Abstract
Background
The clinical benefits of a concomitant mitral valve (MV) surgery in patients with moderate ischemic mitral regurgitation (iMR) undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) remain controversial.
Methods
The study involved 710 patients (mean age, 65.0±8.9 years; 504 males) with moderate iMR undergoing CABG between 1990 and 2015. Of these, 116 (16.3%) patients underwent a concomitant MV surgery (MVS; replacement in 10, repair in 106) and 594 (83.7%) underwent CABG only. Clinical and echocardiographic outcomes were compared before and after adjustment with the use of propensity score (PS) analyses.
Results
Early mortality occurred in 22 (3.7%) and 13 (11.2%) patients in CABG-only and CABG with MVS group, respectively (P=0.001). After adjustment, CABG with MVS group showed significantly increased risks of early death (P<0.001), low cardiac output syndrome (LCOS) (P=0.001) and surgical bleeding (P=0.014). During a median follow-up of 78.0 months (quartile 1–3, 33.6–115.9 months), overall mortality occurred in 286 (40.3%) patients. The addition of an MV surgery showed an increased risk of overall mortality [hazard ratio (HR), 1.34; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.99–1.80; P=0.055], which became comparable 1 year after surgery on landmark survival analysis (HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.64–1.39; P=0.772). Improved left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction and LV reverse remodeling were observed in both groups without significant intergroup differences.
Conclusions
The addition of a concomitant MV surgery increased the risk of early mortality and complications in patients with moderate iMR undergoing CABG. In long-term clinical and echocardiographic outcomes, a concomitant MV surgery seemed to confer no significant clinical benefits.
Keywords: Ischemic mitral regurgitation (iMR), coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), mitral valve surgeryv
Introduction
Functional ischemic mitral regurgitation (iMR) is a significant contributor to cardiac failure and mortality (1). The structural remodeling and enlargement of the left ventricle (LV) that accompanies coronary artery disease (CAD) incapacitate the mitral valve (MV) from functioning normally, regardless of the structural integrity of the valve per se (2). Despite the growing evidence predicting poor survival outcomes in patients with uncorrected iMR during surgical revascularization (3), a clear consensus has not yet been established on whether a concomitant MV surgery during coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) can improve the prognosis in such patients (4). Several previous studies have reported some reductions in the severity of MR, following a concomitant MV surgery, but there is limited evidence supporting any benefits regarding the long-term survival or cardiac function (5-7). Furthermore, an additional MV surgery during CABG may also pose problems inherent to the inevitably prolonged duration of surgery and its procedural complexities.
A recent prospective randomized study (8) showed that a concomitant MV surgery during CABG did not produce any significant clinical benefits and increased the risk of early complications, when compared to CABG alone. However, the interpretations from the study were limited by the short follow-up duration of 2 years. Long-term comparative data on clinical outcomes with a reasonable sample size based on the performance of a concomitant MV surgery are scarce. Thus, we evaluated the early and long-term clinical outcomes of patients with moderate iMR, who either underwent CABG alone or CABG with an MV surgery to elucidate any clinical values in performing an additional MV surgery at the time of CABG.
Methods
Study population
From our institutional cardiac surgery database, we identified a total of 7,798 patients with ischemic heart disease who underwent CABG between July 1990 and September 2015 at Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. After the exclusion of patients who had (I) structural MV or aortic valve (AV) pathologies or (II) concomitant AV or aortic root surgery, the final sample included 710 patients with moderate iMR who underwent either CABG only (CABG-only group, n=594) or CABG with a concomitant MV surgery (CABG + MVS group, n=116).
The severity of iMR was graded as mild, moderate or severe, in accordance with the 2015 American Association for Thoracic Surgery Consensus Guidelines (9). Preoperative echocardiographic evaluations were performed on the entire cohort by experienced cardiologists at our institution, who graded the severity of MR by integrating multiple echocardiographic parameters suggested by the recent guidelines (10,11).
The decision to perform additional MV surgeries was based on patients’ demographic and clinical profiles, ultimately at the discretion of the attending surgeon with consideration of the estimated operative risks, after consulting the patient and the family. This study was approved by the institutional review board and ethics committee of Asan Medical Center (No. 2015-1308), which waived the requirement for informed consent because of the retrospective nature of the study design.
Surgical procedures
All patients underwent surgery through a median full-sternotomy. All surgical procedures were carried out under cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) with intermittent antegrade or retrograde cardioplegia, except the patients (n=254) undergoing off-pump CABG in CABG-only group. In situ left internal mammary artery (IMA) was the first choice for grafting to the left anterior descending coronary artery, whenever possible. Saphenous vein grafts and radial arteries were mainly used as secondary conduits and were all harvested with an open technique.
The ring annuloplasty technique used for the patients in CABG + MVS group varied over the course of the study period; these included commercially available partial flexible annuloplasty band and flexible/semi-rigid/rigid annuloplasty ring. Ring sizing was carried out by measuring the inter-commissural distance and the height of the anterior leaflet to ensure annulus downsizing. During MV replacement, whenever feasible, the subvalvular apparatus was preserved. The prosthetic valve type was chosen by the patients after consultation with the operating surgeon.
Definitions and clinical follow-up
The primary early outcomes of interest were early mortality (within 30 days or in-hospital) and early morbidities: postoperative bleeding, low cardiac output syndrome (LCOS) requiring mechanical circulatory support (MCS) such as intra-aortic balloon pump or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, sternal wound infection, early stroke and new-onset dialysis.
