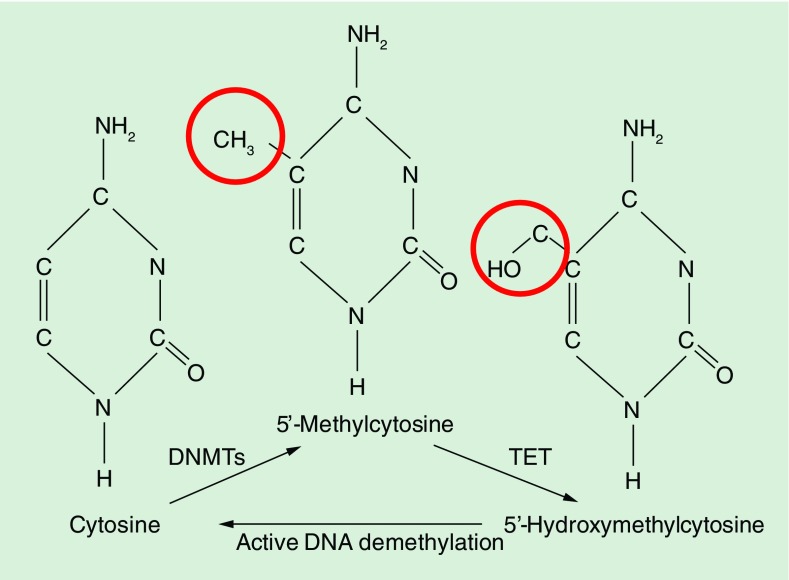
Figure 1. . Modifications to cytosine during DNA methylation.
Addition of a methyl group to the 5′ carbon position of cytosine within cytosine-phosphate-guanosine dinucleotides is a highly efficient mechanism for preventing transcription factor recruitment. DNA methylation is mediated through highly conserved enzymes, so-called DNA methyltransferases. DNA hydroxymethylation is the result of oxidation of methylated cytosine-phosphate-guanosine DNA by ten eleven translocation family enzymes, which makes it an intermediate product during active DNA demethylation processes. Hydroxymethylated cytosine may actively be removed by DNA repair pathways, suggesting a role of DNA hydroxymethylation during active DNA demethylation processes.