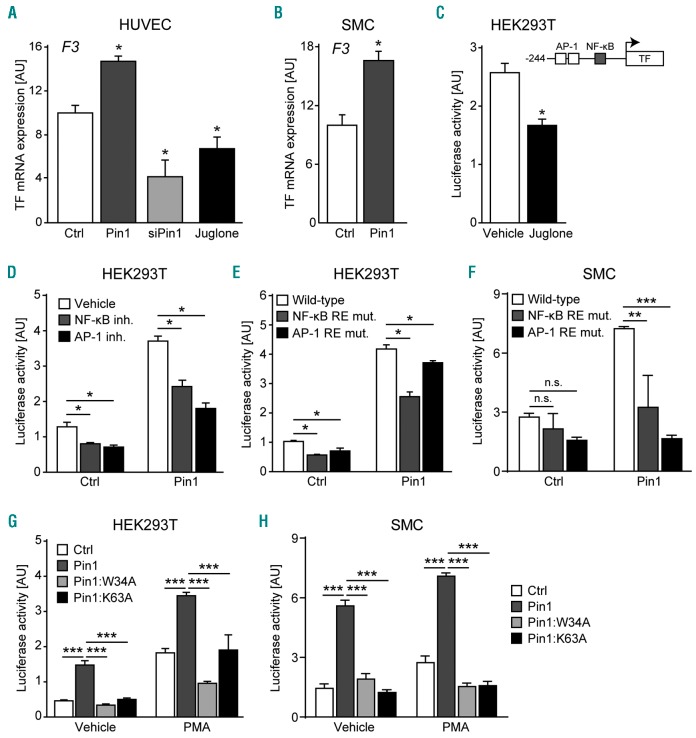
Figure 1.
Pin1 enhances Tissue Factor (TF) mRNA expression and TF promoter activation by NF-κB and AP-1. (A and B) Expression of the TF gene (F3) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and smooth muscle cells (SMC) after Pin1 overexpression, Pin1 knockdown (siPin1), or treatment with the Pin1 inhibitor Juglone. HUVECs were treated with TNF-α for 6 hours to induce TF gene expression. (C) Activity of the wild-type TF gene promoter luciferase reporter construct in PMA-stimulated HEK293T treated with Pin1 inhibitor Juglone or vehicle (DMSO) control. Inset shows schematic representation of the TF gene promoter luciferase reporter construct. (D) Activity of the wild-type TF gene promoter luciferase reporter construct after Pin1 overexpression in PMA-stimulated HEK293T and either vehicle (DMSO), NF-κB signaling inhibitor (BAY-117085), or AP-1 signaling inhibitor (SP600125) treatment. (E and F) Activity of luciferase reporter constructs containing either the wild-type TF gene promoter or the TF gene promoter in which the response element for NF-κB (NF-κB RE) or AP-1 (AP-1 RE) was mutated in PMA-stimulated HEK293T (E) or TNF-α-stimulated SMCs (F) transiently over-expressing Pin1. (G and H) Activity of the wild-type TF gene promoter luciferase reporter construct after transient overexpression of Pin1 or Pin1 mutants containing a disrupted WW-domain (Pin1:W34A) or lacking isomerase activity (Pin1:K63A) in HEK293T (G) or SMCs (H) left untreated or stimulated with PMA. Data are shown as mean±Standard Error of Mean. (A–C) P-values were calculated for comparisons between Pin1 overexpression, Pin1 knockdown (siPin1), or Juglone treatment versus control transduced (Ctrl) or vehicle-treated groups using the two-tailed Student’s t-test. (D–H) P-values were calculated using one-way ANOVA as indicated. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. AU: arbitrary units; mut: mutated.