The primary long-term outcomes of interest consisted of all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiac events (MACE), including stroke, myocardial infarction (MI), repeat revascularization, hospitalization due to cardiovascular causes. For further measures, we evaluated cardiac functions, including left ventricular (LV) contractility, MR grade and the degree of LV reverse remodeling, assessed by post-operative echocardiography. Clinical follow-up data was collected every 3 to 6 months at the outpatient clinics or by telephone interviews, until the end of March 2016.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were operated with R software, version 3.4.0 (R foundation, Vienna, Austria, http://www.r-project.org/). Categorical variables, expressed either as percentages or frequencies, were compared with the χ2 test. Continuous variables, expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median with range (quartile 1–3), were compared with independent samples t-test. The survival and MACE-free survival data of each group were represented as Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank tests were used to compare their inter-group differences.
To adjust for the differences in the baseline variables between CABG-only and CABG + MVS group, we performed the propensity score (PS) analysis as a weighting variable to yield two well-balanced groups (12). PS was defined as the probability of a patient receiving CABG with a MV surgery in either of the two groups, and was estimated from the multiple logistic regression analysis, incorporating the 26 baseline variables listed in Table 1. Given a long duration of data collection, we included the operative year in the PS analyses to adequately address the time effect; the period was divided based on year 2008, when two surgeons left our institute. In the methodology of inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW), scores for patients in CABG + MVS group were weighted using the formula 1/PS, whereas those for patient in CABG-only group were weighted using the formula 1/(1-PS). The adjustment using IPTW was based on trimmed stabilized weights with robust standard errors. The balance between the two groups after weighting was assessed by standardized mean difference (SMD). Afterwards, the impacts of a concomitant MV surgery on the clinical outcomes were assessed by the weighted logistic regression model and the weighted Cox proportional-hazard model. The proportionality assumption in the Cox model was evaluated with Schoenfeld residuals. Landmark survival analysis was also carried out with a landmark set at 1-year to address whether the impact of a MV surgery on the mortality risk varies across the early and late postoperative periods.
Table 1. Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics.
| Variables | Unadjusted | Balance table (IPTW-adjusted) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CABG-only (n=594) | CABG + MVS (n=116) | P value | CABG-only (n=594) | CABG + MVS (n=116) | SMD (%) | ||
| Age, years | 65.2±8.8 | 63.7±9.4 | 0.101 | 64.9±9.1 | 64.7±8.8 | 3.1 | |
| Female gender | 425 (71.5) | 79 (68.1) | 0.525 | 29.2 | 30.9 | 3.9 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.1±2.8 | 24.2±2.6 | 0.817 | 24.1±2.8 | 24.1±2.4 | 1.2 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 307 (51.7) | 65 (56.0) | 0.449 | 52.5 | 53.7 | 2.4 | |
| Hypertension | 423 (71.2) | 72 (62.1) | 0.064 | 69.8 | 69.3 | 1.1 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 71 (12.0) | 5 (4.3) | 0.023 | 10.7 | 9.8 | 3.0 | |
| COPD | 18 (3.0) | 3 (2.6) | >0.99 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 2.9 | |
| Atrial fibrillation | 62 (10.4) | 11 (9.5) | 0.887 | 10.2 | 10.3 | 0.2 | |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.5±1.7 | 1.7±2.3 | 0.498 | 1.5±1.7 | 1.6±2.2 | 5.0 | |
| Severe CKD | 78 (13.1) | 13 (11.2) | 0.678 | 12.8 | 11.4 | 4.2 | |
| Dialysis | 46 (7.7) | 10 (8.6) | 0.895 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 0.4 | |
| Recent MI (<3 months) | 111 (18.7) | 21 (18.1) | 0.986 | 18.6 | 20.5 | 4.6 | |
| History of stroke | 123 (20.7) | 16 (13.8) | 0.112 | 19.4 | 16.1 | 8.6 | |
| Previous PCI | 111 (18.7) | 21 (18.1) | 0.986 | 18.6 | 19.4 | 2.0 | |
| NYHA class 3 or 4 | 67 (11.3) | 15 (12.9) | 0.726 | 11.6 | 12.6 | 3.0 | |
| CCS class 3 or 4 | 59 (9.9) | 13 (11.2) | 0.804 | 10.1 | 9.3 | 2.5 | |
| Multi-vessel disease | 582 (98.0) | 115 (99.1) | 0.637 | 97.8 | 99.5 | 14.6 | |
| 1-vessel disease | 12 (2.0) | 1 (0.9) | 2.2 | 0.5 | |||
| 2-vessel disease | 63 (10.6) | 18 (15.5) | 10.8 | 12.9 | |||
| 3-vessel disease | 519 (87.4) | 97 (83.6) | 87.0 | 86.6 | |||
| Left main involvement | 140 (23.6) | 30 (25.9) | 0.682 | 23.9 | 23.1 | 1.8 | |
| Echocardiographic data | |||||||
| LV ejection fraction, % | 43.3±13.3 | 39.2±12.5 | 0.002 | 42.6±13.4 | 41.9±12.9 | 5.5 | |
| LVESD, mm | 42.8±9.5 | 45.7±9.0 | 0.002 | 43.3±9.6 | 43.8±8.5 | 5.0 | |
| LVEDD, mm | 56.8±7.4 | 59.7±7.1 | <0.001 | 57.3±7.5 | 58.0±6.5 | 9.7 | |
| LA diameter, mm | 43.9±5.5 | 46.4±5.9 | <0.001 | 44.4±5.6 | 44.8±5.6 | 8.8 | |
| Peak TR pressure gradient, mmHg | 29.8±11.3 | 33.8±12.9 | 0.001 | 30.6±12.1 | 31.6±12.6 | 7.8 | |
| TR ≥ moderate | 20 (3.4) | 10 (8.6) | 0.020 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 0.2 | |
| Emergency | 7 (1.2) | 3 (2.6) | 0.456 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 2.2 | |
| Operative years | 0.618 | 3.5 | |||||
| 1990–2008 | 382 (64.3) | 78 (67.2) | 64.8 | 63.1 | |||
| 2009–2015 | 212 (35.7) | 38 (32.8) | 35.2 | 36.9 | |||
In the left column, values are n (%) or mean ± SD, unless otherwise indicated. In the right column (IPTW-adjusted), values are % or mean ± SD, unless otherwise indicated. CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; BMI, body mass index; CKD, chronic kidney disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; MI, myocardial infarction; NYHA, New York Heart Association; CCS, Canadian cardiovascular society; LV, left ventricle; LA, left atrium; TR, tricuspid regurgitation; SD, standard deviation.
