Abstract
The present longitudinal study examined religious beliefs and behaviors, spiritual health locus of control (SHLOC), and selected health-related behaviors and outcomes in a national sample of 766 African American adults. Participants were interviewed by telephone three times over a five-year period. Results indicated that stronger religious beliefs and religious behaviors were associated with greater changes in active SHLOC. There was some evidence of direct effects of religious beliefs and behaviors on changes in health behaviors. Religious behaviors were related to greater passive SHLOC over time across some health outcomes. Passive SHLOC was associated some less desirable health outcomes over time.
Keywords: Religion, African American, Locus of Control, Health Behaviors, Longitudinal
Religion, Health, and African Americans
Religiosity is an important facet of American culture in general and African American culture in particular (Belgrave & Allison, 2010). African Americans report high levels of religious beliefs and behaviors (Chatters, Taylor, Bullard, & Jackson, 2009), with a substantial amount of research demonstrating a link between religiosity and health behaviors among this population (Bediako et al., 2011; Landor, Simons, Simons, Brody, & Gibbons, 2011; Mattis & Watson, 2009; Waldron-Perrine et al., 2011). Recent research among African Americans has identified underlying mechanisms or mediators between religiosity and health, including social support (Holt, Schulz, Williams, Clark, & Wang, 2014), self-esteem and self-efficacy (Holt, Clark, Debnam, & Roth, 2014). Given that African Americans have higher rates of mortality than Whites from heart disease, cerebrovascular disease (stroke), kidney disease, and some cancers (National Center for Health Statistics, 2007), it is important to expand our understanding of the mechanisms linking religiosity and physical health behaviors and outcomes in this population.
There is a substantial amount of research on the relationship between religiosity and mental health. In their review, Mattis and Watson (Mattis & Watson, 2009) note that among African Americans, research suggests that religiosity is related to reporting fewer stressors (Ellison, Boardman, Williams, & Jackson, 2001), lower distress (Mattis & Watson, 2009), and less depression and anxiety (Jang & Johnson, 2004). Among African American youth, religiosity is associated with higher self-esteem and life satisfaction (Blaine & Crocker, 1995).
Most studies on religiosity and health are cross-sectional and do not lend themselves to an examination of causal pathways. The present study examines spiritual health locus of control (SHLOC) as a mediator of the religiosity-health connection in a three wave longitudinal design in a national sample of African Americans. Because the SHLOC construct integrates a person’s perceptions of God’s agency with their beliefs about health determinants, it has the potential to be a significant mediator in the relationship between religious beliefs/behaviors and health-related behaviors and outcomes.
Locus of Control and Physical and Mental Health
The current study is based on Rotter’s social learning theory (Rotter, 1954) which states that a person’s behavior is a function of (1) one’s expectancy that their behaviors will lead to a particular outcome and (2) the value of the outcome to the person. The locus of control (LOC) construct grew out of Rotter’s theory and is a generalized expectancy that designates the extent to which individuals attribute their actions to personal agency (e.g., ability) or to external forces outside of their control (e.g., powerful others, fate, luck). Therefore, LOC is an abstraction derived from many expectancy-behavior outcome cycles in which people viewed the causes of their failures and successes as being under internal (internal LOC) or external (external LOC) control (Clark, 2008).
Many researchers have developed more specific LOC measures, including measures for health-related domains. Holt and colleagues designed and validated the spiritual health locus of control (SHLOC) scale to assess an individual’s views about God’s role in health-related behaviors and outcomes. SHLOC consists of active and passive factors that are distinct from the external and internal dimensions of other locus of control measures (Holt, Clark, Kreuter, & Rubio, 2003; Holt, Roth, Huang, & Clark, 2015). The active SHLOC factor is characterized by the belief that that the individual is responsible for his or her health and should work with God in achieving desired ends. In contrast, the passive SHLOC factor is characterized by the belief that God determines one’s health, making it unnecessary for the individual to engage in health-promoting behaviors (Holt et al., 2015). In a sample of African American adults, active SHLOC was associated with higher fruit consumption and lower alcohol consumption, while passive SHLOC was associated with lower vegetable and higher alcohol consumption. Further, there were some gender differences such that for women, passive SHLOC was associated with lower vegetable consumption but for men, passive SHLOC was associated with lower vegetable consumption and higher alcohol consumption (Debnam, Holt, Clark, Roth, Foushee, et al., 2012).
Research on the role of personal beliefs about God’s influence on health, specifically cancer screening, has utilized qualitative inquiry as well as a God Locus of Health Control scale (Wallston et al., 1999) and the Spiritual Health Locus of Control measure (Holt et al., 2015). In a study of African American women at high risk for breast cancer, the belief that God controlled health was associated with a lower likelihood of following consensus-approved recommendations for clinical breast examinations and mammograms (Kinney, Emery, Dudley, & Croyle, 2002). Further, there seem to be gender differences in the impact of SHLOC and religious beliefs and behaviors associated with elevated cancer risk. Among African American women, high active SHLOC accentuates the effect of high levels of religious behaviors in reducing alcohol and tobacco use, however for men, high passive SHLOC in conjunction with lower levels of religious beliefs are associated with greater alcohol and tobacco use (Holt et al., 2015).
Studies on the relationship between LOC and mental health have yielded mixed results. Some studies suggest that higher internal LOC and/or lower external LOC are associated with less depressive symptoms. In a sample of older in-patients, those who were depressed showed a more external LOC orientation than those who were not depressed (Bjorklof et al., 2016). In a sample of cancer patients, internal health locus of control (HLOC) was associated with lower depression but there was no association between depression and external HLOC (Goldzweig, Hasson-Ohayon, Alon, & Shalit, 2016). The mixed findings for the LOC-depression relationship may be due to a variety of factors, including the type of locus of control assessed (e.g., general, health) as well as the variability in samples (e.g., type of patient).
The concept of SHLOC is consistent with current research on the religiosity-health connection. Our factors of active and passive SHLOC are relevant to Pargament’s concepts of collaborative and deferring problem solving (Pargament, Kennell, Hathaway, Grevengoed, Newman, & Jones, 1988), respectively. Research by Pargament and Exline has explored religious and spiritual struggle that includes the factors of entitled divine (God has let me down), demonic (felt threatened by the devil or evil spirits), interpersonal (felt mistreated by religious people), ultimate meaning (questioned whether life matters), and doubt (trying to figure out what I really believe) (Exline, Pargament, Grubbs, & Yali, 2014). Avoiding these spiritual struggles (Dworsky, Pargament, Wong, & Exline, 2016) also may be associated with having a higher Passive SHLOC or a lower Active SHLOC. Perceiving God as distant (Exline, Grubbs, & Homolka, 2015) may be related to having a higher passive SHLOC or a lower Active SHLOC. Exline, Hall, Pargament, and Harriott (2017) note that one predictor of growth as a result of religious struggle was positive religious coping that focuses on actions that people initiate in order to engage more deeply with God. However, a second predictor of growth was the perception that God had initiated some type of helpful action, such as communication, intervention, or providing support. These two predictors of growth after spiritual struggle may be related with Active and Passive SHLOC, respectively.
