 A homologous series of electronically tuned ligands were prepared and some of their corresponding Fe complexes were prepared and a Hammett plot of the rates of O2 reduction allowed us to infer important details of the mechanism.
A homologous series of electronically tuned ligands were prepared and some of their corresponding Fe complexes were prepared and a Hammett plot of the rates of O2 reduction allowed us to infer important details of the mechanism.
Abstract
A homologous series of electronically tuned 2,2′,2′′-nitrilotris(N-arylacetamide) pre-ligands (H3LR) were prepared (R = NO2, CN, CF3, F, Cl, Br, Et, Me, H, OMe, NMe2) and some of their corresponding Fe and Zn species synthesized. The iron complexes react rapidly with O2, the final products of which are diferric mu-oxo bridged species. The crystal structure of the oxidized product obtained from DMA solutions contain a structural motif found in some diiron proteins. The mechanism of iron mediated O2 reduction was explored to the extent that allowed us to construct an empirically consistent rate law. A Hammett plot was constructed that enabled insightful information into the rate-determining step and hence allows for a differentiation between two kinetically equivalent O2 reduction mechanisms.
Introduction
Molecular oxygen (O2) dependent iron oxygenases are important in a variety of life processes such as respiration and drug metabolism. Therefore, a fundamental grasp of the elementary steps involved is of great significance. However, the diverse1,2 primary and secondary coordination sphere of the enzyme active sites that cause different selectivity3,4 and observed reactive intermediates5,6 make a general understanding of the mechanism a complicated matter. The initial step in a mechanism involving O2 produces a formally Fe(iii)-superoxide species via an inner or outer sphere electron transfer mechanism. These two limiting cases are difficult to distinguish.7,8 Studies that might enable differentiation by testing specific hypotheses in enzymatic O2 activation require systematic variations of a metalloprotein active site. However, a major challenge to this approach is the inherent difficulty associated with changes to an active site by means of site-directed mutagenesis, not to mention loss of activity that may result from such alterations. The systematic electronic and steric tuning of synthetic enzyme models offers a potential solution to this dilemma.9–11
One of the most powerful techniques used to investigate mechanism that takes advantage of systematic changes is the linear free energy relationship in the form of a Hammett plot.12 While linear free energy relationships have been used to great success in understanding O2 activation,10,13 the specific use of the Hammett plot in inorganic and organometallic reactions is not as common and, to our knowledge, only a few reports have demonstrated the utility of the Hammett plot in O2 reduction by synthetic non-heme iron complexes.14,15 The first step in O2 activation at non-heme centers, namely the two limiting cases of inner vs. outer sphere reduction of O2, has not been thoroughly addressed when compared to heme analogues that have been extensively studied.7,16–18 In fact, the discussion about O2 binding and reduction in non-heme centers is predominantly described as an inner sphere process.9,19 While an inner sphere reduction to form FeIII-superoxo species is reasonable and probably true in many cases, the alternative outer sphere description is equally plausible.
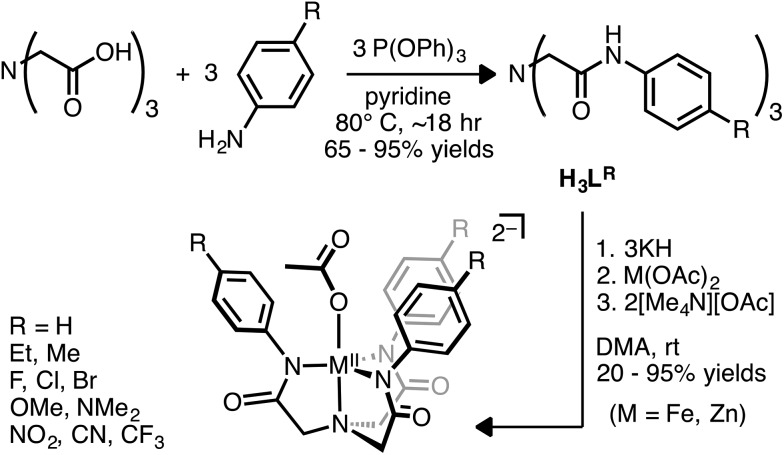
To this end, we report a systematically varied series of N-arylacetamide ligands that contain remote substituents for electronic tuning of metal–ligand bonding for the purpose of using a Hammett plot to gain insight into the rate-limiting step of O2 reduction. Herein we report the synthesis and characterization of these new ligands in addition to the biologically relevant Fe and Zn metal complexes. Finally, the iron complexes react with molecular oxygen and the mechanism of this reaction was deciphered with the aid of a Hammett plot. To our knowledge, this study serves as the first kinetic analysis that specifically attempts to address the outer vs. inner sphere hypothesis in non-heme iron enzyme model complexes.
Results and discussion
Synthesis of ligands
The new ligands described in this report are based after the tris-acetamide ligands first used by Borovik and coworkers.20 They prepared a variety of aliphatic and aryl acetamide ligands and used them in coordination chemistry studies with first-row transition metal complexes including O2 activation21–23 and stabilization of unusual electronic24,25 and coordination environments.20 We adopted the synthetic strategy for the known 2,2′,2′′-nitrilotris(N-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)acetamide) compound (H3Ldmp)25 to prepare the new ligands, which involves heating a solution of nitrilotriacetic acid in pyridine and triphenylphosphite with the appropriate aniline (Scheme 1). Eleven ligands H3LR (R = NO2, CN, CF3, F, Cl, Br, Et, Me, H, OMe, NMe2) were thus obtained in good yield and high purity. A plot of the 1H-NMR acetamide NH resonance vs. the Hammett parameters reveals a linear correlation (Fig. S1†) confirming electronic communication between the substituents and the arylacetamide nitrogen atom26,27 that will serve as the donor to a transition metal ion.
