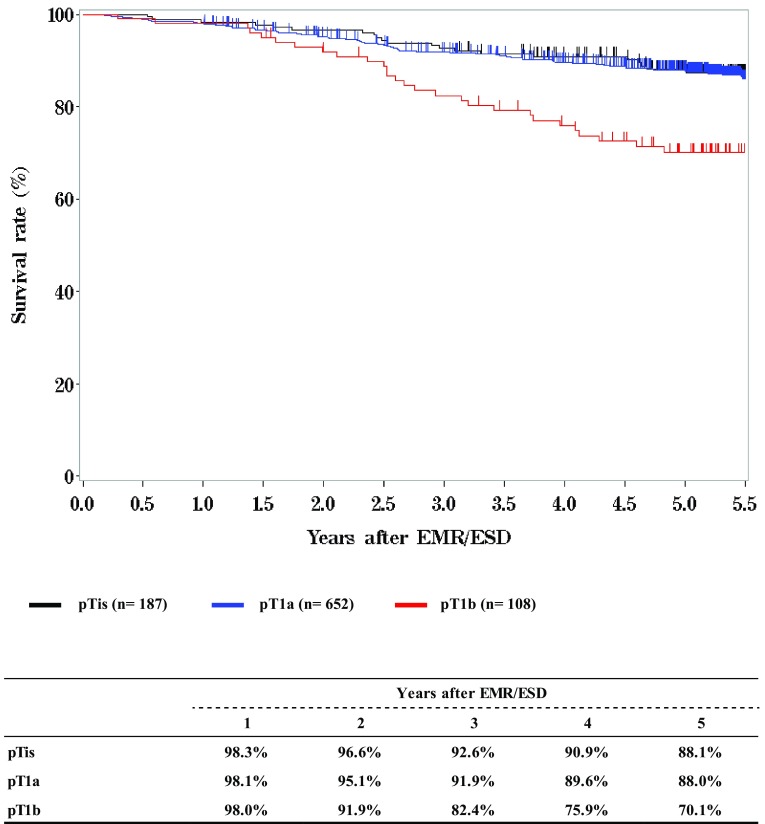
- Figure 2 Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD according to the pathological depth of tumor invasion (pT)
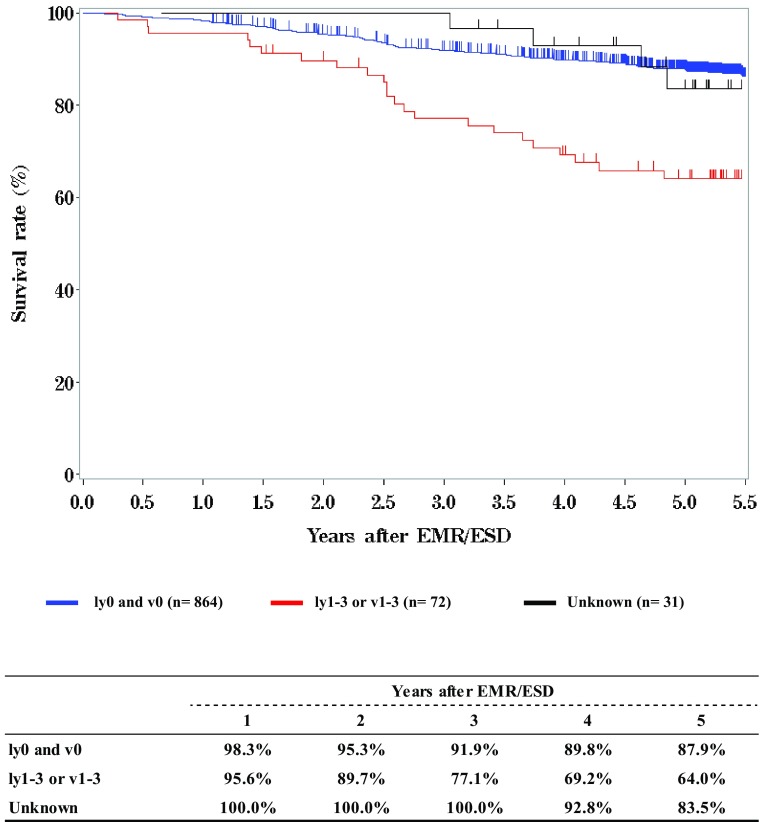
- Figure 3 Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD according to the lymphatic and venous invasion
-
III.Results in patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in 2011
- Table 12 Dose of irradiation (non-surgically treated cases)
- Table 13 Dose of irradiation (surgically treated cases)
- Figure 4 Survival of patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy
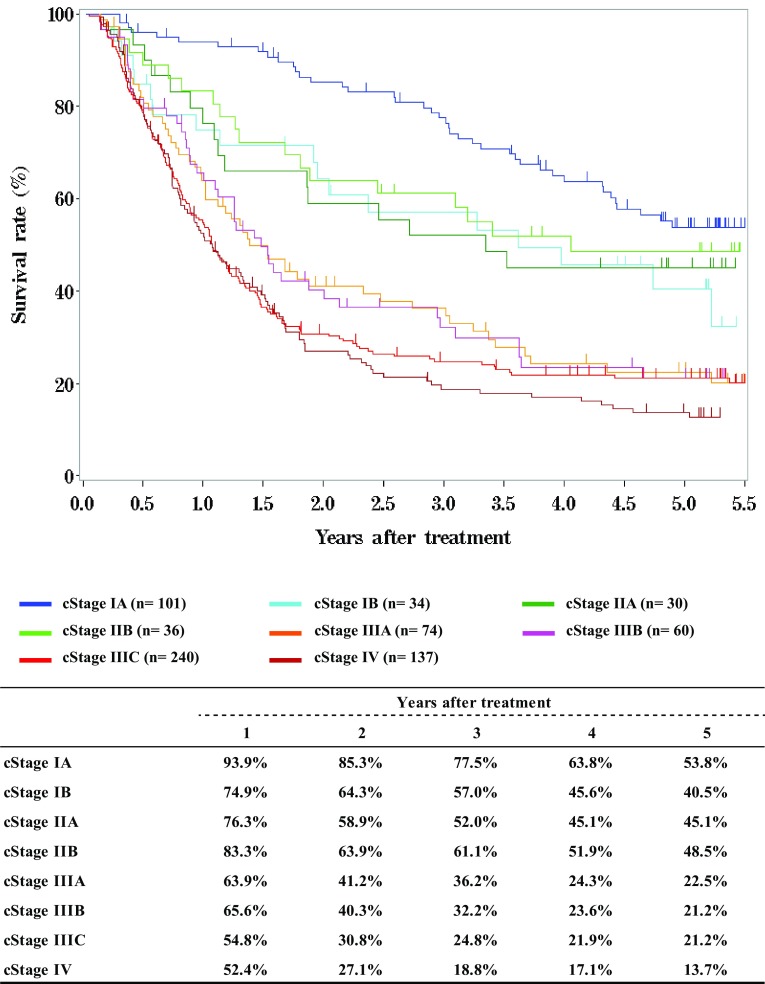
- Figure 5 Survival of patients treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
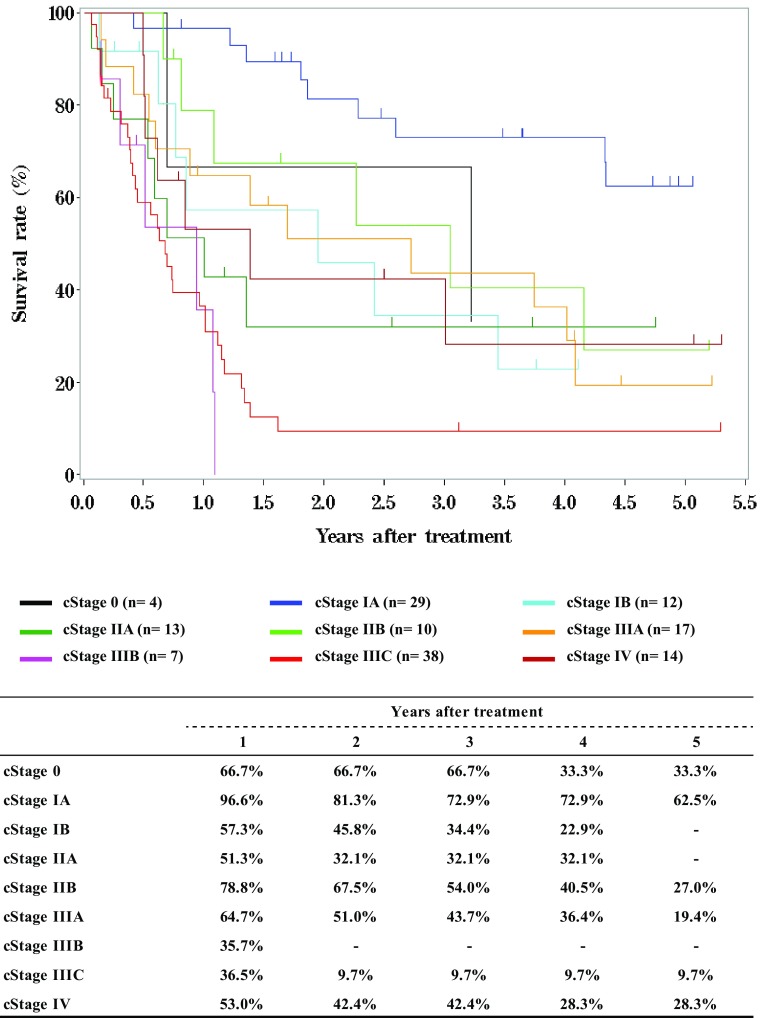
