Abstract
Synchronization of biological functions to environmental signals enables organisms to anticipate and appropriately respond to daily external fluctuations and is critical to the maintenance of homeostasis. Misalignment of circadian rhythms with environmental cues is associated with adverse health outcomes. Cortisol, the downstream effector of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) activity, facilitates synchronization of peripheral biological processes to the environment. Cortisol levels exhibit substantial seasonal rhythmicity, with peak levels occurring during the short-photoperiod winter months and reduced levels occurring in the long-photoperiod summer season. Seasonal changes in cortisol secretion could therefore alter its entraining capabilities, resulting in a season-dependent modification in the alignment of biological activities with the environment. We develop a mathematical model to investigate the influence of photoperiod-induced seasonal differences in the circadian rhythmicity of the HPA axis on the synchronization of the peripheral circadian clock and cell cycle in a heterogeneous cell population. Model simulations predict that the high-amplitude cortisol rhythms in winter result in the greatest entrainment of peripheral oscillators. Furthermore, simulations predict a circadian gating of the cell cycle with respect to the expression of peripheral clock genes. Seasonal differences in cortisol rhythmicity are also predicted to influence mitotic synchrony, with a high-amplitude winter rhythm resulting in the greatest synchrony and a shift in timing of the cell cycle phases, relative to summer. Our results highlight the primary interactions among the HPA axis, the peripheral circadian clock, and the cell cycle and thereby provide an improved understanding of the implications of circadian misalignment on the synchronization of peripheral regulatory processes.
Mathematical modeling shows that seasonal differences in cortisol circadian rhythmicity can result in differential synchronization of the circadian clock and mitosis in a simulated cellular population.
Numerous biological functions are entrained to adopt circadian rhythms that are synchronous with the 24-hour diurnal fluctuations of light and darkness. Environmental photic cues, initially relayed to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), are converted into hormonal, metabolic, or neuronal signals, which subsequently synchronize physiological activities (1). Cortisol, the primary glucocorticoid (GC) in humans, is one such circadian hormone (2) and signaling mediator that entrains the dynamics of processes such as metabolism, immune function, and cardiovascular activity. Given its influential effects, homeostatic regulation of the levels and rhythm of endogenous circulating cortisol is critical for the maintenance of a healthy state (3). Chronic disease conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis (4, 5), advanced breast cancer (6), and type 2 diabetes (7), are typically characterized by substantial disruptions in cortisol circadian profiles in comparison with profiles in healthy controls (8, 9).
Plasma cortisol concentrations also vary substantially with changing seasons, wherein cortisol levels are highest in the winter months and lowest during the summer (10–12). In temperate regions, the photoperiod, or the duration of light in the day, varies throughout the year such that it decreases as the season progresses from summer through winter and increases toward summer. This environmental cue is a powerful entrainer of seasonal physiological plasticity (13), inducing seasonal changes in immune function (14) as well as GC secretion (15). Additionally, coregulated proinflammatory gene expression, interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling, and C-reactive protein levels (16) are increased in winter. Fascinatingly, inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis have also been found to exhibit aggravated symptoms (17) and peak incidence (18) in winter.
Alignment of the internal circadian dynamics with external environmental signals is critical for the health and fitness of an organism with misalignment, leading to detrimental health outcomes (19). Blunted cortisol circadian profiles are associated with circadian misalignment whereby endogenous circadian rhythms become asynchronous with 24-hour environmental/behavioral cycles and blood pressure; in addition, the expression of inflammatory markers, such as IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, and C-reactive protein, are increased (20–22). This potentially explains why shift workers, with behavioral patterns uncoupled from the environment, often have hypertension (23), cardiovascular disease risk (24), and inflammation (25, 26). Furthermore, uncoupling of circadian clock gene expression from the centrally entrained cortisol rhythm has been observed in the peripheral blood leukocytes of humans following in vivo acute endotoxin administration (27, 28).
In addition to optimal alignment with environmental cues, the synchronization of internal homeostatic mechanisms is critical to the maintenance of host fitness. The synchronization of biological activities, such as immune function (29), glucose homeostasis (30), and steroidogenesis (31), is regulated by the peripheral molecular circadian clock. Despite their intrinsic ability to oscillate autonomously, clock component expression is regulated by humoral signals, such as GCs (1). Administration of dexamethasone promotes the oscillation of Bmal1, Cry1-2, Dbp, Npas2, Per1-3, and Rev-Erbα in mesenchymal stem cells, whereas oral dosing of Cortef (Pfizer), a synthetic glucocorticoid, induces phase shifts of Per2-3 and Bmal1 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (32). In vitro analysis of circadian gene expression in mouse fibroblast cells indicates that although these individual clock components oscillate robustly and independently in culture, a loss of synchrony among cells results in the dampening of the ensemble rhythm over time (33). Synchronous clock gene expression can be restored via pulsed dexamethasone treatment (34). This GC-induced regulation of molecular clock expression is mediated, at least in part, by the functional glucocorticoid response element in the Per1 promoter region (35).
Another tightly synchronized biological process is the cell cycle, which describes the series of events leading to cell division. Cell cycle progression is regulated by a family of cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) that are activated following binding to cyclin proteins (36). Cell cycle dynamics are regulated by the molecular clock as well as by GCs. Synchronization between the cell cycle and molecular clock has been observed experimentally in mouse fibroblast NIH3T3 cells as cell division occurs approximately 5 hours before Rev-Erbα peak expression (37), with a robust 1:1 phase-locking between the two oscillators (38). The influence of GCs in regulating cell cycle dynamics is controversial because dexamethasone, a cortisol analog, can induce cell cycle arrest (39) but also rescue aberrant cell cycle rhythms (40, 41) and stimulate tumor cell proliferation (42–44). Just as with the molecular clock, GCs can also entrain the cell cycle. In conjunction with enhancing cell cycle synchrony, pulsed dexamethasone treatment promotes cellular regeneration and suppresses inflammatory cytokine production by asthmatic epithelial cells following mechanical scrape-wounding (45). Furthermore, circadian variations in cortisol have been correlated to the circadian increases in bone marrow cell proliferation and neutrophil numbers, suggesting that the circadian rhythms in humoral signaling mediators can influence cell cycle dynamics (46). Moreover, in addition to augmented cortisol levels and increased proinflammatory signaling observed in the winter, there are distinct seasonal differences in immune cell proliferation, with CD4+ and CD25+ T-cell and CD20+ B-cell counts peaking in the winter and reaching a minimum during the summer months (47).
Given the influential impact of GCs in regulating the molecular clock and cell cycle dynamics, seasonal changes in cortisol’s circadian rhythm could differentially modulate the synchronization of a heterogeneous population of cells and influence cell proliferation. Expanding on our previous simulations, which investigated the role of cortisol in modulating seasonal changes in the immune dynamics of a single cell (48) and a cohort of virtual patients (49), we consider the effect of a seasonally varying cortisol signal in entraining molecular clock and cell cycle dynamics in a simulated heterogeneous cell population. Seasonal changes in cortisol’s ability to adequately synchronize peripheral processes could result in a seasonal susceptibility to circadian misalignment, inflammatory disease development, and symptom severity. Moreover, investigations into seasonal differences in the synchronization of the peripheral clock and the cell cycle phase could have potential clinical relevance by motivating the development of treatment strategies that take advantage of this rhythmic variation.
Model simulations show that peripheral circadian clock rhythms were strongly entrained to the seasonally varying cortisol rhythms with distinct seasonal differences in the extent of peripheral clock entrainment. In general, we find that winter models exhibit the strongest entrainment whereas summer models exhibit the weakest entrainment of the peripheral circadian clock to endogenous glucocorticoid rhythm. Additionally, model simulations predict a seasonal influence of cortisol and the peripheral circadian clock on cell cycle dynamics, with results indicating a circadian gating of the cell cycle. Notably, our results suggest that the high-amplitude winter cortisol profile results in augmented mitotic synchrony in comparison with cortisol profiles associated with other seasons. We speculate that the greater mitotic synchrony over the course of a day in the winter might result in an increased circadian peak in cell number in specific peripheral immune cell populations, such as neutrophils. In agreement with experimental results, our simulations predict a shift in the acrophase of the DNA synthetic phase (S phase) of the cell cycle, to later hours of the day when moving from summer to winter. Our results suggest that a consideration of both circadian and circannual dynamics of the cell cycle could be important in the development of chemotherapeutic and immunologic strategies. Therefore, our results have the potential to provide an improved understanding of the systems-level dynamics by which seasonal changes in environmental signals influence regulatory processes at the interface of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, the peripheral circadian clock, and the cell cycle.
Materials and Methods
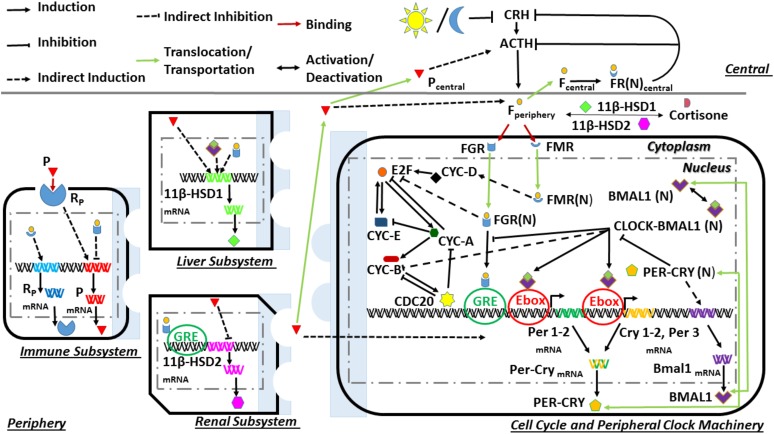
The biological system was divided into central and peripheral compartments, as can be seen in Fig. 1. The central compartment consists of the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland, whereas the periphery comprises the immune, renal, hepatic, and adrenal subsystems with accompanying cell cycle and molecular clock machinery. This model expands on our previous work through the development of a model structure that accounts for seasonal differences in the influence of the HPA axis and the peripheral circadian clock on the dynamics of the cell cycle in a heterogeneous cell population. Details regarding the mathematical equations [Supplemental Eqs. (1) through (32)] describing the HPA axis and peripheral circadian clock dynamics are provided in the Supplemental Material. The reader is referred to our previous report (49) on these equations with accompanying parameter values and descriptions. Briefly, the central compartment is entrained to the seasonally varying light-dark cycle, which ultimately results in the photoperiod-induced seasonal changes in cortisol’s circadian profile. The light profiles for each season (Supplemental Fig. 1) were modeled by using a step function of equal intensity (1 a.u.) but with differing photoperiods. Spring was modeled with 12 hours of light and 12 hours of dark (12L/12D), whereas the photoperiods of summer, autumn, and winter were modeled with 16L/8D, 10L/14D, and 8L/16D respectively. This light-dark cycle–mediated entrainment was simulated via the light function in the degradation term of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) [Supplemental Eq. (1)]. The seasonally entrained cortisol signal subsequently regulates the dynamics of the molecular clock and cell cycle, immune function, and its own regulatory enzymes [11β−hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (HSD1) and 11β−hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2] via binding and activation of its two receptors; the mineralocorticoid (MR) and glucocorticoid (GR) receptors. These 11β−HSD1 and 11β−hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 enzymes regulate the bioavailability of cortisol in the periphery.