Scheme 1. Synthesis of H3LR and metal complexes.
Metal complex synthesis and characterization
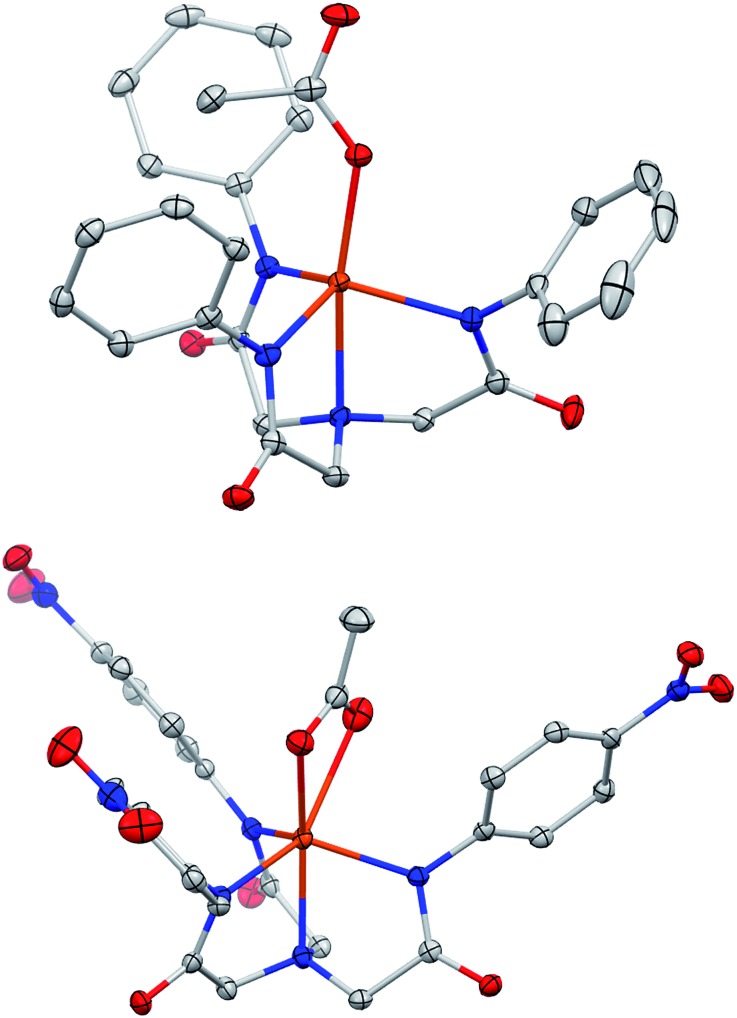
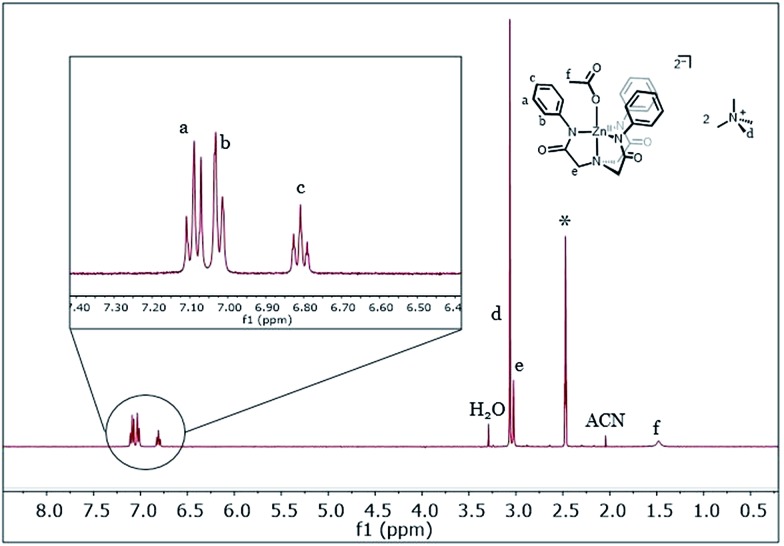
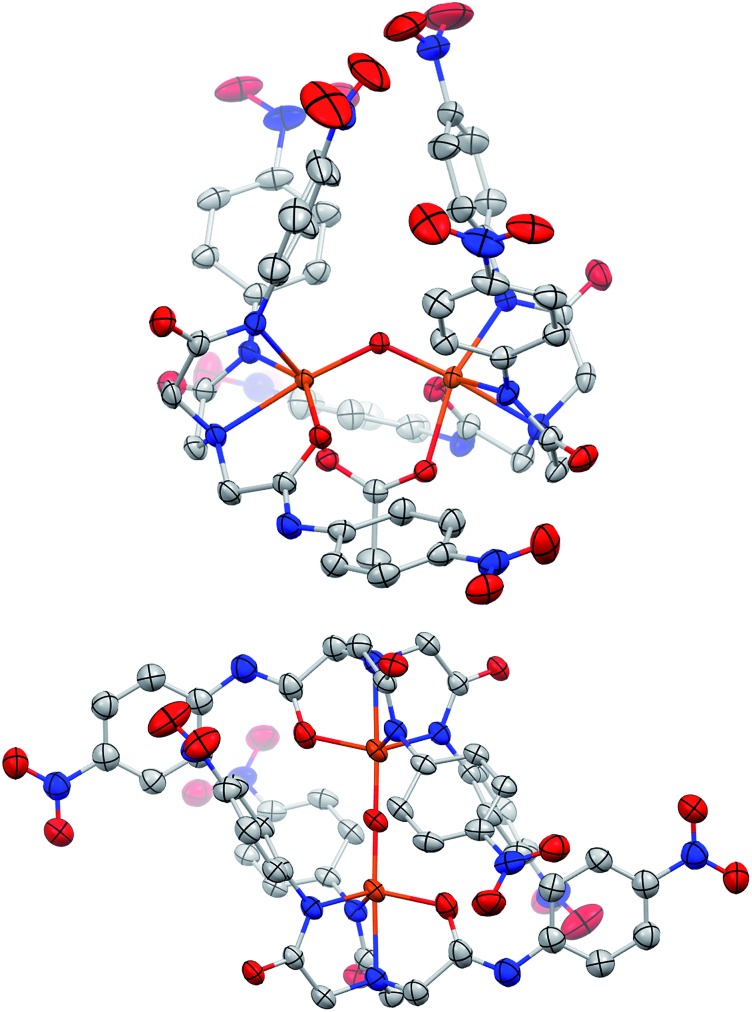
The ligands can be deprotonated in dimethylacetamide (DMA) solvent with three equiv. of KH to afford the respective ligand salt. These are then treated with M(OAc)2 (M = Fe or Zn) followed by two equiv. of [Me4N][OAc]. The resulting KOAc is easily removed by filtration and subsequent recrystallization of the complexes afford [Me4N]2[MLR(OAc)] salts. The [Me4N]2[MLNO2(OAc)] and [Me4N]2[MLH(OAc)] (M = Fe, Zn) salts were characterized by XRD. The [Me4N]2[MLH(OAc)] complexes adopt trigonal bipyramidal geometries while the [Me4N]2[MLNO2(OAc)] (M = Zn, Fe) species have distorted six-coordinate geometries (Fig. 1 and S3, Table S1†). When M = Fe, the acetato ligand adopts a bidentate orientation for R = NO2 (1NO2) rather than the monodentate mode in the R = H molecules (1H), possibly indicating a more electron deficient metal. The acetate ligation in the respective Zn complexes (R = H, NO2) is similar to the iron complexes except that the long Zn–O in [ZnLNO2(OAc)] is about 0.4 Å longer. The solution state-structure of the two Zn complexes (R = H and NO2) was probed by 1H-NMR spectroscopy. With the exception of a broadened peak for the acetato ligand, which might indicate fluxional ligation or exchange, the peaks are sharp and reveal a C3 symmetric coordination-geometry on the NMR time scale (Fig. 2 and S2†). Hence, we assume that the solution-state structure of the Fe(ii) ions is somewhat similar to the Zn complexes.28,29 The iron salt [Me4N]2[Fe(ii)LNO2(OAc)] (1NO2) was characterized by Mössbauer spectroscopy in the solid state and has parameters consistent with an S = 2 species. This is in agreement with the room temperature solution NMR Evans' method magnetic moment of μeff = 4.91 μB.
Fig. 1. Molecular structures of [Me4N]2[FeLH(OAc)] (1H) (top) and [Me4N]2[FeLNO2(OAc)] (1NO2) (bottom); solvent and counter ion molecules not shown. Ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability and H-atoms removed for clarity. Color scheme: orange = iron; blue = nitrogen; red = oxygen; grey = carbon.
