Summary
B lymphocytes can suppress immunity through interleukin (IL)-10 production in infectious, autoimmune, and malignant diseases. Here, we have identified a natural plasma cell subset that distinctively expresses the inhibitory receptor LAG-3 and mediates this function in vivo. These plasma cells also express the inhibitory receptors CD200, PD-L1, and PD-L2. They develop from various B cell subsets in a B cell receptor (BCR)-dependent manner independently of microbiota in naive mice. After challenge they upregulate IL-10 expression via a Toll-like receptor-driven mechanism within hours and without proliferating. This function is associated with a unique transcriptome and epigenome, including the lowest amount of DNA methylation at the Il10 locus compared to other B cell subsets. Their augmented accumulation in naive mutant mice with increased BCR signaling correlates with the inhibition of memory T cell formation and vaccine efficacy after challenge. These natural regulatory plasma cells may be of broad relevance for disease intervention.
Keywords: B cells, plasma cells, interleukin-10, LAG-3, immune regulation, infection, checkpoint receptor, natural regulatory plasma cell, CD72, BCR, TLR
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
-
•
LAG-3 expression identifies natural regulatory plasma cells
-
•
LAG-3+CD138hi plasma cells express IL-10 within hours of stimulation
-
•
LAG-3+CD138hi plasma cells have a unique epigenome poised to express IL-10
-
•
LAG-3+CD138hi plasma cells develop via an antigen-specific mechanism
Plasma cells secrete antibodies and play a key role in host defense against infection. Lino et al. identify a novel subset of natural regulatory plasma cells characterized by the expression of LAG-3 that develops at steady state independently of microbiota, and respond to innate stimulation by producing immunosuppressive IL-10.
Introduction
The immune system protects the host from infectious diseases and helps to remove its damaged components. Its activity is controlled by stimulatory and inhibitory forces. Inhibitory pathways are important to prevent its spontaneous hyperactivation and to regulate established immune reactions.
B lymphocytes have emerged as important players in the negative regulation of immunity via the production of interleukin-10 (IL-10) and IL-35 (Fillatreau et al., 2002, Shen and Fillatreau, 2015). This B cell function has noticeable effects in autoimmune, allergic, infectious, and malignant diseases (Shen and Fillatreau, 2015). The phenomenology of B cell-mediated suppression is well established, yet the B cells mediating these activities in vivo remain incompletely defined. Their identification has been approached by isolating known B cell subsets and assessing their capacity to produce IL-10 in vitro and to suppress immunity in recipient mice upon adoptive transfer. B cells expressing high amounts of CD1d, including marginal zone B cells and transitional T2-like B cells, as well as B1a cells and Tim-1hi B cells, have the capacity to suppress immunity in an IL-10-dependent manner in such assays (Blair et al., 2009, Yanaba et al., 2008, Yang et al., 2012). However, only a fraction of the cells within these subsets express IL-10 after activation in vitro, even when strong pharmacological agents such as ionomycin and phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) are used, and the phenotype of the B cells actually producing IL-10 in vivo in the recipient is not defined after transfer. Other studies have used IL-10 reporter mice to identify IL-10-producing cells ex vivo without re-stimulation. These have revealed CD138hi plasmocytes (plasmablasts and plasma cells) as the major source of B cell-derived IL-10 in vivo in autoimmune, infectious, and malignant diseases (Matsumoto et al., 2014, Neves et al., 2010, Shalapour et al., 2015, Shen et al., 2014, Teichmann et al., 2012). A hypothesis reconciling these findings could be that B cell-mediated regulation is an inducible function acquired by B cells such as CD1dhi B cells upon activation and differentiation into IL-10- or IL-35-producing plasmocytes.
Here, we addressed whether IL-10-producing plasmocytes defined a separate subset using a model of infection by the bacterium Salmonella Typhimurium. In this model, B cell-derived IL-10 is produced exclusively by plasmocytes that emerge before day 1 post-infection (p.i.) and leads to a rapid modulation of immunity to Salmonella (Neves et al., 2010). We reasoned that the rapidity of this response would facilitate the identification of the precursors of immunosuppressive IL-10-producing plasmocytes without having to recourse to adoptive transfer protocols susceptible to creating non-physiological cellular responses.
Results
LAG-3 Identifies IL-10-Expressing Plasma Cells in Infected Mice
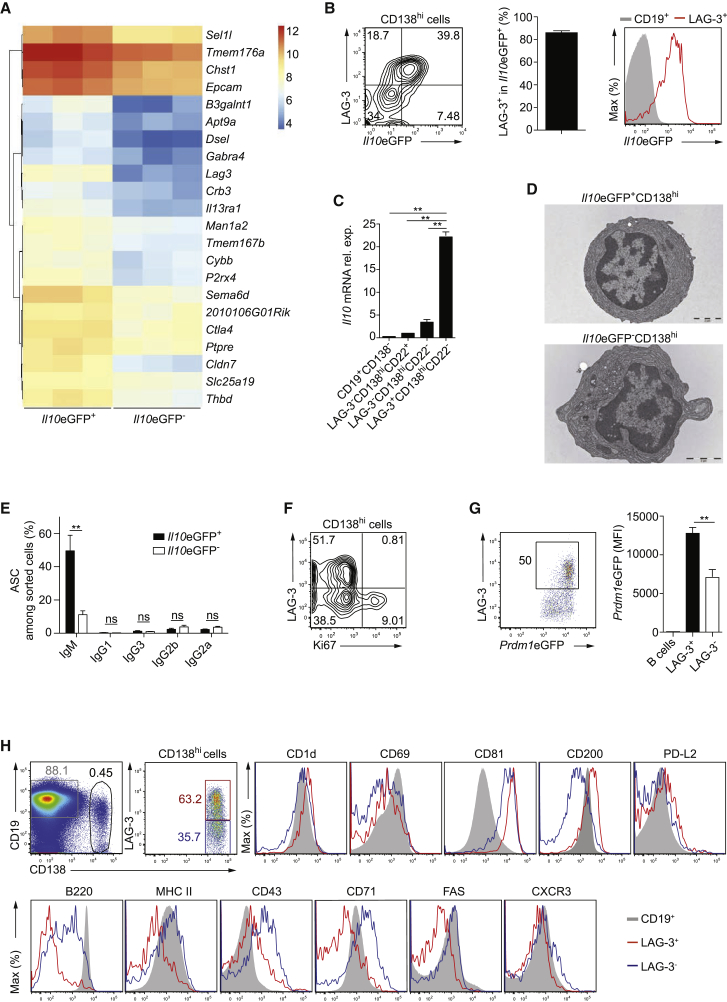
Salmonella infection results in the rapid appearance of IL-10+CD138hi cells. To assess whether these cells defined a particular subset, we compared their transcriptome to the one of IL-10−CD138hi cells from Il10eGFP mice on day 1 p.i. This yielded 22 genes coding for transmembrane receptors overexpressed in IL-10+ cells (Figure 1A), including lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (Lag3; CD223) that was previously identified as a marker for IL-10-producing T regulatory type (Tr1) cells (Gagliani et al., 2013).
Figure 1.
LAG-3 Identifies IL-10-Producing Plasma Cells in Infected Mice
Mice were infected i.v. with Salmonella (SL7207, 107 CFU), and plasmocytes characterized in spleen on day 1 p.i.
(A) mRNA amounts for receptors overexpressed in IL-10+ compared with IL-10− plasmocytes from Il10eGFP mice. Microarrays in triplicate. Expression amounts normalized using GCRMA are shown (Log2 transformed). Lag3 is expressed 9.4-fold higher in Il10eGFP+CD138hi than Il10eGFP−CD138hi cells.
(B) Flow cytometry plots showing IL-10 and LAG-3 expression in CD138hi cells (left); frequency of LAG-3+ in IL-10+CD138hi cells (middle); expression of IL-10 in B cells (CD19+CD138−) and LAG-3+CD138hi cells (right). Representative of six experiments.
(C) Il10 mRNA expression in isolated subsets from C57BL/6 mice. Pool of two experiments.
(D) Transmission electron microscopy images of plasmocytes from Il10eGFP mice. Scale bar is 2 μM.
(E) Frequencies of antibody-secreting cells (ASCs) in IL-10+CD138hi and IL-10−CD138hi cells from Il10eGFP mice by ELISPOT. Pool of three experiments.
(F) Flow cytometry plots of LAG-3 and Ki67 expression in CD138hi cells from C57BL/6 mice. Representative of four experiments.
(G) Flow cytometry plot of LAG-3 and BLIMP-1 in BLIMP-1+CD138hi cells (left), and amounts of BLIMP-1 (MFI) in B cells and plasmocytes in Prdm1eGFP mice (n = 4) (right). Representative of two experiments.
(H) Surface molecules expression on LAG-3+CD138hi (red), LAG-3−CD138hi (blue), and CD19+CD138− B cells (gray) from C57BL/6 mice. Representative of two experiments.
Data show mean ± SEM (nsp > 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01). See also Figure S1.
LAG-3 protein was found on most IL-10+CD138hi cells on day 1 p.i., and IL-10 was expressed uniformly in LAG-3+CD138hi cells (Figure 1B). LAG-3 was not detected on CD19+CD138− cells (Figure S1A). This staining was specific because it was not observed on Lag3−/− plasma cells (Figure S1B). Consistently, Il10 mRNA was predominantly expressed in LAG-3+CD138hi cells compared to other B cell subsets in infected C57BL/6 mice (Figure 1C).
IL-10+LAG-3+CD138hi cells displayed typical plasma cell features including a plasmacytoid morphology (Figure 1D), the spontaneous secretion of antibodies (Figure 1E), a non-proliferative state (Figure 1F), and an elevated expression of BLIMP-1 (Figure 1G). LAG-3+CD138hi cells also differed from LAG-3−CD138hi cells in their higher expression of CD1d and CD200, as well as their lower expression of B220, MHC-II, CD43, CD71, and Fas (Figure 1H).
We conclude that LAG-3+CD138hi plasma cells define the main population of IL-10-expressing B cells in infected mice.
LAG-3+CD138hi Plasma Cells Develop Independently of Microbe-Derived Signals in Naive Mice
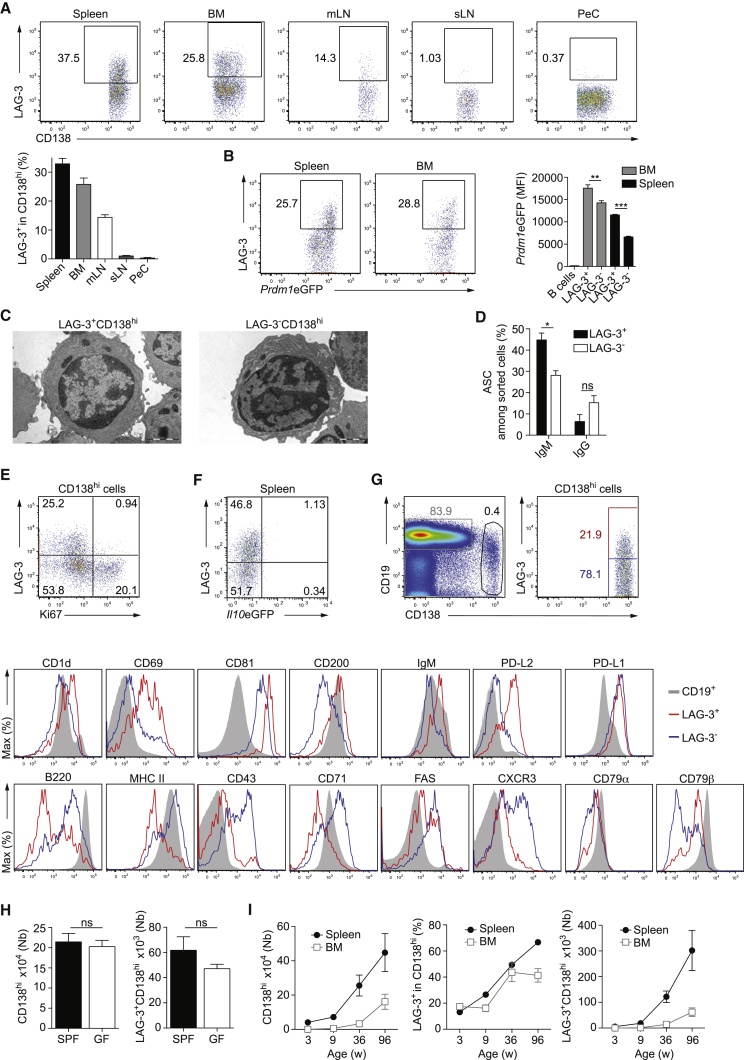
The non-proliferating status of IL-10+LAG-3+CD138hi cells was unexpected because B cell differentiation into plasma cell normally requires cell proliferation over several days. This led us to hypothesize that LAG-3+CD138hi cells were already present in naive mice. Indeed, LAG-3+CD138hi cells were detected in the spleen, bone marrow (BM), and mesenteric lymph nodes (mLN) of naive mice (Figures 2A and S2A). They had the key attributes of plasma cells such as high BLIMP-1 expression (Figures 2B and S2B), a plasmacytoïd morphology (Figure 2C), and the spontaneous secretion of antibodies (Figure 2D). In contrast to proliferating LAG-3−CD138hi plasmablasts, LAG-3+CD138hi cells were non-proliferative and produced mostly IgM (Figures 2D and 2E). These features of LAG-3+CD138hi cells therefore did not change between day 0 and day 1 p.i., except for the induction of IL-10 expression after challenge (Figure 2F). LAG-3+CD138hi cells also differed from LAG-3−CD138hi cells in their higher expression of CD1d, CD69, CD81, CD200, and CD273 (PD-L2), as well as their lower expression of B220, MHC-II, CD43, CD71, FAS, and CXCR3 in naive mice (Figure 2G). PD-L1 was highly expressed by both plasmocyte subsets. LAG-3+CD138hi cells expressed surface IgM, CD79α, and CD79β (Figure 2G). LAG-3 expression was not observed on B cells (Figure S2C).
