Abstract
Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) are one of the important cell types affected in many ocular neurodegenerative diseases. Oxidative stress is considered to be involved in retinal RGCs death in ocular neurodegenerative diseases. More and more attention has been focused on studying the agents that may have neuroprotective effects. Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) is a key nuclear transcription factor for the systemic antioxidant defense system. This review elucidates the underlying mechanism of the Nrf2-mediated neuroprotective effects on RGCs in ocular neurodegenerative diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy and retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Several Nrf2 inducers that shield RGCs from oxidative stress-induced neurodegeneration via regulating Nrf2 signaling are discussed.
Keywords: retinal ganglion cells, neurodegenerative diseases, oxidative stress, Nrf2, Keap1
Introduction
RGCs and oxidative stress in ocular diseases
Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), specialized projection neurons, are located adjacent to the inner retinal surface of the eye. These neurons obtain visual information from photoreceptors and are the brain's only portal to the visual world 1. RGCs can transmit visual information in the form of action potential from the retina to some regions in the brain. RGCs are one of the important cell types affected in optic neuropathies, such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy (DR) 2. Oxidative stress, which is characterized by the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as superoxide anion (O2-), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl radical (-OH), is thought to be involved in causing retinal RGCs death in many ocular neurodegenerative diseases, such as glaucoma, DR 2, 3, and retinal ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury 4. Under normal condition, there is a balance between the systemic ROS production and biological antioxidants' capacity to remove the oxidants or to repair the oxidative stress induced damages. Overproduction of ROS or dysfunction of anti-oxidative enzymes can result in oxidative stress and lead to cellular damages (e.g. lipid peroxidation of cell membranes, oxidative damage to DNA and proteins).
Transcription factors like nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) signaling in ocular diseases
Nrf2 is a key nuclear transcription factor for the systemic antioxidant defense system. In normal condition, Nrf2 binds to Kelch-like erythroid-cell-derived protein with CNC homology (ECH)-associated protein 1 (Keap1) as a complex and is restricted to the cytoplasm where it undergoes ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Under the stressed condition, Nrf2 is separated from Keap1 (a primary Nrf2 inhibitor) and is translocated into the nucleus where it binds to the phase 2 of antioxidant response element (ARE) in the DNA promoter region. Then, Nrf2 initiates the transcription of ARE controlled anti-oxidative enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, glutathione S-transferase (GSTP) 5, NAD (P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) 6, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) 7, thioredoxin reductase (TrxR), glutathione reductase (GR) and glutathione-S-transferase (GST) 8, 9, which detoxify ROS through glutathione (GSH) regulation 10. Nrf2 is known as the molecular switch of the Nrf2 signaling (also known as Nrf2/Keap1 or Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling) and serves as a foremost component of ROS signaling pathway that can be activated by oxidative stress inducers, such as sulforaphane (SF) 11, hyperoside 12, hyperglycemia 3 and inhibited by oxidative stress factors such as homocysteine (Hcy) 13, O2 fluctuation 14 and hypoglycemia under hypoxia 15. The protective role of Nrf2 against oxidative stress in ocular diseases has been explained in the following researches: DR 3, retinal I/R injury 4, etc. Nrf2 also promotes neuronal survival in neurodegeneration, acute nerve damage 16 and optic neuritis 17, 18.
Increasing evidences have demonstrated that oxidative stress leads to the loss of RGCs in many ocular neurodegenerative diseases. More attention has been focused on studying the agents which may confer the role of neuroprotection. This review sets out to elucidate the underlying mechanism of the Nrf2-mediated neuroprotective role in RGCs in ocular neurodegenerative diseases, such as DR, retinal I/R injury, and highlight several Nrf2 inducers which shield RGCs from oxidative stress-induced neurodegeneration via regulating Nrf2 signaling.
Nrf2 inducers for RGCs protection in ocular neurodegenerative diseases
Sox2 overlapping transcript (Sox2OT) knockdown
DR is the most common complication of diabetes and the foremost cause of vision loss in adults. DR has been considered as a vascular disease for a long time. Lately, it is detected that retinal neuronal cells can also be influenced by high glucose stress, and ROS is associated with DR 2. The injury of RGCs is the essential pathological characters of retinal neurodegeneration induced by diabetes. Mounting attention is drawn to find strategies for defending against RGCs injury. Long noncoding RNAs have been found as key regulators of pathological courses of diabetic complication, such as cell proliferation, immune response, as well as an inflammatory reaction 19-22. Sox2 overlapping transcript (Sox2OT), a long non-coding RNA 23, is greatly enriched in the human brain detected by qRT-PCR analysis. The retina and optic nerve are a part of the human brain. Li et al. 24 found that Sox2OT expression is considerably decreased in the retinas of diabetic mice as well as in the RGCs with high glucose. Sox2OT knockdown shields RGCs against high glucose-stimulated damage in vitro and has a neuroprotective role in DR-related neurodegenerative disorders in vivo. Recently, Nrf2 has attracted the extensive interest of researchers exploring its role in inflammatory disorders as well as neurodegenerative diseases 25, 26. Additionally, Protein-IP experiments found that Sox2OT knockdown could interrupt Nrf2/Keap1 connection in the cytosol of RGCs and lead to the accumulation of Nrf2 protein as well as nuclear translocation. Thus, Sox2OT knockdown also plays an anti-oxidative role through regulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Sox2OT knockdown could be a promising approach for the treatment of diabetic retinal neurodegeneration.
Serum response factor (SRF)
SRF is a transcription factor extensively expressed in the MADS-box gene family 27-29. SRF can regulate gene expression through binding with serum response elements located in the promoters of the major immediate-early genes, such as c-fos, early growth response protein 1 (EGR-1), as well as tissue-specific genes 30, which has been involved in apoptosis, cell proliferation 31, 32, and oxidation resistance 33. Fos-related antigen 1 (Fra-1) is an oncogene, which encodes a nucleoprotein Fos 34, 35. It is reported that Fra-1 is essential in controlling oxidative stress and regulating expression of Nrf2 36. Cao et al. reported that SRF up-regulated the expression of Nrf2 to shield against damage induced by high-glucose in the RGCs via controlling the expression of Fra-1. A better understanding of the potential mechanism of RGCs injury induced by high glucose might provide new insight into the DR treatment.