Relatedly, Schieman and colleagues have examined the sense of divine control, defined as the perception of the extent to which God controls the direction and outcomes of daily life and life trajectory, which also seems connected to our concept of SHLOC. For example, Schieman and colleagues explain that prior work suggests religious beliefs can be used to solve problems and feel effective. Further, Christians use phrases like “God is my co-pilot” and repeat the often quoted Bible verse of “I can do all things through Christ who strengthens me” (Philippians 4:13). However, religious beliefs also can be used to relinquish control to and rely on God, thereby reducing worry and self-blame (Schieman, Nguyen, and Elliott, 2003; Schieman, Pudrovska, & Milkie, 2005). Again, these notions appear consistent with our concepts of Active and Passive SHLOC, respectively. Ellison (1993) and Schieman et al. (2005) also suggest that relinquishing of control, which is similar to our Passive SHLOC, may decrease potency by detracting from personal efforts to solve the problem. On the other hand, it may be adaptive in situations where one can do little to improve health outcomes. However, Schieman et al. (2005) found that among White older adults, a higher sense of divine control was related to lower personal mastery, yet among African American older adults there was little relationship between sense of divine control and personal mastery. They also observed that, among African Americans, sense of divine control was positively correlated with self-esteem, especially among African American women. In sum, the research of SHLOC is consistent with other research on God-related control and prior research suggesting it is predictive of some health behaviors and outcomes.
Locus of Control as a Possible Religion-Health Mediator
Several studies have examined perceived control as a mediator for the religiosity-health relationship for mental health outcomes. For example, Ryan and Francis (2012) found that higher awareness of God was associated with higher internal locus, which in turn, was related to better psychological health. Further, they found that participants’ perceived instability in their relationship with God was associated with higher external locus, which was then associated with poorer psychological health. In other research, religiosity/spirituality predicted higher perceived control, which in turn, predicted higher subjective well-being in a sample of later life adults (Jackson & Bergeman, 2011). Another study found that religiosity predicted increased perceptions of control which, in turn, was related to less distress (Jang & Johnson, 2004). These studies examined psychological health, but we were not able to locate any prior research with perceived control as a mediator of the religiosity-physical health relationship. Similarly, we were not able to locate any longitudinal studies that examined LOC as a mediator.
The Present Study
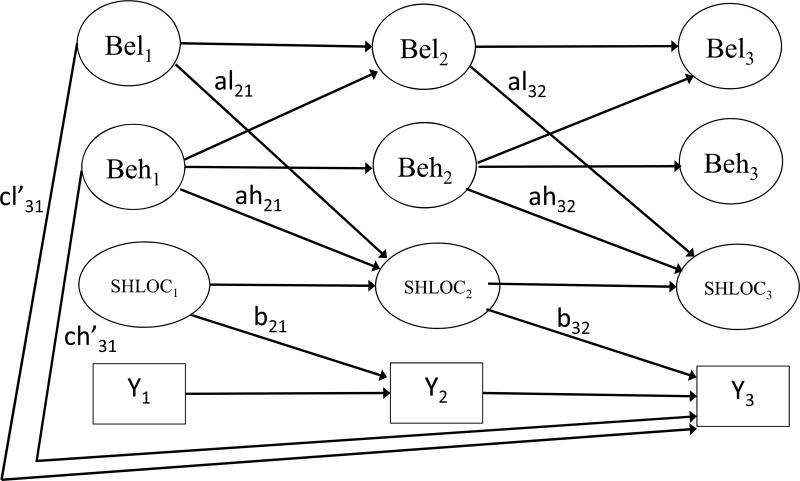
The aim of the present study is to expand religiosity-health research by examining the relationship between religious beliefs and religious behaviors, SHLOC, and selected physical and mental health behaviors and outcomes in a three wave longitudinal study of African Americans. In this study, we are examining religious beliefs and religious behaviors at Time 1, active and passive SHLOC at Time 2, and changes in physical and mental health behaviors and outcomes from Time 2 to Time 3. Figure 1 diagrams the model. Our hypotheses are:
Figure 1.
Longitudinal model of religious social support as a mediator of the religious involvement -- health connection.
Active SHLOC Models
H1: Religious beliefs and religious behaviors will predict increases in Active SHLOC over time (Holt, Clark, & Klem, 2007; Holt et al., 2015). These are paths al (religious beliefs) and ah (religious behaviors) in Figure 1.
H2: Active SHLOC will predict changes in many of our health behaviors and outcomes such that Active SHLOC will be related to higher levels of health enhancing behaviors (e.g., fruit and vegetable consumption) and lower levels of health compromising behaviors (e.g., binge alcohol consumption) (Debnam, Holt, Clark, Roth, Foushee, et al., 2012; Holt et al., 2007; Holt et al., 2003; Holt et al., 2015). Active SHLOC will predict a decrease in depressive symptoms and an increase in emotional functioning (Goldzweig et al., 2016). This is path b32 in Figure 1.
H3: Active SHLOC will mediate the relationship between both religious beliefs and religious behaviors and changes in psychological (depression, emotional functioning) health outcomes (Jackson & Bergeman, 2011; Jang & Johnson, 2004; Ryan & Francis, 2012). While we did not find any prior research suggesting that active SHLOC would mediate the relationships between religious beliefs and behaviors with physical health behaviors, we nonetheless predicted that active SHLOC also would mediate the relationship between both religious beliefs and behaviors and changes in physical health behaviors and outcomes. These are paths al*b32 (religious beliefs) and ah*b32 (religious behaviors) in Figure 1.
Passive SHLOC Models
H4: Religious beliefs and religious behaviors will predict increases in passive SHLOC over time (Holt et al., 2007; Holt et al., 2015). These are paths al (religious beliefs) and ah (religious behaviors) in Figure 1.
H5: Passive SHLOC will predict many of our health behaviors and outcomes such that higher passive SHLOC will be related to lower levels of health enhancing behaviors (e.g., fruit and vegetable consumption) and higher levels of health compromising behaviors (e.g., binge alcohol consumption) (Debnam, Holt, Clark, Roth, Foushee, et al., 2012; Holt et al., 2007; Holt et al., 2003; Holt et al., 2015). Passive SHLOC will predict increases in depressive symptomology and decreases in emotional functioning (Ryan & Francis, 2012). This is path b32 in Figure 1.
Direct Effects
H6: Regarding direct effects, religious beliefs (but not religious behaviors) will predict less depressive symptomology and better emotional functioning (Holt, Clark, & Roth, 2014; Waldron-Perrine et al., 2011). This will be tested in both the Active and Passive SHLOC models. This is path cl in Figure 1.
H7: Regarding direct effects, religious behaviors (but not religious beliefs) will be related to increased health enhancing behaviors (e.g., fruit and vegetable consumption, physical functioning, physical activity, cancer screening) and related to lower levels of health-compromising behaviors (e.g., binge alcohol consumption (Holt, Clark, & Roth, 2014). This will be tested in both the Active and Passive SHLOC models. This is path ch in Figure 1.
Method
RHIAA Study
Participants are from the “Religion and Health in African Americans” (RHIAA) study, which was specifically designed to examine religion-health mediators in a national sample of African American adults. The RHIAA study is comprised of two sub-samples of participants who completed the same telephone interview protocol, with the exception that subsample 1 (N=2,370) reported on lifestyle behaviors while subsample 2 (N=803) reported on physical/emotional functioning. Both subsamples reported on depressive symptoms. The study sample was developed and data collection conducted by an external subcontractor (OpinionAmerica). Sampling and recruitment methods are described in detail elsewhere (Debnam, Holt, Clark, Roth, & Southward, 2012; Holt et al., 2015). Eligible participants spoke English, self-identified as African American, and were 21 years of age or older.
