An erroneous panel was included in Figure 6 in a previous version of this paper. The representative image of mEPSC recording traces shown in Figure 6A was not correct and inadvertently copied from that of Figure 2C. The correct panel in Figure 6A has now been corrected online. This error was only incurred during figure preparation and does not affect the results and conclusions of the study. The authors deeply regret this oversight.
Figure 6A.
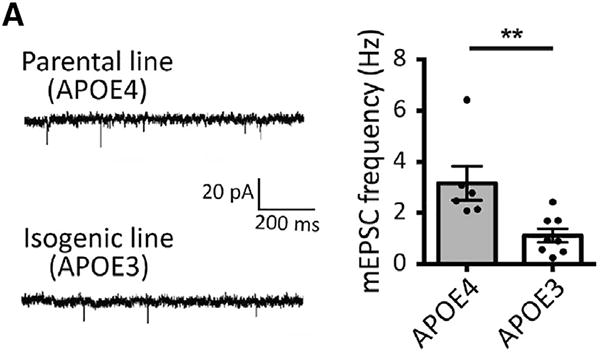
Converting APOE4 to APOE3 Attenuates AD-Related Phenotypes in sAD iPSC-Derived Neurons, Glia, and Organoids (corrected)
Figure 6A.
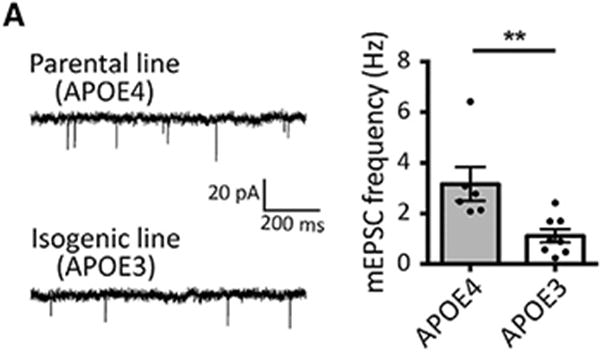
Converting APOE4 to APOE3 Attenuates AD-Related Phenotypes in sAD iPSC-Derived Neurons, Glia, and Organoids (original)