Intergroup as well as intragroup differences in the cardiac function before and after surgery were evaluated by the paired t-test between the PS-matched pairs. The PS-matched pairs were generated by matching between CABG-only and CABG + MVS group on the logit of the PS using calipers of width ≤0.2 of the SD of the logit of the PS. For subgroup analyses, the PS-adjusted hazard ratio (HR) was calculated by incorporating the PS into the Cox model as a covariate. For all statistics, two-sided P values were used, and statistical significance was defined as P value <0.05.
Results
Baseline characteristics and operative profiles
The baseline demographics and clinical characteristics between the two groups are summarized in Table 1. The baseline variables were equivalent for both groups except for hyperlipidemia (P=0.023). Regarding echocardiographic profiles, the patients in CABG + MVS group presented with lower LV ejection fractions (P=0.002), both greater LV end-systolic (LVESD; P=0.002) and end-diastolic dimensions (LVEDD; P<0.001), greater left atrial (LA) diameters (P<0.001) and higher peak tricuspid regurgitation (TR) pressure gradients (P=0.001), compared to CABG-only group. The patients in CABG + MVS group also had more frequent cases of ≥ moderate TR (8.6% vs. 3.4%; P=0.020) than those in CABG-only group.
Operative and coronary grafting profiles were not significantly different between the groups. The number of distal anastomoses and the use of arterial conduit were not different. Among 116 patients in CABG + MVS group, MV repair was performed in 106 (91.4%) patients and the remaining 10 (8.6%) underwent MV replacement (Table 2).
Table 2. Coronary grafting and operative profiles.
| Variable | CABG-only (n=594) | CABG + MVS (n=116) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coronary grafting profiles | |||
| Distal anastomosis | 3.2±1.1 | 3.4±1.2 | 0.090 |
| 1 | 28 (4.7) | 6 (5.2) | |
| 2 | 138 (23.2) | 23 (19.8) | |
| 3 | 225 (37.9) | 33 (28.4) | |
| ≥4 | 203 (34.2) | 54 (46.6) | |
| Use of bilateral ITA | 26 (4.4) | 7 (6.0) | 0.593 |
| No use of ITA | 25 (4.2) | 6 (5.2) | 0.829 |
| Total arterial grafting | 145 (24.4) | 28 (24.1) | 0.931 |
| Operative profiles | |||
| CPB use | 340 (57.2) | 116 (100.0) | |
| CPB time, minutes | 113 [76–166] | 176 [134–219] | <0.001 |
| ACC time, minutes | 68 [50–90] | 75 [54–112] | 0.004 |
| MV surgery | 116 (100.0) | ||
| MV replacement | 10 (8.6) | ||
| MV repair | 106 (91.4) | ||
| Partial flexible band | 32 (27.6) | ||
| Flexible ring | 19 (16.4) | ||
| Rigid ring | 24 (20.7) | ||
| Semi-rigid ring | 23 (19.8) | ||
| Suture technique | 8 (6.9) |
Values are n (%), or mean ± SD or median with range (quartile 1–3), unless otherwise indicated. ITA, internal thoracic artery; CPB, cardiopulmonary bypass; ACC, aorta cross-clamp; MV, mitral valve.
Unadjusted outcomes
Early deaths occurred in 22 (3.7%) patients in CABG-only group, and 13 (11.2%) in CABG + MVS group (P=0.001). Regarding the contributors to early morbidities, the patients in CABG + MVS group were significantly more susceptible to LCOS requiring MCS than those in CABG-only group (10.3% vs. 4.7%; P=0.029). The incidence of other morbidities was similar for both groups (Table 3).
Table 3. Early and long-term outcomes of CABG only vs. CABG with MV surgery group.
| Outcomes | CABG-only (n=594) | CABG + MVS (n=116) | P value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early outcomes, n (%) | |||
| Early mortality | 22 (3.7) | 13 (11.2) | 0.001 |
| Early major morbidity | |||
| LCOS requiring MCS | 28 (4.7) | 12 (10.3) | 0.029 |
| Stroke | 16 (2.7) | 2 (1.7) | 0.776 |
| Bleeding | 20 (3.4) | 7 (6.0) | 0.268 |
| New-onset dialysis | 23 (3.9) | 7 (6.0) | 0.420 |
| Sternal wound infection | 18 (3.0) | 4 (3.4) | >0.99 |
| Long-term outcomes, n (%/PY) | |||
| All-cause mortality | 232 (5.8) | 54 (7.5) | 0.115 |
| MACE | 92 (2.3) | 22 (3.1) | 0.218 |
| Myocardial infarction | 27 (0.7) | 6 (0.8) | 0.621 |
| Repeat revascularization | 10 (0.3) | 1 (0.1) | 0.501 |
| Stroke | 33 (0.8) | 7 (1.0) | 0.741 |
| Hospitalization due to cardiac cause | 48 (1.2) | 13 (1.8) | 0.165 |
| All-cause mortality + MACE | 277 (7.0) | 62 (8.6) | 0.239 |
Values are n (%) for early outcomes and n (% per PY) for long-term outcomes. *, χ2 test for early outcomes and log-rank test for late outcomes. CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; MVS, mitral valve surgery; LCOS, low cardiac output syndrome; MCS, mechanical circulatory support; PY, patient-year; MACE, major cardiac adverse event.