Figure 1.
Model schematic depicting dynamic processes of the central and peripheral compartments. The central compartment is entrained to the seasonally varying light/dark cycle and describes HPA axis functionality through the activities of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH), and cortisol (F). Peripheral cortisol, after binding to the glucocorticoid (GR) and mineralocorticoid (MR) receptors, entrains the circadian clock [FGR(N)] and cell cycle [FGR(N) and FMR(N)]. Cell cycle dynamics are also regulated by the clock component, CLOCK–BMAL1, in conjunction with the actions of the activated cyclin/Cdk complexes, E2 factor (E2F) and CDC20. Ebox, enhancer box; GRE, glucocorticoid response element; mRNA, messenger RNA.
Cell cycle dynamics
Equations (1) through (6) characterize the dynamics of the cell cycle regulatory components. These equations are a modified form of the skeletal cell cycle model developed by Gérard and Goldbeter (50) that now incorporates entrainment facilitated by cortisol and the molecular clock. It is assumed that the cyclin/Cdk complexes are already in an inducible state with the transcription, translation, translocation, and complex formation processes neglected. The activated cyclin D/Cdk4-6 complex [CYCD, Eq. (1)] promotes gap 1 phase (G1) progression and subsequently activates the E2 factor (E2F) transcription factor [E2F, Eq. (2)]. E2F promotes the activation of cyclin E/Cdk2 [CYCE, Eq. (3)] and cyclin A/Cdk2 [CYCA, Eq. (4)]. CYCE, which facilitates the G1/S transition, further reinforces E2F activation [Eq. (3)]. The S phase, whose progression is moderated by CYCA, is exited following the CYCA-mediated inhibition of E2F and stimulation of cyclin B/Cdk1 [CYCB, Eq. (5)] activity. CYCB, which promotes the growth 2 (G2)/mitosis (M) phase transition, activates the cell-division cycle protein 20 [CDC20, Eq. (6)]. With the accumulation of CDC20, the activity of CYCA and CYCB is inhibited via phosphorylation and the cell exits the mitotic phase.
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
| (6) |
The influence of the circadian clock in regulating cell cycle dynamics was accounted for via the inclusion of the CLOCK–BMAL1 term in Eq. (5). CLOCK–BMAL1 has been implicated as a primary circadian entrainer of the cell cycle because it promotes transcription of the gene, which encodes for kinase, an inhibitor of the cyclin B/cyclin-dependent kinase-1 complex (51). Our model does not include kinase dynamics, and so an indirect response model was used to describe the resultant inhibitory effect of CLOCK–BMAL1 on CYCB activity. Indirect response models are typically used to characterize pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic responses influenced by unknown or indirect mechanisms (52). The contradictory effects of GCs on cell cycle progression and growth display a dose dependence, whereby high doses of dexamethasone generally inhibit growth whereas lower concentrations stimulate it (53). These responses may be mediated by different receptors with the proliferative inductive effect arbitrated by the mineralocorticoid receptor and the inhibitory effect by the GC receptor. In an assessment of the response of fetal heart development to cortisol treatment, the MR promoted proliferation whereas the GC receptor induced apoptosis (54). Additionally, promotion of cell proliferation in rat mesangial cells via aldosterone treatment occurs through the MR-mediated activation of CYCD and CYCA (55). Given that GC induces cell cycle arrest by inhibiting E2F (39), cortisol-bound glucocorticoid receptor (nuclear) [FGR(N)] was modeled to inhibit [Eq. (2)] and cortisol-bound mineralocorticoid receptor (nuclear) [FMR(N)] to stimulate CYCD [Eq. (1)]. In contrast to the original model (50), the growth factor (GF) variable, which activates the transition from the quiescent state (G0) to the G1, was omitted. This variable rapidly reaches a steady state, and so its contribution is assumed to be incorporated into the vsd parameter, which represents the basal activation rate of CYCD.
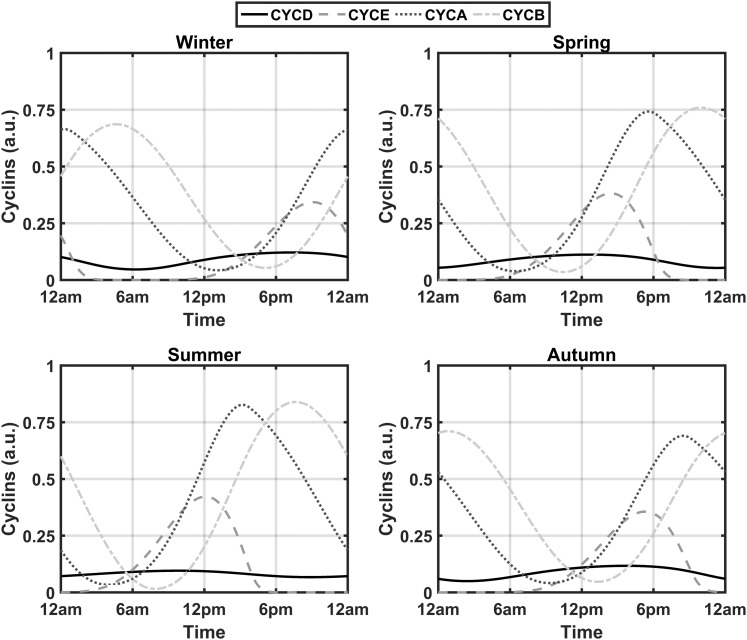
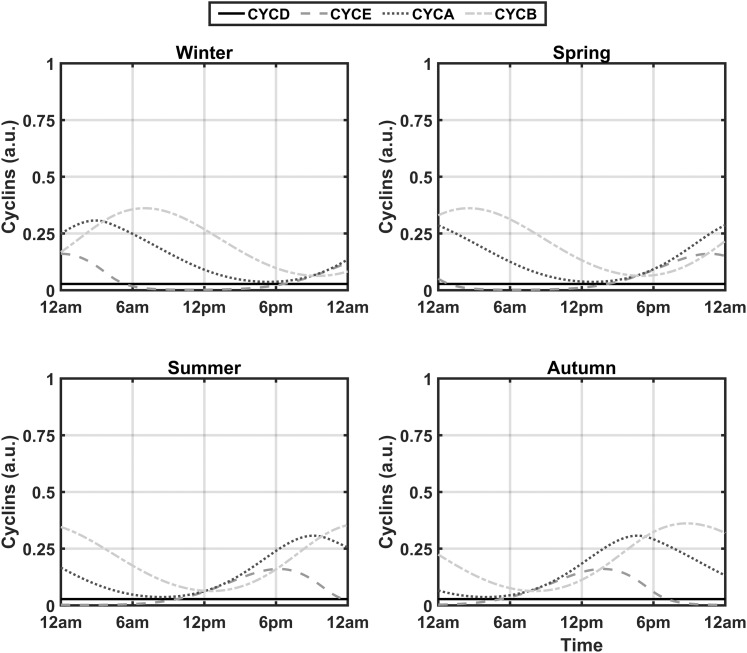
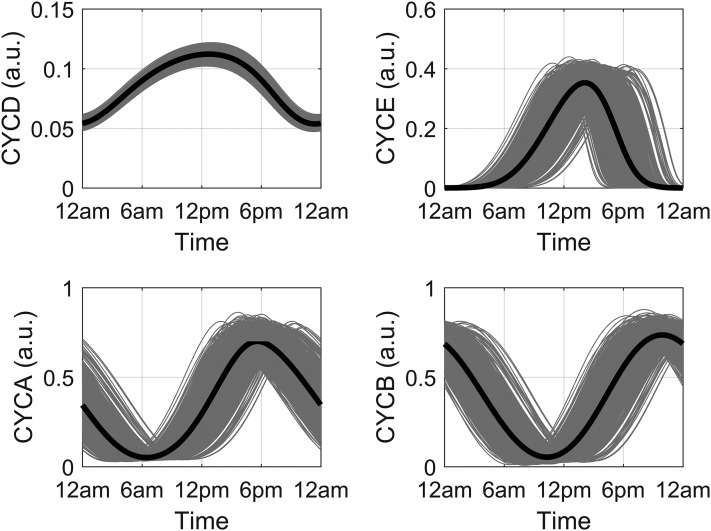
With the inclusion of the three entrainment terms in Eqs. (1), (2), and (5) and the removal of the activating influence of the GF variable, seven new parameters were added to the cell cycle model (vsd, kfd, Kfd, kfe2f, Kfe2f, kcb, and Kcb). Through use of experimental data from Bjarnason et al. (56), these newly introduced parameters were optimized to decrease the sum of squared errors between the acrophases of the experimental and simulated spring model profiles for CYCE, CYCA, and CYCB. The optimized profiles are shown in Fig. 2. The resultant simulated spring acrophases for CYCE, CYCA, and CYCB were 14:12, 17:36, and 22:00 hours, which is similar to the experimentally determined acrophases of 14:59, 16:09, and 21:13 hours for cyclins E, A, and B, respectively. Sustained oscillations should occur in the presence of sufficient GF (50). As mentioned previously, the influence of GF is assumed to be consolidated into the vsd parameter, which should be high enough to ensure the existence of oscillations in the absence of the entraining signals. To assess this, the entrainment-inducing parameters (kfd, kfe2f, and kcb) were set to zero. As is evident in Fig. 3, lower-amplitude oscillations for all cyclin complexes are observed. The occurrence of high-amplitude cell cycle rhythms in the presence of GCs in zebrafish (41) renders our cortisol entrained model qualitatively comparable to experimental findings. We refer the reader to Table A1 of the supplemental data for the description and numerical values of all parameters governing Eqs. (1) through (6).
Figure 2.
Seasonal circadian profiles for cyclin/Cdk complexes. Profiles display robust circadian rhythms in the presence of the systemic entraining cortisol signal. The predicted spring acrophases of CYCE, CYCA, and CYCB are congruent with human experimental data.
Figure 3.
Seasonal circadian profiles for cyclin/Cdk complexes after the removal of the entraining signals for a single cell. The circadian profiles of the activated complexes are substantially damped in the absence of cortisol signaling with a period of oscillation deviating from 24 hours. This trend is consistently observed in each season.