- Figure 6 Survival of patients underwent radiotherapy alone according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
-
IV.Results in patients who underwent esophagectomy in 2011
- Table 14 Treatment modalities of esophagectomy
- Table 15 Tumor location
- Table 16 Approaches to tumor resection
- Table 17 Video-assisted surgery
- Table 18 Fields of lymph node dissection according to the location of the tumor
- Table 19 Reconstruction route
- Table 20 Organs used for reconstruction
- Table 21 Histological classification
- Table 22 Depth of tumor invasion, pT (JES 10th)
- Table 23 Pathological grading of lymph node metastasis, pN (JES 10th)
- Table 24 Pathological findings of lymph node metastasis, pN (UICC 7th)
- Table 25 Pathological findings of distant organ metastasis, pM (JES 10th)
- Table 26 Residual tumor
- Table 27 Causes of death
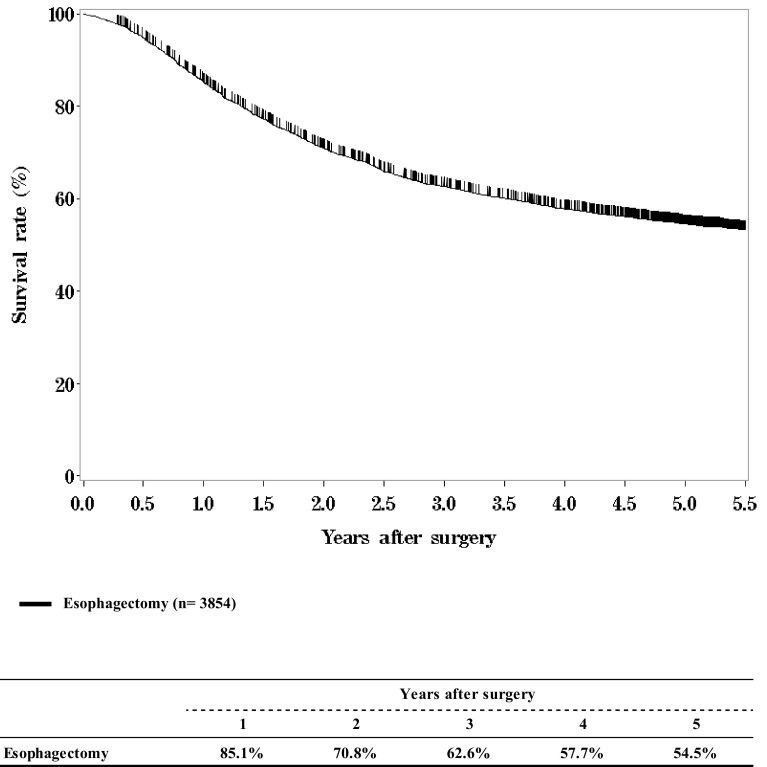
- Figure 7 Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy
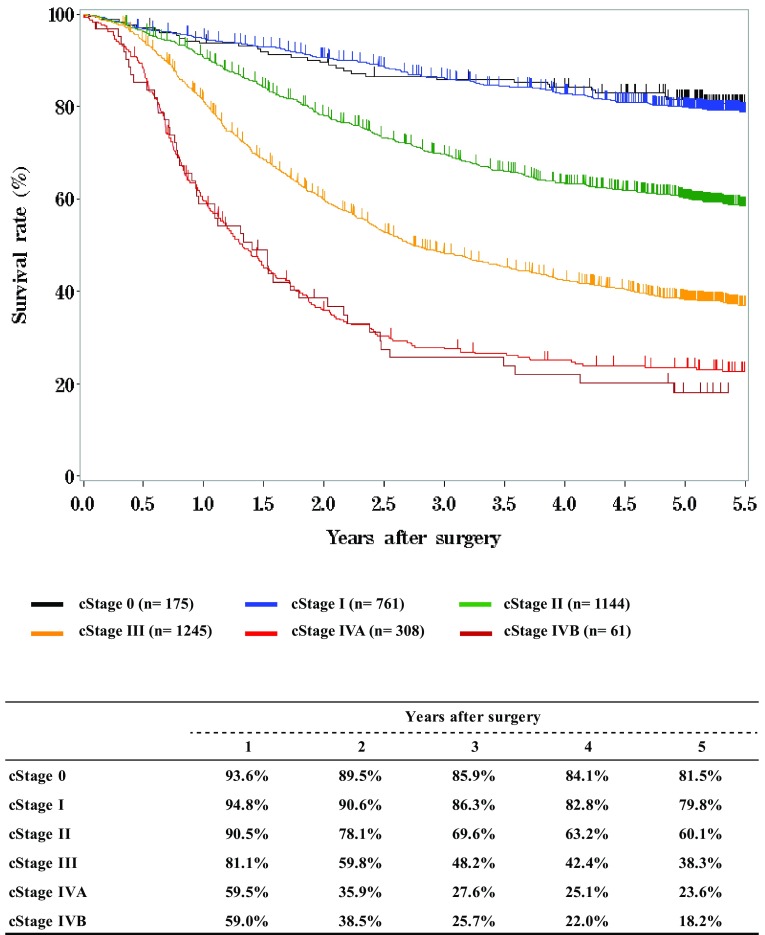
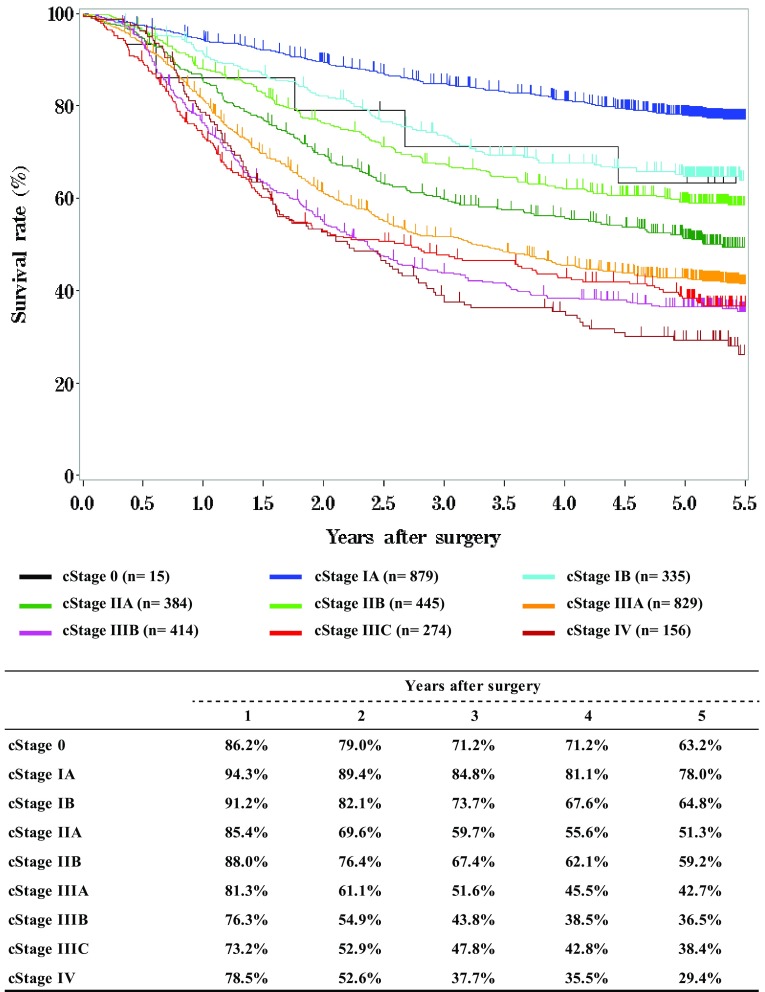
- Figure 8 Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to clinical stage (JES 10th)
- Figure 9 Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to clinical stage (UICC 7th)
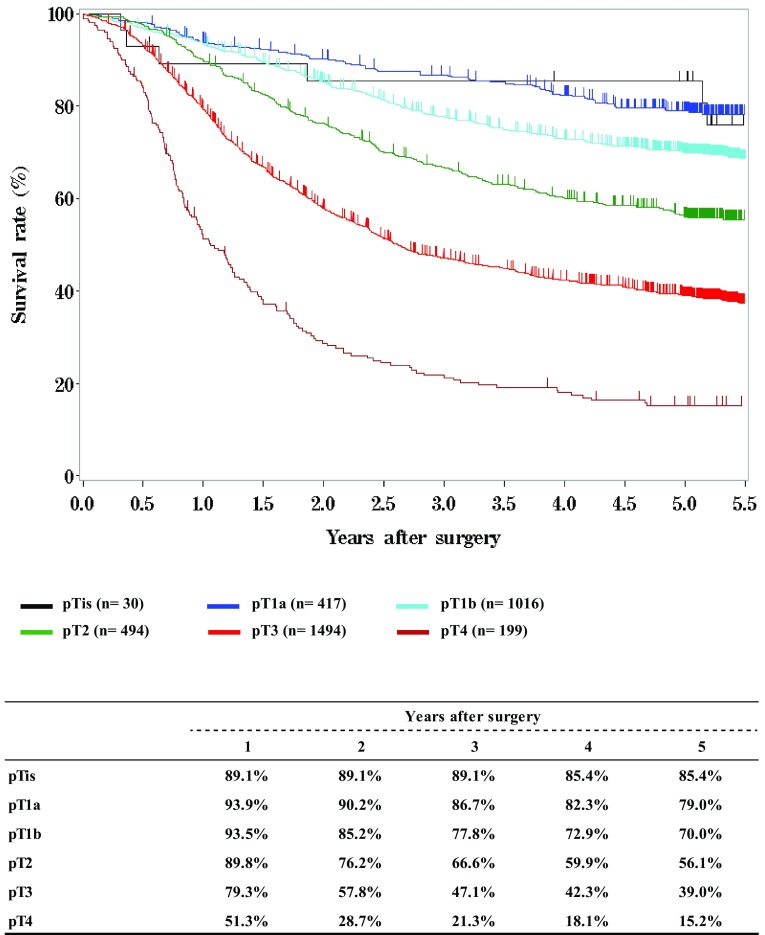
- Figure 10 Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to the depth of tumor invasion, pT (JES 10th)
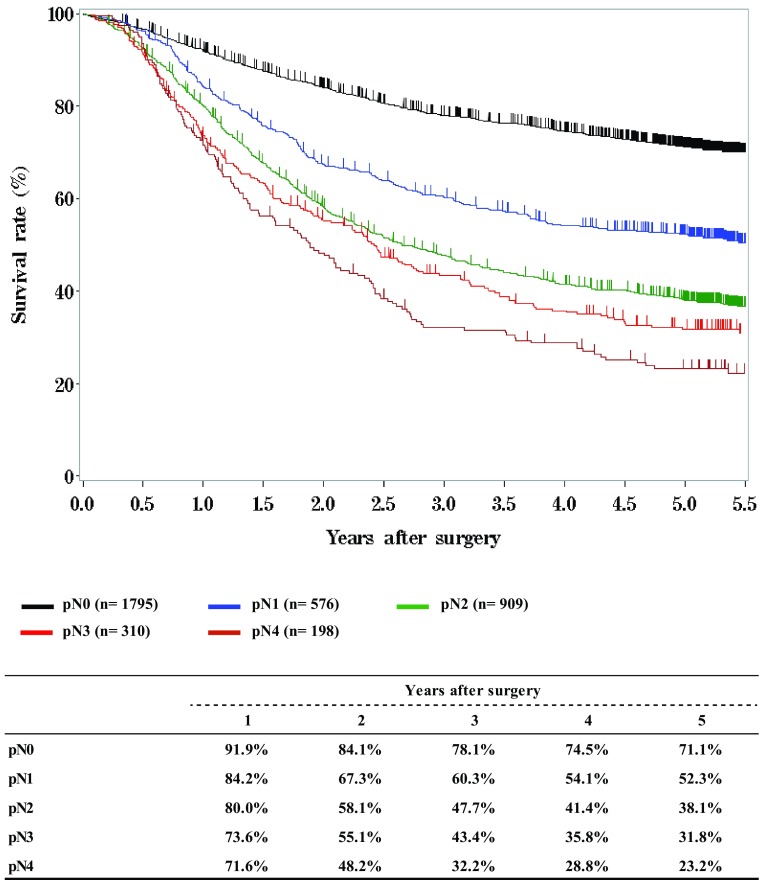
- Figure 11 Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to lymph node metastasis, pN (JES 10th)
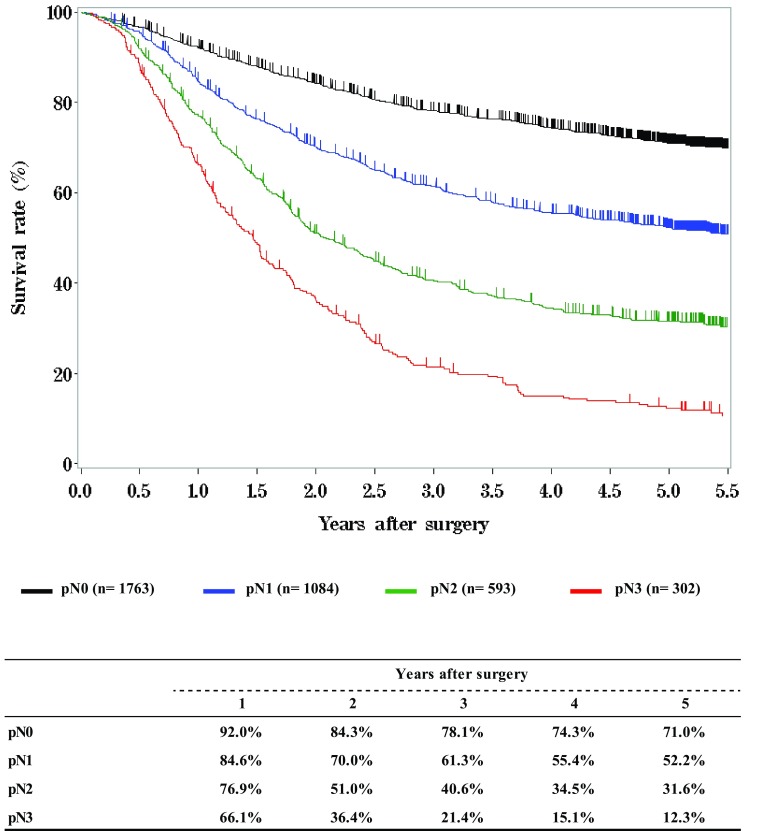
- Figure 12 Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to lymph node metastasis, pN (UICC 7th)