Telephone survey methods
Using probability-based methods, a professional sampling firm generated a list of households from publicly available data such as motor vehicle records from all 50 United States. Trained interviewers dialed telephone numbers from this call list, asking to speak to an adult who lived in the household. Time 1 (T1) response rates were 19% and 27% (respectively), calculated as #accepted / [#accepted + #non-interviewed] (Holt et al., 2013). Upper bound response rates included only those individuals who were eligible upon screening but then refused, and were 94% and 98% (Holt et al., 2013). The interviewers introduced the project and if the individual spoke English and expressed interest, then the interviewer administered a brief eligibility screener to determine whether they self-identified as African American and age 21 or older. Eligible individuals in the first sub-sample were screened for cancer history since cancer diagnosis was an exclusion criterion due to survey questions about cancer screening behaviors. Eligible contacts provided verbal assent after hearing an informed consent script. Upon completion of the interview, participants received a $25 gift card by mail. Each of the three interviews lasted about 45–60 minutes.
A total of 3,173 participants (1281 men, 1892 women) completed measures at T1 and 766 participants completed the measures at T3, resulting in a retention rate from T1 to T3 was 24% (Holt et al., 2015). While the retention rate may seem low, it should be noted that the original study (at T1) did not include a planned follow-up assessment. However, once funding became available, these participants were re-contacted and asked about a possible follow-up. T2 interviews were conducted approximately 2.5 years after the T1 interviews and T3 interviews were conducted approximately 5 years after T1 interviews. The analytic sample for the present paper is comprised of individuals who provided data at each of the three waves of data collection (N=766). Those who completed the T3 interview, compared to those who did not, were significantly older (58.7 years old vs. 52.8 years old, p<.0001) and more likely to be female (OR=1.28, 95% CI: 1.08–1.52; Holt, Le, et al., 2015). After adjusting for age and gender, the retained participants were more likely to have college education (OR=1.42, 95% CI: 1.20–1.69), less likely to report “poor” health condition (OR=0.56, 95% CI: 0.36–0.87), more likely to have income greater than $30k (OR=1.28, 95% CI: 1.06–1.53), and more likely to be single than being married or living with partner (OR=1.52, 95% CI=1.18–1.95). Baseline characteristics for all participants who were interviewed for all 3 waves are in Table 1. Our sample is not representative of all African Americans, but, as noted above, it is a large probability-based sample that includes both men and women.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics for all participants who were interviewed for all 3 waves
| Variable | All participants (n=766) |
|---|---|
|
| |
| Age, mean ± SD | 58.72 ± 12.06 |
|
| |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Female | 491 (64.10) |
| Male | 275 (35.90) |
|
| |
| Education, n (%) | |
| ≥College | 455 (59.55) |
| <College | 309 (40.45) |
|
| |
| Marital status, n (%) | |
| Never been married | 76 (9.95) |
| Currently single | 136 (17.80) |
| Separated or divorced | 138 (18.06) |
| Widowed | 123 (16.10) |
| Currently married or living with partner | 291 (38.09) |
|
| |
| Employment, n (%) | |
| Full-time employed | 252 (33.07) |
| Part-time employed | 89 (11.68) |
| Not currently employed | 83 (10.89) |
| Retired | 250 (32.81) |
| Receiving disability | 88 (11.55) |
|
| |
| Health status, n (%) | |
| Poor | 36 (4.70) |
| Fair | 167 (21.80) |
| Good | 265 (34.60) |
| Very good | 201 (26.24) |
| Excellent | 97 (12.66) |
|
| |
| Income, n (%) | |
| ≤$30,000 | 308 (47.09) |
| >$30,000 | 346 (52.91) |
Note: Also reported in Holt, Roth, Huang, Park, & Clark (2017).
Measures
Religious involvement
Religious involvement was assessed using an instrument validated for use with African Americans (Lukwago, Kreuter, Bucholtz, Holt, & Clark, 2001; Roth et al., 2012). This 9-item instrument assesses two dimensions of involvement: religious beliefs (e.g., “I feel the presence of God in my life.”; “I have a close personal relationship with God.”; Cronbach’s α = .92 in present sample using the 766 participants who completed all three waves of data collection) and religious behaviors (e.g., church service attendance, involvement in other church activities; talking openly about faith with others; Cronbach’s α = .74 in the present sample). Seven items use a 5-point Likert-type format, and two service attendance items use a 3-point response format. Scores can range from 4-20 for religious beliefs and 5-21 for religious behaviors, with higher scores indicating greater religious involvement.
Spiritual health locus of control
The spiritual health locus of control (SHLOC) scale is a 13-item measure that has two dimensions. Active SHLOC (11 items) involves the belief that God empowers the individual to be proactive about health behaviors and works in partnership with God to maintain good health (e.g., God gives me the strength to take care of myself; α = 0.92 in the present study). Passive SHLOC (2 items) measures the belief that because God has control over one’s health, the individual does not need to engage in healthy behaviors (e.g., There is no point to taking care of myself when it’s all up to God anyway; r = 0.58 in the present study). Participants respond to these items on a 5-point Likert type scale (strongly disagree, disagree, neutral, agree, strongly agree). Even though the Passive SHLOC subscale has only two items, the two-factor structure and predictive validity have been demonstrated for this instrument (Debnam, Holt, Clark, Roth, & Southward, 2012; Holt et al., 2003).
Depressive symptoms
Depressive symptoms were assessed with the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) (Radloff, 1977). Participants rated how frequently during the past week they experienced a list of 20 symptoms (e.g., “I had crying spells.”, “I felt that everything I did was an effort.”) from 1 (“rarely/less than 1 day”) to 4 (“all of the time/5–7 days”). High internal consistency has been reported in both normal and patient populations (Radloff, 1977), as well as in the present sample (α = .89). The CES-D has previously shown acceptable validity in African American samples (Makambi, Williams, Taylor, Rosenberg, & Adams-Campbell, 2009; Roth, Ackerman, Okonkwo, & Burgio, 2008).
Physical and emotional functioning
Physical and emotional functioning were assessed using the Medical Outcomes Survey Short Form SF-12.v2. This is a widely-used instrument measuring physical (e.g., “Does your health now limit you in these activities? If so, how much?” Moderate activities such as moving a table, pushing a vacuum cleaner, bowling or playing golf”) and emotional (e.g., [how often during past 4 weeks] “Have you felt calm and peaceful?; Did you have a lot of energy?”) functioning (Ware, Kosinski, & Keller, 1996). The brief, 12-item form has demonstrated reliability and validity similar to the longer versions, and was more appropriate for our telephone survey methodology to keep participant burden down. Test-retest reliability was acceptable for both the physical (0.89) and emotional (0.76) functioning subscales (Ware et al., 1996).
Health behaviors
To assess fruit and vegetable consumption, an adaptation of the National Cancer Institute’s 5-A-Day Survey was used (Block et al., 1986). This instrument was validated with the study population (Kreuter et al., 2005). Seven items assess fruit consumption and 5 items assess vegetable consumption (e.g., “In a typical week, about how many times do you have…a piece of fresh fruit, like an apple, orange, banana, or pear?”). Fifteen different fruits and 18 vegetables are assessed specifically within these items. The response scale ranges from 0 to 8 or more servings per week. Servings per day were computed by summing all items and dividing by 7. The test-retest reliability over a 2-week period (intraclass correlation coefficient) for the both the fruit (r = .52, p < .001) and the vegetable (r = .60, p < .001) portions were adequate in previous research (Kreuter et al., 2005).