Generating a heterogeneous cell population
We accounted for biological intercellular variability as we considered the ability of a systemic cortisol circadian rhythm to entrain a simulated heterogeneous population of generic cells with a relatively short cell cycle duration (∼24 hours per division). Prior work by other groups used simulated generic cell types or model structures to explore various facets of cell cycle regulation (57, 58). A population of cells was simulated by sampling the parameters of Supplemental Eqs. (9) through (32), which describe most of the peripheral processes. We assume that heterogeneity in the cell cycle results from variability in the receptor-mediated GC signaling and in peripheral circadian clock expression. The phase of the molecular clock is inherited by daughter cells upon division (34), and the duration of the mammalian cell cycle is correlated within a lineage (59). Given this, parameters characterizing cell cycle dynamics [Eqs. (1) through (6)] were kept constant across the simulated cell population. Through use of Latin hypercube sampling and a population of n = 1000 cells, intercellular variability was introduced by varying the aforementioned parameters by ±10% of their nominal values. We previously used such a method for generating a heterogeneous virtual populations of cells (60). The dynamics of cortisol in the peripheral compartment (Fperiphery) [Supplemental Eq. (3)], cortisone (E) [Supplemental Eq. (32)], and the central compartment components [Supplemental Eqs. (1) and (4) through (8)], the core systemic drivers, were assumed to be homogenous and regulated by the ensemble average of the peripheral signals. As such, Supplemental Eqs. (2), (3), and (32) from our previous model (49) were adjusted as shown below in Eqs. (7) through (9). The coupling constant (kc) of Supplemental Eq. (16) was also kept constant. For a given cell, the stimulatory influence of the proinflammatory mediator (P) on Per–CrymRNA (messenger RNA) [Supplemental Eq. (16)] and 11β–HSD1mRNA [Supplemental Eq. (28)] transcription was modeled to be autocatalytic and not the result of paracrine or endocrine signaling. Modulation of 11β−HSD1mRNA expression and activity by proinflammatory cytokines occurs via autocrine mechanisms (61, 62), whereas CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-β, whose expression, localization, and activity are controlled by autocrine signaling (63), is believed to mediate the induction of gene expression by IL-6 (64).
The following are modified equations accounting for cell population influence on core processes:
| (7) |
| (8) |
| (9) |
where <.> represents the population average of the specified mediator, and ACTH represents adrenocorticotropic hormone.
Quantifying mitotic and peripheral clock synchrony
Two metrics were used to quantify synchronization among the cellular component oscillations. Temporal profile synchronization was computed by using Rsyn [Eq. (10)], which compares the ratio of the variance of the mean oscillations to the mean variance of each oscillator (65). M is the average profile of all oscillators, Vi represents the ith oscillator, and n is the number of oscillators. ρ, the other synchronization index, is based on Shannon entropy and compares the distribution of the circadian metrics to a uniform distribution (66). This metric is computed by using Eq. (11). N is the number of bins; Smax represents maximum entropy given by Smax = ln(N); and the distribution’s entropy, S, is measured by . pk represents the proportion of cells in a given bin. For both metrics, a value of 1 indicates synchronization whereas 0 indicates the most asynchronous state.
| (10) |
| (11) |
Results
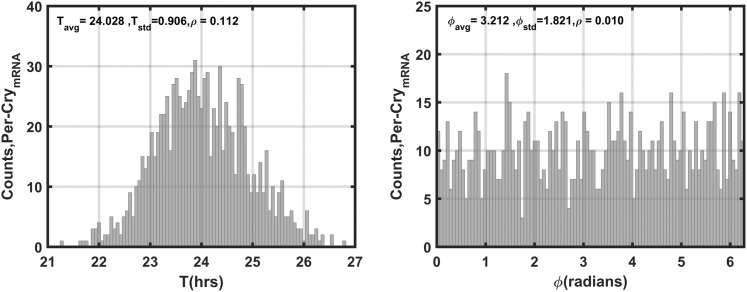
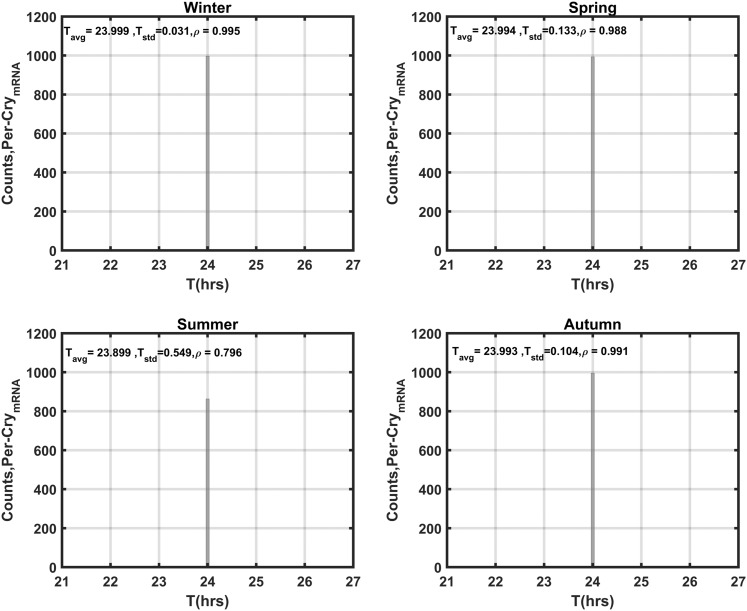
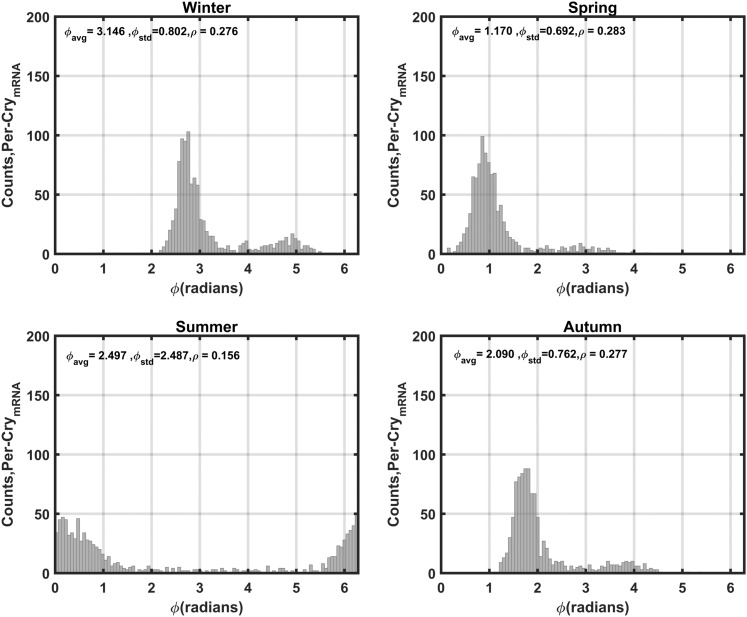
The seasonal circadian profiles for cortisol agree with our previous findings (48, 49) and with experimental data (10–12): They displayed the highest amplitude for the winter season and the lowest for the summer season (Supplemental Fig. 2). The phase delay predicted to occur with decreasing photoperiod is also congruent with observed human data (15). Per–CrymRNA is used as our representative variable for the synchronization assessment of the molecular clock. Figure 4 depicts the distributions of the periods (T) and phases (ϕ) of Per–CrymRNA for the unentrained oscillators with both kf and kc, which describe the entrainment strength of P and FGR(N), respectively [Supplemental Eq. (16)], set to 0 for all cells. In the absence of systemic entraining signals, the Per–CrymRNA components oscillate with an average period of 24 ± 0.9 hours (± standard deviation) between 21 and 27 hours. Furthermore, the unentrained oscillators display a broad distribution of phases with very low synchronization indices (ρ).
Figure 4.
Distributions of Per–CrymRNA periods and phases for the unentrained oscillators. In the absence of entraining signals, intercellular variability results in asynchrony among Per–CrymRNA oscillators. The population exhibits a mean period (Tavg) of ∼24 hours with a standard deviation (Tstd) of ∼0.9 hours. The average phase of oscillation (ϕavg) is ∼3.2 radians with a standard deviation (ϕstd) of ∼1.8. The low ρ values for both circadian measures reflect population asynchrony.
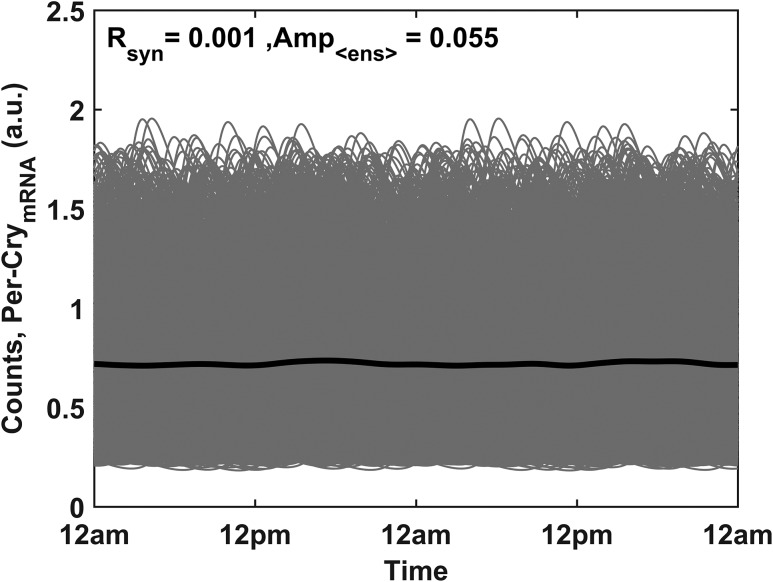
In Fig. 5, the circadian profiles of the unentrained Per–CrymRNA for the population of 1000 cells are shown. The Rsyn metric provides a similar quantification of synchronization, indicating little to no synchrony among the Per–CrymRNA oscillations of the cell population. As a consequence of the asynchrony, a damped, low-amplitude ensemble average profile is observed (black plot).
Figure 5.
Circadian profiles of the unentrained Per–CrymRNA oscillators (gray). In the absence of entraining signals, the circadian rhythmicity of the ensemble average (solid black line) is substantially damped. The low synchronization index (Rsyn) and ensemble average (Amp<ens>) values denote low synchrony among the cell population.
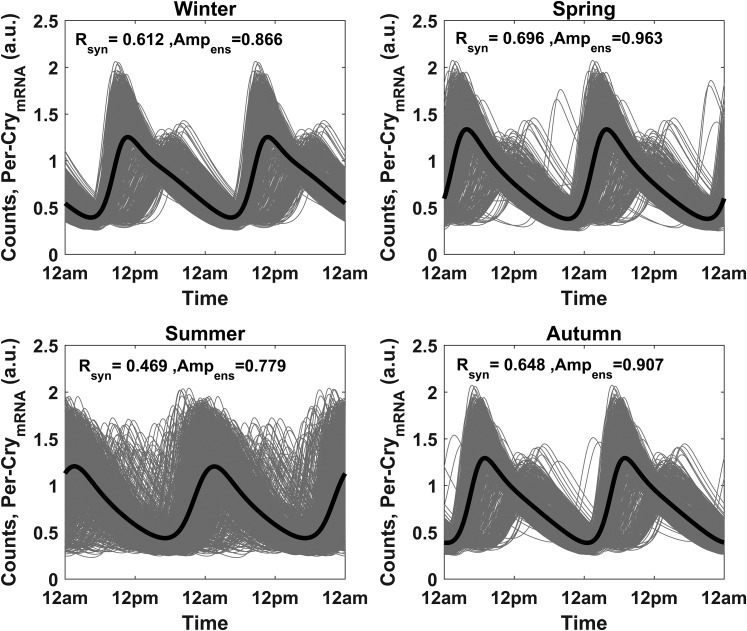
By setting kc to its nonzero nominal value and using the sampled parameter values for Supplemental Eqs. (9) through (32) (including kf) as previously described, simulations were repeated to explore the impact of entrainment on Per–CrymRNA oscillations. Figure 6 reflects the distribution of periods of Per–CrymRNA following entrainment. With coupling to FGR(N) and P, entrainment is substantially augmented with all individual molecular clocks adopting a period (~24 hours) equivalent to the external photoperiod. The summer season displayed the weakest entrainment to the systemic signal. The phase distributions of the entrained Per–CrymRNA oscillations (Fig. 7) is much broader than that of the period distributions with a relatively low synchronization index, ρ. The spring, autumn, and winter seasons are more synchronized than the summer season. The distinct bimodal phase distribution disappears as the season progresses through autumn, spring, and summer. With the exception of summer, a distinct subpopulation of phase-delayed, low-amplitude Per–CrymRNA oscillations among the cell populace is observed, which is also evident in the oscillations (Fig. 8). In line with the ρ parameter, the Rsyn metric further testifies to the seasonal differences in synchrony with spring exhibiting the most synchronous oscillations and summer the most asynchronous.