Fig. 2. 1H-NMR 400 MHz 1H-NMR of [Me4N]2[ZnLH(OAc)] (* = d6-DMSO NMR solvent). See ESI Fig. S2† for 1H-NMR of [Me4N]2[ZnLNO2(OAc)].
Bulk oxidation of [FeLNO2(OAc)]2– with O2
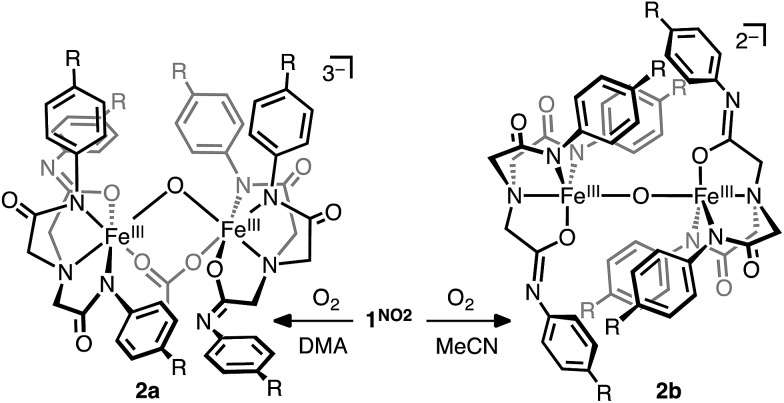
The iron complexes react rapidly with molecular oxygen (pure O2 or in air) forming a red compound (2R). Preparative scale reactions performed using O2 and 1NO2 in DMA or MeCN resulted in good isolated yield (≥88%) of [Me4N]3[{FeIIILNO2}2-(μ-O)-(μ-κ2-(O,O′)-OAc)] (2a) or [Me4N]2[{FeIIILNO2}2-μ-O] (2b), respectively (Scheme 2). In contrast to previous studies using O2 on similar platforms,23 the final products isolated herein are dimeric μ-oxido complexes rather than mononuclear complexes with terminal hydroxido ligands. The lack of steric protection is the probable cause for this difference since the bulky aliphatic-acetamide ligand LiPr stabilizes the terminal hydroxido K[FeLiPr(OH)].23,25 Another major difference between 2a/b and monomeric ferric hydroxido complexes with similar ligands is that one of the ligand arms in 2a/b has an altered binding mode, having undergone tautomerization. As such, each iron center in 2a/b contains one anionic oxygen donor from one of the acetimidate moieties and two anionic nitrogen donors binding in the usual fashion from the other two acetamidate arms. The assignment of the charges on the donor groups is supported by the number of counter ions in the unit cell and the substantial differences in the C–N bond lengths (Table 1). For example, the {K[LdmpFeNO]}7 complex has C–N bond distances of 1.34 Å, which is comparable to 1NO2 and 1H and consistent with the acetamidate ligation. Similarly, two of the C–N bonds in each of the crystallographically related halves of the 2a and 2b molecules are 1.34 and 1.35 Å, respectively, further indicating acetamidate ligation. The remaining C–N bond distance in 2a and 2b is shorter, 1.30 Å, and supports the assignment of acetimidate ligation.
