FIG 7 .
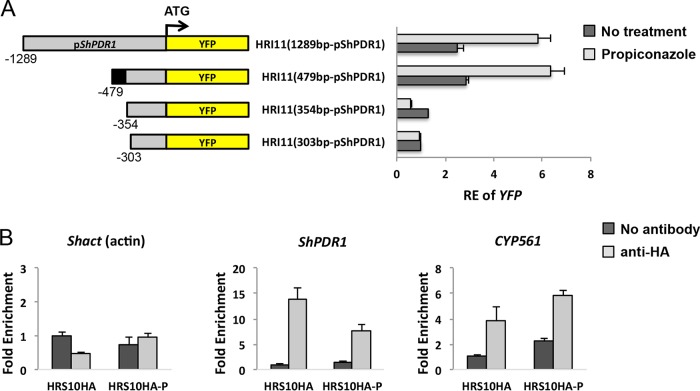
Detection of xenobiotic-responsive element (XRE) and interaction between ShXDR1 and the promoter region of the ShXDR1 target gene regulon. (A) Promoter deletion analysis of pShPDR1-YFP chimeric constructs. The promoter 5′ deletions in ShPDR1 are schematized with their corresponding plasmid constructs and S. homoeocarpa mutants. Relative expression (RE) of YFP is given for each mutant before and after exposure to propiconazole. The black region in −479 bp upstream of ShPDR1 indicates the potential promoter region containing the ShXDR1 binding motif. (B) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis of HA-tagged fusion ShXDR1 occupancy on promoters of ShPDR1 (−448 bp to −342 bp) and CYP561 (−493 bp to −387 bp) in the absence and presence of propiconazole. The presence of the promoter region of ShPDR1, CYP561, or Shact (as a negative control) sequence was assayed by quantitative PCR. The y axis depicts the fold enrichment over a mock immunoprecipitation control that lacks HA antibody. HRS10HA-P indicates HA-expressing strain HRS10 treated with propiconazole (1 µg ml−1).