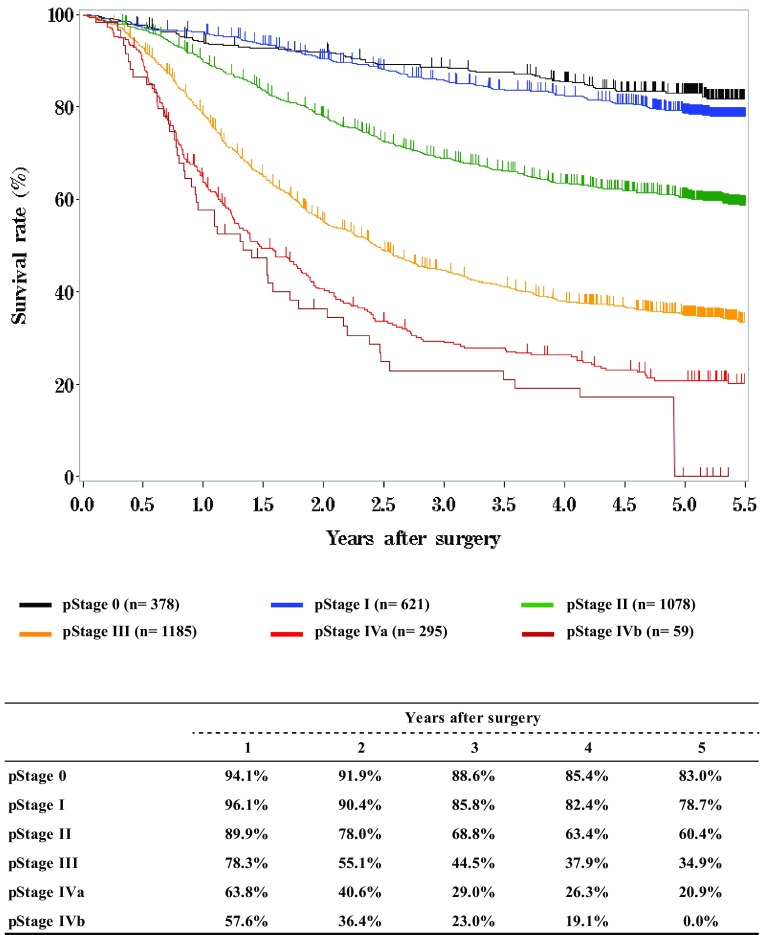
- Figure 13 Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to pathological stage (JES 10th)
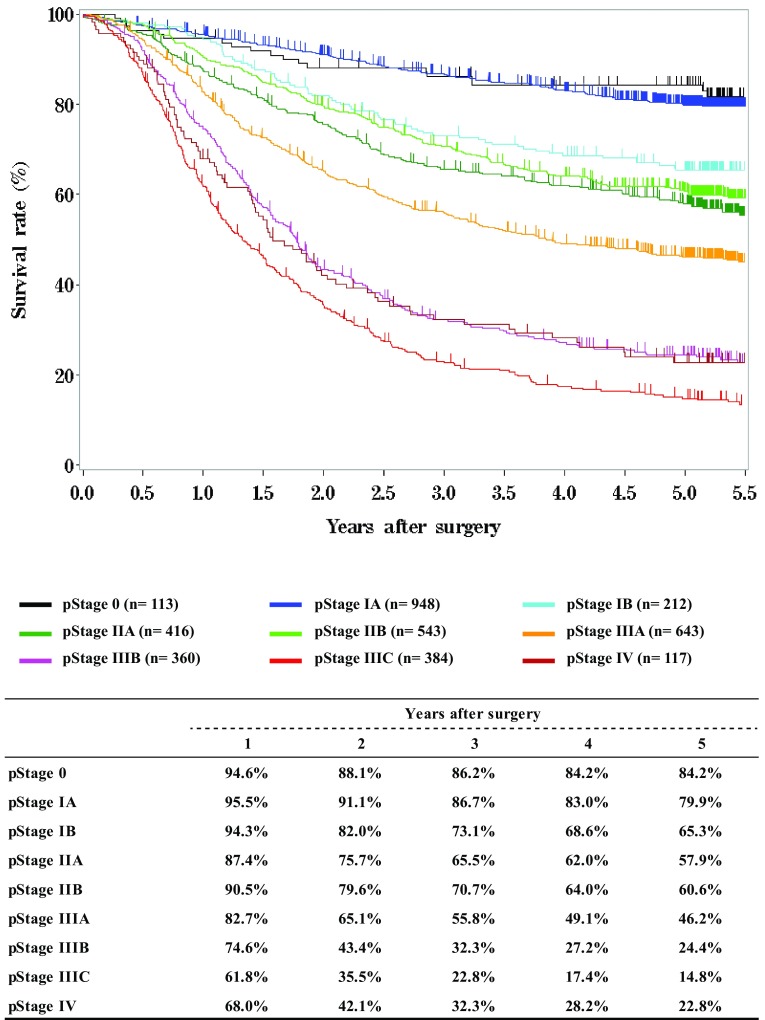
- Figure 14 Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to pathological stage (UICC TNM 7th)
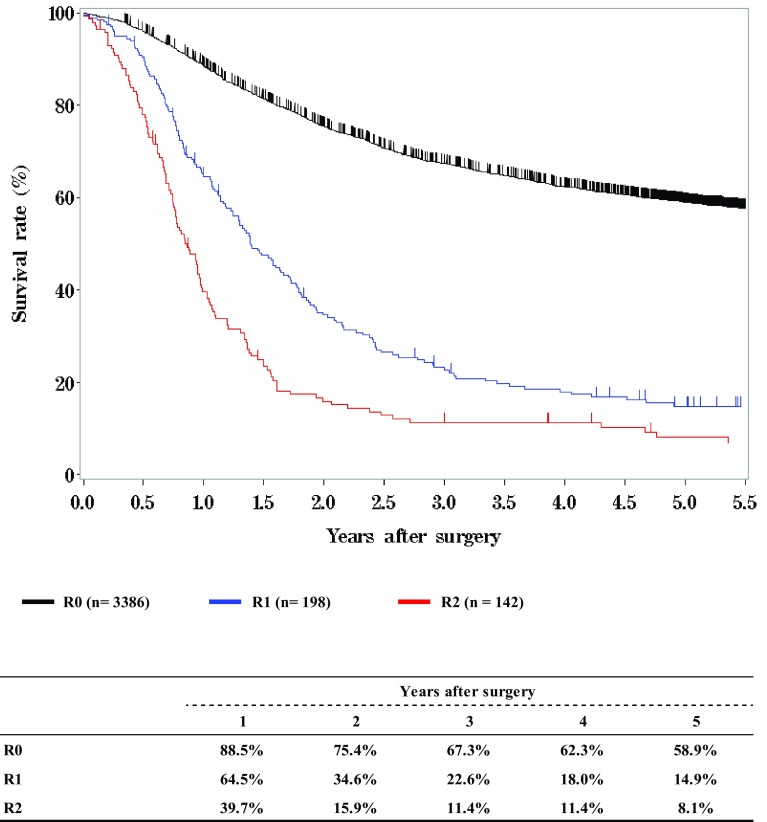
- Figure 15 Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to residual tumor (R)
Table 1.
Age and gender
| Age | Male | Female | Cases (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤ 29 | 4 | 1 | 5 (0.1%) |
| 30 – 39 | 22 | 8 | 30 (0.4%) |
| 40 – 49 | 142 | 47 | 189 (2.7%) |
| 50 – 59 | 878 | 173 | 1051 (15.0%) |
| 60 – 69 | 2531 | 360 | 2891 (41.3%) |
| 70 – 79 | 1941 | 333 | 2274 (32.5%) |
| 80 – 89 | 442 | 90 | 532 (7.6%) |
| 90– | 13 | 8 | 21 (0.3%) |
| Total | 5973 | 1020 | 6993 |
Table 2.