Scheme 2. Synthesis of 2a and 2b (R = NO2) from 1NO2.
Table 1. Crystallographic bond metrics for the Fe complexes with comparative examples a .
| MR | 1H | 1NO2 | 2a | 2b | K[LiPrFeIIIOH] b | {K[LdmpFeNO]}7 c |
| Fe–Namine (Å) | 2.235(2) | 2.231(1) | 2.251(2) | 2.245(2) | 2.194(3) | 2.198(2) |
| Fe–Namidate ave (Å) | 2.015 | 2.158 | 2.114 | 2.027 | 2.022 | 2.026 |
| Ccarbonyl–Nimidate | — | — | 1.304(4) | 1.295(4) | — | — |
| Ccarbonyl–Namidate | 1.338(3) | 1.355(2) | 1.339(4) | 1.349(4) | 1.307(6) | 1.339(3) |
| 1.339(3) | 1.324(2) | 1.341(3) | 1.350(4) | 1.314(5) | 1.339(3) | |
| 1.331(2) | 1.335(2) | — | — | 1.321(4) | 1.341(3) | |
| Fe–Oimidate | — | — | 2.071(2) | 1.977(2) | — | — |
| Fe–X (Å) | 2.046(1) (X = OAc) | 2.111(1) (X = OAc) | 1.800 (X = O) | 1.782(1) (X = O) | 1.876(3) (X = OH) | 1.748(2) (X = NO) |
| Fe–O–Fe (°) | — | — | 128.1 | 180 | — | — |
A key difference between the 2a and 2b is the coordination number at the iron centers (Fig. 3). 2b attains a five coordinate geometry with loss of local three-fold symmetry in the primary coordination sphere due to the tautomerization and hence an asymmetrical binding mode. In contrast, the iron centers in 2a are six-coordinate due to the additional ligation of the bridging acetate ligand. The synthetic procedure for 2a and 2b differ only in the solvent used (DMA and MeCN, respectively). Thus, the formation of two similar dimeric μ-oxido complexes is likely caused by the greater extent to which DMA can stabilize the trianionic 2a during crystallization.
Fig. 3. Molecular structures of [Me4N]3[{FeIIILNO2}2-(μ-O)-(μ-κ2-(O,O′)-OAc)] (2a, top) and [Me4N]2[{FeIIILNO2}2-μ-O] (2b, bottom); solvent and counter ion molecules not shown. Ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability and H-atoms removed for clarity. Color scheme: orange = iron; blue = nitrogen; red = oxygen; grey = carbon. Fe···Fe distance 3.2371(5) Å for 2a and 3.5647(7) Å for 2b.
Interestingly, the structure of 2a resembles carboxylate-oxo-bridged diiron enzymes that are important in a number of biological transformations that use molecular oxygen.30,31 It is well established that the bridging ligands strongly influence the magnetic properties of these active sites and influence chemistry. Similarly here, the binding of acetate to the diferric core appears to influence the magnetic properties of the complex. For example, 2b has a magnetic moment of 2.26 μB (DMSO, room temperature) that is similar to other μ-oxido differic complexes and 2a has a higher magnetic moment of 3.01 μB.32 However, little can be said about these differences because the solution speciation of 2a appears to be complicated. For instance, the UV-vis spectra of 2a and 2b are essentially identical in DMA and suggest that the binding is minimal in solution. In fact, treatment of a solution of 2b in DMA with 0.10, 1.0, 10 and 30 equivalents of [Me4N][OAc] causes a shift in the UV-vis spectrum to lower energy to occur with no isosbestic point implicating multiple binding modes or complicated equilibria (Fig. S6†).
The formation of the mu-oxo species 2NO2 likely forms from the condensation of O2 derived {Fe(iii)OH}n (n = 1 or 2) species.33 To test this premise, we quantified the water produced in the reaction between 1NO2 and O2 in bulk oxidations using 19F-NMR spectroscopy and the water sensitive reagent iodosobenzene difluoride (PhIF2).34 Specifically, the volatiles from a solution of freshly prepared 2b were transferred to a clean, dry flask via trap-to-trap vacuum distillation on a high-vacuum line. The distillate was transferred into a glove box and treated with freshly prepared PhIF2 in solvent dried with newly activated alumina and the solution contents were analyzed by 19F-NMR spectroscopy. Any water in solution reacts with PhIF2 to form the [FHF]– anion, which can be quantified using BF4– internal standard. It was found that about 0.5 equivalent H2O formed per molecule of 1NO2 used (three runs, 54%, 37%, and 30% yield H2O based on iron).
