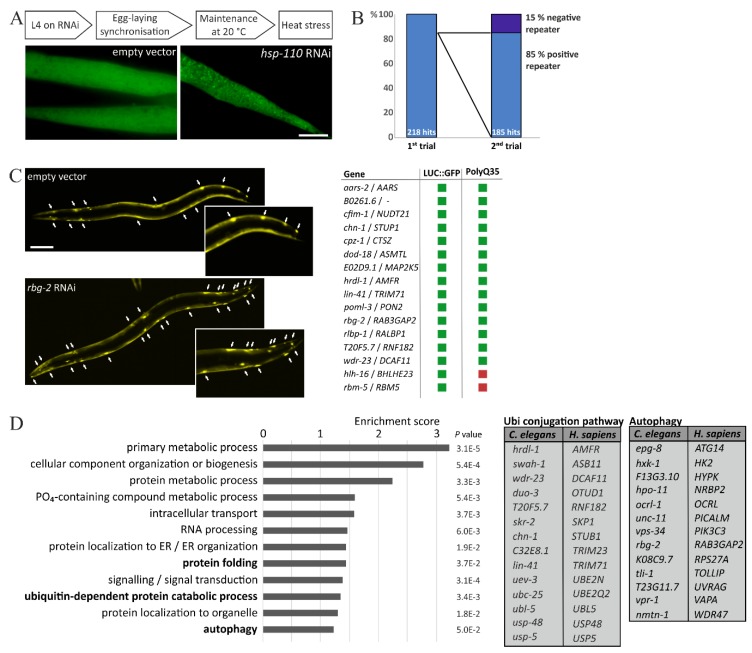
Figure 1.
Evaluation of the heat stress-based RNAi screen. (A) Schematic sequence of the RNAi approach and representative fluorescence images of body wall muscle cells of LUC::GFP-expressing worms after heat stress and the respective RNAi treatment. Scale bar: 20 µm. (B) Statistics of first and second trial. Initially, 218 candidates were identified, of which 85 % repeated their effects on LUC::GFP upon heat stress. (C) Representative fluorescence images of PolyQ35::YFP after RNAi treatment. Arrows indicate aggregates. Scale bar: 100 µm. The table summarizes candidates that were evaluated for their impact on PolyQ35::YFP aggregation. Green square: increased aggregation; Red square: no impact on aggregation. (D) Human orthologs of identified candidates were analyzed for functional clusters employing the bioinformatics tool DAVID. The tables depict candidates functionally associated with the ubiquitin conjugation pathway or autophagy, respectively.