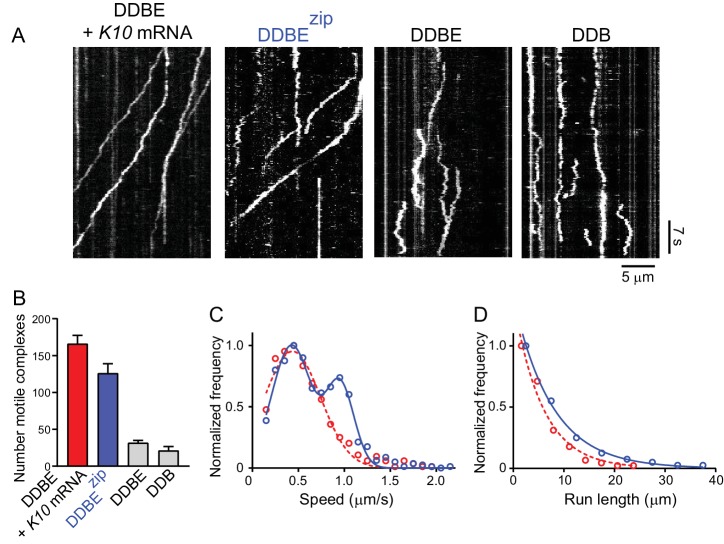
Figure 10. A truncated Egl-leucine zipper construct supports motility in the absence of mRNA.
(A) Kymographs illustrating motion of mRNPS reconstituted from dynein-dynactin-BicD-Egl-K10 mRNA, dynein-dynactin-BicD-Eglzip, dynein-dynactin-BicD-Egl, or dynein-dynactin-BicD. (B) Run frequency normalized to dynein concentration and time for the same four scenarios illustrated in panel A. (C) Bimodal speeds of dynein-dynactin-BicD-Eglzip (blue circles), with the slower population moving at 0.43 ± 0.21 μm/s and the faster population at 0.95 ± 0.15 μm/s (n = 633). For comparison, dynein-dynactin-BicD-Egl-K10 mRNA (red circles) moved at 0.44 ± 0.31 μm/s (n = 560) (p<0.001, t-test, mean ± SD) (D) Run lengths of dynein-dynactin-BicD-Eglzip (blue circles) were longer than those of dynein-dynactin-BicD-Egl-K10 mRNA (red circles) (7.6 ± 0.03 μm, n = 84 vs. 5.7 ± 0.09 μm, n = 106; p=0.03, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, mean ± SE). See Figure 10—source data 1.