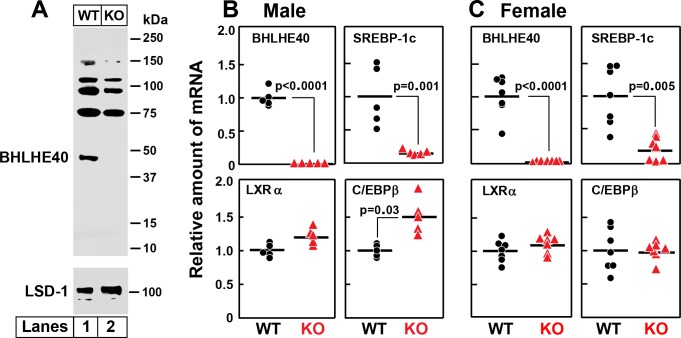
Figure 9. Knockout of Bhlhe40 gene in mice decreases SREBP-1c mRNA in livers of refed animals.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of liver nuclear extracts from wild type (WT) and Bhlhe40−/− (KO) mice. Nuclear extracts (20 µg protein) were subjected to 4–12% SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis with 1.5 µg/ml of rabbit polyclonal anti-BHLHE40 (directed against amino acids 1–60 of rat BHLHE40 protein). LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) served as a loading control and was immunoblotted with a 1:1000 dilution of rabbit monoclonal anti-LSD1. Proteins were detected with the LI-COR Odyssey Infrared Imaging System using a 1:5000 dilution of anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. (B and C) WT and Bhlhe40 KO mice were fasted overnight and then refed a high-carbohydrate diet for 4 hr, after which total liver RNA was prepared and subjected to quantitative RT-PCR. Each circle (WT) or triangle (KO) represents an individual mouse. The mean value for WT mice is defined as 1.0. (B) mRNAs in livers of male WT and KO mice (age 6 wk; 5 mice/group). Mean Ct values for BHLHE40, SREBP-1c, LXRα and C/EBPβ in WT mice were 21.2, 22.2, 21.7, and 22.1, respectively. (C) mRNAs in livers of female WT and KO mice (age 7 wk; 7 mice/group). Mean Ct values for BHLHE40, SREBP-1c, LXRα and C/EBPβ in WT mice were 21.5, 21.0, 22.3, and 22.5, respectively. p-Values calculated using Student t-test.