Figure 6.
Seasonal distributions of Per–CrymRNA periods for the entrained oscillators. In the presence of entraining signals, the individual Per–CrymRNA oscillators are more aligned with the external 24-hour photoperiod. The period distribution for all seasons is narrowed after entrainment, and the winter population is the most synchronous, with a high synchronization index (ρ). Tavg, average period; Tstd, standard deviation.
Figure 7.
Seasonal distributions of Per–CrymRNA phases for the entrained oscillators. As was seen with cortisol, the mean phase of the cell population was most advanced in the summer and delayed in the winter (right shift of distribution). Synchrony was relatively low for all seasons, and a small but distinct phase-delayed subpopulation of cells is observed for winter, autumn, and spring. ρ is the synchronization index; and are the phase average and standard deviation, respectively.
Figure 8.
Seasonal circadian profiles of the entrained Per–CrymRNA oscillators. Per–CrymRNA rhythms in the summer exhibit the least synchrony in comparison with those in other seasons. Furthermore, a distinct low-amplitude, phase-delayed cell population is observed in winter, autumn, and spring. Amp<ens>, ensemble average amplitude; Rsyn, synchronization index.
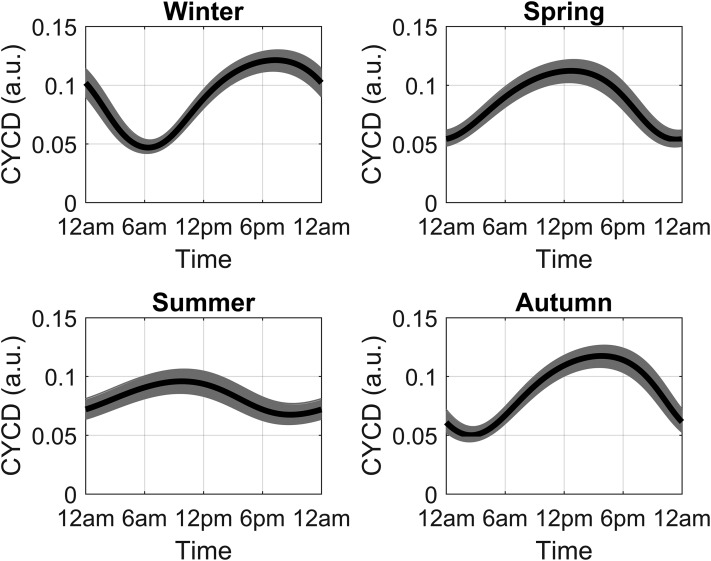
Figure 9 shows the circadian profiles of CYCD, CYCE, CYCA, and CYCB for the spring season. Despite the introduction of intercellular variability, the cell cycle components oscillated robustly with a period approximating 24 hours for all seasons. Amplitude and phase differences were predicted for all seasons, with phase advanced cyclin profiles in the summer and delayed profiles in the winter. Figure 10 shows seasonal CYCD oscillations for the cell population. Because of the stimulatory influence of cortisol [arbitrated by the FMR(N) variable], low-amplitude oscillations of CYCD were predicted for the summer model with its damped cortisol profile. Alternatively, higher CYCD oscillations were predicted for the winter model, with an amplitude fluctuation that parallels its cortisol profile.
Figure 9.
Representative circadian profiles of the cyclins for the spring model. Individual (gray lines) and ensemble average (black line) profiles for active cyclin complexes D (CYCD), E (CYCE), A (CYCA), and B (CYCB) in a population of 1000 simulated cells.
Figure 10.
Seasonal circadian profiles of CYCD. Individual (gray lines) and average (black line) profile for the active cyclin D complex in a population of 1000 simulated cells for each season. Phase-advanced and -damped rhythms were predicted for summer, with higher-amplitude and phase-delayed rhythms observed in winter.
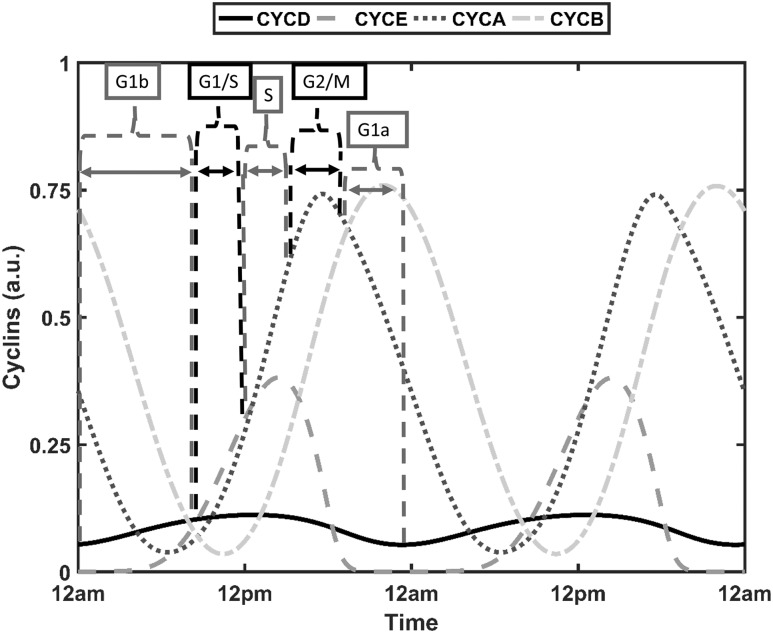
The transition between cell cycle phases is a result of adequate accumulation of cyclins (67). In the context of mathematical modeling, the relative amplitude of cyclin oscillations has been used to predict transitions from one phase to another, with large-amplitude cyclin B oscillations used to estimate proliferating cells (50). Because of seasonal and intercellular variability, the amplitudes of the cyclin/Cdk complexes are diverse. Biologically, basal steady-state concentrations of the cell cycle components result in quiescence. As is the case with our model, it becomes challenging to characterize this quiescent state in the presence of persistent oscillations. There exists, therefore, no one objective threshold that can be used to globally indicate the transition from one phase to another. In line with the method used by Toettcher et al. (68), it was assumed that all cells would progress through the cell cycle but that transition into a subsequent phase occurred when the corresponding cyclin/Cdk complex, for a given cell, exceeded a 90% threshold. With such an implementation, we ensure that all cells progress through the cell cycle for all seasons. Intervals between successive cyclin/Cdk complex peak thresholds were used to determine the cell cycle phase of a given cell. Figure 11 summarizes the approach used to assign cell cycle phases. The late G1 phase (G1b) is initiated with increasing levels of CYCD and ends when levels exceed 90% of the maxima of CYCD. At this time, the cell enters the G1/S phase with transition into the S phase occurring above 90% of CYCE maximum levels. Termination of the S phase and initiation of the G2/M phase occurs at 90% of peak CYCA levels, with the cell entering the G1 phase when the threshold of 90% of CYCB is surpassed. For some cells, there exists a dormant phase before CYCD levels begin ascending. This time window is assigned the G1a phase. Figure 12 shows the time duration distributions of cell cycle phases for the spring model. For all seasons, the total duration of the cell cycle was on the order of 20 hours, which is consistent with the findings by Hahn et al. (69).
Figure 11.
Cyclin levels used for cell-cycle phase determination in single cells. For each individual cell in the heterogeneous population, the G1a phase ranges from 90% of the CYCB peak to the minimum of CYCD, the G1b phase from the minimum of CYCD to 90% of the CYCD peak, the G1/S phase from 90% of CYCD to 90% of the CYCE peak, the S phase from 90% of the CYCE peak to 90% of the CYCA peak, and the G2/M phase from 90% of CYCA peak to 90% of the CYCB peak.
Figure 12.
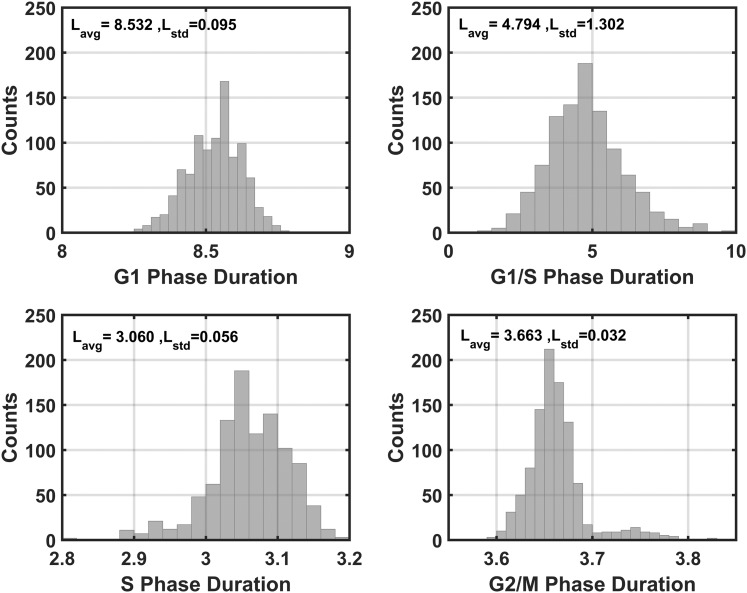
Representative distribution for duration of cell cycle phases for the spring model. On average, the model predicts that the G1 phase is the longest phase of the cell cycle, accounting for ∼8.5 hours. The G1/S transition and S phase last for ∼4.8 hours and ∼3 hours, respectively. The G2/M phase lasts ∼3.6 hours and has the narrowest distribution. Lavg, mean phase duration; Lstd, duration standard deviation.