Figure 2.
LAG-3+CD138hi Plasma Cells Are Present in Naive Mice
Analyses performed in spleen (except when indicated) of naive mice.
(A) Flow cytometry plots of LAG-3 on CD138+/hi cells (top) and frequencies in spleen (n = 23), BM (n = 19), mLN (n = 10), subcutaneous LN (sLN) (n = 10), and PeC (n = 10) (bottom) of C57BL/6 mice.
(B) Flow cytometry plots of LAG-3 and BLIMP-1 in BLIMP-1+CD138hi cells (left), and amounts of BLIMP-1 (MFI) in B cells and plasmocytes in Prdm1eGFP mice (n = 4) (right). Representative of three experiments.
(C) Electron microscopy images of plasmocytes from C57BL/6 mice. Scale bar is 2 μM.
(D) ASCs in plasmocytes from C57BL/6 mice by ELISPOT. Pool of two experiments.
(E) Flow cytometry plot of LAG-3 and Ki67 in CD138hi cells from C57BL/6 mice. Representative of four experiments.
(F) Flow cytometry plot of LAG-3 and IL-10 in CD138hi cells. Representative of six experiments.
(G) Expression of indicated molecules on cells from C57BL/6 mice. Representative of 3–4 experiments.
(H) Numbers of plasmocytes in SPF (n = 8) and GF (n = 8) C3H/HeOuJ mice.
(I) Numbers and frequencies of plasmocytes in C57BL/6 mice of indicated ages (n = 6/age, pool of 2 experiments).
Data show mean ± SEM (nsp > 0.05, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001). See also Figure S2.
Plasma cells are normally induced upon foreign antigen stimulation. LAG-3+CD138hi cells, however, were present in similar numbers in germ-free and specific-pathogen-free mice (Figure 2H). These cells are therefore generated via an endogenous response. Their number increased markedly in aging mice (Figures 2I and S2D).
We conclude that, in naive mice, LAG-3+CD138hi cells are a subset of natural plasma cells mainly producing IgM.
LAG-3+CD138hi Cells Rapidly Upregulate IL-10 after Infection
IL-10 expression in CD138hi cells increased already at 3 hr p.i. compared to naive mice (p = 0.0009; unpaired t test) (Figure 3A). IL-10 was expressed predominantly in LAG-3+CD138hi cells during the first 24 hr p.i. (Figure 3A). IL-10 is thus programmed for a rapid expression in LAG-3+CD138hi cells, whose numbers were similar at day 0 and day 1 p.i. (Figure 3B). As expected, IL-10 and LAG-3 were not detected in CD19+CD138− B cells (Figure S3A).
Figure 3.
LAG-3+CD138hi Cells Upregulate IL-10 Expression upon Infection
Analyses performed in spleen p.i. (SL7207, 107 CFU) or with naive mice.
(A) Kinetics of IL-10 expression in CD138hi cells (left), frequency of LAG-3+ in IL-10+CD138hi cells (middle), numbers of LAG-3+IL-10+CD138hi (LAG-3+) and LAG-3−IL-10+CD138hi (LAG-3−) cells (right) p.i. in Il10eGFP mice. Pool of two experiments (n = 6/time point).
(B) Numbers of LAG-3+CD138hi cells in C57BL/6 mice. Pool of four experiments (n = 11/time point).
(C) Isolated cells from naive C57BL/6 mice were stimulated in vitro for 18 hr, and IL-10 measured in supernatants. LAG-3+CD138hi and LAG-3−CD138hi cells indicated as LAG-3+ and LAG-3−, respectively. Pool of five experiments.
(D) Numbers of CD138hi and LAG-3−CD138hi cells (left), LAG-3+IL-10+CD138hi cells (middle), frequency of LAG-3+ (red line) or IL-10+ (green line) cells in CD138hi cells (right) p.i. in Il10eGFP mice. Pool of 4 experiments; at least 12 mice per group.
(E) Numbers of IL-10+CD138hi and IL-10−CD138hi cells at day 3 p.i. in B-Il10eGFP and B-Lag3−/−Il10eGFP chimeric mice.
(F) Il10eGFP mice were vaccinated and challenged 90 days later (vaccinated), along with age-matched naive Il10eGFP mice (challenged). Frequencies of LAG-3+ in CD138hi cells (left), and of IL-10+ in CD138hi cells (right). Pool of two experiments; at least six mice per group.
(G) Il10eGFP mice treated as in (F) and analyzed at day 1 and 2 post-re-challenge. Flow cytometry plots show LAG-3 and CD138 on IL-10+CD138hi cells (right, day 1) with quantifications (left). Pool of two experiments; at least six mice per group.
(H) Il10eGFP mice were treated as in (F). Frequency of ASC in indicated plasmocytes on day 1 post-re-challenge by ELISPOT. Pool of two experiments; at least six mice per group.
Data shown are mean ± SEM (nsp > 0.05, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001). See also Figure S3.
The immediate upregulation of IL-10 in LAG-3+CD138hi cells led us to compare the capacity of CD138hi cells and other B cell subsets to produce IL-10 in vitro. CD138hi plasmocytes secreted markedly more IL-10 than CD1dhiCD19+ B cells (Figure 3C), and their IL-10 production derived mostly from LAG-3+CD138hi cells (Figure 3C).
We then examined IL-10 expression at later time points p.i. during the extra-follicular response. The number of CD138hi cells increased progressively p.i., and they represented 10% of all splenocytes on day 8 p.i. (Figures 3D and S3B). This increase reflected the accumulation of LAG-3−CD138hi cells, while IL-10+LAG-3+CD138hi cells did not expand greatly after day 1 p.i. (Figure 3D). IL-10 expression was associated with LAG-3+CD138hi cells at all time points (Figure S3C). The frequencies of LAG-3+ and IL-10+ cells within CD138hi cells sharply decreased from day 1 p.i. onward (Figure 3D). These results emphasize the unique response dynamics of IL-10+LAG-3+CD138hi cells. Because LAG-3 has been implicated in the regulation of humoral immunity (Butler et al., 2011), we asked whether LAG-3 expressed on CD138hi cells modulated the plasmocyte response p.i. To this end, we crossed Lag3−/− mice on an Il10eGFP background and generated mixed bone marrow chimera in which only B cells lacked Lag3 but could express Il10eGFP. A LAG-3 deficiency in plasma cells did not alter the number of IL-10+CD138hi cells p.i., yet led to an increased accumulation of IL-10−CD138hi cells (Figure 3E). Thus, LAG-3+CD138hi cells control the expansion of LAG-3−CD138hi cells in a LAG-3-dependent manner.
An important property of the adaptive immune system is immunological memory. To assess whether LAG-3+CD138hi cells acquire features of memory B cells, we compared their response in vaccinated and naive mice p.i. As expected, vaccinated mice better controlled Salmonella than naive mice (Figure S3D). IL-10 and LAG-3 expression in CD138hi cells were comparable in the two groups p.i. (Figures 3F and 3G). Thus, LAG-3+CD138hi cells did not display the typical sign of an amplified response upon rechallenge. IL-10+CD138hi cells isolated from vaccinated mice on day 1 p.i. produced mostly IgM (Figure 3H), indicating that they had not undergone isotype switching away from IgM, unlike what is observed in classical memory B cell responses.
These data show that LAG-3+CD138hi cells can rapidly upregulate IL-10 expression without dividing, and inhibit the expansion of LAG-3−CD138hi cells p.i.
LAG-3+CD138hi Cells Have a Unique Plasma Cell Epigenome
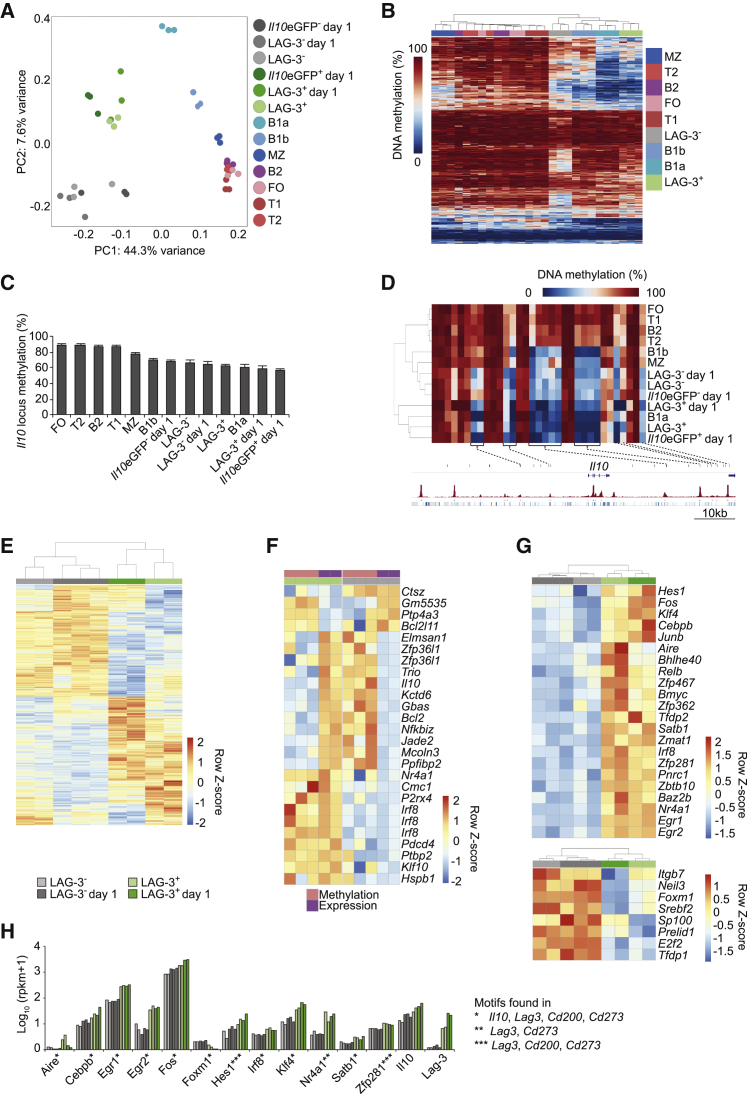
We next examined the hypothesis that LAG-3+CD138hi cells were a distinct subset of plasma cells epigenetically poised to rapidly produce IL-10. To this end, we compared the genome-wide DNA-methylomes of LAG-3+CD138hi cells, LAG-3−CD138hi cells, and peripheral B cell subsets from naive mice. In addition, we included LAG-3+CD138hi, LAG-3−CD138hi, IL-10+CD138hi, and IL-10−CD138hi cells isolated at day 1 p.i.
Genome-wide DNA-methylation profiling was performed by reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) covering on average 3–4 million CpG sites per sample. An unsupervised principal component analysis (PCA) placed LAG-3+CD138hi and IL-10+CD138hi cells at a distinctive position relative to LAG-3−CD138hi and IL-10−CD138hi cells, as well as to other B cell subsets, underlying their unique methylome profile. The position of LAG3+CD138hi cells taken at day 0 and day 1 p.i. was similar and showed a striking co-localization with IL-10+CD138hi cells (Figure 4A), underlining the intimate relationship between these subsets. The various groups of CD138hi cells localized at the same position on PC1, which separated B cells from plasma cells. In keeping with the described hypomethylation of plasma cells’ genome (Kulis et al., 2015), the various CD138hi subsets analyzed here displayed the lowest degree of genome-wide methylation (Figure S4A). Thus, LAG-3+CD138hi and IL-10+CD138hi cells have a plasma cell epigenetic profile but with unique features. A pairwise comparison of LAG-3+CD138hi and LAG-3−CD138hi cells from naive mice identified 469 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) showing a genome-wide distribution (Figure S4B). In a hierarchical analysis, these DMRs separated CD138hi cells and B1 cells away from the other B cell subsets (Figure 4B), with LAG-3+CD138hi cells showing the highest similarity to B1a cells (Figures 4B and S4C). A particular cluster of DMRs was found at the Il10 locus. IL-10+CD138hi cells, LAG-3+CD138hi cells, and B1a cells not only exhibited the lowest overall degree of DNA methylation at the Il10 locus (Figure 4C) but also shared distinct patterns of hypomethylated regions around the Il10 gene. Many of these hypomethylated sites overlapped with B cell-specific DNase hypersensitive sites, indicating an epigenetic “preprogrammed” open chromatin state of Il10 in IL-10+CD138hi, LAG-3+CD138hi, and B1a cells (Figures 4D and S4D). Of note, IL-10+CD138hi cells, LAG-3+CD138hi cells, and B1a cells also showed a preferential epigenetic relationship at the 469 DMR (Figure S4E).
Figure 4.
Molecular Characterization of LAG-3+CD138hi Cells
(A) Unsupervised PCA of genome-wide DNA methylation data of cells from C57BL/6 mice.
(B) Methylation of the CpG found in the 469 DMR distinguishing LAG-3+CD138hi cells and LAG-3−CD138hi cells.
(C) DNA methylation of Il10 locus (mean ± SEM).