Alcohol and tobacco use were assessed using modules from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS). Items demonstrated adequate test-retest reliability over a 21-day period in a previous sample of African Americans (Stein, Lederman, & Shea, 1993). The module on alcohol consumption included an initial question on any alcohol use in the preceding 30 days. For those who answered “yes,” additional items assessed binge and heavy drinking (“Considering all types of alcoholic beverages, how many times during the past 30 days did you have 4/5 or more drinks on an occasion?”; “During the past 30 days, what is the largest number of drinks you had on any occasion?”). The tobacco use item asked whether the individual smoked cigarettes every day, some days, or not at all. The short form of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) (Craig et al., 2003) was used to assess physical activity in the last week. This instrument asks about the number of days in the past week (frequency) and amount of time (duration) participants spent engaging in vigorous and moderate activity and walking. Minutes per week are computed. This instrument has been validated with an African American population (Wolin, Heil, Askew, Matthews, & Bennett, 2008).
Cancer screening behaviors
Participants were asked about age- and sex-appropriate cancer screening behaviors using items based on the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) (Stein et al., 1993). Screenings included time since last mammogram, ever had a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, and ever had a colonoscopy for all age-eligible participants. Screening items were dichotomized for analysis into recommendation compliant vs. not at the time of the T1 interview, based on guidelines from the American Cancer Society (American Cancer Society, 2014).
Demographics
Participant sex, race, date of birth, marital status, years of education, employment status, and self-rated health status were recorded in the survey demographics module.
Statistical analyses
All analyses were conducted using the structural equation modeling (SEM) procedures of Mplus version 7.0 (Muthén & Muthén, 2013). Maximum likelihood estimation was used. A modification of the traditional two-step approach (Anderson & Gerbing, 1988) was used such that confirmatory factor analysis models were run first that specified latent factors for religious beliefs, religious behaviors, and the mediator from the observed items for all three constructs. Structural models were then estimated that included both mediated and unmediated causal effects among the latent constructs after satisfactory fit was obtained for the measurement model. Similar methods were used in Holt, Roth, Huang, Park, & Clark (2017).
For the measurement model, separate latent factors were extracted for each construct at each data collection wave, and the factor loadings were constrained to be invariant or equal across the three data collection waves (T1, T2, and T3). This ensured that the identification of the latent factors was the same across measurement waves. Item measurement residuals were also estimated at each measurement wave and allowed to correlate across time for each item to account for any item-specific method variance that could not be accounted for by the underlying latent factors. The fit of the measurement model was evaluated using the chi-square goodness-of-fit test and the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA). An RMSEA less than 0.06 was considered to be indicative of excellent model fit (Hu & Bentler, 1999), and the chi-square statistic from the measurement model served as the reference point for evaluating the fit of the structural model.
After achieving adequate measurement model fit, the structural models were estimated that tested the significance of the longitudinal direct and mediated effects of religious involvement at T1 on the health outcomes at T3. The basic autoregressive structural model used to test these relationships is illustrated in Figure 1. Autoregressive paths were included such that each variable (religious beliefs, religious behaviors, mediator, and the outcome variable denoted as Y) at T2 and at T3 was predicted by the same variable at the earlier measurement wave. Consequently, because of these autoregressive covariate adjustments, any other variable that predicts a variable at Time t is actually predicting change in that variable from Time t-1 to Time t. This includes the paths for the mediated and unmediated effects.
The mediation paths in Figure 1 extend on the classic a, b, and c paths from the mediation literature (MacKinnon, 2008). In addition, we use subscripts to denote measurement waves, and “l” and “h” to denote paths from religious beliefs and religious behaviors, respectively. The path a121, for example, predicts the mediator at T2 from religious beliefs at T1 (after accounting for the other predictive paths or covariates) as illustrated in Figure 1. Similarly, ch31 depicts the unmediated predictive effect of religious behaviors at T1 on the health outcome at T3. Additional paths from religious behaviors at time t to religious beliefs at the subsequent data collection wave were also included in the model based on findings from an earlier two-wave analysis (Roth et al., 2016).
Religious beliefs, religious behaviors, and the mediator are drawn with ovals to represent that these are latent factors from the measurement model. The individual items, factor loadings, and correlated item residuals are not illustrated in Figure 1 in the interest of clarity. In addition, unanalyzed correlations were estimated among all four variables at each measurement wave (i.e., pairwise residual correlations between Bel3, Beh3, Med3 and Y3 at T3, and also for T2 and for T1), but these associations are also not depicted in Figure 1 for parsimony and to focus the figure on the mediation paths of interest.
The study consisted of a fairly consistent inter-wave interval of approximately 2.5 years and additional parsimony was achieved 1) by restricting the analysis to those participants who provided data at all 3 times, and 2) by constraining to be equal the T1 → T2 paths with the T2 → T3 paths for the same variables as long as those effects were also adjusted for the same covariates at each wave. Thus, the autoregressive paths for religious beliefs, religious behaviors, and the mediator were all constrained to be equal (e.g., Bel1 → Beh2 was constrained to be equal to Bel2 → Bel3). In addition, al21 was constrained to be equal to al32, and ah21 was constrained to be equal to ah32. The mediated paths al21*b32 for religious beliefs and ah21*b32 for religious behaviors were tested for statistical significance using Sobel’s delta method (Sobel, 1982). The unmediated paths cl31 and ch31 were also tested for statistical significance by obtaining a Z statistic from the maximum likelihood estimate for that effect divided by its standard error. As with the measurement model, the RMSEA was used as the primary indicator of overall fit for the structural model. Parameter estimates shown in the tables are standardized values (STDYX).
Results
Measurement Model
Descriptive statistics for our measures are in Table 2. The measurement model was fit for both active and passive SHLOC using participants who completed all three waves of interviews (n=766). The fit indices for active SHLOC were χ2 = 5416.09, df = 1870, RMSEA = .050 for passive SHLOC were χ2 = 1190.60, df = 556, RMSEA = .039.
Table 2.
Descriptives of study outcomes at the three study waves
| Variable | N | Time 1 | Time 2 | Time 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religious beliefs (/20 max) | 756 | 17.74 (2.91) | 17.83 (2.77) | 17.81 (2.82) |
| Religious behaviors (/21 max) | 742 | 16.24 (3.42) | 16.51 (3.39) | 16.40 (3.38) |
| Active SHLOC (/55 max) | 728 | 45.04 (7.44) | 45.46 (7.67) | 43.98 (7.68) |
| Passive SHLOC (/10 max) | 753 | 3.70 (1.58) | 3.72 (1.64) | 3.74 (1.59) |
| Depressive symptoms (/60 max) | 737 | 9.98 (9.25) | 10.55 (9.08) | 10.68 (9.04) |
| SF-12 physical (/100 max) | 196 | 45.01 (11.31) | 43.66 (11.25) | 43.58 (11.53) |
| SF-12 mental (/100 max) | 196 | 53.68 (8.06) | 52.62 (9.77) | 52.10 (9.72) |
| Fruit servings per day (/8 max) | 564 | 2.62 (1.34) | 2.38 (1.21) | 2.38 (1.21) |
| Vegetable servings per day (/5.71 max) | 564 | 2.21 (0.94) | 2.12 (0.94) | 1.98 (0.88) |
| Drinking alcohol Y/N in the past 30 days (%) | 563 | 0.40 (0.49) | 0.40 (0.49) | 0.39 (0.49) |
| 4/5 or more alcohol drinks (%) | 509 | 0.51 (2.28) | 0.37 (1.96) | 0.52 (2.73) |
| Largest number of drinks^ | 520 | 1.01 (1.94) | 0.92 (1.79) | 0.93 (2.07) |
| Currently smoking (%) | 562 | 0.17 (0.38) | 0.16 (0.37) | 0.15 (0.36) |
| Vigorous activities minutes / week | 536 | 170.07 (268.43) | 162.29 (234.51) | 138.59 (226.48) |
| Moderate activities minutes / week | 523 | 148.41 (249.87) | 131.59 (206.18) | 133.15 (219.34) |
| Walking minutes / week | 527 | 232.24 (294.37) | 217.78 (280.85) | 176.72 (249.50) |
| Ever had a mammogram (%) | 348 | 0.95 (0.21) | 0.95 (0.22) | 0.97 (0.17) |
| Last mammogram: past 2 years vs. > 2 years or never (%) | 348 | 0.90 (0.30) | 0.88 (0.33) | 0.89 (0.31) |
| Ever had a PSA test (%) | 157 | 0.78 (0.42) | 0.87 (0.34) | 0.89 (0.32) |
| Ever had a colonoscopy (%) | 382 | 0.74 (0.44) | 0.82 (0.38) | 0.87 (0.34) |
NOTE: Sample sizes, means, standard deviations, and percentages are reported.