Primary treatment
| Treatments | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Surgery | 4236 (60.7%) |
| Esophagectomy | 4147 (59.4%) |
| Palliative surgery | 89 (1.3%) |
| Chemotherapy/radiotherapy | 1549 (22.2%) |
| Endoscopic treatment | 1198 (17.2%) |
| Total | 6983 |
Table 3.
Tumor location
| Location of tumor | Endoscopic treatment (%) | Surgery | Chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esophagectomy (%) | Palliative surgery (%) | ||||
| Cervical | 33 (2.8%) | 127 (3.1%) | 4 (4.5%) | 147 (9.5%) | 311 (4.5%) |
| Upper thoracic | 116 (9.7%) | 517 (12.5%) | 18 (20.2%) | 256 (16.5%) | 907 (13.0%) |
| Middle thoracic | 687 (57.3%) | 1873 (45.2%) | 46 (51.7%) | 732 (47.3%) | 3338 (47.8%) |
| Lower thoracic | 296 (24.7%) | 1235 (29.8%) | 20 (22.5%) | 345 (22.3%) | 1896 (27.2%) |
| EG | 41 (3.4%) | 300 (7.2%) | 0 | 36 (2.3%) | 377 (5.4%) |
| E = G | 9 (0.8%) | 47 (1.1%) | 0 | 1 (0.1%) | 57 (0.8%) |
| GE | 5 (0.4%) | 40 (1.0%) | 1 (1.1%) | 2 (0.1%) | 48 (0.7%) |
| Unknown | 11 (0.9%) | 8 (0.2%) | 0 | 30 (1.9%) | 49 (0.7%) |
| Total | 1198 | 4147 | 89 | 1549 | 6983 |
E esophageal, G gastric
Table 4.
Histologic types of biopsy specimens
| Histologic types | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 6164 (88.3%) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 4369 (62.6%) |
| Well differentiated | 378 (5.4%) |
| Moderately differentiated | 1054 (15.1%) |
| Poorly differentiated | 363 (5.2%) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 281 (4.0%) |
| Barrett’s adenocarcinoma | 90 (1.3%) |
| Adenosquamous carcinoma | 15 (0.2%) |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 4 (0.1%) |
| Basaloid carcinoma | 35 (0.5%) |
| Neuroendocrine cell tumor | 26 (0.4%) |
| Undifferentiated carcinoma | 8 (0.1%) |
| Sarcoma | 6 (0.1%) |
| Malignant melanoma | 19 (0.3%) |
| Carcinosarcoma | 22 (0.3%) |
| GIST | 7 (0.1%) |
| Other tumors | 92 (1.3%) |
| Unknown | 214 (3.1%) |
| Total | 6983 |
Table 5.
Depth of tumor invasion, cT (UICC TNM 7th)
| cT | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| cTX | 71 (1.0%) |
| cT0 | 10 (0.1%) |
| cTis | 198 (2.8%) |
| cT1a | 1051 (15.1%) |
| cT1b | 1292 (18.5%) |
| cT2 | 905 (13.0%) |
| cT3 | 2408 (34.5%) |
| cT4a | 384 (5.5%) |
| cT4b | 530 (7.6%) |
| Unknown | 134 (1.9%) |
| Total | 6983 |
Table 6.
Lymph node metastasis, cN (UICC TNM 7th)
| cN | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| cNX | 187 (2.7%) |
| cN0 | 3195 (45.8%) |
| cN1 | 1864 (26.7%) |
| cN2 | 1199 (17.2%) |
| cN3 | 459 (6.6%) |
| Unknown | 79 (1.1%) |
| Total | 6983 |
Table 7.
Distant metastasis, cM (UICC TNM 7th)
| cM | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| cM0 | 6128 (87.8%) |
| cM1 | 722 (10.3%) |
| Unknown | 133 (1.9%) |
| Total | 6983 |
Table 8.
Clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
| Clinical stage | Endoscopic treatment (%) | Surgery | Chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esophagectomy (%) | Palliative surgery (%) | ||||
| Stage 0 | 151 (12.6%) | 15 (0.4%) | 0 | 7 (0.5%) | 173 (2.5%) |
| Stage IA | 809 (67.5%) | 937 (22.6%) | 1 (1.1%) | 161 (10.4%) | 1908 (27.3%) |
| Stage IB | 2 (0.2%) | 363 (8.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | 58 (3.7%) | 424 (6.1%) |
| Stage IIA | 3 (0.3%) | 419 (10.1%) | 3 (3.4%) | 60 (3.9%) | 485 (6.9%) |
| Stage IIB | 4 (0.3%) | 470 (11.3%) | 1 (1.1%) | 63 (4.1%) | 538 (7.7%) |
| Stage IIIA | 10 (0.8%) | 898 (21.7%) | 14 (15.7%) | 147 (9.5%) | 1069 (15.3%) |
| Stage IIIB | 6 (0.5%) | 456 (11.0%) | 9 (10.1%) | 99 (6.4%) | 570 (8.2%) |
| Stage IIIC | 32 (2.7%) | 292 (7.0%) | 27 (30.3%) | 390 (25.2%) | 741 (10.6%) |
| Stage IV | 40 (3.3%) | 165 (4.0%) | 25 (28.1%) | 434 (28.0%) | 664 (9.5%) |
| Unknown | 141 (11.8%) | 132 (3.2%) | 8 (9.0%) | 130 (8.4%) | 411 (5.9%) |
| Total | 1198 | 4147 | 89 | 1549 | 6983 |
Table 9.
Details of endoscopic treatment for curative intent
| Treatment details | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| EMR | 190 (17.9%) |
| EMR + YAG laser | 13 (1.2%) |
| ESD | 829 (78.1%) |
| ESD + EMR | 5 (0.5%) |
| ESD + PDT | 0 |
| ESD + YAG laser | 5 (0.5%) |
| PDT | 2 (0.2%) |
| YAG laser | 18 (1.7%) |
| Total | 1062 |
EMR endoscopic mucosal resection, ESD endoscopic submucosal dissection, YAG yttrium aluminum garnet, PDT photodynamic therapy
Table 10.
Complications of EMR/ESD
| Complications of EMR/ESD | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 969 (93.0%) |
| Perforation | 13 (1.2%) |
| Bleeding | 3 (0.3%) |
| Mediastinitis | 3 (0.3%) |
| Stenosis | 49 (4.7%) |
| Others | 4 (0.4%) |
| Total | 1042 |
Table 11.
Pathological depth of tumor invasion of EMR/ESD specimens
| Pathological depth of tumor invasion (pT) | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| pTX | 3 (0.3%) |
| pT0 | 7 (0.7%) |
| pTis | 201 (19.3%) |
| pT1a | 703 (67.5%) |
| pT1b | 114 (10.9%) |
| pT2 | 3 (0.3%) |
| Unknown | 11 (1.1%) |
| Total | 1042 |
Fig. 1.
Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD
Fig. 2.
Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD according to the pathological depth of tumor invasion (pT)
Fig. 3.
Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD according to the lymphatic and venous invasion
Table 12.