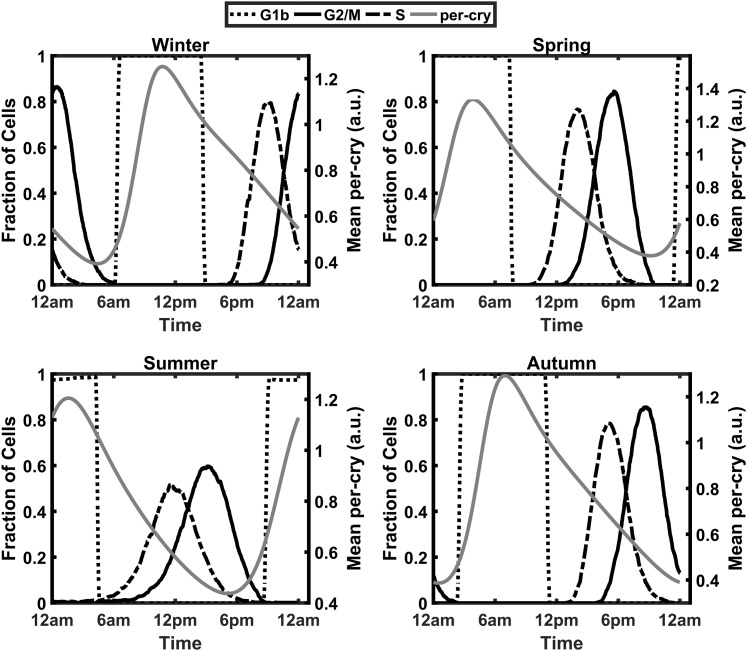
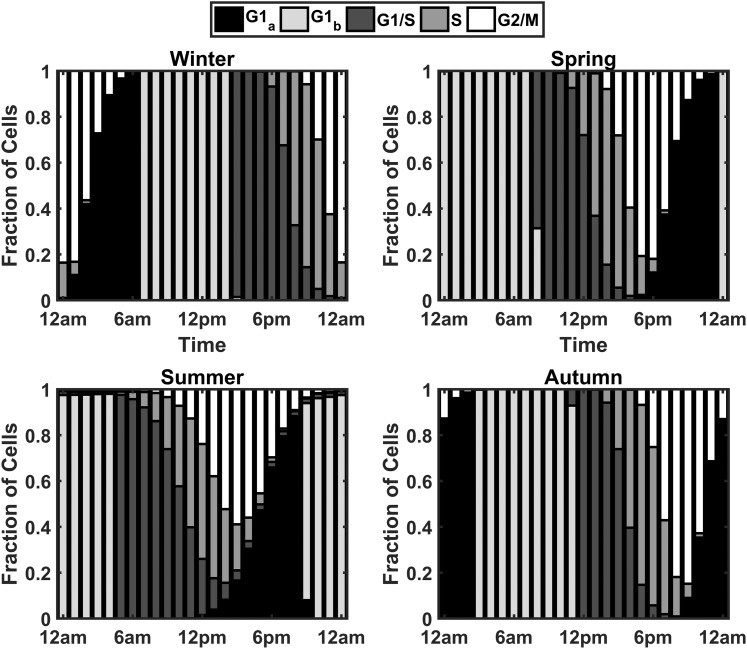
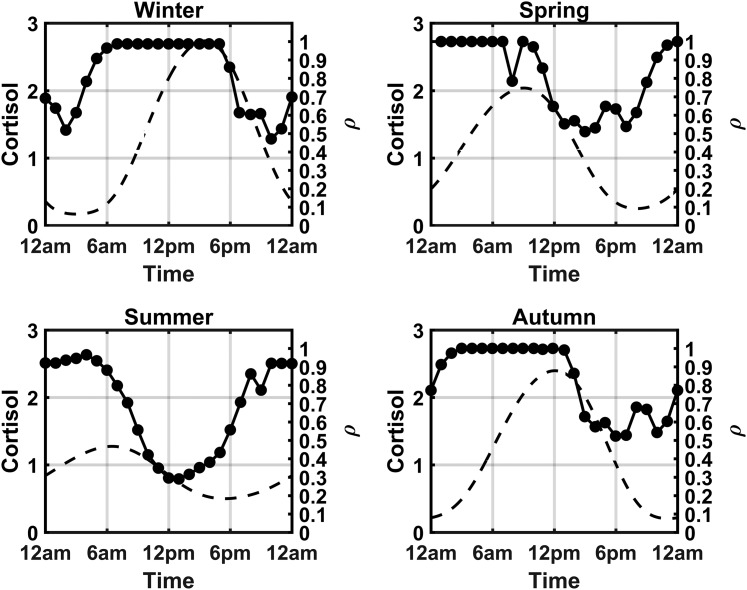
To assess the circadian and seasonal changes in cell cycle synchrony, the fraction of cells occupying each phase of the cell cycle at each hour of the simulated day was determined. Figure 13 shows a dependence of the cell cycle on Per–CrymRNA expression, with the greater fraction of cells in the G1 phase during the circadian peak in Per–CrymRNA expression, whereas the circadian minima in Per–CrymRNA expression is associated with an increase in the fraction of cells in the S and G2/M phases of the cell cycle. The bar plots in Fig. 14 depict these variations in cell cycle phase occupancy. The plots indicate a time-of-day and seasonal variation in the cell cycle oscillations of the population. For the spring model, the G1b phase is predominantly occupied in the early hours of the morning, with transition into the subsequent phases as the day advances. This G1b phase is later in the day for the winter model, indicating an acrophase shift. This phase shift was a consequence of the seasonal variation in cortisol profiles. To quantify the degree of synchrony throughout the day for each of the modeled seasons, we again used the synchronization metric previously used in the molecular clock entrainment simulations. The index has been modified to quantify synchrony at each hour of the day [Eq. (12)]. pk(t) represents the proportion of cells in a given cell cycle phase at a select time point. In Fig. 15, we superimpose plots of ρ(t) and Fperiphery vs the time of day for each season. The dashed line represents the circadian variation in cortisol’s profile, whereas the beaded plot represents the synchronization metric. The circadian variation of ρ(t) is congruent with the cell cycle phase progression depicted in the bar plots of Fig. 14. In the early morning of the winter model, for instance, there is a trough in cell cycle synchrony at 2 am corresponding to more cells occupying the G1a phase at this time. The sharp decrease in synchrony at 8 am in the spring model is a consequence of an increase in the transition of cells into the G1/S phase. Overall, the winter model displayed the greatest consistency in cell cycle synchrony throughout the day, with summer exhibiting the lowest. Figure 15 reflects the cortisol dependence of the circadian rhythm of cell cycle synchrony. In general, cell cycle synchrony increased with increasing levels of cortisol.
Figure 13.
Gating of the cell cycle by the circadian clock. The circadian increase in Per–CrymRNA expression is associated with an increase in the fraction of cells in the G1 phase, whereas a decrease in Per–CrymRNA expression is associated with an increase in the fraction of cells in the S and G2/M phases.
Figure 14.
Circadian and seasonal variations in cell cycle progression. Each bar denotes the fraction of cells in a particular cell cycle phase during a specific 1-hour increment over the course of a day. The model predicts a shift in the acrophases of the S and G2/M phases of the cell cycle to later times of the day as seasons progress from summer to winter.
Figure 15.
Seasonal and circadian variation in cell cycle synchronization and cortisol levels. Peripheral cortisol level Fperiphery (left) and cell cycle synchrony ρ (right) for each season. Synchrony is greatest during winter, and the circadian increase in synchrony is correlated with the circadian rise and peak in cortisol levels.
| (12) |
Discussion
In the absence of entrainment by cortisol, the approximate 24-hour ensemble period, broad range of unentrained cell periods, and prediction of dampened ensemble oscillations (Figs. 4 and 5) agree with experimental data (33, 34). With the implementation of entrainment, arbitrated by both the proinflammatory mediator and activated cortisol-GC receptor complex FGR(N), Per–CrymRNA rhythms for cells of all seasons adopted periods of oscillations identical or extremely close to the entraining signal’s 24-hour period.
As defined by Johnson et al. (70), entrainment quantifies the degree to which the free-running period of the peripheral clock conforms to the 24-hour period of the environment, whereas synchrony measures how well rhythms coincide. In this regard, all our seasonal profiles were sufficiently entrained to the environmental cycle despite displaying moderate intercellular differences in synchronization, quantified on the basis of their phase distributions and circadian profiles. We establish, therefore, that entrainment is necessary but not sufficient for synchrony.
The Per–CrymRNA oscillations were strongly entrained to the environmental signal, with the winter and summer models displaying the strongest and weakest entrainments, respectively, to the environmental photoperiod (Fig. 6). Both photoperiod and amplitude characterize the strength of a zeitgeber and its ability to robustly entrain (71). Through use of a generic amplitude-phase oscillator and square-wave entrainment signal, the greatest range of entrainment was predicted for a photoperiod with equal durations of light and darkness (72). The spring model, therefore, with a light profile described with equal hours of light and darkness (12L/12D), represents the optimum entraining photoperiod. Experimentally, however, the identification of an optimum entraining photoperiod remains elusive and might depend, to a certain extent, on the specific network properties of the circadian clock (73, 74). The activity of the Southern flying squirrel can be entrained to light schedules ranging from 1 second to 18 hours a day (75), whereas intermittent light exposure is capable of entraining the human biological clock (76). As discussed by Schmal et al. (72), although the strength of the zeitgeber may be photoperiod dependent, the effective entraining intensity relies on the organism’s sensitivity to the zeitgeber, an emergent property of the systemic network. Within the framework of our developed model, the effective intensity of the zeitgeber signal is manifested in the circadian characteristics of cortisol, which is regulated by the seasonally varying photoperiod and adrenal sensitivity (modeled with seasonal coefficient: nseason). This seasonal coefficient simulates the documented increase in adrenal sensitivity to ACTH stimulation in winter (77), which is hypothesized to be effected via the autonomous nervous pathway (78). Moreover, the ensemble amplitude of SCN neuronal activity is augmented in shorter days (79–82). Consequentially, the higher-amplitude cortisol oscillations during winter (Supplemental Fig. 2) resulted in greater entrainment of Per–CrymRNA oscillations in winter than in summer. In conjunction with reduced entrainment, the Per–CrymRNA oscillations of the cells in the summer model were the least synchronous (Fig. 8).
Unlike the extensively investigated SCN, documented findings on the effects of photoperiod in modulating entrainment and synchrony of peripheral oscillators are lacking. The transition from long to short days was reported to advance the minima of liver Per2, whereas Rev-Erbα adjusted by lengthening its expression and activity with no discussion on changes in peripheral clock synchrony (83). In Siberian hamsters, photoperiod differentially regulated the expression of Per1 in central and peripheral tissues, with body temperature rhythms and feeding identified as additional pathways of peripheral clock regulation (84). Because of high neuronal connectivity of the SCN and the ability of light to entrain peripheral clocks in an SCN perturbed system, it is speculated that alternative routes of entrainment may involve other hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic nuclei (85). Apart from the aforementioned, environmental factors, such as light intensity and temperature, regulate circadian clock dynamics (86). It is expected that seasonal changes in these cues would also modulate synchronization of the molecular clock with the environment (87). Although our developed model does not capture all the complexities associated with seasonal entrainment of peripheral clocks, it does underscore the shortcomings of a damped cortisol profile in regulating dynamics in the periphery. Weaker entrainment of the peripheral circadian clock resulted in select cells exhibiting Per–CrymRNA with periods >24 hours and <24 hours for summer (Fig. 6). This misalignment between the internal clock and external stimuli is a recently identified risk factor for metabolic disease (88) and can exacerbate cardiovascular disease progression (89, 90).