(D) Methylation for covered CpG in the Il10 locus. Coverage weighted average methylation of three replicates is represented. The positions of selected CpG are indicated by vertical black bars, with the Il10 gene depicted. ENCODE DNase I data are in red for splenic CD43− B cells. PhastCons Vert30 conservation scores are in blue.
(E) mRNA expression for the 3,631 DEGs that distinguish LAG-3+CD138hi and LAG-3−CD138hi cells on day 0 and 1 p.i. (see Figure S4F).
(F) mRNA expression and local DNA methylation for genes both differentially expressed and methylated between LAG-3+CD138hi and LAG-3−CD138hi cells from naive mice.
(G) Transcription regulators expressed at higher (top) or lower (bottom) amounts on both day 0 and 1 p.i. in LAG-3+CD138hi compared to LAG-3−CD138hi cells.
(H) Expression of transcription regulators differentially expressed between LAG-3+CD138hi cells and LAG-3−CD138hi cells (see G) with predicted binding motif in either the Il10, Lag3, Cd200, or Cd273 loci.
Row z-scores for expression are based on log10(rpkm+1), and for DNA methylation on DNA methylation frequency (%).
Samples were from naive mice (A, C, D, E, G, H) except where indicated. See also Figure S4.
In summary, LAG-3+CD138hi cells are the epigenetically primed precursors of IL-10+LAG-3+CD138hi cells and show a distinct plasma cell-specific epigenome with the Il10 locus primed for expression and features reminiscent of B1a cells.
Transcriptional Properties of LAG-3+CD138hi Cells
We next determined the transcriptomes of LAG-3+CD138hi and LAG-3−CD138hi cells on day 0 and day 1 p.i by mRNaseq. These analyses identified 648 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (pval ≤ 0.01; FDR ≤ 0.05) on day 0 and 2,280 on day 1 p.i. (Figure S4F). A hierarchical clustering with all DEGs confirmed the relative proximity of LAG-3+CD138hi cells from naive mice and day 1 p.i. compared to LAG-3−CD138hi cells (Figure 4E). The top DEGs (Tables S1 and S2) included genes coding for IL-10 and the surface proteins LAG-3, CD200, and CXCR3, whose differential expression was also reflected in protein amount (Figures 1 and 2). A Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (MSigDB) of the 648 DEGs in naive mice highlighted cell cycle regulation as the major pathway discriminating the LAG3− and LAG3+ subsets (Figure S4G). 23 of the 648 DEGs were also differentially methylated between LAG-3+CD138hi and LAG-3−CD138hi cells, including Il10, Bcl2, Zfp36l1, Irf8, and other B cell regulators (Figure 4F). This argues for an epigenetically primed control of their expression.
We finally focused on transcription regulators differentially expressed in higher (or lower) amount on both day 0 and 1 p.i. in LAG-3+CD138hi cells as compared to LAG-3−CD138hi cells. We identified 22 factors (including transcription factors and co-factors, gene expression regulators, and general DNA binding proteins) with higher expression in LAG-3+CD138hi cells and 8 factors with higher expression in LAG-3−CD138hi cells (Figure 4G). LAG-3+CD138hi cells showed a higher expression of Klf4, Bhlhe40, and Bmyc that are involved in the inhibition of proliferation, and of Hes1 that indicates higher Notch signaling activity. They also displayed a higher expression of Fos, Junb, Egr1, Egr2, Cebpb, Irf8, and Satb1 (Figures 4G and 4H), i.e., genes coding for factors for which we found predicted binding sites in the Il10, Lag3, Cd200, and Cd273 (PD-L2) loci (Figure 4H). FOS, JUN-B, and EGR-2 drive IL-10 expression in other immune cells (Iwasaki et al., 2013, Wang et al., 2005, Yoshida et al., 2012). EGR2 was also important in CD4+ T cells for LAG-3 expression, BLIMP-1-mediated induction of IL-10, and their regulatory activity (Iwasaki et al., 2013). The reduced expression of Foxm1 in LAG-3+CD138hi cells (Figures 4G and 4H) might be linked to two effects: their lack of proliferation (Chen et al., 2013) and the control of Il10 transcription since Foxm1 binding sites were predicted in this locus (Figure 4H).
We conclude that LAG-3+CD138hi cells exhibit a distinct transcriptome, partially linked to epigenetic changes, keeping them in a quiescent state primed for IL-10 expression. This molecular program could explain why only this subset of plasmocytes expresses IL-10 and other immune checkpoint receptor molecules.
BCR Repertoire and Developmental Origin of LAG-3+CD138hi Cells
The differentiation of B cells into plasma cells requires the engagement of their BCR by antigen. Our observation that LAG-3+CD138hi cells develop independently of the microbiota prompted us to examine whether they express a particular BCR repertoire.
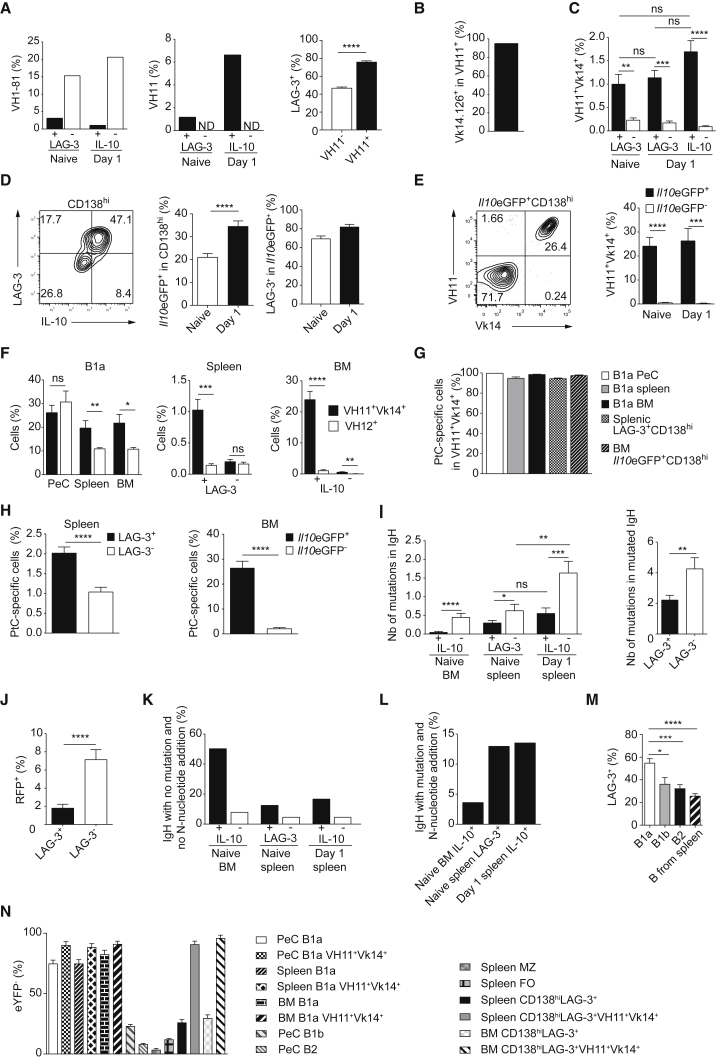
Single-cell analysis of their IgH and Igk revealed that LAG-3+CD138hi cells and IL-10+CD138hi cells displayed a lower utilization of IgH VH1-81 and a higher usage of VH7, VH10, and VH11 segments compared to LAG-3−CD138hi cells and IL-10−CD138hi cells (Figures 5A and S5A). The majority of VH11+ IgH were associated with a Vk14.126+ (formerly Vk9) Igk (Figure 5B), forming a combination typical of B1a cells (Hardy et al., 2004). Flow cytometry analyses confirmed the presence of a VH11+Vk14.126+ BCRs on splenic LAG-3+CD138hi cells and IL-10+CD138hi cells but not on LAG-3−CD138hi cells or IL-10−CD138hi cells (Figures 5C and S5B). Of note, the BM from naive mice contained IL-10+CD138hi cells (Figure 5D) enriched in VH11+Vk14.126+ cells (Figure 5E). Thus, some LAG-3+CD138hi and IL-10+CD138hi cells carry a VH11+Vk14.126+ BCRs typical of B1a cells (Figures S5C and S5D). However, the other VH segment classically associated with B1a cells, namely VH12, was not found in spleen LAG-3+CD138hi cells, and only on about 1% of BM IL-10+CD138hi cells (Figure 5F). The VH11+ IgH from LAG-3+CD138hi and IL-10+CD138hi cells had few mutations as well as N-additions, and a large proportion contained the CDR3 characteristic of the anti-phosphatidylcholine (PtC) response (Figures S5E and S5F). Accordingly, nearly all VH11+Vk14.126+ cells displayed reactivity against PtC (Figure 5G), and about 2% of splenic LAG-3+CD138hi cells as well as 26% of BM IL-10+CD138hi cells in naive mice reacted toward this particular antigen (Figure 5H). In BM, more than 80% of PtC-reactive CD138hi cells expressed IL-10 (Figure S5G). Taken together, these data strongly suggest that VH11+Vk14.126+LAG-3+CD138hi spleen and BM cells derive from B1a cells. Some LAG-3+CD138hi cells expressing other BCR might also derive from B1a cells because LAG-3+CD138hi and IL-10+CD138hi cells had overall fewer IgH somatic mutations than LAG-3−CD138hi and IL-10−CD138hi cells (Figure 5I). This correlated with a lower AID fate-mapping marking of LAG-3+CD138hi cells (Figure 5J). Furthermore, a higher proportion of IgH from LAG-3+CD138hi and IL-10+CD138hi lacked both somatic mutation and N-addition as compared to LAG-3−CD138hi and IL-10−CD138hi cells (Figure 5K). Nonetheless, some LAG-3+CD138hi and IL-10+CD138hi cells expressed IgH sequences with mutations and N-additions (Figure 5L), suggesting an additional origin for LAG-3+CD138hi cells.
Figure 5.
BCR Repertoire of LAG-3+ and IL-10+ Plasmocytes
(A) Frequency of Igh containing VH1-81 (left) or VH11 (middle) in spleen LAG-3+CD138hi (n = 253), LAG-3−CD138hi (n = 150), Il10eGFP+CD138hi (n = 181), and Il10eGFP−CD138hi (n = 121) cells on day 0 and day 1 p.i. (SL7207; 107 CFU). Frequency of LAG-3+ in VH11+CD138hi and VH11−CD138hi spleen cells of naive mice (n = 12) (right).
(B) Frequency of Vk14.126+ cells in VH11+ cells for spleen and BM cells described in Figure S5A.
(C) Frequency of VH11+Vk14.126+ cells by flow cytometry. Pool of two experiments (6–7 mice/group/time point).
(D) Flow cytometry plot of LAG-3 versus Il10eGFP in CD138hi BM cells at day 1, and quantifications. Pool of four experiments (n = 12–17/time point).
(E) Flow cytometry plot and frequency of VH11+Vk14.126+ cells in IL-10+CD138hi cells in BM of Il10eGFP mice. Pool of two experiments (n = 6–7/time point).
(F) Frequency of VH11+Vk14.126+ and VH12+ cells in B1a cells from indicated tissues (left), spleen LAG-3+ and LAG-3− (middle), and BM IL-10+ and IL-10− (right) plasmocytes from naive mice. Pool of two experiments (n = 7).
(G) Frequency of PtC-reactive cells in VH11+Vk14.126+ cells for indicated cells from naive mice. Pool of two experiments (n = 7).
(H) Frequency of PtC-reactive cells in indicated plasmocytes from naive mice. Pool of four experiments (n = 12).
(I) Mutations in IgH sequences (naive BM Il10eGFP+CD138hi, n = 165; Il10eGFP−CD138hi, n = 151; naive spleen LAG-3+CD138hi, n = 231; LAG-3−CD138hi, n = 129; day 1 spleen Il10eGFP+CD138hi, n = 155; Il10eGFP−CD138hi, n = 108) (left). Number of somatic mutations per sequence for mutated IgH (LAG-3+CD138hi cells, n = 31; LAG-3−CD138hi cells, n = 19) (right).
(J) Aicda-cre-ERT2-ROSA-STOP-RFP mice were treated with tamoxifen and analyzed 15 days after the last treatment. Frequency of RFP+ cells in LAG-3+CD138hi and LAG-3−CD138hi spleen cells. Pool of five experiments (n = 14).
(K) Frequency of IgH sequences (as in I) having no mutation and no N-nucleotide addition.
(L) Frequency of IgH sequences (as in I) with mutation and N-nucleotide addition.
(M) Frequency of LAG-3+ in spleen CD138hi cells 3 weeks after transfer of indicated cell fractions into Rag2−/− mice. Pool of three experiments (n = 6–7/group).
(N) Frequency of eYFP− cells in indicated cells of naive Cd21-cre-ROSA-STOP-eYFP mice. Pool of three experiments (n = 6).
Groups were compared using two-tailed unpaired t test with Welch’s correction in case of inequal variances (C–I) or using Mann-Whitney test (M). Data are mean ± SEM (nsp > 0.05, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). See also Figure S5.