Hence, it is reasonable to assume that “Fe(iii)OH” moieties form in the reaction, likely through a C–H bond cleavage reaction. To further test this hypothesis, we included 10 equiv. of dihydroanthracene (DHA) in a bulk oxidation reaction, but we did not observe anthracene as a product. A likely reactive intermediate in the oxidation of 1R is a superoxo species with an accessible active site that is exposed to free solvent; for such an intermediate, DHA may not be able to compete kinetically with solvent molecules in a bimolecular reaction. Recently, it has been shown that enzymatic and synthetic iron-superoxo species are competent for such transformations,6,19,35–37 but other intermediate species (e.g., oxo) are also possible.
Mechanism of iron mediated O2 reduction
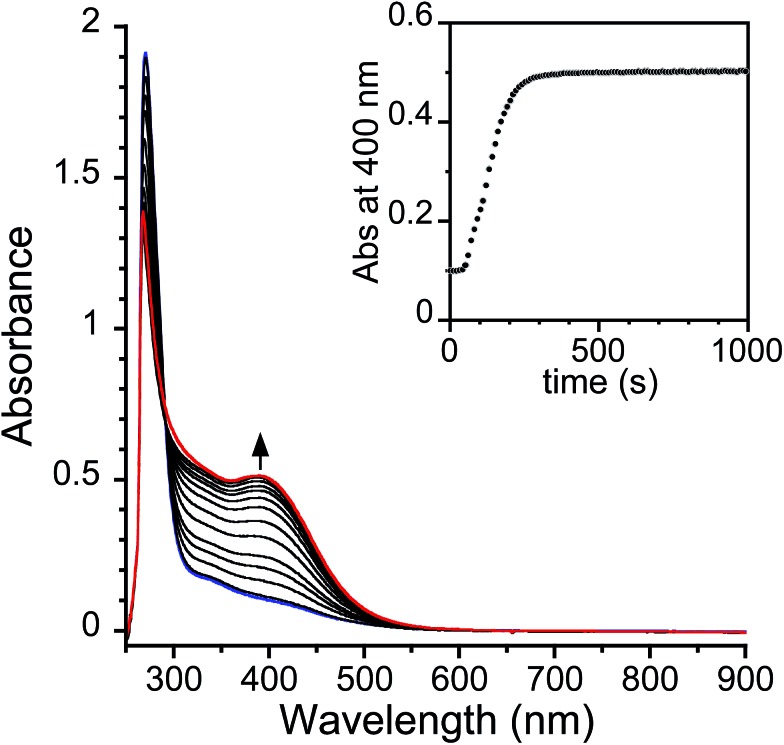
The kinetics of the reactions of [FeLH(OAc)]2– (1H), [FeLCl(OAc)]2– (1Cl), and 1NO2 with O2 in DMA were investigated with UV-vis spectroscopy. The reactions with O2 and 1R in DMA were carried out in Schlenk UV-vis cuvettes that were degassed and equilibrated at 20 °C prior to exposure to 0.75 atm of pure, dry O2. The dissolution of O2 initially causes complication in the kinetic analysis and has been described before as prohibitive to mechanistic studies.38 However, we have conducted a mass transfer analysis that accounts for this complication and is further enabled by the fact that O2 saturation occurs early enough that we can determine first order rate constants (see ESI†). A representative plot of spectra obtained by treatment of 1H in DMA with O2 is shown in Fig. 4. In the case of 1NO2, the UV-vis spectrum of the final species (designated 2NO2) in low concentration experiments is almost identical to 2b with added acetate in solution (Fig. S6†). Specifically, the λmax of the final product is shifted by 10 nm from 2b and has a lower extinction coefficient.32 Considering the complicated equilibrium between 2b and [Me4N][OAc], we propose that the final product generated in UV-vis cuvettes is an isomer of 2a that converts into 2a upon crystallization at higher concentrations. To avoid complications from incomplete knowledge about the speciation of 2R, we performed our kinetic analysis by following the consumption of 1R by method of extent of reaction.
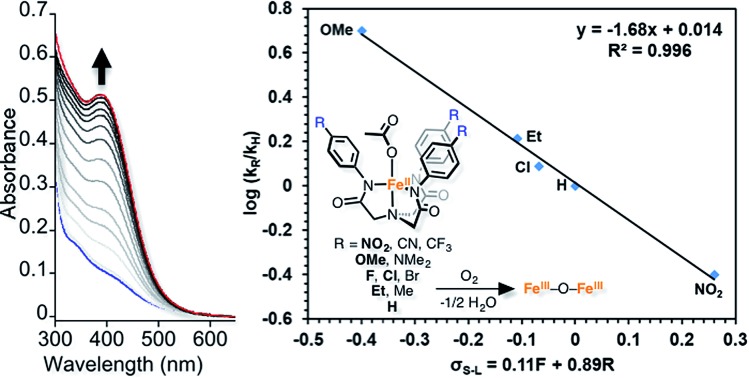
Fig. 4. Representative UV-vis spectra monitoring the oxidation of 1H (0.1 mM) with O2 (0.75 atm) in DMA (20 °C) (blue spectrum = 1H at t = 0; red spectrum = final product at t = 1000). Inset: 400 nm trace with 10 seconds intervals between spectra.