Dose of irradiation (non-surgically treated cases)
| Dose of irradiation (Gy) | Definitive | Palliative (%) | Recurrence (%) | Others (%) | Unknown (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiation alone (%) | Chemoradiotherapy (%) | ||||||
| − 29 | 6 (3.5%) | 13 (1.7%) | 32 (10.9%) | 0 | 2 (5.7%) | 0 | 53 (4.1%) |
| 30–39 | 4 (2.3%) | 17 (2.2%) | 40 (13.6%) | 0 | 2 (5.7%) | 0 | 63 (4.9%) |
| 40–49 | 8 (4.6%) | 33 (4.2%) | 34 (11.6%) | 0 | 10 (28.6%) | 0 | 85 (6.6%) |
| 50–59 | 29 (16.8%) | 177 (22.7%) | 71 (24.1%) | 1 (25.0%) | 11 (31.4%) | 1 (50.0%) | 290 (22.5%) |
| 60–69 | 116 (67.1%) | 516 (66.1%) | 108 (36.7%) | 3 (75.0%) | 9 (25.7%) | 0 | 752 (58.3%) |
| 70– | 9 (5.2%) | 12 (1.5%) | 3 (1.0%) | 0 | 1 (2.9%) | 0 | 25 (2.2%) |
| Unknown | 1 (0.6%) | 13 (1.7%) | 6 (2.0%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (50.0%) | 21 (1.6%) |
| Total | 173 | 781 | 294 | 4 | 35 | 2 | 1289 |
| Median (min–max) | 60.0 (4.4–70.0) | 60.0 (1.8–120.0) | 50.4 (3.6–159.0) | 60.0 (50.0–61.2) | 50.0 (21.6–109.0) | 54.0 (54.0–54.0) | 60.0 (1.8–105.0) |
Table 13.
Dose of irradiation (surgically treated cases)
| Dose of irradiation (Gy) | Preoperative irradiation (%) | Postoperative irradiation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| –29 | 5 (2.2%) | 3 (6.0%) |
| 30–39 | 39 (17.1%) | 0 |
| 40–49 | 156 (68.4%) | 8 (16.0%) |
| 50–59 | 15 (6.6%) | 15 (30.0%) |
| 60–69 | 6 (2.6%) | 15 (30.0%) |
| 70– | 1 (0.4%) | 0 |
| Unknown | 6 (2.6%) | 9 (18.0%) |
| Total | 228 | 50 |
| Median (min–max) | 40.0 (1.8–70.0) | 50.4 (2.0–66.0) |
Fig. 4.
Survival of patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy
Fig. 5.
Survival of patients treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
Fig. 6.
Survival of patients underwent radiotherapy alone according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
Table 14.
Treatment modalities of esophagectomy
| Treatments | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Esophagectomy alone | 1699 (41.2%) |
| Esophagectomy + endoscopic treatment | 89 (2.2%) |
| Esophagectomy + chemoradiotherapy | 590 (14.3%) |
| Concurrent chemoradiotherapy | 370 (9.0%) |
| Other | 220 (5.3%) |
| Esophagectomy + chemoradiotherapy + endoscopic treatment | 21 (0.5%) |
| Esophagectomy + chemotherapy | 1657 (40.2%) |
| Preoperative | 1295 (31.4%) |
| Postoperative | 198 (4.8%) |
| Preoperative and postoperative | 57 (1.4%) |
| Recurrence | 107 (2.6%) |
| Other | 20 (0.5%) |
| Esophagectomy + chemotherapy + endoscopic treatment | 1 (0.0%) |
| Esophagectomy + radiotherapy | 67 (1.6%) |
| Preoperative | 17 (0.4%) |
| Postoperative | 13 (0.3%) |
| Recurrence | 5 (0.1%) |
| Other | 32 (0.8%) |
| Esophagectomy + radiotherapy + endoscopic treatment | 3 (0.1%) |
| Total | 4127 |
Table 15.
Tumor location
| Locations | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Cervical | 127 (3.1%) |
| Upper thoracic | 517 (12.5%) |
| Middle thoracic | 1873 (45.2%) |
| Lower thoracic | 1235 (29.8%) |
| E > G | 300 (7.2%) |
| E = G | 47 (1.1%) |
| G > E | 40 (1.0%) |
| Unknown | 8 (0.2%) |
| Total lesions | 4147 |
Table 16.
Approaches to tumor resection
| Approaches | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Cervical approach | 96 (2.3%) |
| Right thoracic | 3459 (83.4%) |
| Left thoracic | 67 (1.6%) |
| Left thoracoabdominal | 72 (1.7%) |
| Abdominal | 172 (4.1%) |
| Transhiatal thoracic esophagectomy | 51 (1.2%) |
| Transhiatal lower esophagectomy | 82 (2.0%) |
| Sternotomy | 9 (0.2%) |
| Others | 33 (0.8%) |
| Unknown | 106 (2.6%) |
| Total | 4147 |
Thoracic includes thoracotomy and thoracoscopic. Abdominal includes laparotomy and laparoscopic
Table 17.
Video-assisted surgery
| Video-assisted surgery | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 2389 (57.6%) |
| Thoracoscopy | 768 (18.5%) |
| Thoracoscopy + Laparoscopy | 605 (14.6%) |
| Thoracoscopy + Laparoscopy + Mediastinoscopy | 15 (0.4%) |
| Thoracoscopy + Mediastinoscopy | 2 (0.0%) |
| Laparoscopy | 201 (4.8%) |
| Laparoscopy + Mediastinoscopy | 14 (0.3%) |
| Laparoscopy + Other | 2 (0.0%) |
| Mediastinoscopy | 21 (0.5%) |
| Others | 4 (0.1%) |
| Total | 4147 |
Table 18.
Fields of lymph node dissection according to the location of the tumor
| Field of lymphadenectomy | Cervical | Upper thoracic | Middle thoracic | Lower thoracic | E > G | E = G | G > E | Unknown | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 10 (8.6%) | 13 (3.2%) | 59 (3.5%) | 28 (2.7%) | 13 (5.4%) | 2 (25.0%) | 125 (3.5%) | ||
| C | 36 (31.0%) | 10 (2.4%) | 20 (1.2%) | 3 (0.3%) | 1 (0.4%) | 70 (2.0%) | |||
| C + UM | 21 (18.1%) | 6 (1.5%) | 3 (0.2%) | 1 (0.1%) | 31 (0.9%) | ||||
| C + UM + MLM | 2 (1.7%) | 12 (2.9%) | 28 (1.7%) | 12 (1.1%) | 1 (3.7%) | 55 (1.5%) | |||
| C + UM + MLM + A | 27 (23.3%) | 257 (62.5%) | 800 (47.9%) | 367 (34.8%) | 26 (10.8%) | 6 (15.8%) | 1 (12.5%) | 1484 (41.6%) | |
| C + UM + MLM + A+OT | 1 (0.1%) | 1 (0.0%) | |||||||
| C + UM + A | 2 (1.7%) | 1 (0.2%) | 2 (0.1%) | 2 (0.2%) | 7 (0.2%) | ||||
| C + MLM | 1 (0.1%) | 1 (0.0%) | |||||||
| C + MLM + A | 3 (2.6%) | 1 (0.2%) | 7 (0.4%) | 3 (0.3%) | 14 (0.4%) | ||||
| C + A | 1 (0.9%) | 2 (0.5%) | 4 (0.2%) | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.4%) | 10 (0.3%) | |||
| UM | 4 (3.4%) | 3 (0.7%) | 5 (0.3%) | 3 (0.3%) | 15 (0.4%) | ||||
| UM + MLM | 1 (0.9%) | 7 (1.7%) | 29 (1.7%) | 12 (1.1%) | 1 (0.4%) | 1 (12.5%) | 51 (1.4%) | ||
| UM + MLM + A | 3 (2.6%) | 75 (18.2%) | 627 (37.6%) | 478 (45.4%) | 56 (23.2%) | 5 (13.2%) | 1 (3.7%) | 1 (12.5%) | 1246 (35.0%) |
| UM + A | 1 (0.9%) | 4 (1.0%) | 2 (0.1%) | 2 (0.2%) | 2 (0.8%) | 11 (0.3%) | |||
| MLM | 3 (0.7%) | 10 (0.6%) | 14 (1.3%) | 3 (1.2%) | 30 (0.8%) | ||||
| MLM + A | 1 (0.9%) | 7 (1.7%) | 34 (2.0%) | 102 (9.7%) | 108 (44.8%) | 23 (60.5%) | 17 (63.0%) | 292 (8.2%) | |
| A | 1 (0.9%) | 6 (1.5%) | 22 (1.3%) | 12 (1.1%) | 28 (11.6%) | 3 (7.9%) | 8 (29.6%) | 1 (12.5%) | 81 (2.3%) |
| Unknown | 3 (2.6%) | 4 (1.0%) | 16 (1.0%) | 12 (1.1%) | 2 (0.8%) | 1 (2.6%) | 2 (25.0%) | 40 (1.1%) | |
| Total | 116 | 411 | 1669 | 1054 | 241 | 38 | 27 | 8 | 3564 |
C bilateral cervical nodes, UM upper mediastinal nodes, MLM middle–lower mediastinal nodes, A abdominal nodes
Table 19.