To evaluate the capacity of various B cell subsets to generate LAG-3+CD138hi cells, we adoptively transferred B1a, B1b, and B2 cells from peritoneal cavity (PeC) as well as splenic B cells into Rag2−/− mice (Figure 5M). The analysis of the recipient mice confirmed that several B cell subsets could give rise to LAG-3+CD138hi cells, as observed also upon culture of B cell subsets in vitro (Figure S5H). Marginal zone B cells were not a non-redundant source of LAG-3+CD138hi cells in vivo since mice that lacked marginal zone B cells due to a B cell-restricted deficiency in NOTCH2 (Saito et al., 2003) displayed normal frequency of LAG-3+CD138hi cells (Figure S5I) despite their globally reduced numbers of splenic plasmocytes (data not shown). To further delineate the origin of LAG-3+CD138hi cells in a physiological context, we next developed a fate mapping system using the fact that B1a cells poorly expressed CD21 compared to other B cell susbsets, and crossed Cd21-cre mice to ROSA-STOP-eYFP reporter mice. In Cd21-cre-ROSA-STOP-eYFP mice, most B1a cells were eYFP− in PeC, spleen, and BM, which was even more apparent when focusing on the VH11+Vk14+ fraction of B1a cells (Figure 5N). In contrast, B1b and B2 cells from PeC as well as follicular and marginal zone B cells from spleen were mostly eYFP+ (Figure 5N). The LAG-3+CD138hi cell subset contained an intermediate frequency of eYFP− cells, underlining their heterogeneous origin. Importantly, the LAG-3+CD138hi cells that carried a VH11+Vk14+ BCR were largely eYFP−, indicating that eYFP− B1a cells did not switch-on eYFP expression during their differentiation into LAG-3+CD138hi cells (Figure 5N).
We conclude that LAG-3+CD138hi cells develop from several B cell subsets via a mechanism involving the BCR since they have a distinct BCR repertoire.
Roles of BCR and TLR in LAG-3+CD138hi Plasma Cell Development and Function
We next examined how the BCR influenced the accumulation of LAG-3+CD138hi cells in naive mice and their upregulation of IL-10 after challenge.
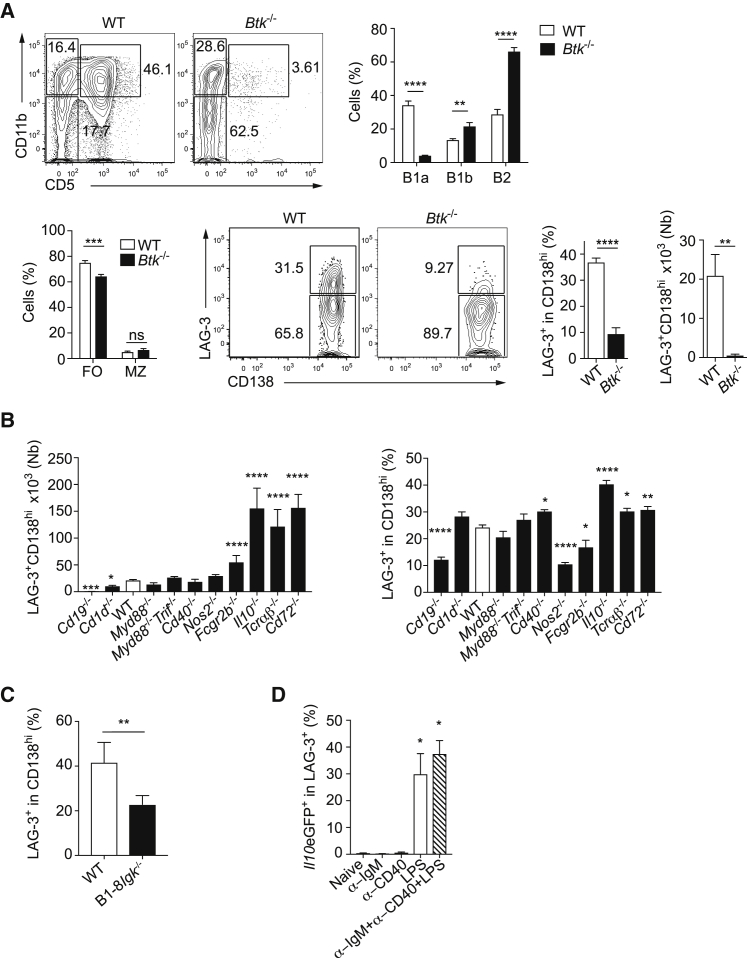
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (Btk) is essential for BCR signaling (Corneth et al., 2016). Btk−/− mice showed a developmental defect in B1a cells but not in B1b cells and marginal zone B cells (Figure 6A). They also displayed reduced frequencies and numbers of LAG-3+CD138hi cells (Figure 6A). We next assessed the effect of the BCR co-receptors CD19 and CD72 for the generation of LAG-3+CD138hi cells. We also studied mice genetically deficient in proteins involved in antigen presentation (CD1d), innate immune signaling (MyD88 and TRIF), T cell:B cell interaction (CD40, T cell receptor for antigen), and inflammation (NOS2, IL-10) (Figure 6B). LAG-3+CD138hi cells were present in lower amounts in mice deficient for CD19, which is a positive regulator of BCR signaling, and in higher numbers in mice lacking CD72, which is an inhibitory BCR co-receptor. In contrast, they were normally present in Myd88−/−Trif−/− mice, which lacked TLR signaling. Mice deficient in CD40 or αβTCR-expressing T cells also generated these cells normally. LAG-3+CD138hi cells can therefore develop independently of canonical T cell:B cell interactions and are thus not strictly dependent on a T cell-dependent antigen. The finding that BCR but not TLR signaling contributed to the formation of LAG-3+CD138hi cells led us to assess whether mice with a restricted BCR repertoire had an altered abundance of these plasma cells. Indeed, B1-8i mice carrying a fixed IgH chain on an Igk-deficient background displayed a 2-fold reduction in the frequency of LAG-3+CD138hi cells compared to controls (Figure 6C). Of note, antibodies cloned from LAG-3+CD138hi cells displayed little polyreactivity when tested as recombinant molecules in ELISA (Tiller et al., 2009), unlike those from BM IL-10−IgM+CD138hi cells (Figure S6A). Considering that BCR signaling contributed to the development of LAG-3+CD138hi cells at steady state, we next asked whether such cells could be generated upon immunization with 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenylacetyl keyhole limpet hemocyanin (NP-KLH), NP-Ficoll, or NP-LPS i.e., classical T cell-dependent, T cell-independent type II, and T cell-independent type I antigens, respectively (Figure S6B). These immunizations induced NP-reactive LAG-3−CD138hi cells, but not NP-reactive LAG-3+CD138hi cells. We conclude that LAG-3+CD138hi cells develop from B cells at steady state upon a particular form of BCR engagement that is not recapitulated by these immunizations.
Figure 6.
Molecules Implicated in the Homeostasis of LAG-3+CD138hi Cells
(A) Flow cytometry plots and quantification of indicated cells in PeC (top) and spleen (bottom) of naive Btk−/− mice and littermate controls. Pool of two experiments (n = 6).
(B) Numbers and frequencies of LAG-3+CD138hi cells in CD138hi plasmocytes in spleen of naive C57BL/6 (n = 40), Cd19−/− (n = 5), Il10−/− (n = 8), Tcrab−/− (n = 7), Cd72−/− (n = 10), Cd1d−/− (n = 6), Myd88−/− (n = 10), Myd88−/−Trif−/− (n = 12), Cd40−/− (n = 6), Nos2−/− (n = 10), and Fcgr2b−/− (n = 5) mice.
(C) Frequencies of LAG-3+ in spleen CD138hi cells of B1-8iIgk−/− and WT mice. Pool of two experiments (n = 4–5).
(D) Frequency of IL-10 in spleen LAG-3+CD138hi of Il10eGFP mice 24 hr after i.v. injection of indicated reagents. Pool of three experiments (n = 6).
Data show mean ± SEM (nsp > 0.05, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). See also Figure S6.
We next asked whether BCR or other signals controlled the upregulation of IL-10 expression in LAG-3+CD138hi cells after challenge. To this end, Il10eGFP mice were injected intravenously with anti-BCR, anti-CD40, or LPS, alone or in combination (Figure 6D). The administration of anti-BCR or anti-CD40 had no effect on IL-10 expression, yet LPS induced a strong upregulation of IL-10 in LAG-3+CD138hi cells. These results demonstrated that IL-10 expression was induced in a polyclonal manner in LAG-3+CD138hi cells upon TLR4 stimulation. This was in agreement with the fact that LAG-3+CD138hi cells from naive mice, as well as of LAG-3+CD138hi cells and IL-10+CD138hi cells from day 1 p.i., had comparable frequencies of VH11+Vk14+ cells (Figure 5C), suggesting that IL-10 was induced in LAG-3+CD138hi cells in a polyclonal manner.
We conclude that the development of LAG-3+CD138hi cells is controlled by the BCR and independent of TLR signaling as well as T cell help, while their upregulation of IL-10 after challenge is determined by TLR signaling.
Elevated Abundance of LAG-3+CD138hi Cells Correlates with Impaired Immunity against Salmonella
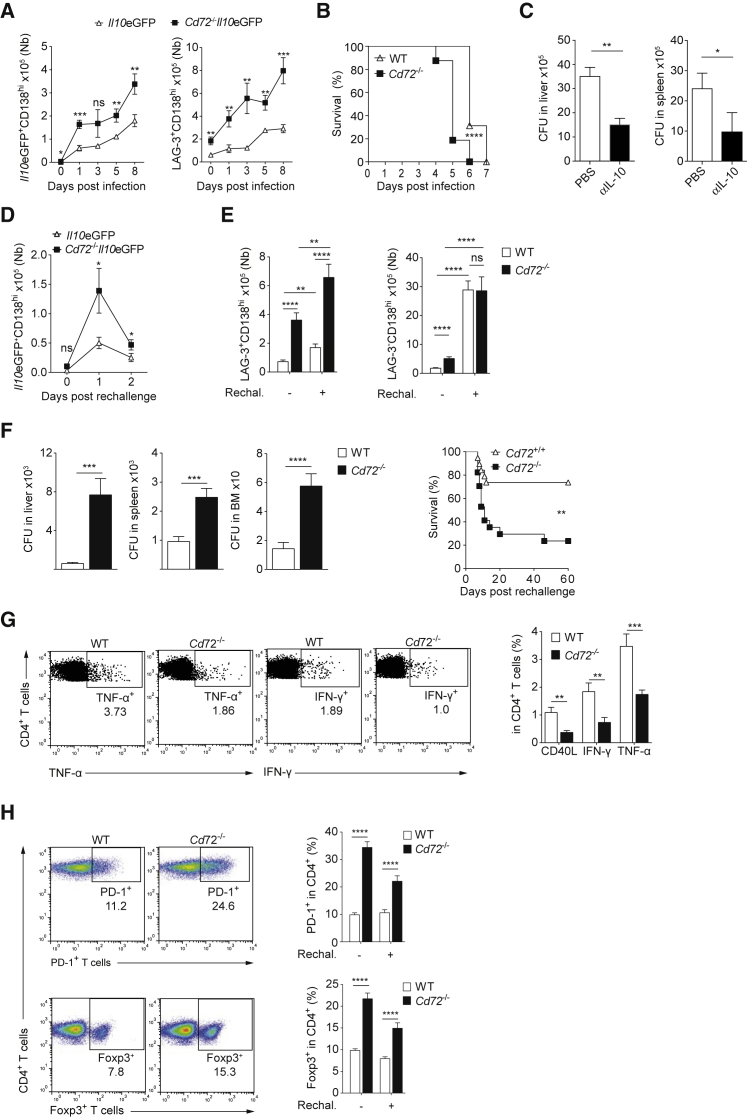
An ablation of IL-10 production by CD138hi plasmocytes increased host defense to Salmonella (Neves et al., 2010). Here, we sought to determine how an increased abundance of LAG-3+CD138hi cells affected host resistance to this infection using Cd72−/− mice.
Cd72−/− mice had an increased number of LAG-3+CD138hi cells, while other B cell subsets did not display any major defect (Figure S7A). The increased accumulation of LAG-3+CD138hi cells in Cd72−/− mutants was confirmed with littermate mice (Figure S7A). After infection, Cd72−/− mice displayed an increased accumulation of IL-10+CD138hi and LAG-3+CD138hi cells (Figures 7A and S7B), an impaired control of the infection (Figure S7C), and a reduced survival (Figure 7B) compared to controls. The CD72 deficiency had no effect in B cell-deficient mice, confirming that the observed differences were due to the lack of Cd72 in B cells (Figure S7D). To validate the inhibitory impact of IL-10 on host defense in Cd72−/− mice, mice were treated intravenously with a combination of anti-IL-10 and anti-IL-10 receptor. This significantly improved the control of the bacteria (Figure 7C). Since LAG-3+CD138hi cells are the major source of IL-10 after infection, this supports the notion that LAG-3+CD138hi cells inhibit host defense through IL-10 provision.
Figure 7.
CD72 Deficiency Enhances Susceptibility to Salmonella
(A) Numbers of indicated spleen cells in Il10eGFP and Cd72−/−Il10eGFP mice p.i. (SL7207, 107 CFU). Pool of three experiments (n = 9–12/time point/group).
(B) Survival of Cd72−/− (n = 16) and controls (n = 16) after infection (SL1344, 100 CFU). Pool of two experiments.
(C) CFU on day 3 p.i. (SL7207, 107 CFU) of anti-IL10 plus anti-IL10R-treated and control Cd72−/− mice. Pool of two experiments (n = 6–10/group).
(D) Mice were vaccinated (SL7207, 106 CFU) and re-challenged on day 90 (SL7207, 107 CFU). Numbers of cells in spleen after re-challenge. Pool of three experiments (n = 9/group/time point).
(E) Mice were vaccinated (SL7207, 106 CFU), rechallenged on day 90 (SL7207, 106 CFU), and analyzed 5 days later with (+) or without (−) rechallenge. Pool of four experiments (n = 15–18/group/time point).