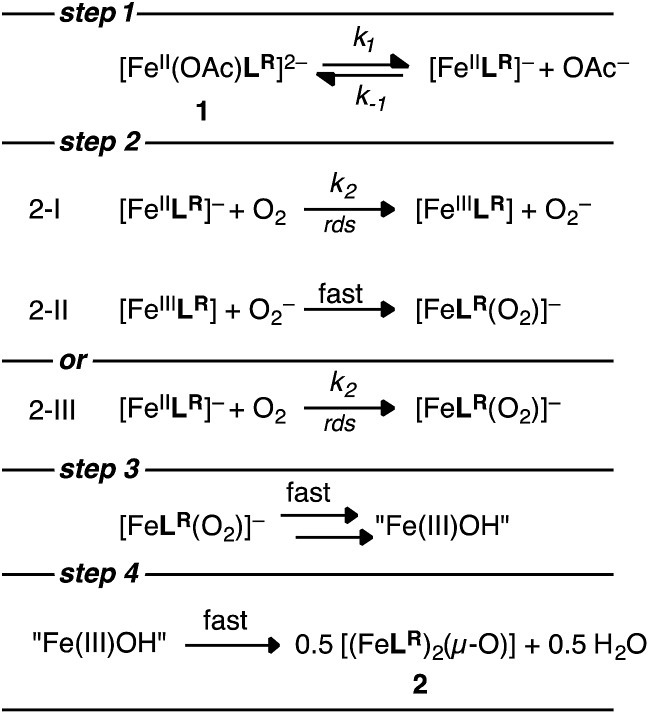
For the three complexes 1H, 1Cl, and 1NO2 it was determined using log–log plots and flooding methods that the reaction is first order in iron and has a complicated dependence on acetate and O2 (Fig. S8–S11†). Taken together, we propose the following mechanism (Scheme 3): (1) reversible acetate dissociation is followed by (2) a rate limiting O2 binding step (step 2-III) or outer sphere electron transfer (step 2-I and 2-II); (3–4) reduction of O2 is then followed by several fast steps to form an iron(iii) compound 2R. A steady-state approximation of the proposed mechanism with the mono anionic [Fe(ii)LR]– serving as the intermediate gives a single term rate law of the following form (see ESI† for derivation):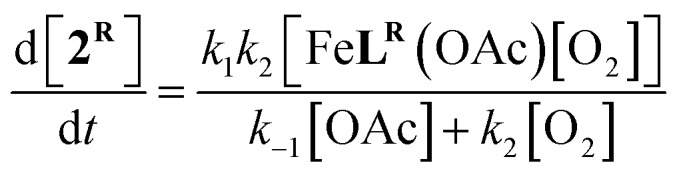
Scheme 3. Proposed O2 reduction mechanism with FeLR.
This rate law simplifies further to kobs [FeLR(OAc)] (eqn S1–S5†). Following consumption of 1R as a function of time provides first order plots with a kobs = 0.017 s–1 ± 0.004 for R = H (Table S2†) that is effectively independent of [FeLR(OAc)]. To further test the rate law, we kept iron concentration constant and varied the concentration of O2 in the presence of additional acetate (20, 30, and 40 equiv. [Me4N][OAc]) and plotted 1/kobs against 1/[O2] (Fig. S10†). The plots with different acetate concentration each furnish a horizontal region with a y intercept = 1/k1 providing a value of k1 = 0.024 ± 0.006 M–1 s–1 (R = H). The values of k2, Keq, and k–1 are 0.39 M–1 s–1, 0.08, and 0.27 M–1 s–1, respectively, were obtained through solving a system of equations (eqn S11–S14†). These values are an estimate that is accurate to the order or magnitude presented due to the tolerance set in the MATLAB code we used to solve the system of equations.
Taking advantage of the fact that the rate law can be approximated by k1[FeLR(OAc)] in the absence of free acetate (k1 ≈ kobs), the rate constant was measured over the temperature range from –10 to 70 °C. Unfortunately, the Eyring plot (see Table S3†) contains a large degree of scatter because the rate has a negligible dependence on temperature; kobs has a value of 0.023 s–1 ± 0.004 from the range of –10 to 70 °C (Table S3†). There also appears to be an inflection point near 10 °C, but the large scatter makes this Eyring plot difficult to interpret and possibly not informative outside the context of other similar studies.
Iron centers that bind O2 often have small enthalpy of activation, reflecting the fact that O2 is a poor ligand.38,39 Our lack of a clear relationship between temperature and rate may also reflect a small entropic contribution. This is only speculative however and there might be other factors such as competing pathways with relatively similar barriers. For instance, Busch observed complicated parabolic dependence of the rate constant with temperature for O2 with myoglobin, hemoglobin, and cyclidene complexes.40 Busch's interpretation of the temperature dependence relied on competing inner and outer sphere O2 reduction pathways in addition to competitive ligand binding – all of which are possible in the system studied here.
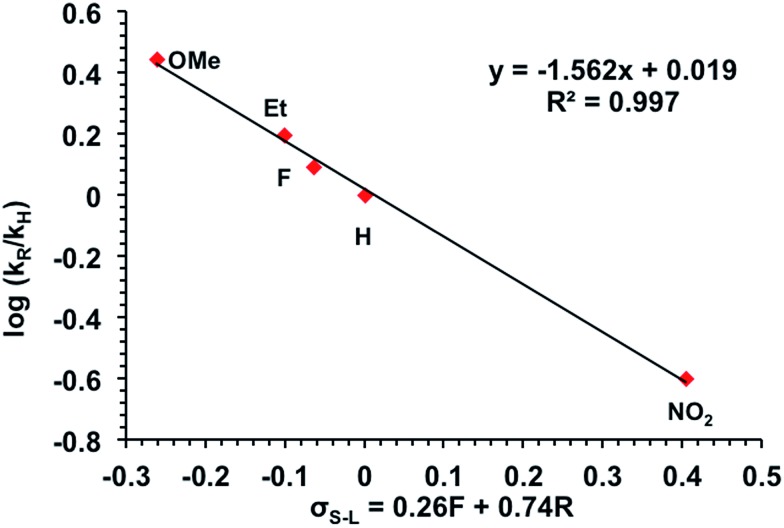
These two possible O2 reduction pathways, one involving rate limiting inner sphere O2 binding and reduction (step 2-III in Scheme 3) and the other rate limiting outer sphere electron transfer followed by rapid superoxide coordination (step 2-I and 2-II, respectively, in Scheme 3), provide the same rate law and are difficult to distinguish. Herein lies the advantage of the Hammett plot to decipher reaction mechanisms. The first order rate constants for five of the 1R complexes were plotted against the Hammett parameter (σ) and from this plot a negative slope was obtained (Fig. 5 and S7†). An even better fit was obtained when we used the Swain–Lupton correlation that takes into account both inductive and resonance effects.41 The negative slope in these plots indicates positive charge build up in the transition state and is expected for an outer sphere electron transfer event. An alternative interpretation is positive charge buildup arises from loss of acetate ligand. However, the rate-determining step is not acetate loss and so we surmise that the data are most consistent with a rate-determining outer sphere electron transfer event.