Interestingly, the bimodal distributions of Per–CrymRNA expression predicted for winter, spring, and autumn (Fig. 7) have been observed experimentally. After 6 days of oral administration of Cortef, a cortisol analog, a significant bimodal rhythm of PER3 expression in PBMCs was found in a subset of cohorts (32). PER3 expression displayed two peaks: one in the morning and another in the early evening. In the experimental study, it was assumed that this bimodal response to GC treatment was the result of different cell populations present within the PBMCs (lymphocytes, monocytes, and dendritic cells). Alternatively, it was speculated that one peak was a result of central clock control whereas the shifted peak was in response to GC administration. Furthermore, a biphasic circadian profile of Per expression, with one major and one minor peak, has also been observed in human oral mucosa and skin tissue samples by Bjarnason et al. (91). However, the authors of this study were unable to confirm whether the biphasic profile was due to the inability of the experimental assay to resolve multiple phase-differentiated isomers, or whether expression exhibited truly biphasic dynamics. Because the peripheral circadian clocks mediate the activation of diverse signaling pathways, we speculate that the presence of biphasic circadian dynamics might have important regulatory implications. In contrast to a unimodal circadian rhythm, biphasic rhythms might lead to a more prolonged activation of important immune and metabolic signaling pathways. The association of the IL-6 receptor, which is indirectly regulated by Per3 (92), with the epidermal growth factor receptor has been implicated in the prolonged activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)–mediated proinflammatory pathways as a result of a second wave of STAT3 activation (93). Moreover, circadian heterogeneity in tissue subpopulations might confer additional adaptive advantages. For example, Janich et al. (94) show that the dormant hair-follicle stem cell niche is composed of coexisting subpopulations of cells with differences in the phase and amplitude of clock genes expression. Furthermore, Bmal1 was found to modulate the rhythmic expression of stem cell regulatory genes in a manner that generated subpopulations that were differentially predisposed to respond to activation stimuli, enabling the existence of both dormant and active subpopulations of stem cells, which might be required to promote homeostasis (94, 95).
For our model, existence of the lower amplitude, phase-delayed oscillations were a result of the simulated intercellular variability in the dynamics of CLOCK–BMAL1. Lower-amplitude CLOCK–BMAL1 oscillations, which predominate in winter, result in diminished inhibition of the FGR(N) entrainment term [Supplemental Eq. (16)]. As a consequence of this, the stronger entrainment resulted in a phase delay of Per–CrymRNA oscillations, which then become aligned with the minima (and not the maxima) of the second entrainer, P. This diminished entrainment signal from P caused these delayed oscillations to exhibit attenuated amplitudes. Summer’s flattened FGR(N) and P profiles preclude the occurrence of this phenomenon in the cell population. Therefore, our results suggest that underlying intercellular heterogeneity in the peripheral circadian clock expression might manifest only in the presence of certain permissive conditions, which in the case of our model are determined by the seasonal variation in cortisol circadian rhythms. This further underscores the importance of accounting for the differential influence of external entrainers on the dynamics of peripheral circadian clock network.
Figure 12 shows that the duration of the cell cycle approximates a day and that although the total duration of the cell cycle was seasonally invariant, there were seasonal differences in the time spent in select phases. In the summer model (data not shown), for instance, the average duration of the G1 phase was 7.6 hours, whereas the average duration of the G1/S phase was ∼6.3 hours. The shorter duration G1 phase was compensated with a prolonged G1/S phase. Compensatory changes in cell cycle phases has been observed in rat-1 fibroblasts induced to overexpress cyclin D1 and E (96). In this study, a shorter-duration G1 phase was followed by a compensatory lengthening of the S phase. Similarly, PC12 cells treated with nerve growth factor spend a prolonged time in the G1 phase but with a parallel reduction of time spent in the S phase (69). Moreover, studies on unicellular photosynthetic algae have shown that photoperiod duration modulates the timing of the S phase, such that there is a minimum duration of time between time of light onset and entry into the S phase (97, 98). The documented shift of the acrophases of the S and G2 phases from late night/early morning in the summer to later in the day in winter in human bone marrow and rectal mucosa tissue is analogous to our model’s predictions (99, 100).
Together with the seasonal dependence on cell cycle synchrony, these observations could be of potential clinical importance. Several proposals suggest the exploitation of cell cycle synchrony with cancer chemotherapy, such that tumors are treated when most cells are in a sensitive phase of the cell cycle (101, 102). Knowledge of endogenous circannual differences in cell cycle synchrony can be leveraged to devise chemotherapeutic dosing regimens that can augment the efficacy of treatment while minimizing side effects. Accordingly, the later initiation of these cell cycle processes as the seasons progress from summer to winter might be an important consideration for the development of chronotherapeutic dosing regimens for anticancer treatments that target a specific cell cycle phase (103).
Our model results predict a gating of the cell cycle with respect to the expression of the peripheral clock genes. Importantly, these correlations between clock gene expression and the phase of mitotic cycle agree with experimental results that suggest that entry into G1 phase is correlated with an increase in Per–CrymRNA and Rev-erb α expression (38, 104). Furthermore, model simulations indicate that the circadian rise in cortisol is correlated with entry into the G1/S and S phases (Figs. 14 and 15). Interestingly, a study by Abrahamsen et al. (46) found a correlation between the fraction of neutrophils and bone marrow cells in the S phase of the cell cycle and the circadian peak of cortisol levels in humans. Likewise, our model predicts that in all seasons, the circadian rise in cell cycle synchrony is correlated with the circadian increase in cortisol rhythms, whereas cell cycle synchrony decreases during the declining phase of cortisol. Additionally, the variability in peripheral clock dynamics further contributes to the decrease in mitotic synchrony at low cortisol levels. Therefore, we speculate that intercellular differences in mitotic regulation might become more apparent when cortisol levels are low.
Seasonal changes in cell cycle synchrony were predicted, with cells being more entrained by the high-amplitude winter cortisol signal (Fig. 15). Reports of seasonal oscillations, as well as the associated mediators of such variations, in cell cycle synchrony are limited. Variations in light exposure have, however, been found to modify the circadian rhythms of cell division in the esophagus of melatonin-deficient ICR mice (105). In this study, the mitotic index (MI), or the ratio between the numbers of cells undergoing mitosis to those of cells that were not, was assessed over 24 hours. Mice exposed to constant darkness exhibited a pronounced diurnal MI variation compared with those in constant light. The phase delayed MI rhythm observed for those in constant light was advanced with the exogenous administration of melatonin. Assuming similar cellular proliferative potential for all conditions, the MI can be considered as a crude measure for cell cycle synchrony. The acrophase shift in MI with melatonin injection implies that systemic signals can mediate in vivo synchronization of the cell cycle. Pulsed GC treatment has been found to restore regenerative synchrony and alleviate the inflamed state of asynchronous and proinflammatory asthmatic cells (45, 106). As discussed by Freishtat et al. (45), the pulsed GC signal is somewhat analogous to the circadian rhythm of cortisol’s profile. The high-amplitude rhythm of the winter model, therefore, acts as a dominant entrainer to synchronize the cell cycle phase.
Seasonal variations in blood composition have been found in recent human studies (16, 107), with general increases in the number of white blood cells and neutrophils in the winter-spring season. Synchronization increases the number of cells present in a given cell cycle phase (108). Abrahamsen et al. (46) also found a correlation between the neutrophil count and the fraction of bone marrow cells in both the S− and S+G2/M phases. Thus, we speculate that despite the anti-inflammatory effects of cortisol, the extended durations of enhanced cell cycle synchronization for a simulated day in winter season could be translated to an increased circadian peak in the cell numbers of specific populations of immune cells. Fascinatingly, such a prediction would also agree with observations from population studies, where the total lymphocyte count as well as the circadian amplitude in lymphocyte count is highest in winter months and lowest in summer months (16, 47, 109).
The model developed provides a preliminary structure that can be used to assess the cross-communication among numerous interacting subsystems. With the developed network, it is possible to incorporate coupling between the cell cycle and circadian oscillators. This can be accounted for with the direct or indirect modeling of the influence of the tumor suppressor protein, p53, which regulates expression (110) and is regulated by (111). Additionally, the dynamic influence of the proinflammatory mediator, P, could be incorporated as nuclear factor-κB, the mediator of proinflammatory signaling, modulates and is itself regulated by the cell cycle (112). However, the model has certain important limitations. We use a simplified version of the cell cycle that does not comprehensively account for the various regulatory features of cell cycle, such as the cell cycle checkpoints, and how these might be influenced by the seasonal cortisol profiles. Moreover, we consider only the unidirectional influence of the circadian clock on the cell cycle, without considering the influence of the cell cycle on clock gene expression. Finally, we account only for the influence of the systemic entrainer, the circadian cortisol rhythm, on cell cycle progression and do not account for intercellular interactions, for example, via gap junctions, that might modulate population cell cycle synchronization (113, 114). With the inclusion of these influences, more experimentally profound circadian and seasonal predictions are expected.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Financial Support: This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant GM24211 (to K.P., R.T.R., C.H., and I.P.A.); National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship DGE-1433187 (to C.H.); and US Department of Education Graduate Assistance in Areas of National Need Grant P200A150131 to the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Rutgers University (C.H.).
Disclosures: The authors have nothing to disclose.