(F) CFU on day 5 post-re-challenge for mice shown in (E) (left). Survival of Cd72−/− (n = 17) and littermate control (n = 19) mice vaccinated (SL7207, 106 CFU) and re-challenged 90 days later (SL1344, 100 CFU). Pool of two experiments (right).
(G) Cd72−/− and WT mice were vaccinated (SL7207, 106 CFU), and BM analyzed on day 90. Flow cytometry plot (left) and quantifications (right) for CD40L, TNF-α, and IFN-γ expression in Salmonella-reactive memory CD4+ T cells. Pool of three experiments (n = 12).
(H) Flow cytometry plots showing PD-1 and FOXP-3 in spleen CD4+ T cells of mice treated as in (E) and analyzed on day 0 and 5 post-rechallenge. Pool of three experiments (n = 12/group).
Groups were compared using two-tailed unpaired t test (nsp > 0.05, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). Survival curves were compared using Wilcoxon test, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Data show mean ± SEM. See also Figure S7.
Finally, we investigated how CD72 deficiency affected the host response to secondary infection. Il10eGFP and Cd72−/−Il10eGFP mice were vaccinated and later challenged with Salmonella. Mice lacking Cd72 displayed a higher accumulation of IL-10+CD138hi cells and LAG-3+CD138hi cells upon re-challenge, while LAG-3−CD138hi and total CD138hi cells were present in comparable numbers in the two groups of mice (Figures 7D, 7E, and S7E). Consistently, CD72 deficiency led to higher bacterial load and reduced survival (Figure 7F), compromising vaccine efficacy. Memory T helper 1 (Th1) cells play a major role in vaccine-induced protection against Salmonella. In vaccinated Cd72−/− mice, numbers of memory Salmonella-reactive Th1 CD4+ T cells in the BM were reduced (Figures 7G and S7F), and accumulation of exhausted PD-1+CD4+ T cells, PD-1+CD8+ T cells, and regulatory Foxp3+CD4+ T cells were increased (Figures 7H and S7G).
These data demonstrate that in the absence of CD72, a higher accumulation of LAG-3+CD138hi plasma cells is associated with impaired immunity to Salmonella.
Discussion
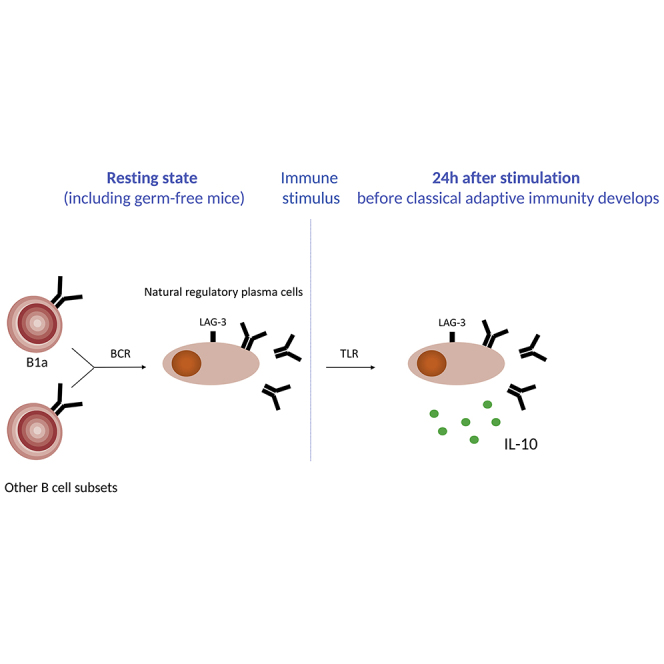
This study demonstrates the existence of natural regulatory plasma cells, which are the major source of IL-10 early after infection with Salmonella.
An unexpected finding was that the cells expressing IL-10 were not reactive plasmablasts but instead resident plasma cells. Upon activation, B cells successively generated antibody-secreting plasmablasts that proliferated and then plasma cells that did not divide and expressed higher amounts of the transcription factor BLIMP-1. LAG-3+CD138hi cells were non-proliferating and expressed higher amounts of BLIMP-1 than LAG-3−CD138hi cells, thus qualifying as bone fide plasma cells. Their non-dividing status correlated with the lack of expression of factors necessary for cell division including the transferrin receptor CD71 and the transcriptional regulator Foxm1, as well as the increased expression of the cell proliferation inhibitors Egr2, Zfp36l1, Pdcd4, Klf4, and Bhlhe40. KLF4 is absent in plasmablasts generated in vitro but is expressed in long-lived BM plasma cells (Schoenhals et al., 2016). LAG-3+CD138hi cells thus display a profile of mature plasma cells, while retaining the capacity to respond to external stimuli, in particular TLR, via the production of IL-10.
LAG-3+CD138hi plasma cells expressed several immune checkpoint receptors implicated in the negative regulation of immunity such as LAG-3, PD-L1, PD-L2, and CD200. LAG-3 is a co-inhibitory receptor related to CD4 and implicated in the down-modulation of T cell immunity. The co-expression of several inhibitory molecules is important because these molecules usually act synergistically, so that their combined blockade achieves greater effect than the neutralization of single molecules. Blockade of LAG-3 and PD-L1 augments immunity toward Plasmodium falciparum by amplifying T cell activation and antibody production (Butler et al., 2011). Here, we found that LAG-3 on plasma cells did not influence their IL-10 expression, but inhibited the accumulation of IL-10−CD138hi cells, which were LAG-3−, early after infection. The suppressive function of LAG-3+CD138hi cells therefore extends beyond IL-10 production, suggesting a more global role in immune regulation.
LAG-3+CD138hi cells developed from several B cell subsets in a BCR-dependent manner. Their preserved accumulation in germ-free mice suggests that they are selected on self-antigens. Our study has not identified the antigens involved in the generation of LAG-3+CD138hi cells. Since these cells increased with age, which has also been associated with an accumulation of damaged cells (Baker et al., 2016), it is tempting to speculate that LAG-3+CD138hi cells react toward antigens released by damaged cells. This hypothesis is consistent with the recognition by natural IgM of senescent cells (Frescas et al., 2017) and by natural antibodies binding PtC of apoptotic cells (Shaw et al., 2000). LAG-3+CD138hi cells may thus provide a feedback mechanism, which senses the number of damaged cells and proportionally downregulates the activation of immunity to limit additional and potentially excessive immunopathology when an immune stimulus arises. Mice lacking the BCR inhibitory co-receptor CD72 had an increased abundance of LAG-3+CD138hi cells and an impaired capacity to control Salmonella infection. The induction of IL-10 in LAG-3+CD138hi cells was primarily controlled by TLR. We cannot, however, exclude that BCR signaling played a role in IL-10 production, even if it was not the major switch for IL-10 expression. For instance, it might contribute to the transcription of Il10 in LAG-3+CD138hi cells at steady state in naive mice and synergize with TLR to upregulate IL-10 expression after challenge. It is indeed possible that these cells express BCR that recognize endogenous antigens already available at steady state and persisting during challenge.
In conclusion, natural regulatory plasma cells can rapidly provide a first layer of B cell-mediated immune regulation in response to TLR signals. They might subsequently be complemented by other subsets of suppressive B cells and plasma cells induced in an antigen-specific manner.
STAR★Methods
Key Resources Table
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| B220 | BioLegend | Clone RA3-6B2; RRID: AB_2563491 |
| CD1d | BD PharMingen/BioLegend | Clone 1B1; RRID: AB_2073521, AB_1236543 |
| CD3 | BioLegend | Clone 145-2C11; RRID: AB_893317 |
| CD4 | BioLegend | Clone GK1.5 or RM4-5; RRID: AB_893323, AB_10898318 |
| CD5 | BD PharMingen/BioLegend | Clone 53-7.3; RRID: AB_394559, AB_2563930 |
| CD8 | BioLegend | Clone 53-6.7; RRID: AB_893423, AB_2561389 |
| CD11b | BioLegend | Clone M1/70; RRID: AB_755986, AB_830642 |
| CD11c | BioLegend | Clone N418; RRID: AB_830649, AB_389306 |
| CD19 | BioLegend | Clone 6D5; RRID: AB_493734, AB_830707 |
| CD21/35 | BD PharMingen/BioLegend | Clone 7G6/7E9; RRID: AB_395070, AB_1953277 |
| CD23 | BD PharMingen/BioLegend | Clone B3B4; RRID: AB_394652, AB_2103038, AB_312829 |
| CD24 | BioLegend | Clone M1/69; RRID: AB_2563464 |
| CD40L | Miltenyi Biotec | Clone MR1; RRID: AB_2661127 |
| CD40 | DRFZ | Clone FGK-45 |
| CD43 | BD PharMingen | Clone S7; RRID: AB_10895376 |
| CD69 | DRFZ | Clone H1.2F3 |
| CD71 | BioLegend | Clone RI7217; RRID: AB_313564 |
| CD72 | BD PharMingen | Clone K10.6; RRID: AB_393982 |
| CD79α | BioLegend | Clone F11-172; RRID: AB_2075634 |
| CD79β | BioLegend | Clone HM79-12; RRID: AB_1575061 |
| CD81 | BioLegend | Clone Eat-2; RRID: AB_313138 |
| CD93 | eBioscience | Clone AA4.1; RRID: AB_469466 |
| CD138 | BD PharMingen/BioLegend | Clone 281-2; RRID: AB_395000, AB_2565621 |
| CD200 | BioLegend | Clone OX-90; RRID: AB_10900996 |
| CXCR3 | BioLegend | Clone CXCR3-173; RRID: AB_1088994 |
| Foxp3 | eBioscience | Clone FJK-16 s; RRID: AB_465243, AB_465936 |
| Fc receptor | DRFZ | Clone 2.4G2 |
| FAS | BD PharMingen | Clone Jo2; RRID: AB_396768 |
| GL-7 | BD PharMingen | Clone GL7; RRID: AB_10894953 |
| IgM | BioLegend | Clone RMM-1; RRID: AB_2650758 |
| IgD | BioLegend | Clone 11-26c.2a; RRID: AB_2562887 |
| IFN-γ | BD PharMingen/BioLegend | Clone XMG1.2; RRID: AB_2034014, AB_1595591 |
| Ki-67 | BioLegend | Clone 16A8; RRID: AB_2561929 |
| LAG-3 (CD223) | eBioscience | Clone C9B7W; RRID: AB_494214, AB_2573428 |
| MHC-II | DRFZ | Clone M5/114 |
| PD-1 | BioLegend | Clone 29F.1A12; RRID: AB_2251944 |
| TCR-β | BD PharMingen | Clone H57-597; RRID: AB_10584335 |
| TNF-α | BD PharMingen/BioLegend | Clone MP6-XT22; RRID: AB_2562918, AB_469508 |
| PD-L1 | BD PharMingen | Clone MIH5; RRID: AB_397018 |
| PD-L2 | BioLegend | Clone TY25; RRID: AB_2566345 |
| VH11 | Prof. Kyoko Hayakawa (Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, USA) | Clone P18-3H7 |
| Vk14 (Vk9) | Prof. Kyoko Hayakawa (Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, USA) | Clone P18-13B5 |
| VH12 | Prof. Klaus Rajewsky (MDC Berlin) | Clone 5C5 |
| IL-10 | BioXCell | Clone JES5-2A5; RRID: AB_1107696 |
| IL-10R | BioXCell | Clone 1B1.3A; RRID: AB_1107611 |
| Ig (H+L) | Southern Biotechnology | Cat. #1010-01; RRID: AB_609680 |
| IgM-AP | Southern Biotechnology | Cat. #1020-04; RRID: AB_619829 |
| IgG-AP | Southern Biotechnology | Cat. #1030-04; RRID: AB_609689 |
| IgG1-AP | Southern Biotechnology | Cat. #1070-04 |
| IgG2b-AP | Southern Biotechnology | Cat. #1090-04; RRID: AB_619828 |
| IgG2c-AP | Southern Biotechnology | Cat. #1079-04; RRID: AB_2692321 |
| IgG3-AP | Southern Biotechnology | Cat. #1100-04 |
| IgA-AP | Southern Biotechnology | Cat. #1040-04; RRID: AB_619826 |
| Goat Anti-Human IgG-UNLB | Southern Biotech | Cat. #2040-01; RRID: AB_617099 |
| Goat Anti-Human IgG-Biotin | Southern Biotech | Cat. #2040-08 |
| Human IgG standard | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. #I2511; RRID: AB_1163604 |
| Streptavidin-Alexa 488 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. #S32354 |
| Streptavidin-PE | BD PharMingen | Cat. #554061 |
| Streptavidin-APC | BD PharMingen | Cat. #554067 |
| Streptavidin-APC-Cy7 | BioLegend | Cat. #405208 |
| Streptavidin-BV421 | BioLegend | Cat. #405225 |
| Streptavidin-BV605 | BioLegend | Cat. #405229 |
| Streptavidin-BV785 | BioLegend | Cat. #405249 |
| Streptavidin-PE/Cy7 | BD PharMingen | Cat. #557598 |
| Streptavidin-PerCP | BD PharMingen | Cat. #554064 |
| Anti-PE | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat. #130-048-801; RRID: AB_244373 |
| B-1a Cell Isolation Kit | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat. #130-097-413 |
| CD19 | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat. #130-052-201 |
| CD43 | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat. #130-049-801 |
| CD11b | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat. #130-049-601 |
| CD11c | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat. #130-052-001 |
| CD4 | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat. #130-049-201 |
| CD8 | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat. #130-049-401 |
| CD90.2 | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat. #130-049-101 |
| Chemical Peptides and Recombinant Proteins | ||
| DAPI | Sigma | Cat. #D8417 |
| Propidium Iodide | Sigma | Cat. #P4864 |
| Glutaraldehyde | Electron Microscopy Sciences | Cat. #16220 |
| Osmiumtetroxide | Polysciences | Cat. #0223D |
| Tannic acid | Polysciences | Cat. #04459 |
| Uranyl acetate | Ted Pella inc | Cat. #19481 |
| CutSmart Buffer | NEB | Cat. #B7204S |
| Trypsin 0.5% EDTA | Life Technologies | Cat. #25300054 |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol | Life Technologies | Cat. #31350010 |
| Calcium chlorure dihydrated | Roth | Cat. #5239.2 |
| TMB | Ebioscience | Cat. #00-4201-56 |
| Tween20 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. #P1379 |