Reconstruction route
| Reconstruction route | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 56 (1.4%) |
| Subcutaneous | 384 (9.3%) |
| Retrosternal | 1437 (34.7%) |
| Posterior mediastinal | 1715 (41.4%) |
| Intrathoracic | 419 (10.1%) |
| Cervical | 35 (0.8%) |
| Others | 34 (0.8%) |
| Unknown | 67 (1.6%) |
| Total | 4147 |
Table 20.
Organs used for reconstruction
| Organs used for reconstruction | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 76 (1.8%) |
| Whole stomach | 63 (1.5%) |
| Gastric tube | 3508 (83.6%) |
| Jejunum | 255 (6.1%) |
| Free jejunum | 76 (1.8%) |
| Colon | 127 (3.0%) |
| Free colon | 13 (0.3%) |
| Skin graft | 1 |
| Others | 14 (0.3%) |
| Unknown | 63 (1.5%) |
| Total organs | 4196 |
| Total cases | 4147 |
Table 21.
Histological classification
| Histological classification | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 3502 (84.4%) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 732 (17.7%) |
| Well differentiated | 645 (15.6%) |
| Moderately differentiated | 1630 (39.3%) |
| Poorly differentiated | 495 (11.9%) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 210 (5.1%) |
| Barrett’s adenocarcinoma | 78 (1.9%) |
| Adenosquamous carcinoma | 31 (0.7%) |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 3 (0.1%) |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | 2 (0.0%) |
| Basaloid carcinoma | 81 (2.0%) |
| Neuroendocrine cell tumor | 15 (0.4%) |
| Undifferentiated carcinoma | 8 (0.2%) |
| Other carcinoma | 9 (0.2%) |
| Carcinosarcoma | 29 (0.7%) |
| Malignant melanoma | 16 (0.4%) |
| GIST | 6 (0.1%) |
| Other | 39 (0.9%) |
| Unknown | 118 (2.8%) |
| Total | 4147 |
Table 22.
Depth of tumor invasion, pT (JES 10th)
| pT category | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| pTX | 57 (1.4%) |
| pT0 | 128 (3.1%) |
| pTis | 31 (0.7%) |
| pT1a | 435 (10.5%) |
| pT1b | 1070 (25.8%) |
| pT2 | 516 (12.4%) |
| pT3 | 1576 (38.0%) |
| pT4 | 24 (0.6%) |
| pT4a | 93 (2.2%) |
| pT4b | 89 (2.1%) |
| Unknown | 128 (3.1%) |
| Total | 4147 |
Table 23.
Pathological grading of lymph node metastasis, pN (JES 10th)
| Lymph node metastasis | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| pN0 | 1970 (47.5%) |
| pN1 | 616 (14.9%) |
| pN2 | 949 (22.9%) |
| pN3 | 323 (7.8%) |
| pN4 | 209 (5.0%) |
| Unknown | 80 (1.9%) |
| Total | 4147 |
Table 24.
Pathological findings of lymph node metastasis, pN (UICC 7th)
| Lymph node metastasis | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| pN0 | 1871 (45.1%) |
| pN1 (1–2) | 1165 (28.1%) |
| pN2 (3–6) | 659 (15.9%) |
| pN3 (7–) | 366 (8.8%) |
| Unknown | 86 (2.1%) |
| Total | 4147 |
Table 25.
Pathological findings of distant organ metastasis, pM (JES 10th)
| Distant metastasis | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| pMX | 195 (4.7%) |
| pM0 | 3886 (93.7%) |
| pM1 | 66 (1.6%) |
| Total | 4147 |
Table 26.
Residual tumor
| Residual tumor | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| RX | 147 (3.5%) |
| R0 | 3624 (87.4%) |
| R1 | 219 (5.3%) |
| R2 | 157 (3.8%) |
| Total | 4147 |
Table 27.
Causes of death
| Cause of death | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Death due to recurrence | 1223 (71.2%) |
| Death due to other cancer | 71 (4.1%) |
| Death due to other disease (rec+) | 42 (2.4%) |
| Death due to other disease (rec−) | 239 (13.9%) |
| Death due to other disease (rec?) | 9 (0.5%) |
| Operative death* | 27 (1.6%) |
| Postoperative hospital death** | 55 (3.2%) |
| Unknown | 51 (3.0%) |
| Total of death cases | 1717 |
rec: recurrence
*Operative death means death within 30 days after operation in or out of hospital
**Hospital death is defined as death during the same hospitalization, regardless of department at time of death
Operative mortality after esophagectomy: 0.65%
Hospital mortality after esophagectomy: 3.76%
![]()
Fig. 7.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy
Fig. 8.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to clinical stage (JES 10th)
Fig. 9.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to clinical stage (UICC 7th)
Fig. 10.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to the depth of tumor invasion, pT (JES 10th)
Fig. 11.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to lymph node metastasis, pN (JES 10th)
Fig. 12.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to lymph node metastasis, pN (UICC 7th)
Fig. 13.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to pathological stage (JES 10th)
Fig. 14.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to pathological stage (UICC TNM 7th)
Fig. 15.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to residual tumor (R)
I. Clinical factors of esophageal cancer patients treated in 2011
Institution-registered cases in 2011
| Institution |
|---|
| Ageo Central General Hospital |
| Aichi Cancer Center |
| Aichi Medical University Hospital |
| Aizawa Hospital |
| Akita Kouseiren Hiraga Hospital |
| Akita University Hospital |
| Arao Municipal Hospital |
| Asahikawa Medical College Hospital |
| Asahikawa-Kosei General Hospital |
| Chiba Cancer Center |
| Chiba Medical Center |
| Chiba Prefectural Sawara Hospital |
| Chiba University Hospital |
| Chigasaki Municipal Hospital |
| Dokkyo Medical University Hospital |
| Dokkyo Medical University Saitama Medical Center |
| Eiju General Hospital |
| Foundation for Detection of Early Gastric Carcinoma |
| Fuchu Hospital |
| Fujioka General Hospital |
| Fujisawa Shounandai Hospital |
| Fujita Health University |
| Fukui Prefectural Hospital |
| Fukui University Hospital |
| Fukui-ken Saiseikai Hospital |
| Fukuoka Dental College and Dental Hospital |
| Fukuoka Saiseikai General Hospital |
| Fukuoka University Chikushi Hospital |
| Fukuoka University Hospital |
| Fukuoka Wajiro Hospital |
| Fukushima Medical University Hospital |
| Fukuyama City Hospital |
| Fussa Hospital |
| Gifu Prefectural General Medical Center |
| Gifu University Hospital |
| Gunma Central General Hospital |
| Gunma Prefectural Cancer Center |
| Gunma University Hospital |
| Gunmaken Saiseikai Maebashi Hospital |
| Hachinohe City Hospital |
| Hakodate Goryokaku Hospital |
| Hakodate National Hospital |
| Hamamatsu University School of Medicine, University Hospital |
| Hannan Chuo Hospital |
| Heartlife Hospital |
| Higashiosaka City Medical Center |
| Hino Memorial Hospital |
| Hino Municipal Hospital |
| Hiratsuka City Hospital |
| Hiratsuka Kyosai Hospital |
| Hirosaki University Hospital |
| Hiroshima City Asa Hospital |
| Hiroshima City Hiroshima Citizens Hospital |
| Hiroshima Red Cross Hospital and Atomic-bomb Survivors Hospital |
| Hiroshima University Hospital |
| Hitachi General Hospital |
| Hofu Institute of Gastroenterology |
| Hokkaido University Hospital |
| Hyogo Cancer Center |
| Hyogo College of Medicine |
| Hyogo Prefectural Nishinomiya Hospital |
| Ibaraki Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Iizuka Hospital |
| Imazu Surgical Clinic |
| Inazawa City Hospital |
| International University of Health and Welfare Hospital |
| International Goodwill Hospital |
| Isehara Kyodo Hospital |
| Ishikawa Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Iwakuni Medical Center |
| Iwate Medical University Hospital |
| Iwate Prefectural Chubu Hospital |
| Iwate Prefectural Isawa Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Fukui Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Ishinomaki Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Kyoto Daini Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Nagaoka Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Okayama Hospital |
| JCHO Kyushu Hospital |
| JCHO Osaka Hospital |
| Jichi Medical University Hospital |
| Jichi Medical University Saitama Medical Center |
| Juntendo University Hospital |