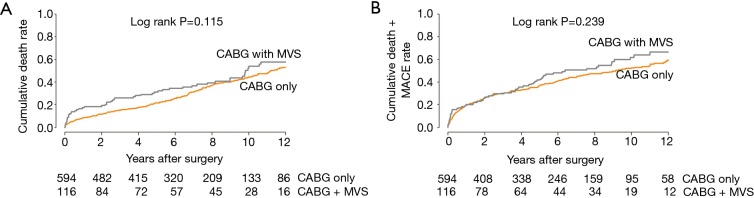
During a median follow-up of 78.0 months [quartile 1–3, 33.6–115.9 months, 4,690.2 patient-years (PY)], the incidence of all-cause mortality was 232 (5.8% per PY) in CABG-only group and 54 (7.5%/PY) in CABG + MVS group (P=0.115). The individual or composite outcomes of MACE between both groups were not significantly different (Table 3). Unadjusted Kaplan-Meier curves did not show significant differences regarding the overall survival (P=0.115) or MACE-free survival (P=0.239) (Figure S1A,B).
Adjusted outcomes
After adjusting with IPTW, the baseline characteristics were well-balanced for both groups, with SMDs <10% for most variables (Table 1, right columns). Table 4 summarizes the results of adjusted risk analyses for clinical outcomes from performing MV surgery. After adjustments, the addition of MV surgery was associated with increased risks for early mortality [odds ratio (OR), 4.62; 95% confidence interval (CI), 2.40–8.77; P<0.001] and several contributors to morbidity: LCOS (OR 3.03; 95% CI, 1.54–5.77; P=0.001), bleeding (OR, 2.73; 95% CI, 1.18–5.93; P=0.014) and new-onset dialysis (OR, 3.45; 95% CI, 1.65–6.97; P=0.001).
Table 4. Comparative outcomes of CABG-only vs. CABG with MV surgery group.
| Outcomes | Unadjusted | IPTW-adjusted | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR/HR* | 95% CI | P value | OR/HR* | 95% CI | P value | ||
| Early outcomes | |||||||
| Early death | 3.28 | 1.56–6.64 | 0.001 | 4.62 | 2.40–8.77 | <0.001 | |
| LCOS requiring MCS | 2.33 | 1.11–4.63 | 0.019 | 3.03 | 1.54–5.77 | 0.001 | |
| Early stroke | 0.63 | 0.10–2.27 | 0.547 | 0.52 | 0.06–2.06 | 0.434 | |
| Bleeding | 1.84 | 0.71–4.27 | 0.176 | 2.73 | 1.18–5.93 | 0.014 | |
| New-onset dialysis | 1.59 | 0.62–3.63 | 0.294 | 3.45 | 1.65–6.97 | 0.001 | |
| Sternal wound infection | 1.14 | 0.33–3.13 | 0.812 | 1.37 | 0.45–3.46 | 0.537 | |
| Long-term outcomes** | |||||||
| All-cause death | 1.27 | 0.94–1.71 | 0.116 | 1.34 | 0.99–1.80 | 0.055 | |
| MACE | 1.34 | 0.84–2.13 | 0.220 | 1.26 | 0.77–2.06 | 0.362 | |
| Death + MACE | 1.18 | 0.90–1.55 | 0.239 | 1.22 | 0.93–1.61 | 0.150 | |
*, Early outcomes are given as OR; long-term outcomes are given as HR. **, Cox proportional hazards assumption (by Schoenfeld residuals): all-cause death (P=0.096), MACE (P=0.093) and Death + MACE (P=0.883). OR, odds ratio; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; IPTW, inverse probability of treatment weighting; LCOS, low cardiac output syndrome; MCS, mechanical circulatory support; MACE, major adverse cardiac event.
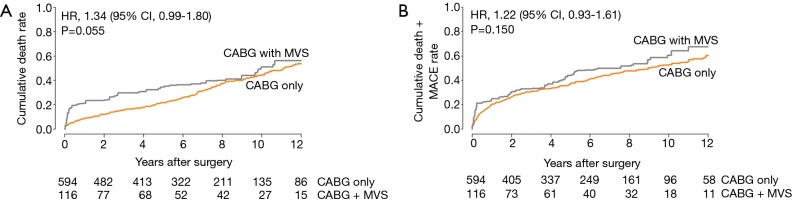
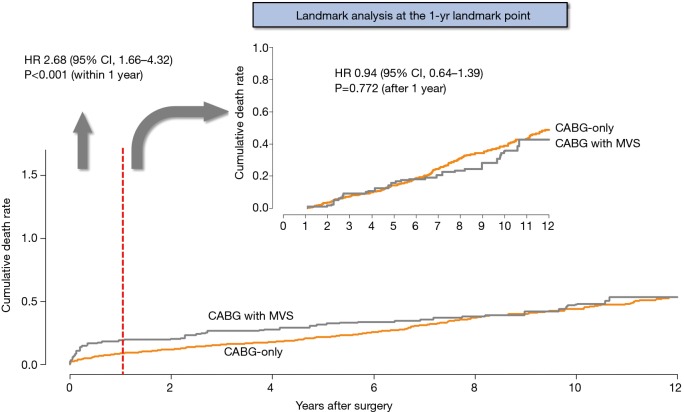
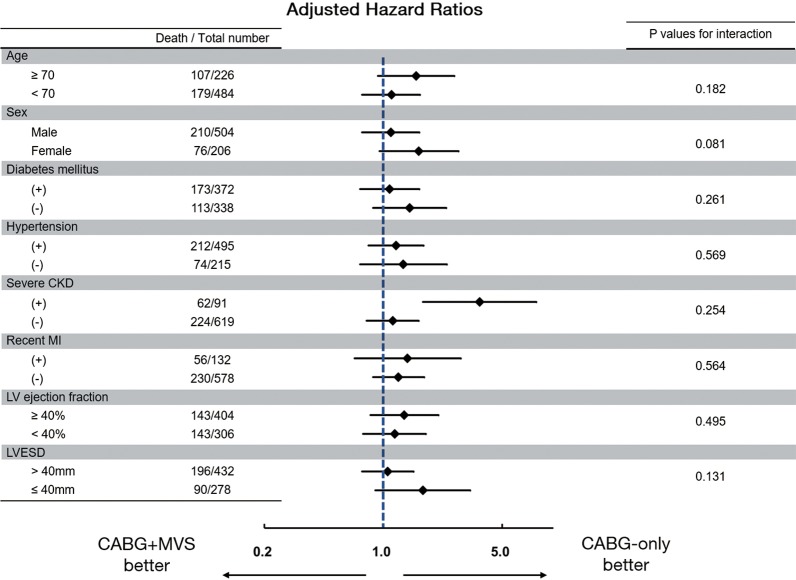
Regarding long-term outcomes, the proportional hazard assumption in the Cox model was satisfied by the evaluation of Schoenfeld residuals (Table 4). In the weighted Cox model, the addition of MV surgery tended to be associated with an increased risk for all-cause death (HR, 1.34; 95% CI, 0.99–1.80; P=0.055) (Figure 1A,B). On the landmark survival analysis, the mortality risk in CABG + MVS group was significantly higher (HR, 2.68; 95% CI, 1.66–4.32; P<0.001) than in CABG-only group within 1 year, which became comparable across the two groups after 1 year (P=0.772) (Figure 2). The increased risk for all-cause death by MV surgery tended to be manifested in most risk subgroups (Figure 3).