Means reflect the majority of participants who reported 0 drinks in the past 30 days for whom a value of 0 was entered.
Active SHLOC Paths
Religious beliefs and behaviors related to change in active SHLOC (Paths al and ah)
Table 3 contains the analyses for active SHLOC. Consistent with H1, across most of the health behavior and outcome variables, we found that religious beliefs were related to changes in active SHLOC such that stronger religious beliefs were associated with greater active SHLOC at the next observation (path al; most ps < .01).
Table 3.
Adjusted model using active SHLOC as mediator
| Outcome | al | ah | b32 | Indirect effect | cl | ch | RMSEA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| al*b32 | ah*b32 | |||||||
| Depressive symptoms1 | 0.115** | 0.140*** | 0.057 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.011 | −0.056 | 0.049 |
| SF-12 physical function1 | 0.089 | 0.321*** | −0.009 | −0.001 | −0.003 | −0.029 | 0.028 | 0.064 |
| SF-12 emotional function1 | 0.075 | 0.325*** | −0.137 | −0.010 | −0.044 | 0.196 | −0.075 | 0.064 |
| Fruit servings per day1 | 0.116** | 0.117** | −0.006 | −0.001 | −0.001 | −0.172** | 0.203** | 0.049 |
| Vegetable servings per day1 | 0.117** | 0.115** | −0.051 | −0.006 | −0.006 | −0.101 | 0.103 | 0.049 |
| Drinking alcohol Y/N in the past 30 days1 | 0.113** | 0.120** | −0.064 | −0.007 | −0.008 | 0.129* | −0.112 | 0.050 |
| 4/5 or more alcohol drinks1 | 0.119** | 0.114** | −0.027 | −0.003 | −0.003 | −0.123 | 0.093 | 0.050 |
| Largest number of drinks1 | 0.113** | 0.122** | −0.013 | −0.001 | −0.002 | 0.061 | −0.039 | 0.049 |
| Currently smoking1 | 0.120** | 0.115** | 0.058 | 0.007 | 0.007 | −0.004 | −0.024 | 0.050 |
| Vigorous activities minutes / week1 | 0.118** | 0.114** | −0.029 | −0.003 | −0.003 | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.049 |
| Moderate activities minutes / week1 | 0.121** | 0.112* | 0.014 | 0.002 | 0.002 | −0.067 | 0.047 | 0.049 |
| Walking minutes / week1 | 0.119** | 0.113* | −0.048 | −0.006 | −0.005 | 0.016 | −0.032 | 0.050 |
| Last mammogram (within last 2 years vs. > 2 years or never)2 | 0.014 | 0.141* | −0.062 | −0.001 | −0.009 | 0.090 | −0.013 | 0.053 |
| Ever had a PSA test2 | 0.187** | 0.072 | −0.005 | −0.001 | 0.000 | −0.122 | 0.307* | 0.062 |
| Ever had a colonoscopy1 | 0.119** | 0.113* | −0.012 | −0.001 | −0.001 | 0.039 | −0.084 | 0.049 |
p<.05
p<.01
p<.001
. Age, gender, education and self-rated health were adjusted.
. Age, education and self-rated health were adjusted.
Consistent with H1, we found that religious behaviors were related to changes in active SHLOC for most of the health behaviors and outcome variables such that religious behaviors were associated with greater active SHLOC at the next observation over time (path ah; most ranged from p< .05 to p<.001).
Active SHLOC related to change in health outcomes over time (Path b32)
Contrary to H2, Active SHLOC at T2 was not related to changes in any of the physical or mental health outcomes from T2 to T3.
Mediation effect for religious beliefs through change in Active SHLOC from T1 to T2 on health outcomes from T2 to T3 (Paths al*b32 and ah*b32)
Contrary to H3, there was no evidence that changes in Active SHLOC mediated the relationship between religious beliefs or religious behaviors and changes in any of physical or mental health behaviors or health outcomes.
Passive SHLOC Paths
Religious beliefs and behaviors related to change in passive SHLOC (Paths al and ah)
Table 4 contains the analyses for passive SHLOC. Contrary to H4, there was no evidence that religious beliefs were related to changes in passive SHLOC for any of the health behaviors or outcomes examined (path al). Somewhat consistent with H4, religious behaviors are associated with greater passive SHLOC at the next observation over time for five of the health outcomes (path ah; p’s < .05).
Table 4.
Adjusted model using passive SHLOC as mediator
| Outcome | al | ah | b32 | Indirect effect | cl | ch | RMSEA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| al*b32 | ah*b32 | |||||||
| Depressive symptoms1 | −0.026 | 0.083 | 0.086* | −0.002 | 0.007 | 0.039 | −0.051 | 0.039 |
| SF-12 physical function1 | −0.039 | 0.101 | 0.071 | −0.003 | 0.007 | −0.026 | −0.001 | 0.059 |
| SF-12 emotional function1 | −0.023 | 0.094 | −0.155 | 0.004 | −0.015 | 0.147 | −0.096 | 0.057 |
| Fruit servings per day1 | −0.050 | 0.104* | 0.018 | −0.001 | 0.002 | −0.177** | 0.208** | 0.041 |
| Vegetable servings per day1 | −0.042 | 0.101 | −0.108* | 0.005 | −0.011 | −0.128* | 0.096 | 0.041 |
| Drinking alcohol Y/N in the past 30 days1 | −0.050 | 0.111* | −0.081* | 0.004 | −0.009 | 0.089 | −0.111 | 0.043 |
| 4/5 or more alcohol drinks1 | −0.051 | 0.110* | −0.018 | 0.001 | −0.002 | −0.134* | 0.083 | 0.042 |
| Largest number of drinks1 | −0.054 | 0.109* | −0.006 | 0.000 | −0.001 | 0.053 | −0.038 | 0.041 |
| Currently smoking1 | −0.047 | 0.104* | 0.051 | −0.002 | 0.005 | 0.021 | −0.013 | 0.042 |
| Vigorous activities minutes / week1 | −0.044 | 0.097 | −0.016 | 0.001 | −0.002 | 0.021 | 0.012 | 0.040 |
| Moderate activities minutes / week1 | −0.042 | 0.093 | 0.017 | −0.001 | 0.002 | −0.060 | 0.056 | 0.040 |
| Walking minutes / week1 | −0.047 | 0.103 | −0.073 | 0.003 | −0.008 | −0.004 | −0.040 | 0.040 |
| Last mammogram (within last 2 years vs. > 2 years or never)2 | −0.093 | 0.115 | −0.059 | 0.005 | −0.007 | 0.065 | −0.014 | 0.044 |
| Ever had a PSA test2 | 0.001 | 0.050 | −0.028 | 0.000 | −0.001 | −0.129 | 0.317** | 0.046 |
| Ever had a colonoscopy1 | −0.045 | 0.096 | −0.070 | 0.003 | −0.007 | 0.026 | −0.075 | 0.040 |
p<.05
p<.01
p<.001
. Age, gender, education and self-rated health were adjusted.
