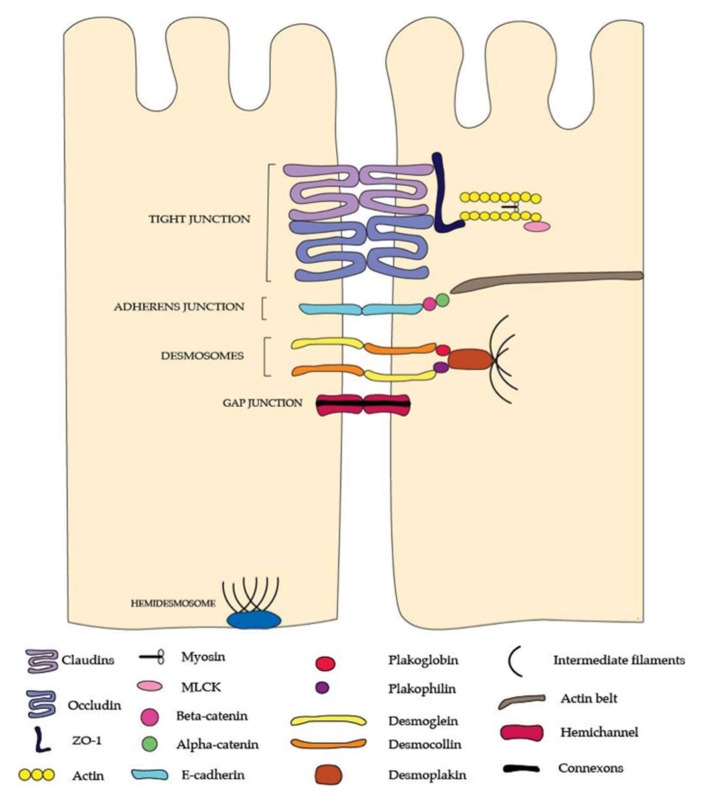
Figure 1.
The junctional complexes of the intestinal barrier. Tight junctions are made up of the claudin and occludinmembrane proteins which bind together to seal the paracellular gap between epithelial cells. Zonulin-1 (ZO-1) binds the tight junction complex to the actin cytoskeleton and also regulates the selective passage of macromolecules through the tight junction. The lower junctional complex is the adherens junction which is made up of E-cadherin proteins that attach adjacent epithelial cells. These proteins are anchored by beta-catenin and alpha catenin to the actin cytoskeleton. The deepest junctional complexes at the baselateral end of the epithelial cells are the desmosomes and hemidesmosomes which attach epithelial cells to each other and also to the basement membrane, respectively. Desmosomes are made up of desmoglein and desmocollin partner proteins which are anchored to the filament lattice structure by plakogobin and plakophilin proteins, which in turn attach to desmoplakin. Whilst tight junctions have a primary role in regulating selective ion absorbance from the lumen to the extracellular internal milieu of the body, adherens junctions, desmosomes, and hemidesmosomesare principally responsible for the mechanical and tensile strength of the barrier. Please note: This figure is not to scale.