Figure 1.
Adjusted Kaplan-Meier curves for (A) overall death and (B) the composite of death and MACE. MACE, major adverse cardiac event; MVS, mitral valve surgery; CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting.
Figure 2.
Adjusted Kaplan-Meier curve for overall death using landmark survival analysis set at 1-year. CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting.
Figure 3.
Adjusted HRs for overall death in CABG + MVS group compared with CABG-only group according to various risk subgroups. MVS, mitral valve surgery; CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; HR, hazard ratio.
Echocardiographic results
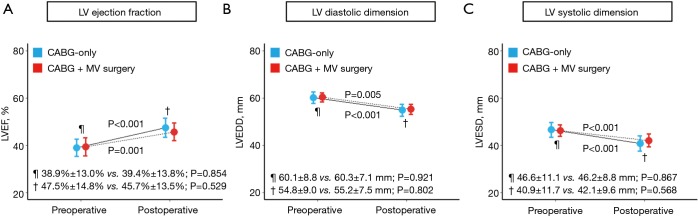
Late echocardiographic data (≥1 year after CABG) were obtained in 386 (54.5%) patients (321 in CABG-only; 65 in CABG + MVS) with a median follow-up of 51.5 months (quartile 1–3, 28.9–86.0 months). After PS matching, a total of 51 pairs, well-balanced across all baseline variables were created. As illustrated in Figure 4, significant improvements in cardiac function, measured by LV ejection fraction, were observed in both CABG-only (P<0.001) and CABG + MVS groups (P=0.001). Also, LV reverse remodeling, manifested by significant interval changes in LVEDD and LVESD, was observed in both groups.
Figure 4.
Echocardiographic results in the propensity-score matched cohorts before and after CABG between CABG-only and CABG + MVS groups. MVS, mitral valve surgery; CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; LV, left ventricle; MV, mitral valve; LVEF, left ventricle ejection fraction; LVEDD, left ventricle end-diastolic dimensions; LVESD, left ventricle end-systolic dimensions.
Regarding MR grade, 33 (64.7%) patients in CABG-only group showed improvements in MR extent. In CABG + MVS group, moderate-to-severe MR remained in 17 (33.3%) patients at the last follow-up. The incidence of MR ≥ moderate was equivalent for both groups (P>0.99) (Figure S2).
Figure S2.
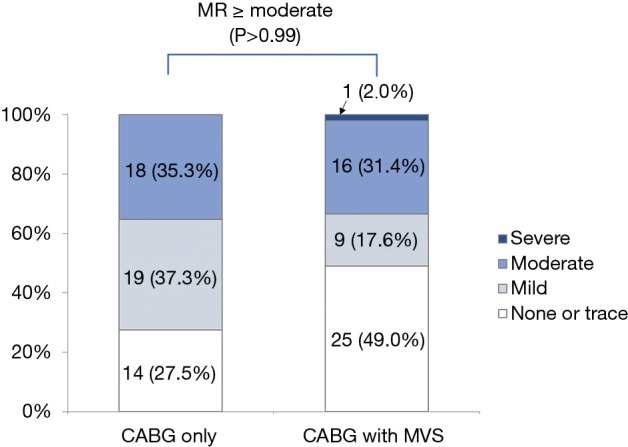
Degree of MR in the propensity score-matched pairs after surgery at the last follow-up. MR, mitral regurgitation; CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; MVS, mitral valve surgery.
Subgroup analysis: patients with CPB use
To adequately address the impact of avoiding CPB on clinical outcomes in CABG-only group, we performed subgroup analyses on 456 patients for whom CPB was used during operation (Table S1). Similar to the analyses results on the entire cohort, the addition of MV surgery was still found to be associated with increased risks for early mortality (OR, 3.21; 95% CI, 1.59–6.48; P=0.001) and other contributors to morbidity: LCOS (OR, 2.64; 95% CI, 1.38–5.00; P=0.002) and new-onset dialysis (OR, 2.88; 95% CI, 1.29–6.36; P=0.009). Regarding long-term outcomes, the mortality risk became similar for both groups after 1 year (P=0.236; Table S2).