L-Carnitine (LC)
LC plays a vital physiological role in transporting the long-chain fatty acids for oxidation and ATP generation. In the human body, LC is originated from both endogenous biosynthesis (25%) and dietary sources (75%). Several experiments and clinical studies revealed that LC treatment exerts positive effects on some disorders in relation to oxidative stress 37, as well as high glucose-induced oxidative stress in RGCs 38. HO-1 is one of the important enzymatic antioxidants involved in defense system. A lot of signaling molecules are regulating the initiation of HO-1, among which Nrf2 is a key transcription factor of HO-139. γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (γ-GCS) is an essential scavenger of ROS, which is regarded as a potential therapeutic target for several cancers 40. Recently, Cao et al. found that LC treatment was correlated with an increased level of Nrf2, γ-GCS and HO-1, as well as a reduced expression of Keap1 protein in high glucose-stimulated RGCs. These results indicate that LC can protect the RGCs against high glucose-induced oxidative injury via Nrf2/Keap1 signal pathway 2.
SNJ-1945
Calpains, the intracellular cysteine proteases, play important roles in various cell processes, such as cell proliferation, signal transduction and apoptosis 41. Both calpain-1 and calpain-2 are the main calpain isoforms 42. Calpains are triggered by locally raised intracellular Ca2+ levels via calcium channels 43. Moreover, it is also related to the degradation of the substrates like α-fodrin that forms the membrane skeleton 44 and induces the apoptosis pathway 45. Lately, inhibition of calpain signaling is regarded as a therapeutic target for DR. Calpastatin, an endogenous specific inhibitor can regulate the level of calpain by binding as well as inhibiting calpain when the levels of calcium are high and releasing it once the levels of calcium decrease 46. SNJ-1945, a potent exogenous calpain inhibitor, was detected to possess a neuroprotective effect against the degeneration of retinal cell in mouse glaucoma models 47. Shanab et al. used Nrf2 knockout (KO) mice to induce oxidative stress and explored the association between ROS and calpain activation. They reported that calpain played a key role in metabolic-stimulated RGCs degeneration induced by hyperglycemia and oxidative stress. Retinal cells cultured with high-glucose without antioxidants presented more RGCs death than those with the treatment of antioxidants. SNJ-1945 considerably protected RGCs against oxidative stress induced by high glucose. Nrf2 KO mice under hyperglycemia stimulation are vulnerable to oxidative stress. RGCs deaths were drastically increased in Nrf2 KO mice, and are decreased notably by SNJ-1945. Both antioxidant and calpain inhibition (Calpastatin and SNJ-1945) provide more opportunities for future neuroprotective management against RGCs death in DR 48.
Monomethyl fumarate (MMF)
Retinal ischemia leads to the degeneration of retinal neurons and plays a vital role in the pathogenesis of severe blinding diseases. Reperfusion of the retina following ischemia contributes to oxidative stress, which is marked by the ROS production and inflammatory responses 49-51. Oxidative stress plays an essential role in neurodegeneration which is exhibited by the loss of RGCs 52. As a key regulator of the antioxidant response, the potential retinal neuroprotective function of Nrf2 after I/R injury is increasingly appreciated 4, 53, 54. Recently, FDA has approved the fumaric acid ester dimethyl fumarate (DMF) for the treatment of multiple sclerosis based on the neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects. After ingested, DMF is quickly metabolized to MMF, which is the active metabolite of DMF 55, 56. Particular attention has been paid to its potential role as a neuroprotective drug for retinal diseases 4. It has also been revealed that MMF exerts neuronal protection in the retina after I/R injury through the Nrf2 signal pathway. MMF treatment considerably improved the expression of Nrf2-regulated anti-oxidative genes, decreased inflammatory gene expression, reduced neuronal cell loss in the ganglion cell layer, and improved the function of the retina after retinal I/R injury in WT mice.
CDDO-Im (2-Cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-imidazolide)
The CDDO-Im is a potent Nrf2 activator, which inhibits ROS increment in the retinal neuronal cell line 661W under oxidative stress. In wild-type (WT) mice, it increased the survival of neuronal cells after I/R injury but not in Nrf2 KO mice 57. These findings reveal that Nrf2 has a retinal neuroprotective function against I/R injury and indicate that activation of Nrf2 might be a therapeutic strategy 57. Oxidative stress is also revealed to participate in nerve crush (NC)-triggered RGCs death. The number of RGCs in Nrf2 KO mice was dramatically lower than that of WT mice after NC. Dramatically, CDDO-Im eliminated the NC-triggered RGCs loss in WT mice by activating Nrf2 translocation and initiating the transcription of phase II as well as antioxidant genes (Nqo1, Gsta4, Ho-1 and Txnrd) indicating that pharmacological reagents which up-regulate Nrf2, such as CDDO-Im, may serve as a potential therapeutic alternative to counteract oxidative stress and protect RGCs 58.
Sulforaphane (SF)
Extracted from vegetables, SF exhibit protective effects against oxidative damages in many tissues 59-62. These protective effects can be promoted by Nrf2-mediated induction of antioxidant enzyme HO-1. I/R increased ROS production, caused marked inflammation, induced the apoptosis of RGCs and led to the thinning of the inner retinal layer. However, these effects were reduced or eliminated by SF pre-treatment. Furthermore, SF pre-treatment notably raised the nuclear accumulation of Nrf2 and the expression of HO-1 in the I/R retinas. Alternatively, ZnPP, the HO-1 inhibitor, reversed the antioxidant effects of SF on I/R retinas. Thus, SF had antioxidant effects on I/R retinas via the activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway 63.