| Critical Commercial Assays | ||
| Gene Chip Mouse 430 2.0 | Affymetrix GmbH | Cat. #900495 |
| Mouse Cell Screening (PE) kit | BioLegend | Cat. #700003 |
| Foxp3 Staining Buffer Set | Ebioscience | Cat. #00-5523-00 |
| BD Cytofix/Cytoperm Plus Kit | BD PharMingen | Cat. #554715 |
| One Step RT-PCR kit | QIAGEN | Cat. #210212 |
| Reverse Transcription System | Promega | Cat. #A3500 |
| LightCycler FastStart DNA MasterPLUS SYBR Green | Roche Diagnostik | Cat. #03515885001 |
| Bio-Plex Pro Mouse Cytokine IL-10 Set, 1 × 96 well | Bio-Rad | Cat. #171-G5009M |
| Deposited Data | ||
| Gene array data | This paper | GEO: GSE103458 |
| RNA-seq and DNA methylation data | This paper | ENA: PRJEB22138 |
| Other | ||
| Expression vectors containing the human IGG1 constant regions | Prof. Dr. Hedda Wardemann, (DKFZ, Heidelberg) | N/A |
| Expression vectors containing the human IGK constant regions | Prof. Dr. Hedda Wardemann, (DKFZ, Heidelberg) | N/A |
| Expression vectors codings for Human monoclonal antibody mGO53 |
Prof. Dr. Hedda Wardemann, (DKFZ, Heidelberg) | N/A |
| Expression vectors codings for Human monoclonal antibody JB40 |
Prof. Dr. Hedda Wardemann, (DKFZ, Heidelberg) | N/A |
| Expression vectors codings for Human monoclonal antibody ED38 |
Prof. Dr. Hedda Wardemann, (DKFZ, Heidelberg) | N/A |
| PtC-containing Liposomes labeled with Texas Red | FormuMax | Cat. #F60103F-TR |
| Lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli 055:B5 | Sigma | Cat. #L2637-25MG |
| Tamoxifen | Sigma | Cat. #T5648-1G |
| Sunflower seed oil from Helianthus annuus | Sigma | Cat. #S5007-250ML |
| NP-KLH | BioCat GmbH | Cat. # N-5060-25 |
| NP-LPS | BioCat GmbH | Cat. # N-5065 |
| NP-AECM-FICOLL | BioCat GmbH | Cat. # F-1420 |
| AffiniPure Fab2 Fragment Goat Anti-Mouse IgM | Dianova GmbH | Cat. #115-006-075 |
| MacConkey Agar | Becton Dickinson GmbH | Cat. #212123 |
| RNeasy Mini Kit | QIAGEN | Cat. #74106 |
| Recombinant murine IL-6 protein | R&D Systems GmbH | Cat. #406-ML-005 |
| Recombinant murine IL-21 protein | R&D Systems GmbH | Cat. #594-ML-010 |
| MultiScreenHTS IP Filter Plate | Millipore | Cat. #MSIPN4510 |
| BCIP/NBT substrate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. #34042 |
| Proteinase K | Sigma Aldrich | Cat. #P2308 |
| Pefabloc SC | Sigma Aldrich | Cat. #76307 |
| HaeIII | New England Biolabs | Cat. #R0108M |
| Klenow Fragment exo- | New England Biolabs | Cat. #M0212L |
| T4-Ligase | New England Biolabs | Cat. #M0202M |
| T4-Ligase | New England Biolabs | Cat. #M0202L |
| RNase H | New England Biolabs | Cat. #M0297L |
| DNA Polymerase I | New England Biolabs | Cat. #M0209L |
| NEBNext High-Fidelity 2X PCR Master Mix | New England Biolabs | Cat. #M0541L |
| TruSeq DNA PCR-Free LT Library Preparation Kit - Set A | Illumina | Cat. #FC-121-3001 |
| Nextera DNA Sample Preparation Kit | Illumina | Cat. #FC-121-1030 |
| EZ DNA Methylation-Gold Kit | Zymo research | Cat. #D5006 |
| HotStarTaq DNA Polymerase | QIAGEN | Cat. #203207 |
| MinElute PCR Purification Kit | QIAGEN | Cat. #28006 |
| Agencourt AMPure XP | Beckman Coulter | Cat. #A63881 |
| mRNA Capture Kit | Roche | Cat. #11787896001 |
| M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase, RNase H Minus, Point Mutant | Promega | Cat. #M3683 |
| Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Kit | Agilent | Cat. #5067-4626 |
| Pfu polymerase | Promega | Cat. #M7745 |
| Hot Taq polymerase | Promega | Cat. #M7805 |
| dNTP Master Mix | Eurogentec | Cat. #NU-0010-100 |
| AgeI–HF | NEB | Cat. #R3552L |
| SalI–HF | NEB | Cat. #R3138L |
| BsiWI | NEB | Cat. #R0553L |
| NEBuffer 1 | NEB | Cat. #B7001S |
| Gel and PCR clean up kit | Macherey-Nagel | Cat. #740609.250 |
| 10X Buffer T4 ligase | Promega | Cat. #C126A |
| T4 ligase | Promega | Cat. #M180B |
| One Shot TOP10 Chemically Competent E.coli | Invitrogen | Cat. #C404006 |
| Luria Broth | Dutscher | Cat. #777495 |
| Luria Agar | Dutscher | Cat. #777494 |
| S.O.C Medium | Life Technologies | Cat. #15544034 |
| Ampicillin sodium salt | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. #A9518 |
| NucleoSpin Plasmid | Macherey-Nagel | Cat. #740588.250 |
| NucleoSpin 96 Plasmid Transfection-grade | Macherey-Nagel | Cat. #740491.4 |
| DMEM | Life Technologies | Cat. #61965026 |
| FBS South America | BIOWEST | Cat. #S1810-500 |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin sol | Life Technologies | Cat. #15140-122 |
| Nutridoma-SP | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. #11011375001 |
| Double strand DNA | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. #31149-10G-F |
| Insulin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. #I9278-5ML |
| Bovine Serum Albumin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. #A7906-100G |
| Extravidin, Peroxidase Conjugate | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. #E2886-1ML |
Contact for Reagent and Resource Sharing
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the Lead Contact, Simon Fillatreau (simonfillatreau@googlemail.com). Certain materials are shared with academic and non-profit research organizations for research and educational purposes only under an MTA to be discussed in good faith with the recipient.
Experimental Model and Subject Details
Mice
C57BL/6, Il10eGFP (Neves et al., 2010), Btk−/−, Cd72−/−, Cd19−/−, Cd1d−/−, Nos2−/−, Rag2−/−, B1-8iIgk−/−, Fcγr2b−/−, Cd19-cre-Notch2fl/fl, Il10−/−, Lag3−/− (Miyazaki et al., 1996, Workman et al., 2004), Tcrα/β−/−, Cd40−/−, Myd88−/−, Myd88−/−Trif−/−, JHT, Cd72−/−JHT, Prdm1eGFP, Cd72−/−Il10eGFP, Lag3−/−Il10eGFP, Cd21-cre-ROSA-STOP-eYFP, Aicda-cre-ERT2-ROSA-STOP-RFP, C3H/HeOuJ were bred under specific pathogen-free conditions. C3H/HeOuJ mice were also bred under germ-free conditions. Mouse strains used in infection experiments were NrampS. B-Lag3−/− mice were obtained by reconstituting recipient mice with a mixture of bone marrow cells from B cell-deficient JHT mice (80%) and Lag3−/− mice (20%). Control B-WT chimera was obtained using a mixture of bone marrow cells from JHT mice (80%) and C57BL/6 mice (20%). B-Lag3−/−Il10eGFP and their B-Il10eGFP controls were obtained using the same strategy. All experiments were reviewed and approved by appropriate institutional review committees (LAGeSo Berlin), and were conducted according to French, and German legislations, in compliance with European community council directive 68/609/EEC guidelines. Mice were of C57BL/6 strain, 6-14 weeks old at start of experiments, unless otherwise stated, and of sex-matched male and female genders.
Method Details
Bacterial infection
Mice were infected with 1x106 or 1x107 CFU for Salmonella typhimurium SL7207 strain or 100 CFU for SL1344 strain intravenously (i.v.). For survival and vaccination plus rechallenge experiments mice were first vaccinated with 1x106 CFU of SL7207 given i.v. and 90 days later were rechallenged with 100 CFU of SL1344 or 1x106 or 107 CFU of SL7207. During survival experiments, mice were daily checked and presented as percentage of live animals. The bacterial loads were determined by plating a series of dilutions of homogenized organs on MacConkey agar plates. Heat-killed S. typhimurium (HKST) was prepared by inactivation of the SL1344 strain in water bath at 70°C for 1 hour. Bacteria were suspended in PBS. Salmonella infection was performed in a blinded manner, and identities of the mice were revealed upon termination of the experiment. No randomization was used. Estimation of size groups was based on our previous experience with these disease models, without a priori determination via power calculation. For neutralization of IL-10 signaling, mice were treated i.v. with a combination of anti-IL-10 (JES5-2A5; 500 μg/mouse/injection; BioXCell) and anti-IL-10R (1B1.3A; 500 μg/mouse/injection; BioXCell) on days −3, −1, and +1 after infection.
Tamoxifen administration
Tamoxifen was resuspended in sunflower seed oil from Helianthus annuus to a final concentration of 20mg/ml. 10mg of tamoxifen was administered by gavage to Aicda-cre-ERT2-ROSA-STOP-RFP mice twice with 5 days interval between the first and second administration. Mice were analyzed 15 days after the last administration.
Immunization and treatment with agonists of BCR, CD40, TLR4
C57BL/6 mice were immunized i.p. with 200 μg NP-KLH precipitated in alum, NP-Ficoll, or NP-LPS. Mice were analyzed 7 days after immunization. In house conjugated APC or PE nitrophenyl hapten was used to detected NP specific B and plasmocytes.
Il10eGFP mice were injected i.v. with 100 μg anti-BCR (Fab2 anti-mouse IgM), 50 μg anti-CD40 (FGK-45), or 10 μg LPS (E. coli 055:B5), alone or in combination. Mice were analyzed 24h later.
Isolation of plasmocytes and B cells
For gene array, quantitative PCR, restimulation in vitro, ELISPOT assays and transmission electron microscopy analysis, plasmocytes and B cell subsets were obtained from C57BL/6 or Il10eGFP mice, naive or on day 1 p.i. with 107 CFU Salmonella (SL7207) by a two steps process. First, CD138+ cells were enriched by autoMACS after incubation with anti-CD138-PE followed by anti-PE microbeads. CD138+ cells obtained after autoMACS were then stained with anti-CD19, CD138, LAG-3, CD22 and CD11b/CD11c/TCR-β/DAPI. The following populations were sorted by FACS Sorter Aria I and/or II from this fraction: CD138hiCD22+LAG-3-CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI-, CD138hiCD22-LAG-3-CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI-, CD138hiCD22-LAG-3+CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI-, CD138hiCD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI-, CD138hiIl10eGFP+CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI- and CD138hiIl10eGFP-CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI-, CD138hiLAG-3+CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI- and CD138hiLAG-3-CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI-. The cells from the CD138-negative fraction after autoMACS were stained with anti-CD19, CD138, CD1d, CD21, CD23 and CD11b/CD11c/TCR-β/DAPI. CD19+CD138-CD11b-CD11c-TCRβ-DAPI-; CD19+CD1dhiCD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI- and CD19+CD1dlowCD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI-; CD19+CD1dlowCD21+CD23+CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI- (FO) and CD19+CD1dhighCD21highCD23low/-CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI- (MZ) were then isolated from this fraction by FACS Sorter Aria I and/or II. Total B cells were obtained by magnetic isolation using negative selection with anti-CD11b, CD11c, and CD43 microbeads. For PeC, cells were incubated with B-1a Cell Biotin-Antibody Cocktail (Miltenyli Biotec) for 5 minutes at 2-8°C and then with anti-Biotin Microbeads for an additional 10 minutes in the same conditions in order to deplete non-B cells, according to Manufacturer’s instructions. LD columns were used for removing the non-B cells. Unlabeled cells were collected representing the pre-enriched B1a cell fraction that contained all PeC B cells fractions.
For single cell sorting, single CD138hiIl10eGFP+CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI- or CD138hiIl10eGFP-CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI-, CD138hiLAG-3+CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI-, CD138hiLAG-3-CD11b-CD11c-TCR-β-DAPI- plasmocytes were directly sorted into 96-well PCR plates supplemented 1X RT-PCR buffer. Plates were then covered with microseal B film and immediately frozen on dry ice before storage at −80°C for further experiments.
For epigenetic and RNaseq analysis plasmocyte and B cell populations were sorted by FACS Sorter Aria I and/or II from spleen and PeC of naive C57BL/6 mice using the gating strategy illustrated in Methods S1.