Table S1. Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics in the subgroup of patients using CPB.
| Variables | Unadjusted | Balance table (IPTW-adjusted) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CABG-only (n=340) | CABG + MVS (n=116) | P value | CABG-only (n=340) | CABG + MVS (n=116) | SMD (%) | ||
| Age, years | 64.8±8.1 | 63.7±9.4 | 0.226 | 64.5±8.5 | 64.4±8.8 | 1.4 | |
| Female gender | 107 (31.5) | 37 (31.9) | >0.99 | 31.6 | 33.5 | 4.2 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.2±2.8 | 24.2±2.6 | 0.979 | 24.2±2.8 | 24.3±2.6 | 2.6 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 179 (52.6) | 65 (56.0) | 0.600 | 54.3 | 54.7 | 0.9 | |
| Hypertension | 240 (70.6) | 72 (62.1) | 0.112 | 68.9 | 69.6 | 1.4 | |
| Hyperlipidaemia | 53 (15.6) | 5 (4.3) | 0.003 | 12.7 | 14.1 | 4.1 | |
| COPD | 10 (2.9) | 3 (2.6) | >0.99 | 2.8 | 2.1 | 4.1 | |
| Atrial fibrillation | 36 (10.6) | 11 (9.5) | 0.872 | 10.5 | 9.4 | 3.9 | |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.6±2.0 | 1.7±2.3 | 0.586 | 1.6±2.0 | 1.8±2.3 | 9.2 | |
| Severe CKD | 39 (11.5) | 13 (11.2) | >0.99 | 11.1 | 12.7 | 5.0 | |
| Dialysis | 26 (7.6) | 10 (8.6) | 0.891 | 7.8 | 10.9 | 10.8 | |
| Recent MI (<3 months) | 59 (17.4) | 21 (18.1) | 0.966 | 17.6 | 20.4 | 7.3 | |
| History of stroke | 63 (18.5) | 16 (13.8) | 0.307 | 16.9 | 14.9 | 5.4 | |
| Previous PCI | 58 (17.1) | 21 (18.1) | 0.909 | 17.6 | 17.4 | 0.4 | |
| NYHA class 3 or 4 | 23 (6.8) | 15 (12.9) | 0.060 | 8.9 | 8.5 | 1.4 | |
| CCS class 3 or 4 | 19 (5.6) | 13 (11.2) | 0.066 | 6.9 | 6.1 | 3.4 | |
| Multi-vessel disease | 334 (98.2) | 115 (99.1) | 0.806 | 98.0 | 99.5 | 13.5 | |
| 1-vessel disease | 6 (1.8) | 1 (0.9) | 2.0 | 0.5 | |||
| 2-vessel disease | 33 (9.7) | 18 (15.5) | 10.8 | 12.3 | |||
| 3-vessel disease | 301 (88.5) | 97 (83.6) | 87.3 | 87.3 | |||
| Left main involvement | 75 (22.1) | 30 (25.9) | 0.476 | 22.7 | 23.4 | 1.5 | |
| Echocardiographic data | |||||||
| LV ejection fraction, % | 41.8±13.2 | 39.2±12.5 | 0.063 | 40.9±13.4 | 40.2±12.4 | 5.4 | |
| LVESD, mm | 43.4±9.1 | 45.7±9.0 | 0.019 | 44.1±9.1 | 44.5±8.5 | 5.0 | |
| LVEDD, mm | 57.2±7.2 | 59.7±7.1 | 0.001 | 57.9±7.3 | 58.3±6.6 | 6.3 | |
| LA diameter, mm | 44.3±5.5 | 46.4±5.9 | 0.001 | 44.9±5.7 | 45.5±5.4 | 11.5 | |
| Peak TR pressure gradient, mmHg | 29.5±10.4 | 33.8±12.9 | <0.001 | 30.9±11.7 | 31.0±12.2 | 1.5 | |
| TR ≥ moderate | 16 (4.7) | 10 (8.6) | 0.181 | 6.0 | 6.9 | 3.7 | |
| Emergency | 6 (1.8) | 3 (2.6) | 0.871 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 3.1 | |
| Operative years | 0.066 | 2.0 | |||||
| 1990–2008 | 260 (76.5) | 78 (67.2) | 73.6 | 72.7 | |||
| 2009–2015 | 80 (23.5) | 38 (32.8) | 26.4 | 27.3 | |||
In the left column, values are n (%) or mean ± SD, unless otherwise indicated. In the right column (IPTW-adjusted), values are % or mean ± SD, unless otherwise indicated. CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; BMI, body mass index; CKD, chronic kidney disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; MI, myocardial infarction; NYHA, New York Heart Association; CCS, Canadian cardiovascular society; LV, left ventricle; LA, left atrium; TR, tricuspid regurgitation.
Table S2. Comparative outcomes of CABG-only vs. CABG with MV surgery in the subgroup of patients using CPB.
| Outcomes | Unadjusted | IPTW-adjusted | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR/HR* | 95% CI | P value | OR/HR* | 95% CI | P value | ||
| Early outcomes | |||||||
| Early death | 2.40 | 1.11–5.09 | 0.023 | 3.21 | 1.59–6.48 | 0.001 | |
| LCOS requiring MCS | 1.67 | 0.78–3.43 | 0.174 | 2.64 | 1.38–5.00 | 0.002 | |
| Early stroke | 0.83 | 0.12–3.51 | 0.823 | 0.36 | 0.02–1.99 | 0.340 | |
| Bleeding | 1.50 | 0.55–3.69 | 0.398 | 2.22 | 0.91–5.23 | 0.069 | |
| New-onset dialysis | 1.50 | 0.55–3.69 | 0.398 | 2.88 | 1.29–6.36 | 0.009 | |
| Sternal wound infection | 1.07 | 0.29–3.19 | 0.912 | 0.82 | 0.22–2.36 | 0.731 | |
| Long-term outcomes** | |||||||
| All-cause death | 1.32 | 0.96–1.80 | 0.083 | 1.40 | 1.04–1.91 | 0.029 | |
| Up to 1 year | 1.66 | 0.97–2.87 | 0.067 | 1.76 | 1.04–2.96 | 0.035 | |
| After 1 year | 1.18 | 0.80–1.74 | 0.394 | 1.26 | 0.86–1.84 | 0.236 | |
| MACE | 1.14 | 0.70–1.84 | 0.605 | 1.07 | 0.65–1.77 | 0.786 | |
| Death + MACE | 1.10 | 0.82–1.46 | 0.534 | 1.15 | 0.86–1.52 | 0.342 | |
*, Early outcomes are given as odds ratio; long-term outcomes are given as HR; **, Cox proportional hazards assumption (by Schoenfeld residuals): all-cause death (P=0.203), MACE (P=0.056) and Death + MACE (P=0.514). OR, odds ratio; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; IPTW, inverse probability of treatment weighting; LCOS, low cardiac output syndrome; MCS, mechanical circulatory support; MACE, major adverse cardiac event.