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBP)
LBP, extracted from the wolfberries, is a traditional Chinese medicine with the proposed effect of anti-aging 64. Various researches have revealed the beneficial effects of LBP in various tissues 65-68. Recently, several studies have examined its protective effects in some ocular disease models, such as protecting RGCs in permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion -induced retinal I/R 69, 70. He et al. reported that LBP treatment drastically increased the nuclear accumulation of Nrf2 and the expression of HO-1 in the retina after I/R injury. It also reversed the increased apoptosis and declined a number of viable cells detected in the ganglion cell layer (GCL) in I/R retina. These results reveal that LBP partially exerts its beneficial neuroprotective effects through activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Nevertheless, the drugs studied above are in early stages 71, clinical trials or human safety data are still needed.
Limb remote ischemic conditioning (LRIC)
LRIC offers a physiologic strategy for managing the body's endogenous protective abilities against injury caused by I/R in the central nervous system 72, 73. Zhang et al. reported that LRIC might be used as a noninvasive neuroprotective approach, which provides retinal protection from I/R injury via the upregulation of antioxidants such as Nrf2 and HO-1. Both of them might be used as biomarkers of I/R injury, and pharmacologic agents could be focused on the Nrf2 and HO-1 signal pathway 74. As both of them are related to clinical applicability, further studies should be desired to differentiate and calibrate changes in Nrf2 and HO-1.
MicroRNA-141
Ultraviolet (UV) is an electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 10-400 nm, which is longer than X-rays and shorter than visible light. UV radiation-induced ROS production and cell death in cultured human RGCs. Activation of Nrf2 signaling could protect cells from UV radiation 18. MicroRNA-141, a Keap 1 inhibitor, provoked Nrf2 activation and nucleus translocation in UV-exposed RGCs. Then the transcription of ARE controlled antioxidant genes (NOQ1, HO-1, γ-glutamylcysteine ligase catalytic subunit) is enhanced which leads to the attenuation of UV-induced oxidative stress and cell death 75. In opposite, there is depletion of microRNA-141 up-regulated Keap1 expression and accelerated Nrf2 degradation leading to the aggravation of UV-induced death of RGCs 75. These results demonstrate that microRNA-141 targets Keap1 to provoke Nrf2 activation and attenuates UV-induced oxidative stress in RGCs 75.
Hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S) donor drugs
H2S, an endogenously produced gas by the human body participates in physiological processes, such as neuronal survival, ROS elimination, vasodilation, and inflammation 76-79. It has been considered as one of the important cellular neuromodulators 80. Combination of both glutamate (Glu) and buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) was employed to induce the oxidative stress in the cultured mouse RGC-5 cells. cell viability and apoptosis assay revealed that the H2S releasing compounds (ADTOH and NAHS) inhibited Glu/BSO-induced cell death in cultured RGC-5 cells by up-regulation of Nrf2, HO-1, GST, GSH, p-serine-threonine kinase (p-Akt), Protein kinase C alpha (PKC-α), X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), and down-regulation of NF-κB 81. These results implicate that H2S donor compounds are promising neuroprotectants in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases 81.
R-α-lipoic acid (R-LA)
R-LA is a cofactor for α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase 82. It was reported that R-LA possesses the antioxidant ability that may reduce the lipid peroxidation in aging rats 83 as well as protect RGCs against I/R induced injury 84. It was also revealed R-LA have a dramatic neuroprotective effect against oxidative stress-triggered the RGC-5 cell death cultured in vitro by promoting the Nrf2 translocation to the nucleus and increasing the expression of anti-oxidative enzyme HO-1 via the regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathways. In addition, R-LA transiently produced ROS. Meantime, ROS scavenger N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) or NADPH oxidase inhibitor (Diphenyliodonium chloride) prohibited R-LA-triggered Nrf2 translocation and HO-1 generation. R-LA dramatically attenuated RGCs cell death and accumulation of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE), a final product of lipid peroxidation, in the retina of mouse induced by optic nerve injury through regulation of HO-1. R-LA exhibited the neuroprotective role in retinal neurons against oxidative stress by inducing HO-1 via Nrf2 signaling pathway 85.
Nipradilol
Nipradilol has nitric oxide (NO)-donating as well as α1- and β-adrenoceptor antagonist properties. It is known as an anti-glaucomatous agent clinically. It also exhibited a significant neuroprotective effect against oxidative stress-induced RGCs death in cultured RGC-5 cells and optic nerve injury in mice model. NO scavenger dramatically reversed the neuroprotective effect of nipradilol. It was further proved that the neuroprotective effect of nipradilol against oxidative stress-induced RGCs death was through a HO-1 activity-dependent mechanism by inducing Keap1 S-nitrosylation, Nrf2 nucleus translocation and transcription of HO-1 (a NO-dependent antioxidant enzyme). These results elucidate a potential neuroprotective effect of nipradilol against oxidative stress-induced the death of RGCs 86.
Long-acting (1R)-isoPropyloxygenipin (IPRG001)
Genipin is an herbal iridoid with neuroprotective effects. IPRG001, a genipin derivative, was reported to protect the H2O2 induced cell death in cultured rat RGC-5 accompanied by the increased antioxidant enzymes production (such as HO-1) and NO generation. NOR1 (a NO donor) showed a similar tendency of neuroprotective effects with IPRG001 by increasing the cell viability and HO-1 expression in RGC-5, while c-PTIO (a NO scavenger) or cycloheximide (a protein synthesis inhibitor) completely inhibited the protective action of PRG001. Furthermore, IPRG001 induced HO-1 expression was found to be regulated via inducing the S-nitrosylation of Keap1 and the nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Nrf2 redistribution was blocked by wortmannin (a PI3K inhibitor) and overexpression of HO-1 was inhibited by the combined application of wortmannin and LY294002 (also a PI3K inhibitor). Accompanied by HO-1 generation, pre-exposure to IPRG001almost totally diminished the optic nerve injury (ONI) induced apoptosis and 4-HNE overexpression in RGCs of rat retina in vivo. These results indicate that IPRG001 protect the RGCs against oxidative stress through the PI3K/Nrf2/ARE pathway via S-nitrosylation of Keap1 and genipin and can be a promising therapeutic medication for degenerative neuronal diseases 87.