For adoptive transfer, 106 of flow cytometry-sorted B1a, B1b, and B2 cells from PeC, as well as CD19+CD138- splenic B cells were administered i.p. into Rag2−/− mice, which were analyzed 3 weeks later.
B cell stimulation and cytokine production measurement
Plasmocytes and/or B cell subsets were stimulated at 5x105 or 1x105 cells per well in 96-well flat or round bottom plates, respectively, in complete RPMI or with LPS (1μg/ml), α-IgM (Fab) (Dianova GmbH, 5μg/ml), agonistic α-CD40 antibody (clone FGK-45, produced in house at 10μg/ml), and in combinations in the presence of IL-6 (20ng/ml; R&D Systems GmbH), IL-21 (20ng/ml; R&D Systems GmbH). For analysis of cytokine production, 150μl supernatant of activated cells was collected and transferred into new 96 well plates and kept at −20°C until further use. 50μl of supernatant was used to measure cytokine concentration using Bio-Plex kits (Bio-Rad) according to the manufacturer’s instruction.
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Sorted cells, fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde (EM grade), were sedimented in warm low melting agarose (2% in PBS) and left to set. Excised bits of agarose containing cell-groups were then postfixed in 0.5% osmium tetroxide, contrasted with tannic acid and 2% uranyl acetate, dehydrated in a graded ethanol series and embedded in epoxy resin. After polymerization, sections were cut at 60 nm and contrasted with lead citrate. Specimens were analyzed in a Leo 906E transmission electron microscope at 100KV (Zeiss, Oberkochen, DE) using a side mounted digital camera (Morada; SIS-Olympus Münster DE).
Gene array hybridization
cRNA were hybridized on Affymetrix MG 430 2.0 arrays using standard Affymetrix protocol after quality control with Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer and quantification with NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer.
Library preparation for methylation analysis of plasmocytes and B cell subsets
Sorted cells were lysed and digested with proteinase K followed by addition of 1mM Pefabloc SC (Sigma-Aldrich) to inhibit protease activity. Cell lysates were digested overnight with 50U HaeIII (New England Biolabs) followed by inactivation at 80°C. A-tailing was performed using 5U Klenow exo- (New England Biolabs), and Illumina TruSeq adaptors were ligated at 16°C overnight using 2000U T4-Ligase (New England Biolabs). DNA fragments were purified with 1.5x Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter) and bisulfite treated using the EZ DNA Methylation-Gold Kit (Zymo research) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The libraries were amplified by 14-15 cycles of PCR using HotStarTaq DNA Polymerase (QIAGEN), and purified with 0.9x Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter). The library quality was assessed using Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer, and the quantity was measured using Qubit® dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The Illumina HiSeq 2500 system was used for 100 bp single-end sequencing.
Library preparation for mRNA Seq
mRNA Capture Kit (Roche) was used to isolate mRNA with the modification that cell pellets (105 cells) were lysed in 49μl lysis buffer, and 1μl of the biotin labeled oligo(dT)20 working solution was added to the lysate. After immobilization and washing of mRNA in streptavidin coated tubes first strand synthesis was performed in 50μl using 400U M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase RNase H- (Promega) at 37°C for 1h. For second strand synthesis 400U T4-Ligase, 5U RNase H, and 50U DNA Polymerase I (New England Biolabs) were used at 16°C for 2.5h. The double stranded cDNA was fragmented and tagged with sequencing adapters using the Nextera DNA Library Preparation Kit (Illumina) with the deviation that 0.2μl of the Tagment DNA Enzyme 1 were used in a 50μl reaction. After incubation at 55°C for 5 minutes the reaction was stopped and the DNA was released from the tubes by the addition of 250μl of Buffer PB (QIAGEN). The DNA was purified using MinElute PCR Purification Kit (QIAGEN) following the manufacturer’s protocol, and the elution step was performed with 11.5μl distilled water. The libraries were amplified for 12 cycles using NEBNext High-Fidelity 2X PCR Master Mix (New England Biolabs) and 0.2μM Index adapters (AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACAC[i5]TCGTCGGCAGCGTC and CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGAT[i7]GTCTCGTGGGCTCGG). The libraries were purified with 0.8x Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter), and sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq 2500 system with 1x100 bp single-end reads.
Analysis of mRNA expression by B cells and plasmocytes
Sorted or cultured B cells and plasmocytes were lysed in RLT buffer (QIAGEN) and kept at −80°C until use. Total RNA was extracted using RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. After DNase treatment, cDNA was synthesized from RNA with a Reverse Transcription System (Promega). Quantitative RT-PCR was performed on an MX3005P QPCR System (Stratagene), with LightCycler FastStart DNA Master SYBR Green I (Roche). Transcripts were quantified using β-actin as standard, and the following forward (FP) and reverse (RP) primers (MWG Biotech): β-actin FP: 5′-TGGAATCCTGTGGCATCCATGAAAC-3′, β-actin RP: 5′-TAAAACGCAGCTCAGTAACAGTCC-3′; IL-10 FP: 5′-AGCCGGGAAGACAATAAC TG-3′, IL-10 RP: 5′-CATTTCCGATAAGGCTTG G-3′.
Ig gene amplification from single cells
Single cells sorted in 96-well PCR plate were immediately frozen on dry ice and stored at −80°C until further use. To amplify Ig gene from single cells, a nested PCR approach was used. Reverse transcription (RT) and the first PCR step for Igμ (IgM) and Igκ variable gene transcripts were carried out in a one-step reaction using the QIAGEN OneStep RT-PCR kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The Ig gene primers were chosen based on Tiller et al. (2009). The second round of PCR was carried out with 2μl of a 100-fold dilution of the unpurified first PCR product at 94°C for 4 minutes followed by 50 cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 60°C (Igμ) or 48°C (Igκ) for 30 s, 72°C for 45 s, and final incubation at 72°C for 10 minutes. The second PCR products were analyzed on 2% agarose gels.
The Ig gene PCR products from different plasmocyte subsets were sequenced (LGC) with the respective forward primers. Nucleotide sequences were then analyzed using IMGT/V-Quest to determine germline V, D, and J gene members, somatic hypermutation (counted for CDR1-FWR3 inclusively), CDR3 sequences, N-nucleotide addition.
Cloning of mouse Ig genes into expression vectors
After identifying V and J gene segment, second PCR reactions were repeated using 5μl of a 100-fold dilution of the unpurified first PCR product as template with specific V and J gene primers containing restriction sites to clone directly into expression vectors. PCR products were purified using Gel and PCR clean up kit before digestion with AgeI and SalI (Igh), AgeI and BsiWI (Igk). Digested Igh and Igk PCR products were purified from 0.9% agarose before ligation into expression vectors containing the human IGG1 and IGK constant regions, respectively. Ligation products were transformed into competent E.Coli via heat shock at 42°C, then E.Coli cells were plated on Ampicillin plates (100μg/ml) overnight at 37°C. Inserted genes were screened by PCR in Ampicillin resistant bacterial colonies.
Expression of recombinant immunoglobulin
Four single positively bacterial clones of each Igh and Igk gene were grown overnight at 37°C in 5ml of LB medium containing 100μg/ml Ampicillin. Plasmids were purified using NucleoSpin Plasmid - plasmid Miniprep kit (Macherey-Nagel), followed with digestion and analysis on 1% agarose. Inserted plasmids were then sequenced (GATC) to confirm identity with the second round PCR product and no mutation which probably is introduced by polymerase.
One day before transfection, 4x106 HEK293 T cells were plated in T175 culture flasks in complete DMEM (DMEM + 10% (v/v) FCS + Penicillin (100U/ml)/Streptomycin (100 μg/ml) + 2-Mercaptoethanol (50 μM). The cell should be 80% confluency on the day of transfection. Transient transfections were performed with calcium-phosphate precipitation. In brief, equal amounts of IgH (7μg) and corresponding IgK chain vector were mixed with sterile water and 124μl of 2M CaCl2. An equal volume of 1ml of 2X HBS was added drop-wise to the above mixture under slow vortexing and incubated at room temperature for 15min to allow formation of precipitates. The resulting solution was distributed to the culture flask. On the next day, cells were washed with 5ml of serum-free DMEM and 20ml of DMEM supplemented with 1% Nutridoma-SP, Penicillin (100U/ml)/Streptomycin (100 μg/ml) and 2-Mercaptoethanol (50 μM) was added. Supernatant were harvested at day 6 post transfection, cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 800 g for 10 minutes and culture supernatants were stored at −20°C.
Detection of antibody reactivity by ELISAs
IgG concentration in the supernatants were determined by ELISA. In brief, enhanced protein-binding ELISA plates were coated with 50μl of Goat Anti-Human IgG-UNLB diluted in carbonate buffer as capture antibody at 4°C overnight. Plates were washed 3 times with PBS. Unspecific binding was blocked by 200μl PBS/ 3%BSA for 1 hour at 37°C and washed again 4 times with PBS/0.1% Tween. Human IgG standard and culture supernatants were added, incubated for 2 hours at 37°C and washed again to remove unbound antibody with PBS/0.1% Tween. 100μl of Biotinylated Goat Anti-Human IgG Secondary Antibody was added, incubated for 1 hour at room temperature and washed again with PBS/0.1% Tween prior to adding ExtrAvidin®−Peroxidase for 1 hour at room temperature. After washing, assays were developed using 100μl TMB solution and incubated at RT for color development. Assays were stopped by H2SO4 and ODs were measured at 450nm. Antibody concentration was determined by Softmax Pro software.
Antibodies with concentration higher than 5μg/ml were selected to test for polyreactivity with LPS, dsDNA and Insulin by ELISA. In brief, enhanced protein-binding ELISA plates were coated with 50μl of LPS (10μg/ml) or insulin (10μg/ml) or dsDNA (10μg/ml) in carbonate buffer and incubated at 4°C overnight. After washing, plates were incubated with 100μl nonpurified antibodies for 2 hours at 37°C and washed again. Nonpolyreactive (mGO53), low polyreactive (JB40), highly polyreactive (ED38) recombinant human monoclonal antibodies served as controls and were included on each plate. Unbound antibodies were removed by washing 4 times with PBS/0.1% Tween before detected using Biotinylated Goat Anti-Human IgG Secondary Antibody, followed with ExtrAvidin®−Peroxidase for 1 hour at room temperature. The rest steps were performed as above mentioned.
Cell staining for flow cytometry
For surface staining, splenocytes, BM, PeC, and lymph node cells were first incubated with anti-Fc receptor antibody (clone 2.4G2) for 15 minutes to block unspecific bindings, and surface staining was then performed with antibodies conjugated directly with fluorochrome for 15 minutes. For biotinylated antibodies, cells were further incubated with Streptavidin conjugated to fluorochrome for 15 minutes. Dead cells were excluded by DAPI or PI.
For cytokine intracellular staining, cells were plated at 5x106 cells per well in flat-bottom 48-well plates with 1ml complete RPMI 1640 containing HKST for 1 hour. Golgistop was added afterward, and cells were incubated for 5 more hours. Cells were harvested and stained for surface markers, including uncoupled pacific orange to exclude dead cells before cells were fixed. Intracellular staining was performed with Cytofix/Cytoperm kit (BD) as recommended.
Ki67 (BioLegend) and Foxp3 nuclear stainings were performed with Foxp3 staining kit (Ebioscience). Stained cells were acquired on FACS Symphony, Fortessa, Canto, LSR II and analyzed with FlowJo software.
ELISPOT Assay
Sorted day 0 CD138hiLAG-3+ and CD138hiLAG-3- cells; day 1 CD138hiIl10eGFP+ and CD138hiIl10eGFP- cells, and day 1 after re-challenge CD138hiIl10eGFP+ and CD138hi Il10eGFP- cells were seeded at a starting number of 104 cells per well, with seven successive three-folds serial dilutions, in MultiScreenHTS IP Filter Plate (Millipore) pre-coated with anti-mouse Ig(H+L) chain (5 μg/ml; Southern Biotechnology Associates, cat number 1010-01). After 3 h incubation, plates were washed, and incubated with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-IgM or total IgG or IgG1 or IgG2b or IgG2c or IgG3 or IgA overnight at 4°C (Southern Biotechnology Associates). ELISPOT were then developed using BCIP/NBT substrate.
Quantification and Statistic Analysis
Data and statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, USA) and data were represented as mean ± SEM. Equality of variances between groups was assessed before analyses by t test. Groups were compared using two-tailed t test, or Wilcoxon test, or Mann-Whitney test. t test was modified using Welch’s correction in case of unequal variance (nsp > 0.05, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗ p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗ p < 0.0001). No sample was excluded from analysis.
Gene array analysis
Normalization of microarrays was performed using gcrma R package (Wu et al., 2004). For each sample, we determined if a probe was present (i.e., expressed) or not using mas5calls function of affy R package (Gautier et al., 2004). The significantly differentially regulated genes were detected using limma R package (Ritchie et al., 2015) with p values adjusted according to Benjamini Hochberg procedure. In order to be selected in a comparison of two conditions, each Affy IDs had to fulfill the following criteria: (i) be present in at least two of the three arrays for at least one of the two conditions compared; (ii) to have a mean signal intensity higher than 50 in at least one of the two conditions; (iii) to show an adjusted (adj.) p value < 0.01 in the comparison of the two conditions. The genes differentially expressed between CD138hiIl10eGFP+ and CD138hiIl10eGFP- plasmocytes (adj. p value < 0.01) were then selected and filtered using the gene ontology resource (www.geneontology.org) to focus on surface molecules. Heat-map of Figure 1A has been produced using pheatmap R package (pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R package version 1.0.2. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap). If several probes were available for a given gene, their signal intensity has been averaged. For the hierarchical clustering, we used ward distance function and complete linkage function.