Discussion
In the development of iMR, mitral tenting in combination with regional LV myocardial scarring is believed to play an important role (13). Although mitral annuloplasty alone can reduce the degree of iMR, it is believed to have little functional benefits on LV recovery (14). Although consensus exists on the lack of need for a surgical repair to treat mild iMR, it remains controversial how moderate iMR should be managed. Different groups have argued for and against the necessity and the benefits of a concomitant MV surgery during CABG in moderate iMR patients. This study provides an additional insight on the issue based on our institutional data including 710 patients in total.
Several groups have trialed giving a concomitant MV surgery during CABG in an attempt to optimize the resolution for moderate iMR and have found clinical benefits from the additional MV surgery. It has been suggested by some groups that revascularization alone may leave many patients with a residual MR (15) and that significant residual MR will result in increased long-term morbidity and mortality (16). A randomized trial, comparing patients receiving CABG + MV surgery group or CABG-alone, reported an improvement in the New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class and LVEF when MV surgery was supplemented to CABG (17). Furthermore, in the recent RIME Trial (the Randomized Ischemic Mitral Evaluation Trial) (18) based on 73 patients, the supplementation of MV surgery to CABG produced some clinical benefits. However, there were no differences in the 30-day mortality and 1-year mortality between the two groups.
Other groups presented with the opposite view, emphasizing the necessity for a concomitant MV surgery, in moderate iMR patients. It has been argued that revascularization alone can improve regional wall motion and MR grade and that a concomitant MV surgery does not prevent a recurrent iMR (19). Furthermore, even if MR remains after an MV surgery, it does not worsen the functional status or long-term survival (7,14). In addition, despite the comparable 30-day mortality rate for CABG + MV surgery and CABG-alone in a randomized trial and meta-analysis (18,20,21), additional operative mortality still remains as a concern, as also shown in this study. A recent prospective study (8), previously alluded to, reported little clinical benefits from an additional MV repair during CABG. Despite a more significant reduction in MR, other clinical outcomes, including mortality and complications, were found equivalent between the CABG-only and CABG with MV repair groups (21). In addition, the MV repair group showed more neurological and cardiac complications. However, the prospective study is yet to publish any long-term data, making it difficult to make a judgement about the long-term clinical benefits of a concomitant MV surgery.
Analysis of our data revealed little long-term clinical differences between the CABG-only and the CABG + MVS group, 1-year post-surgery, providing evidence for no real benefits of an additional MV surgery. The operative outcomes were only significantly different in short-term, and were equivalent for all long-term comparisons, which was also seen in a subgroup of patients with the use of CPB. Of the short-term operative outcomes, early death was significantly greater in the CABG + MVS group than the CABG-only group, suggesting that a concomitant MV surgery may be clinically harmful. LCOS requiring MCS and new-onset dialysis were also greater in the CABG + MVS group than the CABG-only group after adjustment. Therefore, the clinical outcomes only provided evidence against the use of a concomitant MV surgery, as it offered no additional benefits and increased the likelihood of short-term complications.
In addition, the follow-up echocardiographic results showed decreases in the LVESD and LVEDD and improvements in LVEF in both groups, indicating that LV reverse remodeling occurred in both groups independent of a concomitant MV surgery. These results are consistent with the study results by Bouchard et al. (22). Our study results corroborate these findings, suggesting that improvements in MR can be achieved without an MV surgery long-term. As LV reverse remodeling is a continuous and dynamic process, the disruption of the MV geometry to eliminate MR during CABG may lead to the eventual distortion of the sub-valvular apparatus, raising further questions about the efficacy of an MV surgery to treat iMR.
Our data comes into conflict with some of the previous randomized trials, which suggested clinical benefits in a concomitant MV surgery during CABG (17,18). However, these studies excluded patients with recent MI, urgent surgery or low LV ejection fraction (<30%), all of whom were included in our study. Thus, the discrepancies in the selection criteria for the study population may have had some influence on the differences in the results and conclusions between our study and other previous trials. Furthermore, the term ‘ischemic mitral regurgitation’ has often been very loosely defined (23). However, the term iMR has been interchangeably used in many studies to refer to conditions arising either from an infarction or a reversible ischaemia (24). The two causes of what is termed as “iMR” by many studies would lead to very different clinical outcomes. This may be another reason for the conflicting results and conclusions from previous studies.
Limitations
This study is subject to the limitations inherent to a retrospective analysis of observational data from a single-center. Due to the lack of randomization of the study cohorts, despite the rigorous statistical adjustments employed, selection bias or detection bias may have affected the results and thus the conclusions. Additionally, this study included the study cohort of 25-year clinical experience [1990–2015]. Cardiac surgery has evolved greatly in terms of myocardial protection and technical advancement. Although we could not detect any significant trends in the adverse outcomes throughout the study period, there may be a concern of undetected chronological bias in this study. Finally, the preference of MV repair over replacement did not vary over the study period, but MV surgery techniques in this study included heterogenous procedures with varying choices of prosthesis, which may have affected the study results.