| Juntendo University Shizuoka Hospital |
| Kagawa Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Kagawa Rosai Hospital |
| Kagawa University Hospital |
| Kagoshima Kenritsu Satsunan Hospital |
| Kagoshima University Hospital |
| Kameda General Hospital |
| Kanagawa Cancer Center |
| Kanazawa Medical University Hospital |
| Kanazawa University Hospital |
| Kansai Medical University Hospital |
| Kansai Rosai Hospital |
| Kasamatsu Hospital |
| Kashiwa Kousei General Hospital |
| Kawasaki Medical School Hospital |
| Kawasaki Medical School Kawasaki Hospital |
| Kawasaki Municipal Ida Hospital |
| Nara Hospital Kinki University Faculty of Medicine |
| Nara Medical University Hospital |
| National Cancer Center Hospital |
| National Cancer Center Hospital East |
| National Center for Global Health and Medicine |
| National Defense Medical College Hospital |
| National Hospital Organization Beppu Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Chiba Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Chiba-East-Hospital |
| National Hospital Organization Fukuoka-higashi Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Hokkaido Cancer Center |
| National Hospital Organization Iwakuni Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Kanmon Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Kure Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Kyoto Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Kyushu Cancer Center |
| National Hospital Organization Matsumoto Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Nagasaki Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Nagoya Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Okayama Medical Center |
| National Hospital Organization Osaka National Hospital |
| National Hospital Organization Tokyo Medical Center |
| Niigata Cancer Center Hospital |
| Niigata City General Hospital |
| Niigata Prefectural Shibata Hospital |
| Niigata University Medical and Dental Hospital |
| Nikko Memorial Hospital |
| Nippon Medical School Chiba Hokusoh Hospital |
| Nippon Medical School Hospital |
| Nippon Medical School Musashi Kosugi Hospital |
| Nippon Medical School Tama Nagayama Hospital |
| Nishi-Kobe Medical Center |
| Nishinomiya Municipal Central Hospital |
| NTT WEST Osaka Hospital |
| Numazu City Hospital |
| Obihiro Kousei General Hospital |
| Ogaki Municipal Hospital |
| Ohta General Hospital Foundation Ohta Nishinouchi Hospital |
| Oita Red Cross Hospital |
| Oita University Hospital |
| Okayama Saiseikai General Hospital |
| Okayama University Hospital |
| Osaka City University Hospital |
| Osaka Hospital of Japan Seafarers relief Association |
| Osaka International Cancer Institute |
| Osaka Medical College Hospital |
| Osaka Police Hospital |
| Osaka Prefectural Hospital Organization Osaka General Medical Center |
| Osaka Red Cross Hospital |
| Osaka University Hospital |
| Otsu City Hospital |
| Otsu Red Cross Hospital |
| Rinku General Medical Center |
| Ryukyu University Hospital |
| Saga University Hospital |
| Saga-ken Medical Center Koseikan |
| Saiseikai Fukushima General Hospital |
| Saiseikai Kyoto Hospital |
| Saiseikai Utsunomiya Hospital |
| Saiseikai Yahata General Hospital |
| Saitama Cancer Center |
| Saitama City Hospital |
| Saitama Medical Center |
| Saitama Medical University Hospital |
| Saitama Medical University Saitama Medical Center |
| Sakai City Medical Center |
| Saku Central Hospital |
| Sanin Rosai Hospital |
| Sano Kousei General Hospital |
| Sato Clinic |
| Sendai City Hospital |
| Sendai Medical Center |
| Shiga University of Medical Science Hospital |
| Shikoku Cancer Center |
| Shimane University Hospital |
| Shimizu Welfare Hospital |
| Shin Beppu Hospital |
| Shinko Hospital |
| Shizuoka Cancer Center |
| Shizuoka City Shizuoka Hospital |
| Shizuoka General Hospital |
| Showa University Fujigaoka Hospital |
| Showa University Hospital |
| Showa University Koto-Toyosu Hospital |
| Social Insurance Omuta Tenryo Hospital |
| Social Insurance Tagawa Hospital |
| St. Marianna University School of Medical Hospital |
| St. Luke’s International Hospital |
| Sugita Genpaku Memorial Obama Municipal Hospital |
| Suita Municipal Hospital |
| Takasago Municipal Hospital |
| Teikyo University Chiba Medical Center |
| Teikyo University Hospital |
| Tenri Hospital |
| The Cancer Institute Hospital of JFCR |
| The Jikei University Daisan Hospital |
| The Jikei University Hospital |
| The Research Center Hospital for Charged Particle Therapy of NIRS |
| Tochigi Cancer Center |
| Toho University Ohashi Medical Center |
| Toho University Omori Medical Center |
| Toho University Sakura Medical Center |
| Tohoku Kosai Hospital |
| Tohoku University Hospital |
| Tokai University Hachioji Hospital |
| Tokai University Hospital |
| Tokai University Tokyo Hospital |
| Tokushima Red Cross Hospital |
| Tokushima University Hospital |
| Tokuyama Central Hospital |
| Tokyo Dental College Ichikawa General Hospital |
| Tokyo Medical and Dental University Hospital |
| Tokyo Medical University Hospital |
| Tokyo Medical University Ibaraki Medical Center |
| Tokyo Metropolitan Cancer and Infectious Diseases Center Komagome Hospital |
| Tokyo Metropolitan Health and Medical Corporation Toshima Hospital |
| Tokyo Metropolitan Tama Medical Center |
| Tokyo Saiseikai Central Hospital |
| Tokyo University Hospital |
| Tokyo Women’s Medical University Hospital |
| Tokyo Women’s Medical University Medical Center East |
| Tokyo Women’s Medical University Yachiyo Medical Center |
| Tonan Hospital |
| Tone Chuo Hospital |
| Toranomon Hospital |
| Tottori Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Tottori University Hospital |
| Toyama Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Toyama University Hospital |
| Toyonaka Municipal Hospital |
| Tsuchiura Kyodo Hospital |
| Tsukuba University Hospital |
| Tsuruoka Municipal Shonai Hospital |
| University Hospital, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine |
| University of Miyazaki Hospital |
| Urasoe General Hospital |
| Wakayama Medical University Hospital |
| Yamagata Prefectural and Sakata Municipal Hospital Organization |
| Yamagata Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Yamagata Prefectural Shinjo Hospital |
| Yamagata University Hospital |
| Yamaguchi University Hospital |
| Yamaguchi-ken Saiseikai Shimonoseki General Hospital |
| Yamanashi Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Yamanashi University Hospital |
| Yao Municipal Hospital |
| Yokohama Chuo Hospital |
| Yokohama City Municipal Hospital |
| Yokohama City University Medical Center |
| Yokohama Rosai Hospital |
(Total 300 institutions)
Patient background
II. Results of endoscopically treated patients in 2011
III. Results in patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in 2011
IV. Results in patients who underwent esophagectomy in 2011
Compliance with ethical standards
Ethical Statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions.
Informed consent
Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Conflict of interest
All authors have nothing to disclose with regard to commercial support.
Footnotes
These data were first made available on March 2018, as the Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan, 2011. Not all the pages are reprinted here.
The authors were members of the Registration Committee for Esophageal Cancer, the Japan Esophageal Society, and made great contributions to the preparation of this material.
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-018-0624-x.
Change history
6/12/2018
In the original publication of the article, the below name of institutions were not included in the table of Institution-registered cases in 2011.