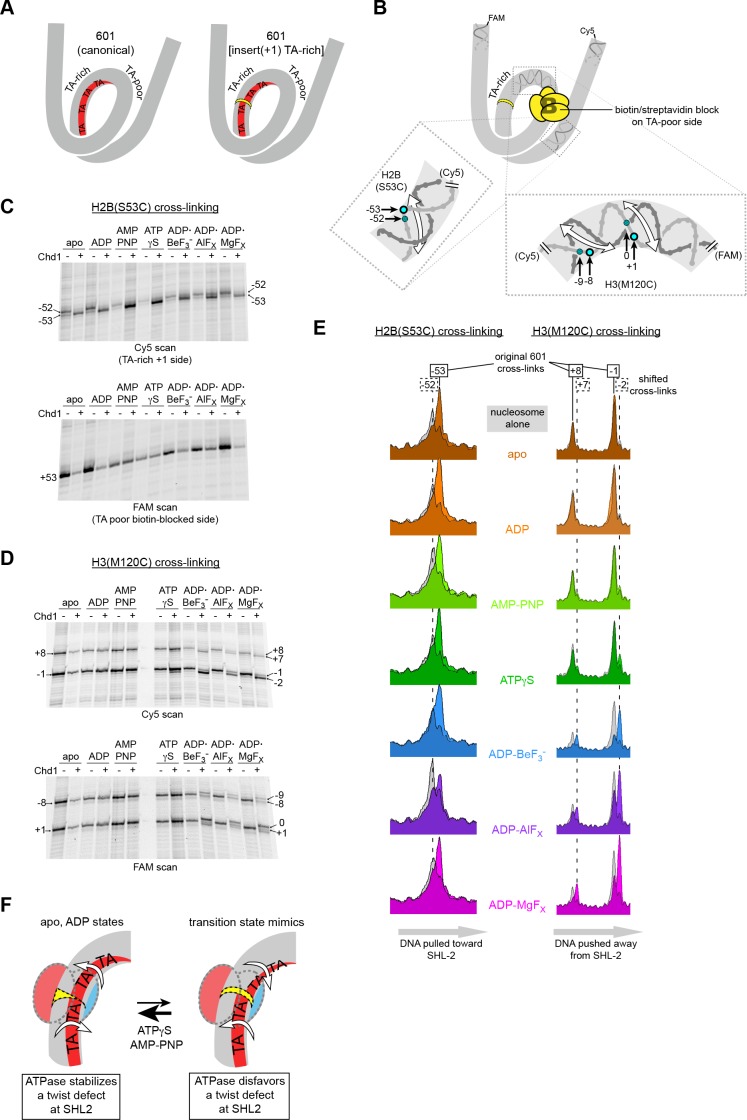
Figure 6. Chd1 binding induces a nucleotide-dependent twist in nucleosomal DNA at SHL2.
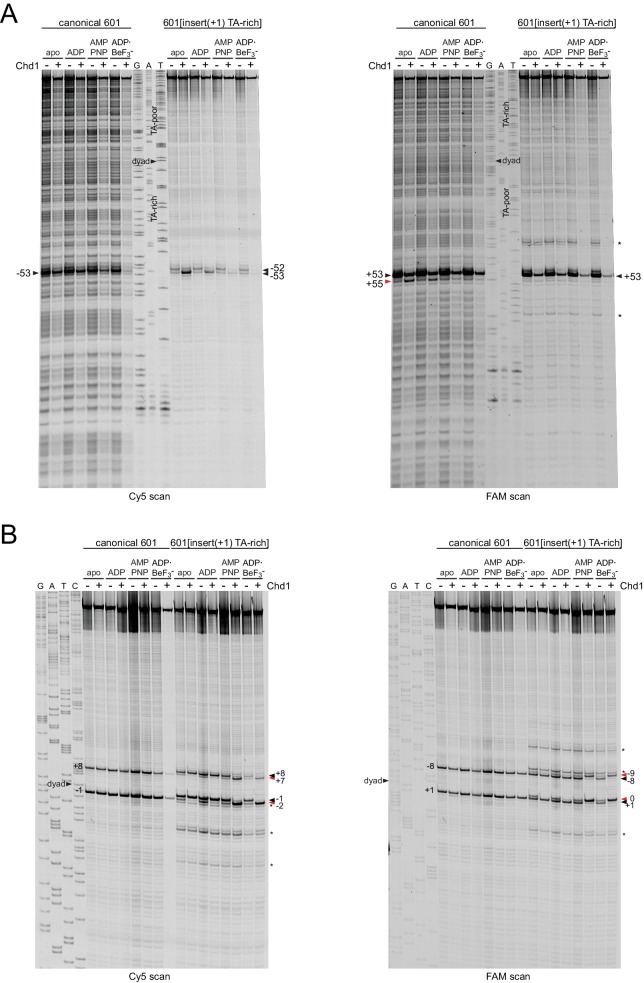
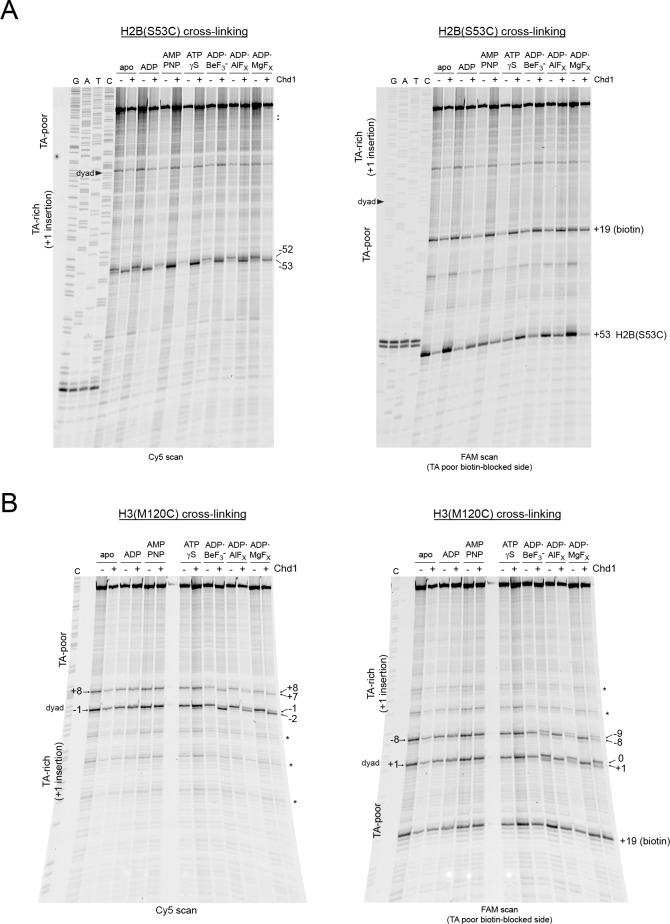
(A) Schematic view of TA steps on the TA-rich side of the 601, which are phased in the canonical Widom 601 (left) and expected to be out-of-phase upon addition of a single bp at position 22 (yellow highlight, right). (B) Experimental design for monitoring histone-DNA contacts of the 601[insert(+1) TA-rich] nucleosomes. The presence of biotin/streptavidin at position 19 on the TA-poor side of the nucleosome will block Chd1 binding to SHL+2. Cross-linking of H2B(S53C) and H3(M120C) will report on the effects of Chd1 binding to SHL–2. In the expanded views, filled blue circles indicate the locations of cross-links as observed on the Cy5-labeled strand. For the H2B(S53C) view, the hatched blue circle denotes cross-links observed due to the +1 bp insertion on the TA-rich side as shown in (C), whereas for the H3(M120C) view, the hatched circles show the new dyad cross-links that appear with Chd1 bound in the presence of transition state analogs as shown in (D). Note that this design represents information gained from two different nucleosomes, each with a biotin/streptavidin block but with unique cross-linking sites. (C) The presence of Chd1 shifts entry DNA of 601[insert(+1) TA-rich] nucleosomes