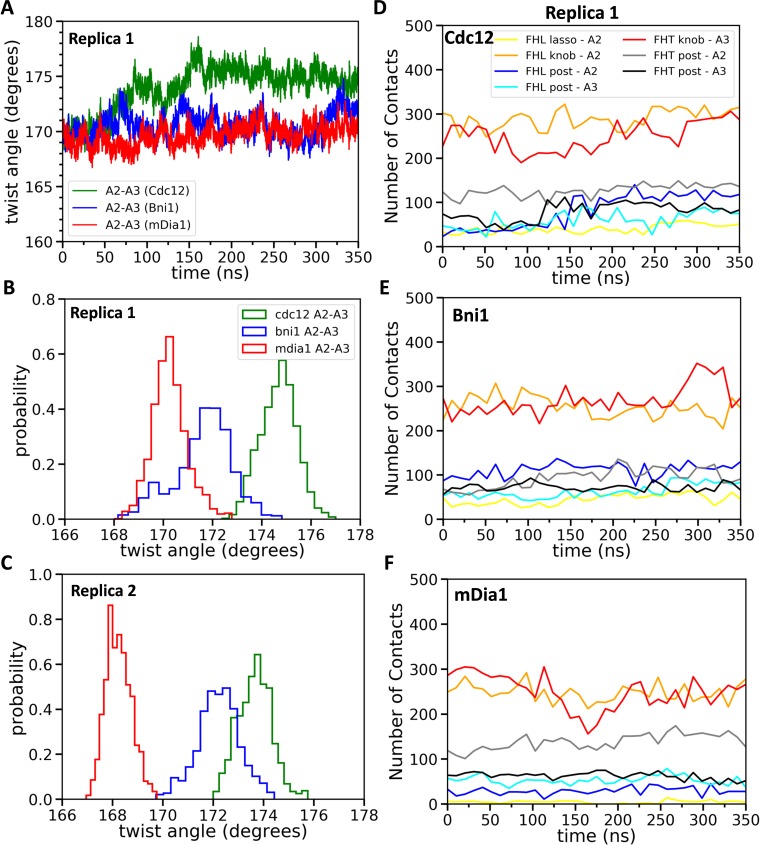
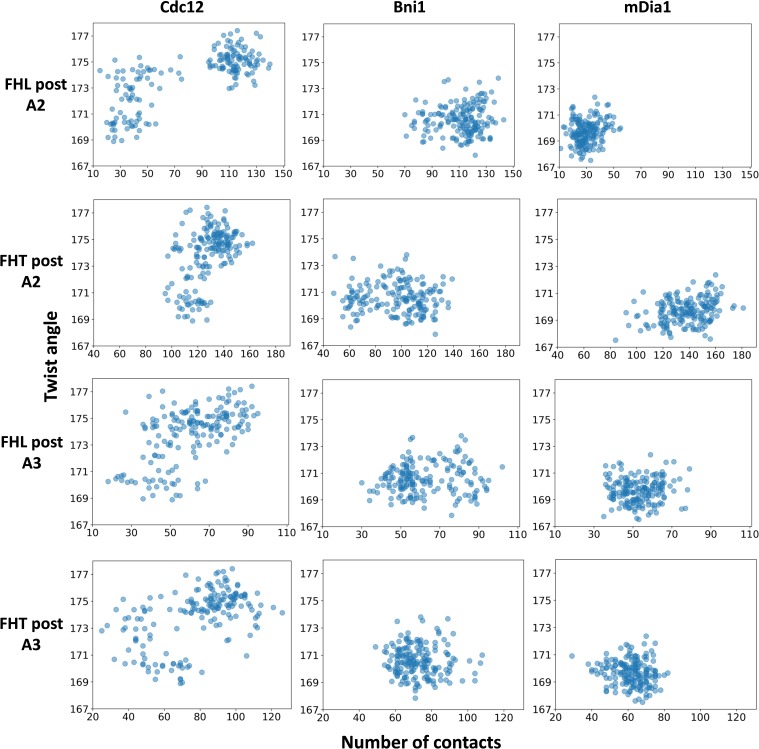
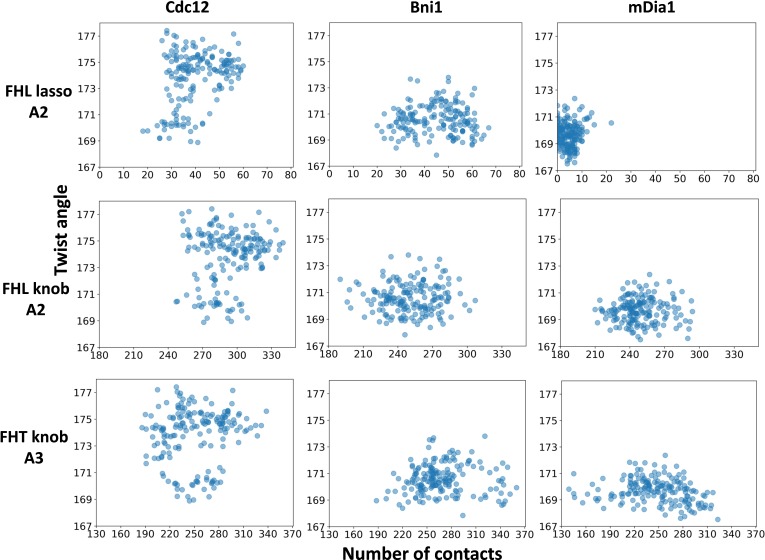
Figure 5. Effect of FH2 domains on the barbed end configurations of actin five-mer filaments before the addition of actin subunit A1.
(A) The helical twist angles between actin subunits A2 and A3 as a function of time during 350 ns of all-atom MD simulations (replica 1) of the FH2 domains of Bni1, Cdc12 and mDia1 associated with the actin filament five-mer consisting of subunits A2, A3, A4, A5 and A6. The initial structures in these simulations were generated by removing subunits A1 and A7 at the end of 200 ns all-atom simulations of the FH2 domains of Bni1, Cdc12 and mDia1 associated with the actin filament seven-mer. (B, C) Comparison of the distributions of angles between actin subunits A2 and A3 during the last time intervals of two independent simulations (replica 1 and replica 2). (B) The last 50 ns of the 350 ns simulations. (C) The last 20 ns of the 200 ns simulations. (D–F) The number of contacts between the lasso, knob and post regions of the FH2 domains and actin subunits A2 and A3 as a function of time during 350 ns of the all-atom MD simulations (replica 1).