Flavonoids
T-butyl peroxide (t-BOOH) and H2O2 treatment are usually used as an exogenous source of ROS to imitate external oxidative stress, whereas GSH depletion is usually employed to imitate the endogenous oxidative stress, and all these three insults may lead to oxidative stress induced RGC-5 cell death in vitro studies.
Mounting evidence has shown that the plant-derived flavonoids which are abundant in vegetables and fruits have neuroprotective effects. Additionally, different flavonoids exhibits distinct neuroprotective pattern against oxidative stress-induced RGC-5 cell death. Several flavonoids such as quercetin, induced HO-1 expression via the Nrf2/ARE pathways, indicating that some flavonoids may serve as promising neuroprotective natural medication for RGCs 88.
Sulbutiamine
Sulbutiamine stimulated the production of GST along with GSH and eliminates ROS. NAC inhibited glutamate/buthionine sulfoximine (GB)-inducing the death of RGC-5 cells cultured in vitro. Furthermore, sulbutiamine significantly increased HO-1, Nrf2 and catalase expression. NAC and sulbutiamine show different neuroprotective functions in GB via different mechanisms 89.
Conclusions and Outlook
Accumulating evidences show that oxidative stress is one of the major mechanisms involved in the loss of RGCs in several eye diseases and aging process that increases the injury in RGCs through various processes such as, oxidation of proteins, DNA damage, apoptosis, cell death, etc. The Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling pathway is considered as one of the main cell defense mechanisms against oxidative stresses. Thus, the induction of the Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling pathway has been estimated as an important target for a neuroprotective role in RGCs. Selected studies on the relationship between Nrf2 inducer/suppressor and RGCs-related diseases were reviewed in this article. Various researches have shown that Nrf2 possesses notable effects on protecting or deteriorating RGCs against oxidative stress, decreasing the aberrant proteins and preventing or causing the RGCs-related disorders (Table 1), such as DR (Figure 1) and I/R (Figure 2). All these encouraging effects have been linked with the antioxidant effects of Nrf2 inducing compounds. In summary, the Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling pathway may be a promising therapeutic target against oxidative stress for RGCs-related diseases.
Table 1.
Selected studies on the relationship between Nrf2 inducer/suppressor and RGCs
| Inducer | Suppressor | Type | Models | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sox2OT knockdown | In vitro | Mice RGCs | Sox2OT knockdown had an anti-oxidative role through regulating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. | 24 | |
| In vivo | STZ-induced Diabetic mice | Sox2OT knockdown had a neuroprotective role in diabetes-induced neurodegeneration. | |||
| SRF | In vitro | Rat RGCs | SRF upregulated Nrf2 to defense against damage induced by high-glucose in the RGCs via Fra-1. | 3 | |
| LC | In vitro | Rat RGCs | LC protected the RGCs against high glucose-induced oxidative damage via Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. | 2 | |
| SNJ-1945 | In vitro | Mouse RGCs | SNJ-1945 protected the RGCs against high glucose-induced cell death. | 48 | |
| In vivo | Nrf2 KO mice | Hyperglycemia-provoked RGCs deaths were increased in Nrf2 KO mice, and declined by SNJ-1945. | |||
| MMF/DMF | In vivo | Nrf2 KO mice | MMF protected retina after I/R injury through the Nrf2 pathway. | 4 | |
| CDDO-Im | In vitro | Retinal neuronal cell line 661W | CDDO-Im inhibited ROS increase in the 661W under oxidative stress. | 57 | |
| In vivo | Nrf2 KO mice | CDDO-Im increased neuronal survival after I/R injury in WT, but not Nrf2 KO mice. | |||
| In vivo | RGCs in Nrf2 KO mice and WT mice with/without NC | CDDO-Im eliminated NC-triggered RGCs loss in WT mice by activating Nrf2 translocation. | 58 | ||
| SF | In vivo | Rats | SF had antioxidant effects on I/R retinas via the activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. | 63 | |
| LBP | In vivo | Rats | LBP exerted neuroprotective effects through the activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. | 90 | |
| LRIC | In vivo | Rats | LRIC provided retinal protection from I/R injury via the increase the level of Nrf2 and HO-1. | 74 | |
| microRNA-141 | UV | In vitro | Primary cultured human RGCs and cultured ARPE-19 | MicroRNA-141 attenuated UV-induced oxidative stress in RGCs via activating Nrf2 signaling. | 75 |
| H2S | In vitro | RGC-5 | ADTOH (slow releasing H2S) is more efficacious than the NAHS (rapid releasing H2S) in inhibiting Glu /BSO-induced ROS production and cell death in RGC-5. | 81 | |
| R-LA | H2O2 | In vitro | RGC-5 | R-LA protected against oxidative stress-triggered the RGC-5 cell death by promoting the Nrf2 translocation and increasing HO-1 via phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathways. | 85 |
| ONI | In vivo | Mouse RGCs | R-LA attenuated RGCs cell death and accumulation of 4HNE in the retina of mouse induced by optic nerve injury through regulation of HO-1 | ||
| Nipradilol | H2O2 | In vitro | RGC-5 | Nipradilol protected against oxidative stress-induced RGC-5 death through Keap1 S-nitrosylation, Nrf2 nucleus translocation and transcription of HO-1. | 86 |
| ONI | In vivo | Mouse RGCs | Nipradilol suppressed RGCs death and accumulated 4-HNE after injury through an HO-1-dependent mechanism. | ||
| IPRG001 | H2O2 | In vitro | Rat RGC-5 | IPRG001 protected H2O2-induced cell death in RGC-5, accompanied by the increased HO-1, NQO-1, GCLC, NO generation. | 87 |
| ONI | In vivo | Rat RGCs | IPRG001diminished the ONI induced apoptosis and 4-HNE overexpression in RGCs. | ||
| Flavonoids | T-butyl t-BOOH,H2O2 GSH depletion | In vitro | RGC-5 | Some flavonoids protected RGC-5 from oxidative induced cell death via Nrf2/ARE/HO-1pathway. | 88 |
| Sulbutiamine | In vitro | RGC-5 | Sulbutiamine stimulated GST, GSH, catalase, Nrf2 and HO-1 expression, but eliminated ROS in glutamate/buthionine sulfoximine (GB)-treated RGC-5 in vitro. | 89 |
Abbreviation: Sox2OT, Sox2 overlapping transcript; SRF, Serum response factor; LC, L-Carnitine; MMF, monomethyl fumarate; DMF, f umaric acid ester dimethyl fumarate; SF, Sulforaphane; LBP, Lycium barbarum polysaccharides; LRIC, Limb remote ischemic conditioning; ARPE-19, human retinal pigment epithelial (ARPE-19) cells; H2S, Hydrogen sulfide gas; R-LA, R-a-lipoic acid; UV, Ultraviolet; RGCs, retinal ganglion cell; I/R, ischemia-reperfusion; STZ, streptozotocin; HFD, fed a high fat diet; KO, knockout; The retinal neuronal cell line 661W; ONI, Optic nerve injury.