. Age, education and self-rated health were adjusted.
Both NCI and Duke sample were used for analysis on depressive symptoms. Duke sample was used for analysis on SF-12 physical and emotional function. NCI sample was used for analysis on other outcomes.
Passive SHLOC related to change in health outcomes over time (Path b32)
Mostly inconsistent with H5, greater passive SHLOC is associated with only three health behavior and outcomes models. Greater passive SHLOC is associated with, from T2 to T3, increased depressive symptoms, fewer vegetable servings per day, and being less likely to have had alcohol in the last month (p’s < .05).
Mediation effect for religious beliefs and behaviors through change in passive SHLOC from T1 to T2 on health outcomes from T2 to T3 (Paths al*b32 and ah*b32)
We did not predict any mediation involving passive SHLOC and there was no evidence of such mediation of religious beliefs (al*b32) nor religious behaviors (ah*b32) and any of the health behaviors or outcomes by passive SHLOC.
Direct Effects
Direct effect of religious beliefs at T1 on the change in health outcomes from T2 to T3 (Path cl)
Similar direct effect paths for models with religious coping as the mediator have been reported previously (Holt et al., 2017). In the present analyses, contrary to H6, religious beliefs did not predict less depressive symptomology and better emotional functioning in either the active or passive SHLOC models. There were direct effects of religious beliefs at T1 associated with two health outcomes from T2 to T3 that we did not predict and were contrary to H6. Unexpectedly, in the active SHLOC model, religious beliefs were related to fewer fruit servings per day from T2 to T3 (p<.01). In the passive SHLOC model, religious beliefs were again associated with fewer fruits servings per day (p<.01), as well as fewer vegetable servings per day (p<.05), from T2 to T3.
Direct effect of religious behaviors at T1 to change in health outcomes from T2 to T3. (Path ch)
Largely inconsistent with H7, direct effects of religious behaviors at T1 were associated with only two health outcomes from T2 to T3. Religious behaviors were associated with more fruit consumption (p’s <.01) and a men’s higher likelihood of ever having had a PSA test (p’s ranged from .05 to .01) in both the active and passive SHLOC models.
Ancillary analyses
The direct effect findings for religious beliefs and religious behaviors on both fruits and vegetable servings per day are noteworthy in both the active and passive SHLOC models. Because the latent factors for religious beliefs and religious behaviors are substantially correlated, these opposing direct effects were further examined in separate mediational models with only religious beliefs or religious behaviors included as a predictor. In those models, religious behaviors continued to have a significant direct effect on fruit servings per day in the passive SHLOC model (ch = 0.082, SE = 0.042, p = 0.048). No statistically significant effects direct effects were found for religious beliefs from the separate models. This indicates that the significant and counteracting negative effects for religious beliefs from the full mediation models (in Tables 3 and 4) represent suppression effects and only emerge as statistically significant when examined in conjunction with religious behaviors.
Discussion
The current study found that while religious beliefs and religious behaviors were consistently related to increasing active SHLOC over time across health-related behaviors and outcomes, they were less consistently related to increases in passive SHLOC over time. Active SHLOC at T2 was not related to changes in any of the physical or mental health outcomes from T2 to T3. However, passive SHLOC at T2 was related to increases in depressive symptoms, decreases in vegetable servings per day, and decreases in having alcohol in the last 30 days from T2 to T3. In addition, there was evidence for direct effects of religious beliefs and behaviors on a few health-related outcomes.
Religiosity is important to the African American community (Chatters et al., 2009) and prior research demonstrates the connection between religiosity and health among African Americans (Bediako et al., 2011; Mattis & Watson, 2009). African Americans suffer higher mortality rates from heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and some cancers (National Center for Health Statistics, 2007). Prior research has demonstrated a relationship between SHLOC and health-related outcomes (Holt et al., 2007; Holt et al., 2003). The current study fills a gap in the prior research by longitudinally examining the relationship between religiosity, SHLOC, and health among African Americans. The study also examined the possible mediating role of SHLOC in the relationship between religious involvement and health behaviors and outcomes. Active and passive SHLOC are related to factors examined in other research programs such as collaborative and deferring problem solving (Pargament et al., 1988), religious and spiritual struggle (Exline, Pargament, Grubbs, & Yali, 2014), and a sense of divine mastery (Schieman et al., 2003; 2005).
Our hypotheses were partially confirmed for the paths related to active SHLOC. Consistent with prior research (Holt et al., 2007; Holt et al., 2015), stronger religious beliefs and religious behaviors were associated with greater changes in active SHLOC over time. It seems that believing one has a close relationship with God and/or attending services and engaging in other church activities increases perceptions that the individual and God work together to address health issues. However, there was much less evidence that active SHLOC was related to changes in physical or mental health outcomes over time, and there was no evidence of mediation by active SHLOC of the religiosity-health relationship. It may be that over the five year period, other more proximal individual difference and contextual factors were more important in impacting changes in health behaviors and outcomes at T3 than active SHLOC at T2. It is also possible that active SHLOC acts more of a moderator than a mediator; that active SHLOC may determine the strength of the religiosity-health relationship, not underlie the relationship (Holt et al., 2015). Further it is possible that limited change over time of active and passive SHLOC precluded a longitudinal mediation effect. Finally, it may be that SHLOC serves as a mediator between religious beliefs/behaviors and health in the context of morally sanctioned health behaviors and outcomes that were not examined in this study such as those related to drug use and sexual practices.
The results for passive SHLOC models varied somewhat from those of active SHLOC models. There was no evidence that religious beliefs were related to changes in passive SHLOC over time. However, there was evidence among some health-related behaviors and outcomes that religious behaviors were related to increases in passive SHLOC over time, such that the more participants engaged in religious behaviors, the more they changed their view to endorse the belief that God is in control and individual efforts are less necessary to address health issues. Perhaps this is due to the messages communicated through church activities (e.g., by the pastor during church services, involvement in other church activities, talking about faith with others) that emphasize the omnipotence of God. Further, inconsistent with past research, passive SHLOC did not consistently predict decreases in health-enhancing and increases in health-compromising behaviors. Passive SHLOC was associated with more depressive symptoms, fewer vegetable servings, and a lower likelihood of alcohol consumption in the past 30 days from T2 to T3. Interestingly, the positive correlation between passive SHLOC and depressive symptoms contrasts with findings by Schieman et al. (2005), who found that sense of divine control was positively correlated with personal mastery and self-esteem among African Americans. We did not predict and did not find any mediation effect by passive SHLOC to explain connections between religious beliefs or religious behaviors and health behaviors.
As with prior research we found some evidence that religious beliefs and religious behaviors were related to health behaviors and outcomes. Religious behaviors were associated with more fruit servings per day and a higher likelihood of (men) ever having a PSA test from T2 to T3. There was also some evidence that religious beliefs were related to a higher likelihood of having consumed alcohol in the last month (active SHLOC model) but a lower likelihood of binge drinking (passive SHLOC model) from T2 to T3.
There are several limitations to the current study. As with most research of this type we relied on self-report from our participants, which may have been affected by memory for their health behaviors and outcomes. Additionally, participants may have responded to the questions in a socially desirable fashion. Also, at the time we collected T1 data, we did not plan to follow up with these participants. When additional funding became available, we were able to collect data at T2 and T3. Those who continued in the study through T3 are different on some demographic variables than those who did not.