Glossary
Abbreviations:
- ACTH
adrenocorticotropic hormone
- CDC20
cell-division cycle protein 20
- Cdk
cyclin-dependent kinase
- CRH
corticotropin-releasing hormone
- CYCA
cyclin A/Cdk2
- CYCB
cyclin B/Cdk1
- CYCD
cyclin D/Cdk4-6 complex
- CYCE
cyclin E/Cdk2
- E
cortisone
- E2F
E2 factor
- FGR
cortisol-bound glucocorticoid receptor
- FMR
cortisol-bound mineralocortioid receptor
- Fperiphery
cortisol in peripheral compartment
- FR
cortisol-bound glucocorticoid receptors in central compartment
- G0 phase
quiescent state
- G1 phase
gap 1 phase
- G2 phase
gap 2 phase
- GC
glucocorticoid
- GF
growth factor
- HPA
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal
- HSD1
hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1
- HSD2
hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2
- IL-6
interleukin-6
- M
mitosis
- MI
mitotic index
- MR
mineralocorticoid receptor
- mRNA
messenger RNA
- P
proinflammatory mediator
- PBMC
peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- S
entropy
- S phase
DNA synthetic phase
- SCN
suprachiasmatic nucleus
- STAT3
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
References
- 1. Mohawk JA, Green CB, Takahashi JS. Central and peripheral circadian clocks in mammals. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35(1):445–462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Selmaoui B, Touitou Y. Reproducibility of the circadian rhythms of serum cortisol and melatonin in healthy subjects: a study of three different 24-h cycles over six weeks. Life Sci. 2003;73(26):3339–3349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Chung S, Son GH, Kim K. Circadian rhythm of adrenal glucocorticoid: its regulation and clinical implications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1812(5):581–591 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Perry MG, Kirwan JR, Jessop DS, Hunt LP. Overnight variations in cortisol, interleukin 6, tumour necrosis factor α and other cytokines in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(1):63–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Straub RH, Paimela L, Peltomaa R, Schölmerich J, Leirisalo-Repo M. Inadequately low serum levels of steroid hormones in relation to interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor in untreated patients with early rheumatoid arthritis and reactive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(3):654–662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Sephton SE, Sapolsky RM, Kraemer HC, Spiegel D. Diurnal cortisol rhythm as a predictor of breast cancer survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92(12):994–1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Lederbogen F, Hummel J, Fademrecht C, Krumm B, Kühner C, Deuschle M, Ladwig KH, Meisinger C, Wichmann HE, Lutz H, Breivogel B. Flattened circadian cortisol rhythm in type 2 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2011;119(9):573–575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Straub RH, Cutolo M. Circadian rhythms in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for pathophysiology and therapeutic management. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(2):399–408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Rao R, DuBois D, Almon R, Jusko WJ, Androulakis IP. Mathematical modeling of the circadian dynamics of the neuroendocrine-immune network in experimentally induced arthritis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016;311(2):E310–E324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Hadlow NC, Brown S, Wardrop R, Henley D. The effects of season, daylight saving and time of sunrise on serum cortisol in a large population. Chronobiol Int. 2014;31(2):243–251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Persson R, Garde AH, Hansen AM, Osterberg K, Larsson B, Orbaek P, Karlson B. Seasonal variation in human salivary cortisol concentration. Chronobiol Int. 2008;25(6):923–937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Walker BR, Best R, Noon JP, Watt GC, Webb DJ. Seasonal variation in glucocorticoid activity in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(12):4015–4019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Hazlerigg DG, Wagner GC. Seasonal photoperiodism in vertebrates: from coincidence to amplitude. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006;17(3):83–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Stevenson TJ, Prendergast BJ. Photoperiodic time measurement and seasonal immunological plasticity. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2015;37:76–88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Vondrasová-Jelínková D, Hájek I, Illnerová H. Adjustment of the human melatonin and cortisol rhythms to shortening of the natural summer photoperiod. Brain Res. 1999;816(1):249–253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Dopico XC, Evangelou M, Ferreira RC, Guo H, Pekalski ML, Smyth DJ, Cooper N, Burren OS, Fulford AJ, Hennig BJ, Prentice AM, Ziegler AG, Bonifacio E, Wallace C, Todd JA. Widespread seasonal gene expression reveals annual differences in human immunity and physiology. Nat Commun. 2015;6(1):7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Hawley DJ, Wolfe F, Lue FA, Moldofsky H. Seasonal symptom severity in patients with rheumatic diseases: a study of 1,424 patients. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(8):1900–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Schlesinger N, Schlesinger M. Seasonal variation of rheumatic diseases. Discov Med. 2005;5(25):64–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Harrington M. Location, location, location: important for jet-lagged circadian loops. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(7):2265–2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Morris CJ, Purvis TE, Hu K, Scheer FAJL. Circadian misalignment increases cardiovascular disease risk factors in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(10):E1402–E1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Mavroudis PD, Scheff JD, Calvano SE, Lowry SF, Androulakis IP. Entrainment of peripheral clock genes by cortisol. Physiol Genomics. 2012;44(11):607–621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Bae SA, Androulakis IP. The synergistic role of light-feeding phase relations on entraining robust circadian rhythms in the periphery. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2017;11:1177625017702393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Ohlander J, Keskin M-C, Stork J, Radon K. Shift work and hypertension: Prevalence and analysis of disease pathways in a German car manufacturing company. Am J Ind Med. 2015;58(5):549–560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Mosendane T, Mosendane T, Raal FJ. Shift work and its effects on the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2008;19(4):210–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Puttonen S, Viitasalo K, Härmä M. Effect of shiftwork on systemic markers of inflammation. Chronobiol Int. 2011;28(6):528–535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Puttonen S, Oksanen T, Vahtera J, Pentti J, Virtanen M, Salo P, Kivimäki M. Is shift work a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis? The Finnish Public Sector study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(4):779–780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Haimovich B, Calvano J, Haimovich AD, Calvano SE, Coyle SM, Lowry SF. In vivo endotoxin synchronizes and suppresses clock gene expression in human peripheral blood leukocytes. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(3):751–758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Namas R, Zamora R, Namas R, An G, Doyle J, Dick TE, Jacono FJ, Androulakis IP, Nieman GF, Chang S, Billiar TR, Kellum JA, Angus DC, Vodovotz Y. Sepsis: something old, something new, and a systems view. J Crit Care. 2012;27(3):314.e1–314.e11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Keller M, Mazuch J, Abraham U, Eom GD, Herzog ED, Volk HD, Kramer A, Maier B. A circadian clock in macrophages controls inflammatory immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(50):21407–21412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Marcheva B, Moynihan Ramsey K, Buhr ED, Kobayashi Y, Su H, Ko CH, Ivanova G, Omura C, Mo S, Vitaterna MH, Lopez JP, Philipson LH, Bradfield CA, Crosby SD. JeBailey L, Wang X, Takahashi JS, Bass J. Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinemia and diabetes. Nature. 2010;466:627–631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Son GH, Chung S, Choe HK, Kim H-D, Baik S-M, Lee H, Lee H-W, Choi S, Sun W, Kim H, Cho S, Lee KH, Kim K. Adrenal peripheral clock controls the autonomous circadian rhythm of glucocorticoid by causing rhythmic steroid production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(52):20970–20975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Cuesta M, Cermakian N, Boivin DB. Glucocorticoids entrain molecular clock components in human peripheral cells. FASEB J. 2015;29(4):1360–1370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Welsh DK, Yoo S-H, Liu AC, Takahashi JS, Kay SA. Bioluminescence imaging of individual fibroblasts reveals persistent, independently phased circadian rhythms of clock gene expression. Curr Biol. 2004;14(24):2289–2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Nagoshi E, Saini C, Bauer C, Laroche T, Naef F, Schibler U. Circadian gene expression in individual fibroblasts: cell-autonomous and self-sustained oscillators pass time to daughter cells. Cell. 2004;119(5):693–705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Yamamoto T, Nakahata Y, Tanaka M, Yoshida M, Soma H, Shinohara K, Yasuda A, Mamine T, Takumi T. Acute physical stress elevates mouse period1 mRNA expression in mouse peripheral tissues via a glucocorticoid-responsive element. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(51):42036–42043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Sherr CJ. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994;79(4):551–555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Bieler J, Cannavo R, Gustafson K, Gobet C, Gatfield D, Naef F. Robust synchronization of coupled circadian and cell cycle oscillators in single mammalian cells. Mol Syst Biol. 2014;10(7):739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Feillet C, van der Horst GTJ, Levi F, Rand DA, Delaunay F. Coupling between the circadian clock and cell cycle oscillators: implication for healthy cells and malignant growth. Front Neurol. 2015;6:96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Rogatsky I, Trowbridge JM, Garabedian MJ. Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated cell cycle arrest is achieved through distinct cell-specific transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17(6):3181–3193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Dickmeis T, Foulkes NS. Glucocorticoids and circadian clock control of cell proliferation: at the interface between three dynamic systems. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011;331(1):11–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Dickmeis T, Lahiri K, Nica G, Vallone D, Santoriello C, Neumann CJ, Hammerschmidt M, Foulkes NS. Glucocorticoids play a key role in circadian cell cycle rhythms. PLoS Biol. 2007;5(4):e78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Kawamura A, Tamaki N, Kokunai T. Effect of dexamethasone on cell proliferation of neuroepithelial tumor cell lines. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1998;38(10):633–638, discussion 638–640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Langeveld CH, van Waas MP, Stoof JC, Sutanto W, de Kloet ER, Wolbers JG, Heimans JJ. Implication of glucocorticoid receptors in the stimulation of human glioma cell proliferation by dexamethasone. J Neurosci Res. 1992;31(3):524–531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Zibera C, Gibelli N, Butti G, Pedrazzoli P, Carbone M, Magrassi L, Robustelli della Cuna G. Proliferative effect of dexamethasone on a human glioblastoma cell line (HU 197) is mediated by glucocorticoid receptors. Anticancer Res. 1992;12(5):1571–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Freishtat RJ, Watson AM, Benton AS, Iqbal SF, Pillai DK, Rose MC, Hoffman EP. Asthmatic airway epithelium is intrinsically inflammatory and mitotically dyssynchronous. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;44(6):863–869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Abrahamsen JF, Smaaland R, Sandberg S, Aakvaag A, Lote K. Circadian variation in serum cortisol and circulating neutrophils are markers for circadian variation of bone marrow proliferation in cancer patients. Eur J Haematol. 1993;50(4):206–212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Maes M, Stevens W, Scharpé S, Bosmans E, De Meyer F, D’Hondt P, Peeters D, Thompson P, Cosyns P, De Clerck L, Bridts C. Seasonal variation in peripheral blood leukocyte subsets and in serum interleukin-6, and soluble interleukin-2 and -6 receptor concentrations in normal volunteers. Experientia. 1994;50(9):821–829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Pierre K, Schlesinger N, Androulakis IP. The role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in modulating seasonal changes in immunity. Physiol Genomics. 2016;48(10):719–738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Pierre K, Schlesinger N, Androulakis IP. The hepato-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal-renal axis: mathematical modeling of cortisol’s production, metabolism, and seasonal variation. J Biol Rhythms. 2017;32(5):469–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Gérard C, Goldbeter A. A skeleton model for the network of cyclin-dependent kinases driving the mammalian cell cycle. Interface Focus. 2011;1(1):24–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Cardone L, Sassone-Corsi P. Timing the cell cycle. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5(10):859–861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Sharma A, Jusko WJ. Characteristics of indirect pharmacodynamic models and applications to clinical drug responses. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998;45(3):229–239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Mattern J, Büchler MW, Herr I. Cell cycle arrest by glucocorticoids may protect normal tissue and solid tumors from cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6(9):1345–1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Feng X, Reini SA, Richards E, Wood CE, Keller-Wood M. Cortisol stimulates proliferation and apoptosis in the late gestation fetal heart: differential effects of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013;305(4):R343–R350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Terada Y, Kobayashi T, Kuwana H, Tanaka H, Inoshita S, Kuwahara M, Sasaki S. Aldosterone stimulates proliferation of mesangial cells by activating mitogen-activated protein kinase 1/2, cyclin D1, and cyclin A. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(8):2296–2305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Bjarnason GA, Jordan RC, Sothern RB. Circadian variation in the expression of cell-cycle proteins in human oral epithelium. Am J Pathol. 1999;154(2):613–622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Csikász-Nagy A, Battogtokh D, Chen KC, Novák B, Tyson JJ. Analysis of a generic model of eukaryotic cell-cycle regulation. Biophys J. 2006;90(12):4361–4379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Fauré A, Naldi A, Chaouiya C, Thieffry D. Dynamical analysis of a generic Boolean model for the control of the mammalian cell cycle. Bioinformatics. 2006;22(14):e124–e131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Pearl Mizrahi S, Sandler O, Lande-Diner L, Balaban NQ, Simon I. Distinguishing between stochasticity and determinism: Examples from cell cycle duration variability. BioEssays. 2016;38(1):8–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Mavroudis PD, Corbett SA, Calvano SE, Androulakis IP. Mathematical modeling of light-mediated HPA axis activity and downstream implications on the entrainment of peripheral clock genes. Physiol Genomics. 2014;46(20):766–778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Cooper MS, Bujalska I, Rabbitt E, Walker EA, Bland R, Sheppard MC, Hewison M, Stewart PM. Modulation of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase isozymes by proinflammatory cytokines in osteoblasts: an autocrine switch from glucocorticoid inactivation to activation. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16(6):1037–1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Hardy RS, Filer A, Cooper MS, Parsonage G, Raza K, Hardie DL, Rabbitt EH, Stewart PM, Buckley CD, Hewison M. Differential expression, function and response to inflammatory stimuli of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in human fibroblasts: a mechanism for tissue-specific regulation of inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(4):R108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Baer M, Williams SC, Dillner A, Schwartz RC, Johnson PF. Autocrine signals control CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β expression, localization, and activity in macrophages. Blood. 1998;92(11):4353–4365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Motzkus D, Albrecht U, Maronde E. The human PER1 gene is inducible by interleukin-6. J Mol Neurosci. 2002;18(1-2):105–109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Gonze D, Bernard S, Waltermann C, Kramer A, Herzel H. Spontaneous synchronization of coupled circadian oscillators. Biophys J. 2005;89(1):120–129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Tass P, Rosenblum MG, Weule J, Kurths J, Pikovsky A, Volkmann J, Schnitzler A, Freund HJ. Detection of n:m phase locking from noisy data: application to magnetoencephalography. Phys Rev Lett. 1998;81(15):3291–3294. [Google Scholar]
- 67. Neganova I, Lako M. G1 to S phase cell cycle transition in somatic and embryonic stem cells. J Anat. 2008;213(1):30–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Toettcher JE, Loewer A, Ostheimer GJ, Yaffe MB, Tidor B, Lahav G. Distinct mechanisms act in concert to mediate cell cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(3):785–790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Hahn AT, Jones JT, Meyer T. Quantitative analysis of cell cycle phase durations and PC12 differentiation using fluorescent biosensors. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(7):1044–1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Johnson CH, Elliott JA, Foster R. Entrainment of circadian programs. Chronobiol Int. 2003;20(5):741–774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Bordyugov G, Abraham U, Granada A, Rose P, Imkeller K, Kramer A, Herzel H. Tuning the phase of circadian entrainment. J R Soc Interface. 2015;12(108):20150282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Schmal C, Myung J, Herzel H, Bordyugov G. A theoretical study on seasonality. Front Neurol. 2015;6:94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Zhang EE, Kay SA. Clocks not winding down: unravelling circadian networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(11):764–776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Abraham U, Granada AE, Westermark PO, Heine M, Kramer A, Herzel H. Coupling governs entrainment range of circadian clocks. Mol Syst Biol. 2010;6:438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. DeCoursey PJ. LD ratios and the entrainment of circadian activity in a nocturnal and a diurnal rodent. J Comp Physiol. 1972;78(3):221–235. [Google Scholar]
- 76. Duffy JF, Wright KP Jr. Entrainment of the human circadian system by light. J Biol Rhythms. 2005;20(4):326–338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Amirat Z, Brudieux R. Seasonal changes in in vivo cortisol response to ACTH and in plasma and pituitary concentrations of ACTH in a desert rodent, the sand rat (Psammomys obesus). Comp Biochem Physiol Comp Physiol. 1993;104(1):29–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Otsuka T, Goto M, Kawai M, Togo Y, Sato K, Katoh K, Furuse M, Yasuo S. Photoperiod regulates corticosterone rhythms by altered adrenal sensitivity via melatonin-independent mechanisms in Fischer 344 rats and C57BL/6J mice. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Schaap J, Albus H, VanderLeest HT, Eilers PH, Détári L, Meijer JH. Heterogeneity of rhythmic suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons: Implications for circadian waveform and photoperiodic encoding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(26):15994–15999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Rohling J, Wolters L, Meijer JH. Simulation of day-length encoding in the SCN: from single-cell to tissue-level organization. J Biol Rhythms. 2006;21(4):301–313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. VanderLeest HT, Houben T, Michel S, Deboer T, Albus H, Vansteensel MJ, Block GD, Meijer JH. Seasonal encoding by the circadian pacemaker of the SCN. Curr Biol. 2007;17(5):468–473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Meijer JH, Michel S, Vanderleest HT, Rohling JH. Daily and seasonal adaptation of the circadian clock requires plasticity of the SCN neuronal network. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;32(12):2143–2151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Sosniyenko S, Parkanová D, Illnerová H, Sládek M, Sumová A. Different mechanisms of adjustment to a change of the photoperiod in the suprachiasmatic and liver circadian clocks. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010;298(4):R959–R971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Carr A-JF, Johnston JD, Semikhodskii AG, Nolan T, Cagampang FR, Stirland JA, Loudon AS. Photoperiod differentially regulates circadian oscillators in central and peripheral tissues of the Syrian hamster. Curr Biol. 2003;13(17):1543–1548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Husse J, Eichele G, Oster H. Synchronization of the mammalian circadian timing system: light can control peripheral clocks independently of the SCN clock: alternate routes of entrainment optimize the alignment of the body’s circadian clock network with external time. BioEssays. 2015;37(10):1119–1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Devlin PF. Signs of the time: environmental input to the circadian clock. J Exp Bot. 2002;53(374):1535–1550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Wikelski M, Martin LB, Scheuerlein A, Robinson MT, Robinson ND, Helm B, Hau M, Gwinner E. Avian circannual clocks: adaptive significance and possible involvement of energy turnover in their proximate control. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008;363(1490):411–423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Li M-D, Li C-M, Wang Z. The role of circadian clocks in metabolic disease. Yale J Biol Med. 2012;85(3):387–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Takeda N, Maemura K. Circadian clock and cardiovascular disease. J Cardiol. 2011;57(3):249–256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Scheff JD, Mavroudis PD, Calvano SE, Lowry SF, Androulakis IP. Modeling autonomic regulation of cardiac function and heart rate variability in human endotoxemia. Physiol Genomics. 2011;43(16):951–964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Bjarnason GA, Jordan RC, Wood PA, Li Q, Lincoln DW, Sothern RB, Hrushesky WJ, Ben-David Y. Circadian expression of clock genes in human oral mucosa and skin: association with specific cell-cycle phases. Am J Pathol. 2001;158(5):1793–1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Guess J, Burch JB, Ogoussan K, Armstead CA, Zhang H, Wagner S, Hebert JR, Wood P, Youngstedt SD, Hofseth LJ, Singh UP, Xie D, Hrushesky WJ. Circadian disruption, Per3, and human cytokine secretion. Integr Cancer Ther. 2009;8(4):329–336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Wang Y, van Boxel-Dezaire AH, Cheon H, Yang J, Stark GR. STAT3 activation in response to IL-6 is prolonged by the binding of IL-6 receptor to EGF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(42):16975–16980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Janich P, Pascual G, Merlos-Suárez A, Batlle E, Ripperger J, Albrecht U, Cheng HY, Obrietan K, Di Croce L, Benitah SA. The circadian molecular clock creates epidermal stem cell heterogeneity. Nature. 2011;480(7376):209–214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Plikus MV, Van Spyk EN, Pham K, Geyfman M, Kumar V, Takahashi JS, Andersen B. The circadian clock in skin: implications for adult stem cells, tissue regeneration, cancer, aging, and immunity. J Biol Rhythms. 2015;30(3):163–182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Resnitzky D, Gossen M, Bujard H, Reed SI. Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14(3):1669–1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Moulager M, Corellou F, Vergé V, Escande ML, Bouget FY. Integration of light signals by the retinoblastoma pathway in the control of S phase entry in the picophytoplanktonic cell Ostreococcus. PLoS Genet. 2010;6(5):e1000957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Moulager M, Monnier A, Jesson B, Bouvet R, Mosser J, Schwartz C, Garnier L, Corellou F, Bouget FY. Light-dependent regulation of cell division in Ostreococcus: evidence for a major transcriptional input. Plant Physiol. 2007;144(3):1360–1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Sothern RB, Smaaland R, Moore JG. Circannual rhythm in DNA synthesis (S-phase) in healthy human bone marrow and rectal mucosa. FASEB J. 1995;9(5):397–403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Laerum OD, Sletvold O, Riise T. Circadian and circannual variations of cell cycle distribution in the mouse bone marrow. Chronobiol Int. 1988;5(1):19–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Tannock IF. The five Rs of chemotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(6):703–705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Sapozink MD, Deschner EE, Hahn EW. Induction of mitotic synchrony by intermittent hyperthermia in Ehrlich carcinoma in vivo. Nature. 1973;244(5414):299–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Smaaland R, Lote K, Sothern RB, Laerum OD. DNA synthesis and ploidy in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas demonstrate intrapatient variation depending on circadian stage of cell sampling. Cancer Res. 1993;53(13):3129–3138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Matsu-Ura T, Dovzhenok A, Aihara E, Rood J, Le H, Ren Y, Rosselot AE, Zhang T, Lee C, Obrietan K, Montrose MH, Lim S, Moore SR, Hong CI. Intercellular Coupling of the cell cycle and circadian clock in adult stem cell culture. Mol Cell. 2016;64(5):900–912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Bogoeva M, Mileva M, Tsanova K, Gabev E. Circadian variations of cell division in mouse esophagus at LL and DD conditions and effects of daily melatonin treatment. Compt Rend Acad Bulg Sci. 2004;57(1):97. [Google Scholar]
- 106. Alcala SE, Benton AS, Watson AM, Kureshi S, Reeves EM, Damsker J, Wang Z, Nagaraju K, Anderson J, Williams AM, Lee AJ, Hayes K, Rose MC, Hoffman EP, Freishtat RJ. Mitotic asynchrony induces transforming growth factor-β1 secretion from airway epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014;51(3):363–369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Liu B, Taioli E. Seasonal variations of complete blood count and inflammatory biomarkers in the US population - analysis of NHANES data. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0142382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Juan G, Hernando E, Cordon-Cardo C. Separation of live cells in different phases of the cell cycle for gene expression analysis. Cytometry. 2002;49(4):170–175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Lévi FA, Canon C, Touitou Y, Reinberg A, Mathé G. Seasonal modulation of the circadian time structure of circulating T and natural killer lymphocyte subsets from healthy subjects. J Clin Invest. 1988;81(2):407–413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Miki T, Matsumoto T, Zhao Z, Lee CC. p53 regulates Period2 expression and the circadian clock. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Gotoh T, Vila-Caballer M, Santos CS, Liu J, Yang J, Finkielstein CV. The circadian factor Period 2 modulates p53 stability and transcriptional activity in unstressed cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2014;25(19):3081–3093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Ankers JM, Awais R, Jones NA, Boyd J, Ryan S, Adamson AD, Harper CV, Bridge L, Spiller DG, Jackson DA, Paszek P, Sée V, White MRH. Dynamic NF-κB and E2F interactions control the priority and timing of inflammatory signalling and cell proliferation. eLife. 2016;5:e10473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Loewenstein WR. Junctional intercellular communication and the control of growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979;560(1):1–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Burton AC, Canham PB. The behaviour of coupled biochemical oscillators as a model of contact inhibition of cellular division. J Theor Biol. 1973;39(3):555–580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.