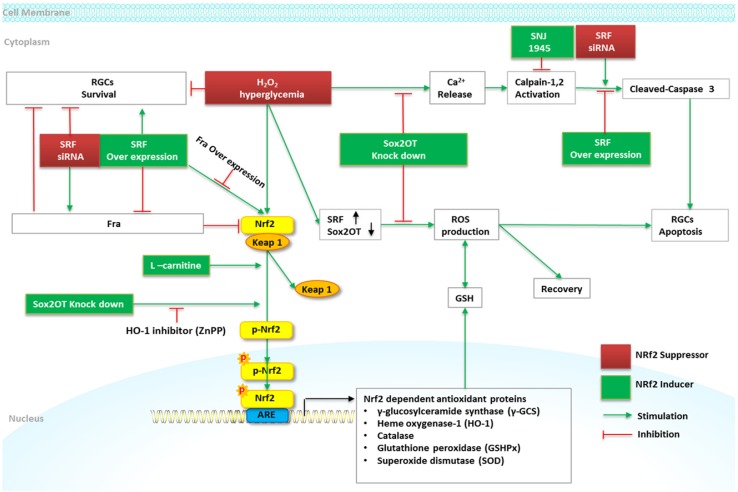
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of Nrf2 signaling and regulation of RGCs in DR. High glucose and H2O2 treatment induces a marked reduction of RGCs viability and increases RGCs apoptosis. Sox2OT knockdown partially reverses high glucose-induced reduction of RGCs apoptosis, and increases Nrf2 and HO-1 protein expression by inducing Nrf2 protein accumulation and nuclear translocation. ZnPP (HO-1 inhibitor) alleviates the beneficial role of Sox2OT knockdown against oxidative stress. The overexpression of SRF attenuates high glucose induced RGCs apoptosis via caspase-3 activity and maintains the cell viability. SRF augments the expression of Nrf2 via the downregulation of Fra-1; overexpression of Fra-1 abolishes the effect of SRF overexpression on Nrf2 and abrogates the protective effect of SRF overexpression on RGCs survival treated with high glucose. L-carnitine increases Nrf2, γ-GCS, HO-1, and decreases Keap1 protein in high glucose stimulated RGCs. SNJ-1945 declines high glucose-induced RGCs deaths.
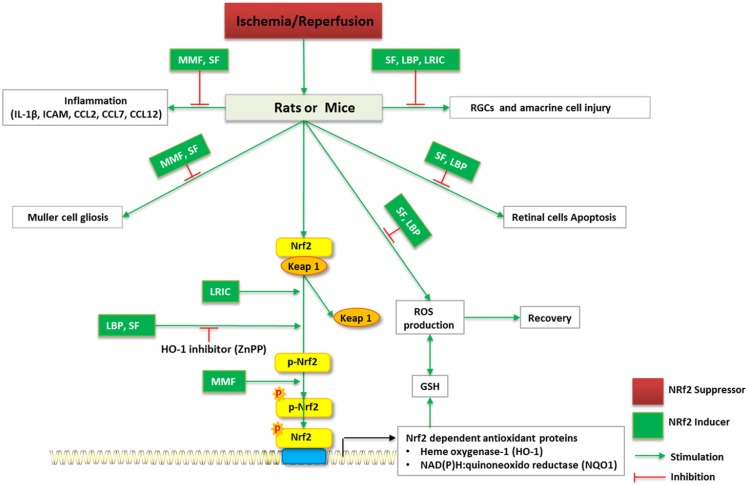
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of Nrf2 signaling and regulation of RGCs in I/R in vivo. I/R induce RGCs and amacrine cell injury, ROS overproduction, inflammation of retina, Muller cell gliosis, as well as retinal cell apoptosis. MMF, SF, LBP, LRIC may reverses I/R-induced neurodegenerative damage to the eye. ZnPP (HO-1 inhibitor) alleviates the beneficial role of LBP, SF against oxidative stress.
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by Development and Reform Commission of Jilin province 2015Y031-1.
Author Contributions
The topic was conceptualized by CL. CL, XL and DZ contributed to the literature database search, and writing of the manuscript. CL, TX, JQ and JH contributed to vital revising. TH and OP contributed to English Polishing.
