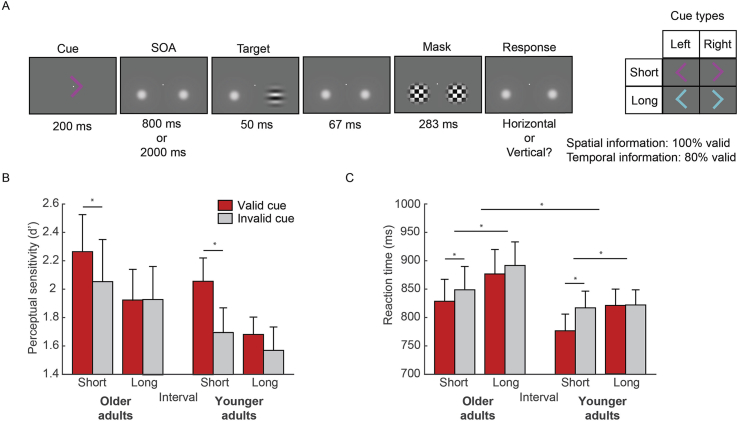
Fig. 1.
Task and behavioural results. (A) Behavioural task. Coloured arrow cues predicted where (bottom left or right, 100% valid) and when (after a short or long interval: 800 or 2000 ms, 80% valid) subsequent targets were likely to occur. Targets consisted of horizontally or vertically oriented Gabor patches followed by a backwards mask. Target discrimination performance was equated across participants by means of an adaptive staircase procedure using only valid spatial-temporal cues. Participants responded to the orientation of the Gabor grating by making left and right index finger responses. Note that stimuli are shown larger than actual size on screen for display purposes. Behavioural results are shown for (B) perceptual sensitivity (d’) and (C) reaction time (RT). Behavioural results are shown separately for older and younger adults, for each cue type (valid/invalid) and interval length (short/long). Error bars show standard error of measurement (SEM). Asterisks indicate statistically significant effects.