Fig. 2.
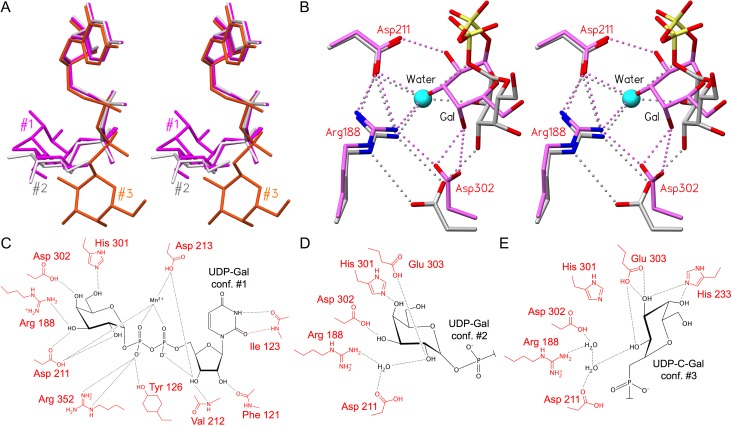
GTA and GTB donors adopt the same series of intermediate and catalytic conformations, each with a distinct set of hydrogen bonds. (A) Overlap of three donor conformations with tucked under conformation #1 in magenta (PDB code 2RJ7), intermediate conformation #2 in light gray (PDB code 5C1L) and “extended” conformation #3 in orange (PDB code 5C3D) (Alfaro et al. 2008; Gagnon et al. 2015). (B) Stereoview of the superposition of AABB (PDB code 2RJ7; conformation #1; magenta) and GTB (PDB code 5C1L; conformation #2; carbon atoms colored light gray) crystal structures depicting salt bridge and hydrogen bond interactions among Arg188, Asp211, Asp302, a water molecule (cyan sphere) and donor galactose. Interactions include a single/bidentate salt bridge between Arg188 and Asp302. In donor conformation #2, a water molecule occupies the same position as donor Gal-O3 in conformation #1. Except where otherwise indicated, atoms are colored by element with oxygen red, nitrogen blue and phosphorous yellow. (C–E) Schematic depictions of hydrogen bond interactions (black lines) between (C) UDP-Gal in tucked under conformation #1 and chimeric enzyme AABB (PDB code 2RJ7), (D) the substrate Gal moiety in the intermediate conformation #2 (PDB code 5C1L; GTB) and (E) in the extended conformation #3 (PDB code 5C3D; ABBB). Key active site resides are labeled in red and the donor sugar in black.