Abbreviations
- RGCs
retinal ganglion cells
- DR
diabetic retinopathy
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- H2O2
hydrogen peroxide
- I/R
ischemia-reperfusion
- Nrf2
transcription factors like nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2
- Keap1
Kelch-like erythroid-cell-derived protein with CNC homology (ECH)-associated protein 1
- ARE
antioxidant response element
- SOD
superoxide dismutase
- GSTP
glutathione S-transferase
- HO-1
heme oxygenase-1
- TrxR
thioredoxin reductase
- GR
glutathione reductase
- GST
glutathione-S-transferase
- GSH
glutathione
- SF
sulforaphane
- Hcy
homocysteine
- Sox2OT
Sox2 overlapping transcript
- SRF
serum response factor
- EGR-1
early growth response protein 1
- Fra-1
fos-related antigen 1
- LC
L-Carnitine
- γ-GCS
γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase
- KO
knockout
- MMF
monomethyl fumarate
- DMF
fumaric acid ester dimethyl fumarate
- NC
nerve crush
- WT
wild-type
- LBP
lycium barbarum polysaccharides
- GCL
ganglion cell layer
- LRIC
limb remote ischemic conditioning
- UV
Ultraviolet
- RPEs
retinal pigment epithelial cells
- H2S
Hydrogen sulfide gas
- Glu
glutamate
- BSO
buthionine sulfoxime
- Akt
serine-threonine kinase
- PKC-α
protein kinase C alpha
- XIAP
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- Bcl-2
B-cell lymphoma 2
- R-LA
R-α-lipoic acid
- NAC
N-acetyl-L-cysteine
- 4-HNE
4-hydroxy-2-nonenal
- NO
nitric oxide
- ONI
optic nerve injury.
References
- 1.Sanes JR, Masland RH. The types of retinal ganglion cells: current status and implications for neuronal classification. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2015;38:221–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-071714-034120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cao Y, Li X, Wang CJ. et al. Role of NF-E2-related factor 2 in neuroprotective effect of l-carnitine against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in the retinal ganglion cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;69:345–8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2014.12.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cao Y, Wang L, Zhao J. et al. Serum Response Factor Protects Retinal Ganglion Cells Against High-Glucose Damage. J Mol Neurosci. 2016;59(2):232–40. doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0708-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cho H, Hartsock MJ, Xu Z, He M, Duh EJ. Monomethyl fumarate promotes Nrf2-dependent neuroprotection in retinal ischemia-reperfusion. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:239. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0452-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhou T, Zong R, Zhang Z. et al. SERPINA3K protects against oxidative stress via modulating ROS generation/degradation and KEAP1-NRF2 pathway in the corneal epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(8):5033–43. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-9729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dinkova-Kostova AT, Talalay P. NAD(P)H:quinone acceptor oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), a multifunctional antioxidant enzyme and exceptionally versatile cytoprotector. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010;501(1):116–23. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.03.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Roy S, Praneetha DC, Vendra VP. Mutations in the Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy-Associated Gene SLC4A11 Render the Cells More Vulnerable to Oxidative Insults. Cornea. 2015;34(6):668–74. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Miyamoto N, Izumi H, Miyamoto R. et al. Transcriptional regulation of activating transcription factor 4 under oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelial ARPE-19/HPV-16 cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(3):1226–34. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rushmore TH, Morton MR, Pickett CB. The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(18):11632–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nakagami Y. Nrf2 Is an Attractive Therapeutic Target for Retinal Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:7469326. doi: 10.1155/2016/7469326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Varma SD, Chandrasekaran K, Kovtun S. Sulforaphane-induced transcription of thioredoxin reductase in lens: possible significance against cataract formation. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013;7:2091–8. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S52678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Park JY, Han X, Piao MJ. et al. Hyperoside Induces Endogenous Antioxidant System to Alleviate Oxidative Stress. J Cancer Prev. 2016;21(1):41–7. doi: 10.15430/JCP.2016.21.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Elanchezhian R, Palsamy P, Madson CJ, Lynch DW, Shinohara T. Age-related cataracts: homocysteine coupled endoplasmic reticulum stress and suppression of Nrf2-dependent antioxidant protection. Chem Biol Interact. 2012;200(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2012.08.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zheng XY, Xu J, Chen XI, Li W, Wang TY. Attenuation of oxygen fluctuation-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in human lens epithelial cells. Exp Ther Med. 2015;10(5):1883–7. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Elanchezhian R, Palsamy P, Madson CJ. et al. Low glucose under hypoxic conditions induces unfolded protein response and produces reactive oxygen species in lens epithelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e301. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xiong W, MacColl Garfinkel AE, Li Y, Benowitz LI, Cepko CL. NRF2 promotes neuronal survival in neurodegeneration and acute nerve damage. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(4):1433–45. doi: 10.1172/JCI79735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Larabee CM, Desai S, Agasing A. et al. Loss of Nrf2 exacerbates the visual deficits and optic neuritis elicited by experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Mol Vis. 2016;22:1503–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huang C, Zhang P, Wang W. et al. Long-term blue light exposure induces RGC-5 cell death in vitro: involvement of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis, oxidative stress, and MAPK signaling pathways. Apoptosis. 2014;19(6):922–32. doi: 10.1007/s10495-014-0983-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yan B, Yao J, Liu JY. et al. lncRNA-MIAT regulates microvascular dysfunction by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Circ Res. 2015;116(7):1143–56. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wallace C, Smyth DJ, Maisuria-Armer M, Walker NM, Todd JA, Clayton DG. The imprinted DLK1-MEG3 gene region on chromosome 14q32.2 alters susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2010;42(1):68–71. doi: 10.1038/ng.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu JY, Yao J, Li XM. et al. Pathogenic role of lncRNA-MALAT1 in endothelial cell dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1506. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Alvarez ML, Distefano JK. The role of non-coding RNAs in diabetic nephropathy: potential applications as biomarkers for disease development and progression. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013;99(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2012.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fantes J, Ragge NK, Lynch SA. et al. Mutations in SOX2 cause anophthalmia. Nat Genet. 2003;33(4):461–3. doi: 10.1038/ng1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang Y, Chen WJ, Gan TQ. et al. Clinical Significance and Effect of lncRNA HOXA11-AS in NSCLC: A Study Based on Bioinformatics, In Vitro and in Vivo Verification. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5567. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05856-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim J, Cha YN, Surh YJ. A protective role of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) in inflammatory disorders. Mutat Res. 2010;690(1-2):12–23. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Calkins MJ, Johnson DA, Townsend JA. et al. The Nrf2/ARE pathway as a potential therapeutic target in neurodegenerative disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11(3):497–508. doi: 10.1089/ars.2008.2242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wong J, Zhang J, Yanagawa B. et al. Cleavage of serum response factor mediated by enteroviral protease 2A contributes to impaired cardiac function. Cell Res. 2012;22(2):360–71. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Baarlink C, Wang H, Grosse R. Nuclear actin network assembly by formins regulates the SRF coactivator MAL. Science. 2013;340(6134):864–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1235038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nam YJ, Song K, Luo X. et al. Reprogramming of human fibroblasts toward a cardiac fate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(14):5588–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301019110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Maggiolini M, Vivacqua A, Fasanella G. et al. The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 mediates c-fos up-regulation by 17beta-estradiol and phytoestrogens in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(26):27008–16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403588200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Aline G, Sotiropoulos A. Srf: A key factor controlling skeletal muscle hypertrophy by enhancing the recruitment of muscle stem cells. Bioarchitecture. 2012;2(3):88–90. doi: 10.4161/bioa.20699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wiese KE, Haikala HM, von Eyss B. et al. Repression of SRF target genes is critical for Myc-dependent apoptosis of epithelial cells. EMBO J. 2015;34(11):1554–71. doi: 10.15252/embj.201490467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Meyer M, Schreck R, Baeuerle PA. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 1993;12(5):2005–15. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Das A, Li Q, Laws MJ, Kaya H, Bagchi MK, Bagchi IC. Estrogen-induced expression of Fos-related antigen 1 (FRA-1) regulates uterine stromal differentiation and remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(23):19622–30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.297663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Motrich RD, Castro GM, Caputto BL. Old players with a newly defined function: Fra-1 and c-Fos support growth of human malignant breast tumors by activating membrane biogenesis at the cytoplasm. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vaz M, Machireddy N, Irving A. et al. Oxidant-induced cell death and Nrf2-dependent antioxidative response are controlled by Fra-1/AP-1. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32(9):1694–709. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06390-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gulcin I. Antioxidant and antiradical activities of L-carnitine. Life Sci. 2006;78(8):803–11. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.05.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cao Y, Li X, Shi P, Wang LX, Sui ZG. Effects of L-carnitine on high glucose-induced oxidative stress in retinal ganglion cells. Pharmacology. 2014;94(3-4):123–30. doi: 10.1159/000363062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Haines DD, Lekli I, Teissier P, Bak I, Tosaki A. Role of haeme oxygenase-1 in resolution of oxidative stress-related pathologies: focus on cardiovascular, lung, neurological and kidney disorders. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2012;204(4):487–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jin X, Song L, Li Z, Newton IP, Zhao M, Liu W. Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene exposure reduces r-GCS via suppressed Nrf2 in HepG2 cells. Environ Toxicol. 2016;31(3):350–9. doi: 10.1002/tox.22049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Perrin BJ, Huttenlocher A. Calpain. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;34(7):722–5. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W, Cong J. The calpain system. Physiol Rev. 2003;83(3):731–801. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00029.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Camins A, Verdaguer E, Folch J, Pallas M. Involvement of calpain activation in neurodegenerative processes. CNS Drug Rev. 2006;12(2):135–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2006.00135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nath R, Raser KJ, Stafford D. et al. Non-erythroid alpha-spectrin breakdown by calpain and interleukin 1 beta-converting-enzyme-like protease(s) in apoptotic cells: contributory roles of both protease families in neuronal apoptosis. Biochem J. 1996;319(Pt 3):683–90. doi: 10.1042/bj3190683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Stys PK, Jiang Q. Calpain-dependent neurofilament breakdown in anoxic and ischemic rat central axons. Neurosci Lett. 2002;328(2):150–4. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(02)00469-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hanna RA, Garcia-Diaz BE, Davies PL. Calpastatin simultaneously binds four calpains with different kinetic constants. FEBS Lett. 2007;581(16):2894–8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.05.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ryu M, Yasuda M, Shi D. et al. Critical role of calpain in axonal damage-induced retinal ganglion cell death. J Neurosci Res. 2012;90(4):802–15. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Shanab AY, Nakazawa T, Ryu M. et al. Metabolic stress response implicated in diabetic retinopathy: the role of calpain, and the therapeutic impact of calpain inhibitor. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;48(3):556–67. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pellegrini-Giampietro DE, Cherici G, Alesiani M, Carla V, Moroni F. Excitatory amino acid release and free radical formation may cooperate in the genesis of ischemia-induced neuronal damage. J Neurosci. 1990;10(3):1035–41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-03-01035.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Korthuis RJ, Granger DN. Reactive oxygen metabolites, neutrophils, and the pathogenesis of ischemic-tissue/reperfusion. Clin Cardiol. 1993;16(4 Suppl 1):I19–26. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960161307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.McCord JM. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 1985;312(3):159–63. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Peng PH, Ko ML, Chen CF. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression and activity. Exp Eye Res. 2008;86(4):637–46. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2008.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wei Y, Gong J, Yoshida T. et al. Nrf2 has a protective role against neuronal and capillary degeneration in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;51(1):216–24. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wei Y, Gong J, Xu Z. et al. Nrf2 in ischemic neurons promotes retinal vascular regeneration through regulation of semaphorin 6A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(50):E6927–36. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512683112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Werdenberg D, Joshi R, Wolffram S, Merkle HP, Langguth P. Presystemic metabolism and intestinal absorption of antipsoriatic fumaric acid esters. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2003;24(6):259–73. doi: 10.1002/bdd.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bomprezzi R. Dimethyl fumarate in the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: an overview. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2015;8(1):20–30. doi: 10.1177/1756285614564152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Xu Z, Cho H, Hartsock MJ. et al. Neuroprotective role of Nrf2 for retinal ganglion cells in ischemia-reperfusion. J Neurochem. 2015;133(2):233–41. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Himori N, Yamamoto K, Maruyama K. et al. Critical role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress-induced retinal ganglion cell death. J Neurochem. 2013;127(5):669–80. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yoon HY, Kang NI, Lee HK, Jang KY, Park JW, Park BH. Sulforaphane protects kidneys against ischemia-reperfusion injury through induction of the Nrf2-dependent phase 2 enzyme. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;75(11):2214–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.02.