Figure 4. BK acidic residues potentially exposed to extracellular medium.
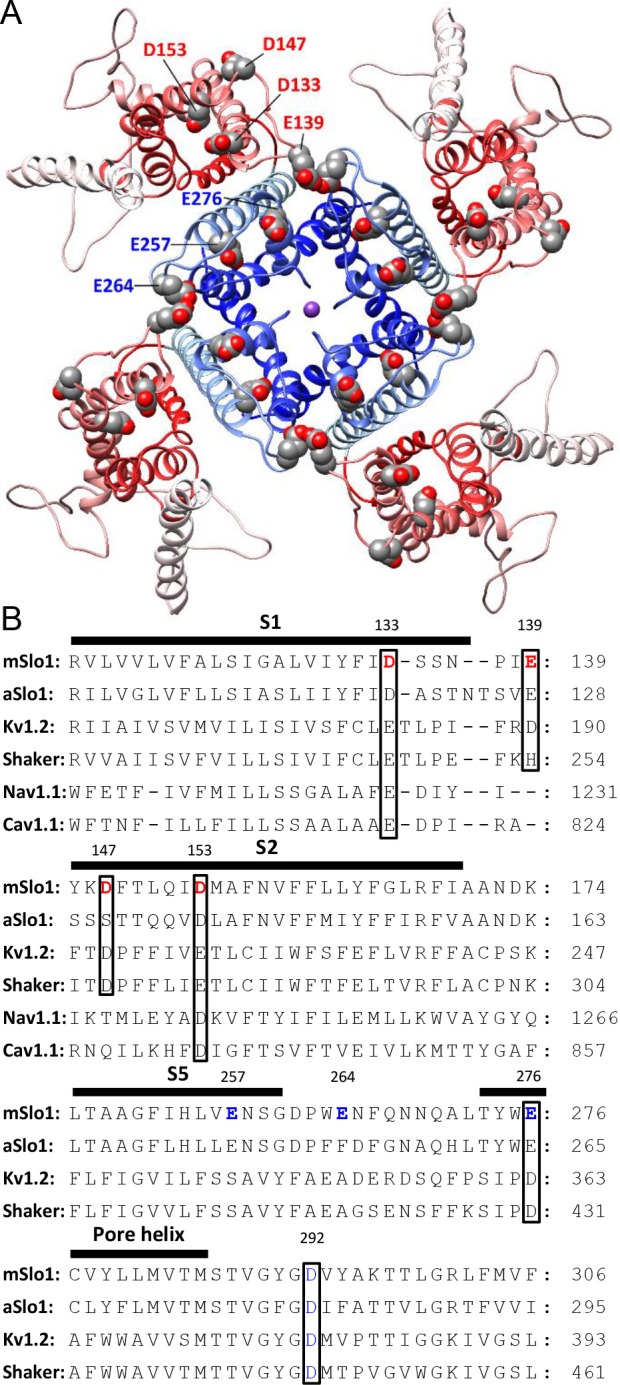
(A) mSlo1 homology model based on the cryo-EM structure of liganded Aplysia BK channel (PDB: 5tj6) viewed from the extracellular side. Acidic residues potentially exposed to extracellular solution are rendered as spheres with oxygen and carbon colored in red and gray, respectively. The BK VSDs and PGD are colored in red and blue, respectively. The purple dot in the center is K+. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of transmembrane segments containing extracellularly accessible acidic residues from mouse and Aplysia homologues of Slo1 (mSlo1, aSlo1), Kv channels (Kv1.2, Shaker), and human Nav1.1 and Cav1.1 channels. For the latter two channels, only the DIII VSD segments were included in the alignment. Extracellularly accessible acidic residues conserved among these channels are indicated by boxes. Residues examined in the present study are bold.