Conclusions
The addition of a concomitant MV surgery increased the risk of early mortality and complications in patients with moderate iMR undergoing CABG. In long-term clinical and echocardiographic outcomes, a concomitant MV surgery in moderate iMR patients seemed not to confer any significant clinical benefits. Thus, CABG-alone should be a preferable surgical option in patients with moderate iMR.
Figure S1.
Unadjusted Kaplan-Meier curves for (A) overall death and (B) the composite of death and MACE. MACE, major adverse cardiac events; MVS, mitral valve surgery.
Acknowledgements
None.
Ethical Statement: This study was approved by the institutional review board and ethics committee of Asan Medical Center (No. 2015-1308), which waived the requirement for informed consent because of the retrospective nature of the study design.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- 1.Gahl K, Sutton R, Pearson M, et al. Mitral regurgitation in coronary heart disease. Br Heart J 1977;39:13-8. 10.1136/hrt.39.1.13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Watanabe N, Ogasawara Y, Yamaura Y, et al. Mitral annulus flattens in ischemic mitral regurgitation: geometric differences between inferior and anterior myocardial infarction: a real-time 3-dimensional echocardiographic study. Circulation 2005;112:I458-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schroder JN, Williams ML, Hata JA, et al. Impact of mitral valve regurgitation evaluated by intraoperative transesophageal echocardiography on long-term outcomes after coronary artery bypass grafting. Circulation 2005;112:I293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kolh P, Windecker S, Alfonso F, et al. 2014 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: the Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2014;46:517-92. 10.1093/ejcts/ezu366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Benedetto U, Melina G, Roscitano A, et al. Does combined mitral valve surgery improve survival when compared to revascularization alone in patients with ischemic mitral regurgitation? A meta-analysis on 2479 patients. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2009;10:109-14. 10.2459/JCM.0b013e32831c84b0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gelsomino S, Lorusso R, De Cicco G, et al. Five-year echocardiographic results of combined undersized mitral ring annuloplasty and coronary artery bypass grafting for chronic ischaemic mitral regurgitation. Eur Heart J 2008;29:231-40. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm468 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mihaljevic T, Lam BK, Rajeswaran J, et al. Impact of mitral valve annuloplasty combined with revascularization in patients with functional ischemic mitral regurgitation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49:2191-201. 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.02.043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Michler RE, Smith PK, Parides MK, et al. Two-Year Outcomes of Surgical Treatment of Moderate Ischemic Mitral Regurgitation. N Engl J Med 2016;374:1932-41. 10.1056/NEJMoa1602003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.American Association for Thoracic Surgery Ischemic Mitral Regurgitation Consensus Guidelines Writing Committee , Kron IL, Acker MA, et al. 2015 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery Consensus Guidelines: Ischemic mitral valve regurgitation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2016;151:940-56. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2015.08.127 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Baumgartner H, Falk V, Bax JJ, et al. 2017 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur Heart J 2017;38:2739-91. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx391 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;63:e57-185. 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.536 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Austin PC, Stuart EA. Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies. Stat Med 2015;34:3661-79. 10.1002/sim.6607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Srichai MB, Grimm RA, Stillman AE, et al. Ischemic mitral regurgitation: impact of the left ventricle and mitral valve in patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Ann Thorac Surg 2005;80:170-8. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.01.068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kang DH, Kim MJ, Kang SJ, et al. Mitral valve repair versus revascularization alone in the treatment of ischemic mitral regurgitation. Circulation 2006;114:I499-503. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.000398 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Aklog L, Filsoufi F, Flores KQ, et al. Does coronary artery bypass grafting alone correct moderate ischemic mitral regurgitation? Circulation 2001;104:I68-75. 10.1161/hc37t1.094706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hickey MS, Smith LR, Muhlbaier LH, et al. Current prognosis of ischemic mitral regurgitation. Implications for future management. Circulation 1988;78:I51-9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fattouch K, Guccione F, Sampognaro R, et al. POINT: Efficacy of adding mitral valve restrictive annuloplasty to coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with moderate ischemic mitral valve regurgitation: a randomized trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009;138:278-85. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.11.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chan KM, Punjabi PP, Flather M, et al. Coronary artery bypass surgery with or without mitral valve annuloplasty in moderate functional ischemic mitral regurgitation: final results of the Randomized Ischemic Mitral Evaluation (RIME) trial. Circulation 2012;126:2502-10. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.143818 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hung J, Papakostas L, Tahta SA, et al. Mechanism of recurrent ischemic mitral regurgitation after annuloplasty: continued LV remodeling as a moving target. Circulation 2004;110:II85-90. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000138192.65015.45 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Smith PK, Puskas JD, Ascheim DD, et al. Surgical treatment of moderate ischemic mitral regurgitation. N Engl J Med 2014;371:2178-88. 10.1056/NEJMoa1410490 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Virk SA, Tian DH, Sriravindrarajah A, et al. Mitral valve surgery and coronary bypass grafting for moderate-to-severe ischemic mitral regurgitation: Meta-analysis of clinical and echocardiographic outcomes. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;154:127-36 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.03.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bouchard D, Jensen H, Carrier M, et al. Effect of systematic downsizing rigid ring annuloplasty in patients with moderate ischemic mitral regurgitation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2014;147:1471-7. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.05.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Borger MA, Alam A, Murphy PM, et al. Chronic ischemic mitral regurgitation: repair, replace or rethink? Ann Thorac Surg 2006;81:1153-61. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.08.080 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sundt TM. Surgery for ischemic mitral regurgitation. N Engl J Med 2014;371:2228-9. 10.1056/NEJMe1412045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]