Fig. 5. Swain–Lupton plot (variation of a Hammett plot) for reaction between 1R and O2 in DMA at 20 °C. The rate constants obtained in triplicate for each substituent are the following: OMe = 0.042 ± 0.01; Et = 0.023 ± 0.005; H = 0.015 ± 0.003; F = 0.018 ± 0.004; NO2 = 0.0038 ± 0.0006. See Fig. S7† for additional Hammett and Swain–Lupton plots.
To put our work in context, Sun and coworkers have studied the O2 reduction dioxygenase model reaction with a six-coordinate non-heme iron complex.15 Assuming that O2 reduction is rate limiting in their reaction, the negative slope in their Hammett plot also indicates that an outer sphere mechanism is operative. This is expected for a six-coordinate iron species. However, Que and coworkers reported a Hammett plot with a positive slope indicating a nucleophilic mechanism for O2 reduction (inner sphere).14 It should be noted that our investigation and Sun's were conducted in DMA and DMF, respectively, whereas Que's investigation was carried out in MeCN. We also briefly investigated the O2 reduction in MeCN and, similarly to Que, constructed a Hammett plot with a positive slope (Fig. S7c†). This positive slope in MeCN suggests an inner sphere mechanism. Hence, the first step in O2 reduction mechanisms appears to have significant solvent dependence.
Conclusions
In summary, we have synthesized eleven new ligands and coordinated them to a variety of first-row transition metals including biologically relevant iron and zinc. The iron compounds react with O2, and we determined the identity of the oxidized iron products for the R = NO2 variant. These products (2NO2) are oxido bridged diferric complexes with unusual acetimidate binding modes resulting from one of the ligand arms of LNO2 having undergone tautomerization. This binding mode has not been observed prior to our work for these acetamidate ligand platforms. Furthermore, the iron centres in 2a are bridged by an acetato ligand and are six-coordinate. The tris-acetamidate ligand platform usually enforces three-fold symmetry that results in the formation of trigonal bipyramidal MIII ions. Hence, the observation of the new six-coordinate binding mode in 2a serves as precedent for hexa coordination of intermediates that might form in water or O2 activation reactions. The differic molecules 2a and 2b also appear to exhibit a fluxional binding of acetate that, in a future study, may provide insight into how acetate binds to differic protein active sites.
The mechanism of the formation of 2R was determined to proceed through a rate limiting reduction of O2 with a rate constant of k2 ≈ 0.4 M–1 s–1. This reduction process was determined to follow acetate dissociation from 1R with an equilibrium constant of 0.08. The dependence of the rate on temperature was minimal, so the Eyring plot was of little value, suggesting that both enthalpy and entropy of activation are close to zero consistent with other O2 binding activation parameters. The use of the Hammett plot revealed a negative slope that is consistent with an outer sphere reduction of O2 in DMA.
The nature of the O2 reduction step in non-heme iron metalloprotein active sites is a fundamental elementary step in O2 activation mechanisms. Thus, this mechanistic investigation – made possible by a series of electronically tuned ligand–metal complexes – serves as an important step in answering questions regarding O2 activation with non-heme iron centres. Namely, what is the nature of the first step in O2 binding in irreversible O2 reduction mechanisms? Is the first elementary step that involves O2 an outer sphere reduction of O2, or is it a binding event that is inner sphere electron transfer in nature? The question has been explored extensively for heme centres, but the situation is rather unclear for non-heme metalloenzyme O2 dependent active sites. Our study serves as the first kinetic analysis that specifically attempts to address the outer vs. inner sphere hypothesis in non-heme iron enzyme model complexes. The data indicates that outer sphere reduction is the first step in DMA, but solvent and probably counterion play a role in changing the mechanism and require further exploration of this challenging problem.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
D. C. L. thanks the University at Buffalo (UB) and the State University of New York Research Foundation start-up funds for financial support. R. S., A. A. D., B.·Y. S. thank the UB Center for Undergraduate Research and Creative Activities Fund. B. Y. S. was additionally supported financially by the UB Honors College Research and Creativity Fund, the UB Department of Chemistry's Peter T. Lansbury Fellowship, and the UB College of Arts and Sciences' Ambassador Academic Enrichment Fund. A. A. D. and R. S were supported in part by the Ralph F. Theuer Chemistry Department Scholarship and R. S. by the UB College of Arts and Sciences Summer Experiential Learning Award for undergraduates. A. E. F. acknowledges S10RR029517 award supporting the instrumentation used for mass spectral analyses. R.G. thanks Dr Yisong Guo for access to CMU Mössbauer instrumentation facilities. R. G. acknowledges start-up funds received from the College of Staten Island and the City University of New York.