Another limitation is that our sample is not representative of all African Americans, but it is a large probability-based sample that includes both men and women. Regarding religious denomination, the RHIAA sample was 54.4% Baptist which is somewhat greater than the national average for African Americans (40%; Pew Forum US, 2009). All other denominations in our sample comprised no more than 5.5%. Regarding annual income, our sample was almost evenly split between those with family incomes below or at $30,000 (54.9%) and above (45.1%) $ 30,000 per year at T3, which is similar to the annual median income of African American households of $36,544 in 2015 according to the American Community Survey (US Census Bureau, 2015a). The educational level of the RHIAA sample is also comparable to national data (US Census Bureau, 2015b).
Finally, while a longitudinal design alone cannot demonstrate causal relationships, it does provide us with more information on the possibility of predictive relationships between religiosity, locus of control, and health behaviors and outcomes.
Future research should examine other mediators of religiosity and health behaviors and outcomes using longitudinal research designs. For example, prior research suggests that general social support, support from one’s faith community, self-efficacy, self-esteem, religious coping, and scriptural influence may mediate the relationship between religiosity and health behaviors (Holt, Clark, Debnam, et al., 2014; Holt, Clark, & Roth, 2014; Holt, Wang, Clark, Williams, & Schulz, 2013). Further, given the sex differences in religious activity involvement (Levin, Taylor, & Chatters, 1994), it may be beneficial to examine these moderated mediation relationships separately for males and females.
This research has significant practical implications. It is important for physicians and mental health professionals to intervene with patients whose psychosocial, religious, or cognitive approach to health puts them at risk of delayed cancer screening and non-adherence to follow-up care (Mohamed, Skeel Williams, Tamburrino, Wryobeck, & Carter, 2005), as well as other health-compromising behaviors (e.g., poor diet, alcohol abuse). For example, Latimer and colleagues investigated the use of cancer prevention and detection messages that are congruent with the psychosocial style of the recipient, styles that included health locus of control. Results suggest individually-tailored health communication can promote mammography and healthy diet (Kreuter et al., 2005; Latimer, Katulak, Mowad, & Salovey, 2005). This information may also be useful to faith communities (churches, etc.) that utilize health ministries, health fairs, and other strategies to encourage their members to take action regarding health promotion. Park and colleagues (Park et al., 2017) recommend increased collaboration between the behavioral medicine community and religious leaders to develop religiously sensitive interventions that can be delivered in the context of one’s faith community.
Acknowledgments
The team would like to acknowledge the work of OpinionAmerica and Tina Madison who conducted participant recruitment/retention and data collection activities for the present study.
This study was funded by grants from the National Cancer Institute, (#1 R01 CA 105202; #1 R01 CA154419) and a grant from the Duke University Center for Spirituality, Theology, and Health, through the John Templeton Foundation (#11993). The study was approved by the University of Maryland Institutional Review Board (#373528-1).
Footnotes
Compliance with Ethical Standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments and the ethical standards of the American Psychological Association.
Eddie M. Clark declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Beverly R. Williams declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Jin Huang declares that she has no conflict of interest.
David L. Roth declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Cheryl L. Holt declares that she has no conflict of interest.
References
- American Cancer Society. American Cancer Society Guidelines for the Early Detection of Cancer. 2014 Retrieved from http://www.cancer.org/healthy/findcancerearly/cancerscreeningguidelines/american-cancer-society-guidelines-for-the-early-detection-of-cancer.
- Anderson JC, Gerbing DW. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin. 1988;103(3):411–423. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.103.3.411. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bediako SM, Lattimer L, Haywood C, Jr, Ratanawongsa N, Lanzkron S, Beach MC. Religious coping and hospital admissions among adults with sickle cell disease. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 2011;34(2):120–127. doi: 10.1007/s10865-010-9290-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belgrave FZ, Allison KW. African American psychology: From Africa to America. 2. Los Angeles: Sage Publications; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bjorklof GH, Engedal K, Selbaek G, Maia DB, Coutinho ES, Helvik AS. Locus of control and coping strategies in older persons with and without depression. Aging and Mental Health. 2016;20(8):831–839. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2015.1040722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaine B, Crocker J. Religiousness, Race, and Psychological Well-Being: Exploring Social Psychological Mediators. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. 1995;21(10):1031–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Block G, Hartman AM, Dresser CM, Carroll MD, Gannon J, Gardner LA. A data-based approach to diet questionnaire design and testing. American Journal of Epidemiology. 1986;124(3):453–469. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatters LM, Taylor RJ, Bullard KM, Jackson JS. Race and ethnic differences in religious involvement: African Americans, caribbean blacks and non-hispanic whites. Ethnic and Racial Studies. 2009;32(7):1143–1163. doi: 10.1080/01419870802334531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark EM. Locus of control. In: Boslaugh S, editor. Encyclopedia of Epidemiology. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2008. pp. 606–610. [Google Scholar]
- Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjostrom M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, Oja P. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2003;35(8):1381–1395. doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000078924.61453.fb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debnam K, Holt CL, Clark EM, Roth DL, Foushee HR, Crowther M, Southward PL. Spiritual health locus of control and health behaviors in African Americans. American Journal of Health Behavior. 2012;36(3):360–372. doi: 10.5993/AJHB.36.3.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debnam K, Holt CL, Clark EM, Roth DL, Southward P. Relationship between religious social support and general social support with health behaviors in a national sample of African Americans. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 2012;35(2):179–189. doi: 10.1007/s10865-011-9338-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworsky CKO, Pargament KI, Wong S, Exline JJ. Suppressing spiritual struggles: The role of experiential avoidance in mental health. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science. 2016;5:258–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison C. Religious involvement and self-perception among Black Americans. Social Forces. 1993;71:1027–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison C, Boardman J, Williams D, Jackson J. Religious involvement, stress, and mental health: Findings from the 1995 Detroit Area Study. Social Forces. 2001;80(1):215–249. doi: 10.1177/0022146510378237. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Exline JJ, Grubbs JB, Homolka SJ. Seeing God as cruel or distant: Links with divine struggles involving anger, doubt, and fear of God's disapproval. International Journal for the Psychology of Religion. 2015;25:29–41. doi: 10.1080/10508619.2013.857255. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Exline JJ, Hall TW, Pargament KI, Harriott VA. Predictors of growth from spiritual struggle among Christian undergraduates: Religious coping and perceptions of helpful action by God are both important. Journal of Positive Psychology. 2017;12:501–508. doi: 10.1080/17439760.2016.1228007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Exline JJ, Pargament KI, Grubbs JB, Yali AM. The religious and spiritual struggles scale: Development and initial validation. Psychology of Religion and Spirituality. 2014;6:208–222. doi: 10.1037/a0036465. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Goldzweig G, Hasson-Ohayon I, Alon S, Shalit E. Perceived threat and depression among patients with cancer: the moderating role of health locus of control. Psychology, Health & Medicine. 2016;21(5):601–607. doi: 10.1080/13548506.2016.1140902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Clark EM, Debnam KJ, Roth DL. Religion and Health in African Americans: The Role of Religious Coping. American Journal of Health Behavior. 2014;38(2):190–199. doi: 10.5993/AJHB.38.2.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Clark EM, Klem PR. Expansion and validation of the spiritual health locus of control scale: Factorial analysis and predictive validity. Journal of Health Psychology. 2007;12(4):597–612. doi: 10.1177/1359105307078166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Clark EM, Kreuter MW, Rubio DM. Spiritual health locus of control and breast cancer beliefs among urban African American women. Health Psychology. 2003;22(3):294–299. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.22.3.