toward SHL–2 in all nucleotide conditions. Histone mapping reactions for biotinylated H2(S53C) nucleosomes plus streptavidin were carried out in the presence and absence of Chd1. The numbers indicate the cross-linking positions relative to the dyad, as observed for the canonical Widom 601 sequence. (D) Chd1 binding changes the position of DNA around the dyad of 601[insert(+1) TA-rich] nucleosomes in a nucleotide-dependent fashion. Cross-linking reactions were performed with biotinylated H3(M120C) nucleosomes in the presence of streptavidin. Gels shown in (C) and (D) are representative of four or more experiments. (E) Chd1 alters the distance between histone-DNA cross-links in a nucleotide dependent manner. Shown are intensity plots of each gel lane shown for Cy5 scans in (C) and (D). Nucleosome alone lanes are shown in gray, overlaid with the positions of cross-links observed for each nucleotide-bound state of Chd1 as colored peaks. The dotted lines indicate the positions of cross-links that are shifted 1 bp from those observed for the canonical 601, and correspond to the hatched blue circles shown in (B). The shift in cross-linking of H2B(S53C) from −52 to −53 corresponds with movement of entry DNA toward SHL–2, whereas the shift in H3(M120C) cross-links from +8/–1 to +7/–2 corresponds with movement of dyad DNA away from SHL–2. (F) A cartoon interpretation of Chd1-dependent changes in nucleosomal DNA.