DNA methylation analysis
Trimming, alignment to the mm10 reference genome and DNA methylation value calling were performed as described before (Durek et al., 2016). Pairwise differential DNA methylation was calculated using the R package methylKit (Akalin et al., 2012) and DMR were defined as 1kb regions covering ≥ 3 CpG sites with ≥ 20% methylation difference (q-value ≤ 0.01) between the cell types. All analyzed CpG were filtered for coverage ≥ 10x and presence in all replicates. Average DNA methylation per cell type was calculated using coverage weighted average methylation of 3 replicates. DMR were annotated to genes and genomic location by using ChipSeek (Chen et al., 2014). Transcription factor binding sites were predicted using TRAP (Thomas-Chollier et al., 2011) and AliBaba2 (http://gene-regulation.com/pub/programs/alibaba2/index.html). The integrated Genome Viewer (IGV) genome browser was used to display data in Figure 4D and Figure S4D.
RNaseq analysis
Adaptor removal and trimming of low quality ends (phred score = 20) of FastQ format reads was performed using Trim Galore! (version 0.3.3) (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/trim_galore/). Alignment to the mm10 reference genome was done using 2-step STAR alignment (Dobin and Gingeras, 2015). PCR duplications were determined using MarkDuplicate (version 1.115) from Picard tools (http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/) and quality control was performed using RNA-seQC (DeLuca et al., 2012). Subsequently, featureCounts (Liao et al., 2014) was used to count reads mapping to the genes from Gencode annotation (vM2) (https://www.encodeproject.org/files/gencode.vM2.annotation). Pairwise differential expression was analyzed using the R package edgeR (Robinson et al., 2010). A p value cutoff of 0.01 and an FDR cutoff of 0.05 was set to select differentially expressed genes. GO Term analysis were performed using GREAT (McLean et al., 2010).
Data and Software Availability
The Affymetrix gene array data have been deposited at NCBI GEO depository and are accessible with the accession number GSE103458, or using the link https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE103458
The RNaseq and DNA methylation data have been deposited at the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA), and will be accessible with the accession number PRJEB22138, or using the links.http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/data/view/PRJEB22138<https://deref-web-02.de/mail/client/dAlzMDs2lmY/dereferrer/?redirectUrl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.ebi.ac.uk%2Fena%2Fdata%2Fview%2FPRJEB22138>
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Kirsch, H. Schliemann, the Regine von Ramin Laboratory (DRFZ), and A.B. Koehler (Max Planck Institute of Infection Biology) for technical help, K. Rajewsky (MDC, Berlin) for VH12, K. Hayakawa (Fox Chase Cancer Center, USA) for VH11 and Vk14 antibodies, H. Wardemann (DKFZ, Heidelberg) for Ig expression plasmids, S. Nutt (WEHI, Australia) for Prdm1eGFP mice, H.J. Fehling (Ulm) for ROSA-STOP-tdRFP mice, and D. Vignali, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, and IGBMC for Lag3−/− mice. S.F. lab is supported by ERC PREG-LAB 647696, AXA Chair Translational Immunology, Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-16-CE18-0007-01), Chair of Excellence (Université Sorbonne Paris Cité), and Infect-ERA project ABIR (031A403), Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (TRR130, FI 1238/1-2). T.T. is supported by JSPS KAKENHI 26293062 and 17H05790 grants. J.W. was supported by the German Ministry for Education and Research BMBF through the grant 01KU1216F (DEEP). V.D.D. received a 4-year PhD fellowship from the Vietnam Ministry of Education and Training (Projects 322 and 911).
Author Contributions
A.C.L., V.D.D., V.L., A.W., J.J., J.P., Q.S., J.T., A.B., V.F., I.S., U.S., S.R., L.J., P.B., T.T., T.A., A.H., T.D., U.Z.-S., A.F.V., K.D., G.L., S.K., C.G., J.-C.W., C.-A.R., S.H.E.K., J.W., and S.F. performed experiments and contributed to project development and writing of the manuscript.
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Published: July 10, 2018
Footnotes
Supplemental Information includes eight figures and two tables and can be found with this article online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.06.007.
Supplemental Information
References
- Akalin A., Kormaksson M., Li S., Garrett-Bakelman F.E., Figueroa M.E., Melnick A., Mason C.E. methylKit: a comprehensive R package for the analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation profiles. Genome Biol. 2012;13:R87. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-10-r87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker D.J., Childs B.G., Durik M., Wijers M.E., Sieben C.J., Zhong J., Saltness R.A., Jeganathan K.B., Verzosa G.C., Pezeshki A. Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature. 2016;530:184–189. doi: 10.1038/nature16932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair P.A., Chavez-Rueda K.A., Evans J.G., Shlomchik M.J., Eddaoudi A., Isenberg D.A., Ehrenstein M.R., Mauri C. Selective targeting of B cells with agonistic anti-CD40 is an efficacious strategy for the generation of induced regulatory T2-like B cells and for the suppression of lupus in MRL/lpr mice. J. Immunol. 2009;182:3492–3502. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler N.S., Moebius J., Pewe L.L., Traore B., Doumbo O.K., Tygrett L.T., Waldschmidt T.J., Crompton P.D., Harty J.T. Therapeutic blockade of PD-L1 and LAG-3 rapidly clears established blood-stage Plasmodium infection. Nat. Immunol. 2011;13:188–195. doi: 10.1038/ni.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Müller G.A., Quaas M., Fischer M., Han N., Stutchbury B., Sharrocks A.D., Engeland K. The forkhead transcription factor FOXM1 controls cell cycle-dependent gene expression through an atypical chromatin binding mechanism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013;33:227–236. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00881-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T.W., Li H.P., Lee C.C., Gan R.C., Huang P.J., Wu T.H., Lee C.Y., Chang Y.F., Tang P. ChIPseek, a web-based analysis tool for ChIP data. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:539. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corneth O.B.J., Klein Wolterink R.G.J., Hendriks R.W. BTK Signaling in B Cell Differentiation and Autoimmunity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016;393:67–105. doi: 10.1007/82_2015_478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca D.S., Levin J.Z., Sivachenko A., Fennell T., Nazaire M.D., Williams C., Reich M., Winckler W., Getz G. RNA-SeQC: RNA-seq metrics for quality control and process optimization. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1530–1532. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobin A., Gingeras T.R. Mapping RNA-seq Reads with STAR. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015;51 doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1114s51. 11 14 11-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durek P., Nordström K., Gasparoni G., Salhab A., Kressler C., de Almeida M., Bassler K., Ulas T., Schmidt F., Xiong J., DEEP Consortium Epigenomic profiling of human CD4+ T cells supports a linear differentiation model and highlights molecular regulators of memory development. Immunity. 2016;45:1148–1161. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillatreau S., Sweenie C.H., McGeachy M.J., Gray D., Anderton S.M. B cells regulate autoimmunity by provision of IL-10. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:944–950. doi: 10.1038/ni833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frescas D., Roux C.M., Aygun-Sunar S., Gleiberman A.S., Krasnov P., Kurnasov O.V., Strom E., Virtuoso L.P., Wrobel M., Osterman A.L. Senescent cells expose and secrete an oxidized form of membrane-bound vimentin as revealed by a natural polyreactive antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:E1668–E1677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1614661114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliani N., Magnani C.F., Huber S., Gianolini M.E., Pala M., Licona-Limon P., Guo B., Herbert D.R., Bulfone A., Trentini F. Coexpression of CD49b and LAG-3 identifies human and mouse T regulatory type 1 cells. Nat. Med. 2013;19:739–746. doi: 10.1038/nm.3179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier L., Cope L., Bolstad B.M., Irizarry R.A. affy--analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:307–315. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R.R., Wei C.J., Hayakawa K. Selection during development of VH11+ B cells: a model for natural autoantibody-producing CD5+ B cells. Immunol. Rev. 2004;197:60–74. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.0100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y., Fujio K., Okamura T., Yanai A., Sumitomo S., Shoda H., Tamura T., Yoshida H., Charnay P., Yamamoto K. Egr-2 transcription factor is required for Blimp-1-mediated IL-10 production in IL-27-stimulated CD4+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013;43:1063–1073. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulis M., Merkel A., Heath S., Queirós A.C., Schuyler R.P., Castellano G., Beekman R., Raineri E., Esteve A., Clot G. Whole-genome fingerprint of the DNA methylome during human B cell differentiation. Nat. Genet. 2015;47:746–756. doi: 10.1038/ng.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Y., Smyth G.K., Shi W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:923–930. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M., Baba A., Yokota T., Nishikawa H., Ohkawa Y., Kayama H., Kallies A., Nutt S.L., Sakaguchi S., Takeda K. Interleukin-10-producing plasmablasts exert regulatory function in autoimmune inflammation. Immunity. 2014;41:1040–1051. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean C.Y., Bristor D., Hiller M., Clarke S.L., Schaar B.T., Lowe C.B., Wenger A.M., Bejerano G. GREAT improves functional interpretation of cis-regulatory regions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010;28:495–501. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T., Dierich A., Benoist C., Mathis D. Independent modes of natural killing distinguished in mice lacking Lag3. Science. 1996;272:405–408. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5260.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neves P., Lampropoulou V., Calderon-Gomez E., Roch T., Stervbo U., Shen P., Kühl A.A., Loddenkemper C., Haury M., Nedospasov S.A. Signaling via the MyD88 adaptor protein in B cells suppresses protective immunity during Salmonella typhimurium infection. Immunity. 2010;33:777–790. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie M.E., Phipson B., Wu D., Hu Y., Law C.W., Shi W., Smyth G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:e47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M.D., McCarthy D.J., Smyth G.K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:139–140. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T., Chiba S., Ichikawa M., Kunisato A., Asai T., Shimizu K., Yamaguchi T., Yamamoto G., Seo S., Kumano K. Notch2 is preferentially expressed in mature B cells and indispensable for marginal zone B lineage development. Immunity. 2003;18:675–685. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenhals M., Jourdan M., Seckinger A., Pantesco V., Hose D., Kassambara A., Moreaux J., Klein B. Forced KLF4 expression increases the generation of mature plasma cells and uncovers a network linked with plasma cell stage. Cell Cycle. 2016;15:1919–1928. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1191709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalapour S., Font-Burgada J., Di Caro G., Zhong Z., Sanchez-Lopez E., Dhar D., Willimsky G., Ammirante M., Strasner A., Hansel D.E. Immunosuppressive plasma cells impede T-cell-dependent immunogenic chemotherapy. Nature. 2015;521:94–98. doi: 10.1038/nature14395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P.X., Hörkkö S., Chang M.K., Curtiss L.K., Palinski W., Silverman G.J., Witztum J.L. Natural antibodies with the T15 idiotype may act in atherosclerosis, apoptotic clearance, and protective immunity. J. Clin. Invest. 2000;105:1731–1740. doi: 10.1172/JCI8472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen P., Fillatreau S. Antibody-independent functions of B cells: a focus on cytokines. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015;15:441–451. doi: 10.1038/nri3857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen P., Roch T., Lampropoulou V., O’Connor R.A., Stervbo U., Hilgenberg E., Ries S., Dang V.D., Jaimes Y., Daridon C. IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature. 2014;507:366–370. doi: 10.1038/nature12979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichmann L.L., Kashgarian M., Weaver C.T., Roers A., Müller W., Shlomchik M.J. B cell-derived IL-10 does not regulate spontaneous systemic autoimmunity in MRL.Fas(lpr) mice. J. Immunol. 2012;188:678–685. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas-Chollier M., Hufton A., Heinig M., O’Keeffe S., Masri N.E., Roider H.G., Manke T., Vingron M. Transcription factor binding predictions using TRAP for the analysis of ChIP-seq data and regulatory SNPs. Nat. Protoc. 2011;6:1860–1869. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2011.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiller T., Busse C.E., Wardemann H. Cloning and expression of murine Ig genes from single B cells. J. Immunol. Methods. 2009;350:183–193. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2009.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z.Y., Sato H., Kusam S., Sehra S., Toney L.M., Dent A.L. Regulation of IL-10 gene expression in Th2 cells by Jun proteins. J. Immunol. 2005;174:2098–2105. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.4.2098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman C.J., Cauley L.S., Kim I.J., Blackman M.A., Woodland D.L., Vignali D.A. Lymphocyte activation gene-3 (CD223) regulates the size of the expanding T cell population following antigen activation in vivo. J. Immunol. 2004;172:5450–5455. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.9.5450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., Irizarry R.A., Gentleman R., Martinez-Murillo F., Spencer F. A model-based background adjustment for oligonucleotide expression arrays. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2004;99:909–917. [Google Scholar]
- Yanaba K., Bouaziz J.D., Haas K.M., Poe J.C., Fujimoto M., Tedder T.F. A regulatory B cell subset with a unique CD1dhiCD5+ phenotype controls T cell-dependent inflammatory responses. Immunity. 2008;28:639–650. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Deng J., Liu Y., Ko K.H., Wang X., Jiao Z., Wang S., Hua Z., Sun L., Srivastava G. IL-10-producing regulatory B10 cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis via suppressing Th17 cell generation. Am. J. Pathol. 2012;180:2375–2385. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida R., Suzuki M., Sakaguchi R., Hasegawa E., Kimura A., Shichita T., Sekiya T., Shiraishi H., Shimoda K., Yoshimura A. Forced expression of stabilized c-Fos in dendritic cells reduces cytokine production and immune responses in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012;423:247–252. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.05.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.