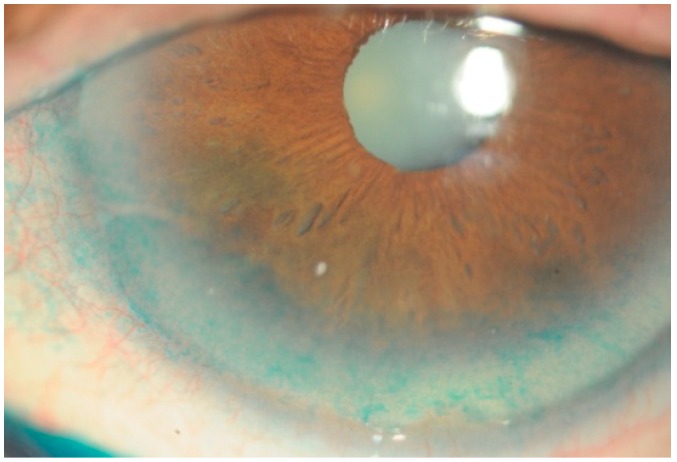
Figure 3.
Dry-eye syndrome is a multifactorial disease of the ocular surface in which oxidative stress is greatly involved. Affected patents suffer from symptoms of discomfort and tear film instability, and visual quality is reduced proportionally to the severity of the disease. The Figure 3 shows an example of corneal epithelium injuries in a patient affected by dry-eye syndrome, as detected by means of Lissamine green staining. Diffuse corneal epithelium alterations appear as green dots in the frame-shift of the inferior cornea surface.