Piezogenic pedal papules (PPPs) were first described by Shelley and Rawnsley.1, 2, 3 As the name piezogenic suggests, lesions are generated by pressure (piesis), inducing herniation of footpad's fat through the dermis.1, 2, 3, 4
PPP comprises herniations of fat tissue into the weight-carrying connective tissue of the heels.5, 6 They occur as a result of continuous pressure on the heels from numerous factors such as excessive weight, jumping, running, or carrying heavy loads.
The pain appears to be caused by the continuous contact between the papules and footwear. Some have also proposed that neurovascular anoxia in the lesions may contribute to this pain.5, 6, 7 Histologic studies find fragmentations of elastic tissue and herniations of subcutaneous fat into the dermis.
Injection lipolysis using deoxycholic acid (DCA) is a minimally invasive technique recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat subcutaneous fat in the submental area.8 Given the efficacy and safety of DCA injection lipolysis in the submental area, its use to treat small and localized fat deposits in other anatomic areas should be considered. We present a case of painful PPP treated successfully with deoxycholic acid injection.
Case report
A 34-year-old obese (121 kg) woman came to our clinic because of intense pain in both her heels for a10-month duration. Examinations found numerous yellowish soft and round nodules, about 0.3 to 1 cm in diameter, appearing on the medial and posterior aspects of her heels. They became prominent when standing and walking. The patient had no personal or family history of connective tissue disorder. The symptoms and signs seen in this patient led to a diagnosis of painful PPP.
The patient was not previously given any treatment except painkillers. The option of DCA injection lipolysis, a minimally invasive treatment, was offered. The patient signed a written consent, and photographs were taken at standing position and with her heels on a hard surface to generate more pressure before, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks after treatment. The same camera, lighting, and distance parameters were used in each instance.
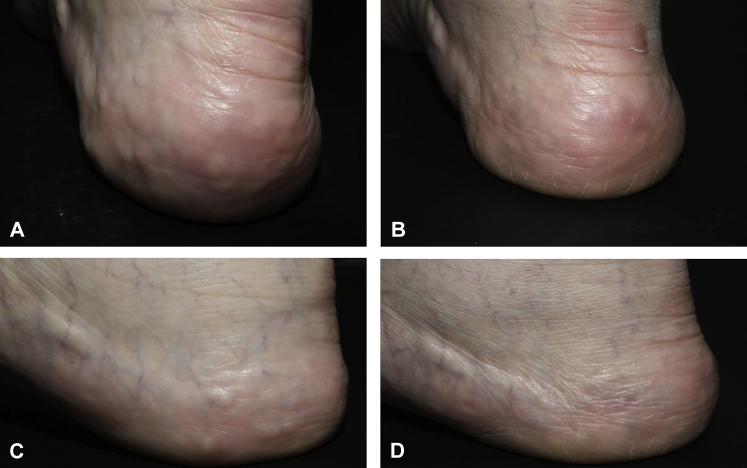
The DCA used here is Revital Celluform (lipolysis); Promoitalia, Italy. It is composed of synthetically derived 1 % DCA-based cosmetic solution. After disinfecting the whole area with alcohol pads, DCA was injected with 30-gauge needle held perpendicularly to the skin. A total of 0.05 mL to 0.1 mL was injected in each nodule relative to its size. Ice was applied 1 minute before and after injection sites to minimize pain. After injection, the patient did not experience any side effects (swelling, bruising, tenderness). In the 2 weeks of follow-up, the previously treated nodules were completely disappearing, and there was no pain experienced during standing and walking (Fig 1).
Fig 1.
A and C, Before injection (left). B and D, Two weeks after (right).
Discussion
PPPs are known to be common in healthy subjects, with most experiencing no symptoms.1, 3 The pain in the remaining patients results from ischemia of blood vessels and associated nerves, with consequent thickness of papillary dermis.1, 4 The main cause for seeking medical care is pain while standing and walking.
Nonpainful PPPs are managed conservatively. For painful conditions, management includes avoiding standing for prolonged periods, reducing foot trauma, using compression stockings, foam-fitting plastic heel cups, weight loss, acupuncture, repeated injections of betamethasone and bupivacaine, and, rarely, surgery.4, 9 However, the treatment outcomes for the mentioned therapeutic modalities are not always satisfactory.
Deoxycholic acid injection, a minimally invasive procedure, was effectively used for reduction of submental fat in many reports.10 Recently, Jegasothy11 injected DCA for bra-line lipolysis in 2 patients with good result. Therefore, I used DCA injection as a treatment for the painful fat herniation that occurs in PPP. This is relatively difficult to treat with the traditional modalities but seems to be responsive to DCA injection.
The fast response in dissolving the nodules and pain relief seen in our patient reinforces the fact that the nodules in PPP are fat herniations rather than real fat accumulations. To the best of our knowledge, we report the first case of DCA treatment for painful PPPs with excellent efficacy of pain relief, which is the main complaint in patients with PPP. This opens up opportunities for the treatment of small, localized fat depositions in in other anatomic areas using injection of deoxycholic acid. Larger scale and more long-term trials are needed to further prove the efficacy and safety of this treatment.
Footnotes
Funding sources: None.
Conflicts of interest: None disclosed.
References
- 1.Kennedy C.T.C., Burd D.A.R., Creamer D. Mechanical and thermal injury. In: Burns T., Breathnach S., Cox N., Griffths C.E., editors. Rook's textbook of dermatology. 8th ed. Wiley-Blackwell; Oxford: 2007. pp. 28–61. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Adams B.B. Pressure injuries. In: Adams B.B., editor. Sports dermatology. Springer; New York: 2006. pp. 250–252. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kahana M., Feinstein A., Tabachnic E., Schewach-Millet M., Engelberg S. Painful pyezogenic pedal papules in patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;17:205–209. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70192-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Doukas D.J., Holmes J., Leonard J.A. A nonsurgical approach to painful piezogenic pedal papules. Cutis. 2004;73:339–340. 346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Graham B.S., Barrett T.L. Solitary painful piezogenic pedal papule. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(5 Pt 1):780–781. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Montgomery F., Fioriti A. Piezogenic pedal papules: treated by resection and hernial closure. The Foot. 1998;8:171–172. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shelley W.B., Rawnsley H.M. Painful feet due to herniation of fat. JAMA. 1968;205:308–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.FDA approves treatment for fat below the chin. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvent/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm444978.htm Available from:
- 9.Redbord K.P., Adams B.B. Piezogenic pedal papules in a marathon runner. Clin J Sport Med. 2006;16:81–83. doi: 10.1097/01.jsm.0000180871.22426.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sykes J.M., Allak A., Klink B. Future applications of deoxycholic acid in body contouring. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jegasothy S.M. Deoxycholic acid injections for bra-line lipolysis. Dermatol Surg. 2017;0:1–3. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]