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ping Z, Liu W, Kang Z. et al. Sulforaphane protects brains against hypoxic-ischemic injury through induction of Nrf2-dependent phase 2 enzyme. Brain Res. 2010;1343:178–85. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.04.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Piao CS, Gao S, Lee GH. et al. Sulforaphane protects ischemic injury of hearts through antioxidant pathway and mitochondrial K(ATP) channels. Pharmacol Res. 2010;61(4):342–8. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2009.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Inan M, Uz YH, Kizilay G. et al. Protective effect of sildenafil on liver injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. J Pediatr Surg. 2013;48(8):1707–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2012.12.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pan H, He M, Liu R, Brecha NC, Yu AC, Pu M. Sulforaphane protects rodent retinas against ischemia-reperfusion injury through the activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e114186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Yu MS, Leung SK, Lai SW. et al. Neuroprotective effects of anti-aging oriental medicine Lycium barbarum against beta-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity. Exp Gerontol. 2005;40(8-9):716–27. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2005.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yang D, Li SY, Yeung CM. et al. Lycium barbarum extracts protect the brain from blood-brain barrier disruption and cerebral edema in experimental stroke. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33596. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Shan X, Zhou J, Ma T, Chai Q. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides reduce exercise-induced oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(2):1081–8. doi: 10.3390/ijms12021081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Chiu K, Chan HC, Yeung SC. et al. Modulation of microglia by Wolfberry on the survival of retinal ganglion cells in a rat ocular hypertension model. J Ocul Biol Dis Infor. 2009;2(2):47–56. doi: 10.1007/s12177-009-9023-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Amagase H, Sun B, Borek C. Lycium barbarum (goji) juice improves in vivo antioxidant biomarkers in serum of healthy adults. Nutr Res. 2009;29(1):19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2008.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Mi XS, Feng Q, Lo AC. et al. Protection of retinal ganglion cells and retinal vasculature by Lycium barbarum polysaccharides in a mouse model of acute ocular hypertension. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e45469. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Li SY, Yang D, Yeung CM. et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides reduce neuronal damage, blood-retinal barrier disruption and oxidative stress in retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 2011;6(1):e16380. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Gao B, Doan A, Hybertson BM. The clinical potential of influencing Nrf2 signaling in degenerative and immunological disorders. Clin Pharmacol. 2014;6:19–34. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S35078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhao H. Ischemic postconditioning as a novel avenue to protect against brain injury after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(5):873–85. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hoda MN, Siddiqui S, Herberg S. et al. Remote ischemic perconditioning is effective alone and in combination with intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator in murine model of embolic stroke. Stroke. 2012;43(10):2794–9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.660373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Zhang X, Jizhang Y, Xu X. et al. Protective effects of remote ischemic conditioning against ischemia/reperfusion-induced retinal injury in rats. Vis Neurosci. 2014;31(3):245–52. doi: 10.1017/S0952523814000121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Cheng LB, Li KR, Yi N, miRNA-141 attenuates UV-induced oxidative stress via activating Keap1-Nrf2 signaling in human retinal pigment epithelium cells and retinal ganglion cells. Oncotarget; 2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Zhang H, Bhatia M. Hydrogen sulfide: a novel mediator of leukocyte activation. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2008;30(4):631–45. doi: 10.1080/08923970802278045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Szabo C. Hydrogen sulphide and its therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6(11):917–35. doi: 10.1038/nrd2425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Lefer DJ. A new gaseous signaling molecule emerges: cardioprotective role of hydrogen sulfide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(46):17907–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709010104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kimura H, Nagai Y, Umemura K, Kimura Y. Physiological roles of hydrogen sulfide: synaptic modulation, neuroprotection, and smooth muscle relaxation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7(5-6):795–803. doi: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Abe K, Kimura H. The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci. 1996;16(3):1066–71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-03-01066.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Majid AS, Majid AM, Yin ZQ, Ji D. Slow regulated release of H2S inhibits oxidative stress induced cell death by influencing certain key signaling molecules. Neurochem Res. 2013;38(7):1375–93. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1034-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Packer L, Roy S, Sen CK. Alpha-lipoic acid: a metabolic antioxidant and potential redox modulator of transcription. Adv Pharmacol. 1997;38:79–101. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60980-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Palaniappan AR, Dai A. Mitochondrial ageing and the beneficial role of alpha-lipoic acid. Neurochem Res. 2007;32(9):1552–8. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Chidlow G, Schmidt KG, Wood JP, Melena J, Osborne NN. Alpha-lipoic acid protects the retina against ischemia-reperfusion. Neuropharmacology. 2002;43(6):1015–25. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Koriyama Y, Nakayama Y, Matsugo S, Kato S. Protective effect of lipoic acid against oxidative stress is mediated by Keap1/Nrf2-dependent heme oxygenase-1 induction in the RGC-5 cellline. Brain Res. 2013;1499:145–57. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.12.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Koriyama Y, Kamiya M, Takadera T. et al. Protective action of nipradilol mediated through S-nitrosylation of Keap1 and HO-1 induction in retinal ganglion cells. Neurochem Int. 2012;61(7):1242–53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Koriyama Y, Chiba K, Yamazaki M, Suzuki H, Muramoto K, Kato S. Long-acting genipin derivative protects retinal ganglion cells from oxidative stress models in vitro and in vivo through the Nrf2/antioxidant response element signaling pathway. J Neurochem. 2010;115(1):79–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Maher P, Hanneken A. Flavonoids protect retinal ganglion cells from oxidative stress-induced death. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46(12):4796–803. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-0397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Majid AS, Yin ZQ, Ji D. Sulphur antioxidants inhibit oxidative stress induced retinal ganglion cell death by scavenging reactive oxygen species but influence nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 signalling pathway differently. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1095–110. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b13-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.He M, Pan H, Chang RC, So KF, Brecha NC, Pu M. Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway contributes to the protective effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides in the rodent retina after ischemia-reperfusion-induced damage. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e84800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]