Footnotes
†Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 1833291–1833295 and 1833299. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c8sc01621f
References
- Neidig M. L., Solomon E. L. Chem. Commun. 2005:5843–5863. doi: 10.1039/b510233m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitgeb S., Nidetzkty B. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008;36:1180–1186. doi: 10.1042/BST0361180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M., Mehn M. P., Jensen M. P., Que Jr L. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:939–986. doi: 10.1021/cr020628n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Omar M., Loaiza A., Hontzeas N. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:2227–2252. doi: 10.1021/cr040653o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kal S., Que Jr L. J. Biol. Inorg Chem. 2017;22:339–365. doi: 10.1007/s00775-016-1431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Donk W. A., Krebs C., Bollinger J. M. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010;20:673–683. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson L. D., Sauer-Masarwa A., Herron N., Fendrick C. M., Busch D. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993;115:3623–3626. [Google Scholar]
- Shikama K. Chem. Rev. 1993;98:1357–1373. doi: 10.1021/cr970042e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahu S., Goldberg D. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016;138:11410–11428. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b05251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015;48:2744–2753. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. A., Borovik A. S. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015;48:2407–2414. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansch C., Leo A., Taft R. W. Chem. Rev. 1991;91:165–195. [Google Scholar]
- Pegis M. L., McKeown B. A., Kumar N., Lang K., Wasylenko D. J., Zhang X. P., Raugei S., Mayer J. M. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016;2:850–856. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.6b00261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou Y.-M., Que Jr L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995;117:3999–4013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y.-J., Huang Q.-Q., Zhang J.-J. ACS Omega. 2017;2:5850–5860. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b00927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momenteau M., Reed C. A. Chem. Rev. 1994;94:659–698. [Google Scholar]
- Sono M., Roach M. P., Coulter E. D., Dawson J. H. Chem. Rev. 1996;96:2841–2887. doi: 10.1021/cr9500500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier B., de Visser S. P., Shaik S. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:3947–3980. doi: 10.1021/cr020443g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mbughuni M. M., Chakrabarti M., Hayden J. A., Bominaar E. L., Hendrich M. P., Münck E., Lipscomb J. D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010;107:16788–16793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010015107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray M., Yap G. P. A., Rheingold A. L., Borovik A. S. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1995:1777–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Shirin Z., Young Jr V. G., Borovik A. S. Chem. Commun. 1997:1967–1968. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas R. L., Zart M. K., Mukherjee J., Sorrell T. N., Powell D. R., Borovik A. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:15476–15489. doi: 10.1021/ja063935+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee J., Lucas R. L., Zart M. K., Powell D. R., Day V. W., Borovik A. S. Inorg. Chem. 2008;47:5780–5786. doi: 10.1021/ic800048e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray M., Golombek A. P., Hendrich M. P., Young Jr V. G., Borovik A. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996;118:6084–6085. [Google Scholar]
- Ray M., Golombek A. P., Hendrich M. P., Yap G. P. A., Liable-Sands L. M., Rheingold A. L., Borovik A. S. Inorg. Chem. 1999;38:3110–3115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhiryakova D., Ivanov I., Ilieva S., Guncheva M., Galunsky B., Stambolieva N. FEBS J. 2009;276:2589–2598. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.06987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhiryakova D., Guncheva M., Ivanov I., Stambolieva N. Catal. Commun. 2009;11:196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Park Y. J., Cook S. A., Sickerman N. A., Sano Y., Ziller J. W., Borovik A. S. Chem. Sci. 2013;4:717–726. doi: 10.1039/C2SC21400H. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sickerman N. S., Park Y. J., Ng G. K.-Y., Bates J. E., Hillkert M., Ziller J. W., Furche F., Borovik A. S. Dalton Trans. 2012;41:4358–4364. doi: 10.1039/c2dt12244h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasniewski A. J., Que Jr L. Chem. Rev. 2018;118:2554–2592. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz Jr D. M., Boice E., Caranto J. D., Frederick R. E., Masitas C. A. and Miner K. D., Iron: Non-Heme Proteins with Diiron-Carboxylate Active Sites, Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry, 10.1002/9781119951438.eibc0105.pub2. [DOI]
- Schugar H. J., Rossman G. R., Barraclough C. G., Gray H. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972;94:2683–2690. [Google Scholar]
- Autooxidation (dissociation of superoxide from ferric center) is also possible. In this case, solvent reduces free superoxide into water that further reacts with the ferric centers to produce the same final products
- Sun H., Wang B., DiMagno S. G. Org. Lett. 2008;10(20):4413–4416. doi: 10.1021/ol8015429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamanaha E., Zhang B., Guo Y., Chang W.-C., Barr E. W., Xing G., St. Clair J., Ye S., Nesse F., Bollinger J. M., Krebs C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016;138:8862–8874. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b04065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. A., Li W., Pierce B. S. Biochemistry. 2011;50:10241–10253. doi: 10.1021/bi2011724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. W., Kleespies S. T., Stout H. D., Meier K. K., Li P.-Y., Bominaar E. L., Que Jr L., Münck E., Lee W. Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014;136:10846–10849. doi: 10.1021/ja504410s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryatov S. V., Rybak-Akimova E. V., Schindler S. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:2175–2226. doi: 10.1021/cr030709z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak-Akimova E. V., Masarwa M., Marek K., Warburton P. R., Busch D. H. Chem. Commun. 1996:1451–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer-Masarwa A., Dickerson L. D., Herron N., Busch D. H. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1993;128:117–137. [Google Scholar]
- Swain C. G., Lupton E. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968;90:4328–4337. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.