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Clark EM, Roth DL. Positive and Negative Religious Beliefs Explaining the Religion-Health Connection Among African Americans. International Journal for the Psychology of Religion. 2014;24(4):311–331. doi: 10.1080/10508619.2013.828993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Le D, Calvanelli JV, Huang J, Clark EM, Roth DL, Williams BR, Schulz E. Participant retention in a national telephone survey of African American men and women. Ethnicity & Disease. 2015;25(1):187–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Roth DL, Huang J, Clark EM. Gender differences in the roles of religion and locus of control on alcohol use and smoking among African Americans. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs. 2015;76:482–492. doi: 10.15288/jsad.2015.76.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Roth DL, Huang J, Park C, Clark EM. Longitudinal effects of religious involvement on religious coping and health behaviors in a national sample of African Americans. 2017 doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.06.014. Submitted for publication. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Schulz E, Williams BR, Clark EM, Wang MQ. Social support as a mediator of religious involvement and physical and emotional functioning in a national sample of African-Americans. Mental Health, Religion & Culture. 2014;17:421–435. [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Wang MQ, Clark EM, Williams BR, Schulz E. Positive and negative religious beliefs that explain the religion-health connection among African Americans. International Journal for the Psychology of Religion. 2014;24:311–331. doi: 10.1080/10508619.2013.828993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt CL, Wang MQ, Clark EM, Williams BR, Schulz E. Religious involvement and physical and emotional functioning among African Americans: The mediating role of social support. Psychology & Health. 2013;28:267–283. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2012.717624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L, Bentler PM. Cutoff Criteria for Fit Indexes in Covariance Structure Analysis: Conventional Criteria versus New Alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling. 1999;6:1–55. doi: 10.1080/10705519909540118. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson BR, Bergeman CS. How does religiosity enhance well-being? The role of perceived control. Psychology of Religion and Spirituality. 2011;3:149–161. doi: 10.1037/a0021597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang SJ, Johnson BR. Explaining religious effects on distress among African Americans. Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion. 2004;43:239–260. [Google Scholar]
- Kinney AY, Emery G, Dudley WN, Croyle RT. Screening behaviors among African American women at high risk for breast cancer: do beliefs about God matter? Oncolology Nursing Forum. 2002;29:835–843. doi: 10.1188/02.ONF.835-843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuter MW, Skinner CS, Holt CL, Clark EM, Haire-Joshu D, Fu Q, Bucholtz DC. Cultural tailoring for mammography and fruit and vegetable consumption among low-income African American women in urban public health centers. Preventive Medicine. 2005;41:53–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2004.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landor A, Simons LG, Simons RL, Brody GH, Gibbons FX. The role of religiosity in the relationship between parents, peers, and adolescent risky sexual behavior. Journal of Youth and Adolescence. 2011;40:296–309. doi: 10.1007/s10964-010-9598-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latimer AE, Katulak NA, Mowad L, Salovey P. Motivating cancer prevention and early detection behaviors using psychologically tailored messages. Journal of Health Communication. 2005;10(S1):137–155. doi: 10.1080/10810730500263364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin JS, Taylor RJ, Chatters LM. Race and gender differences in religiosity among older adults: Findings from four national surveys. Journal of Gerontology. 1994;49:S137–S145. doi: 10.1093/geronj/49.3.s137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukwago SL, Kreuter MW, Bucholtz DC, Holt CL, Clark EM. Development and validation of brief scales to measure collectivism, religiosity, racial pride, and time orientation in urban African American women. Family and Community Health. 2001;24:63–71. doi: 10.1097/00003727-200110000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon DP. Introduction to statistical mediation analysis. New York: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Makambi KH, Williams CD, Taylor TR, Rosenberg L, Adams-Campbell LL. An assessment of the CES-D scale factor structure in black women: The Black Women’s Health Study. Psychiatry Research. 2009;168:163–170. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2008.04.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattis JS, Watson CR. Handbook of African American psychology. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2009. Religion and spirituality; pp. 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed IE, Skeel Williams K, Tamburrino M, Wryobeck J, Carter S. Understanding locally advanced breast cancer: what influences a woman's decision to delay treatment? Preventive Medicine. 2005;41:399–405. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2004.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthén LK, Muthén BO. Mplus User's Guide. 7. Los Angeles, CA: 2013. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Health Statistics. Chartbook on trends in the health of Americans. 2007 Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus07.pdf. [PubMed]
- Pargament KI, Kennell J, Hathaway W, Grevengoed N, Newman J, j Jones W. Religion and the problem solving-process: Three coping styles. Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion. 1988;27:90–104. [Google Scholar]
- Park CL, Masters KS, Salsman JM, Wachholtz A, Clements AD, Salmoirago-Blotcher E, Wischenka DM. Advancing our understanding of religion and spirituality in the context of behavioral medicine. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 2017;40:39–51. doi: 10.1007/s10865-016-9755-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pew Forum, U.S. A Religious Portrait of African-Americans. 2009 Retrieved from http://www.pewforum.org/A-Religious-Portrait-of-African-Americans.aspx.
- Radloff LS. The CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement. 1977;1:385–401. [Google Scholar]
- Roth DL, Ackerman ML, Okonkwo OC, Burgio LD. The four-factor model of depressive symptoms in dementia caregivers: a structural equation model of ethnic differences. Psychology and Aging. 2008;23:567–576. doi: 10.1037/a0013287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth DL, Mwase I, Holt CL, Clark EM, Lukwago S, Kreuter MW. Religious involvement measurement model in a national sample of African Americans. Journal of Religion and Health. 2012;51:567–578. doi: 10.1007/s10943-011-9475-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter JB. Social learning and clinical psychology. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan ME, Francis AJP. Locus of control beliefs mediate the relationship between religious functioning and psychological health. Journal of Religion and Health. 2012;51:774–785. doi: 10.1007/s10943-010-9386-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schieman S, Nguyen K, Elliott D. Religiosity, socioeconomic status, and the sense of mastery. Social Psychology Quarterly. 2003;66:202–221. [Google Scholar]
- Schieman S, Pudrovska T, Milkie MA. The sense of divine control and the self-concept: A study of race differences in later life. Research on Aging. 2005;27:165–196. doi: 10.1177/0164027504270489. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel ME. Asymptotic Confidence Intervals for Indirect Effects in Structural Equation Models. Sociological Methodology. 1982;13:290–312. doi: 10.2307/270723. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Stein AD, Lederman RI, Shea S. The Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System questionnaire: its reliability in a statewide sample. American Journal of Public Health. 1993;83:1768–1772. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.83.12.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Census Bureau. American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. 2015a Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/newsroom/facts-for-features/2017/cb17-ff01.html.
- U. S. Census Bureau. Educational attainment in the United States. 2015b Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/library/publications/2016/demo/p20-578.html.
- Waldron-Perrine B, Rapport LJ, Hanks RA, Lumley M, Meachen SJ, Hubbarth P. Religion and spirituality in rehabilitation outcomes among individuals with traumatic brain injury. Rehabilitation Psychology. 2011;56:107–116. doi: 10.1037/a0023552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallston KA, Malcarne VL, Flores L, Hansdottir I, Smith CA, Stein MJ, Clements PJ. Does God determine your health? The God locus of health control scale. Cognitive Therapy and Research. 1999;23:131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ware JE, Jr, Kosinski M, Keller SD. A 12-item short-form health survey: Construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Medical Care. 1996;34:220–233. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199603000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin KY, Heil DP, Askew S, Matthews CE, Bennett GG. Validation of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short among Blacks. Journal of Physical Activity and Health. 2008;5:746–760. doi: 10.1123/jpah.5.5.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]