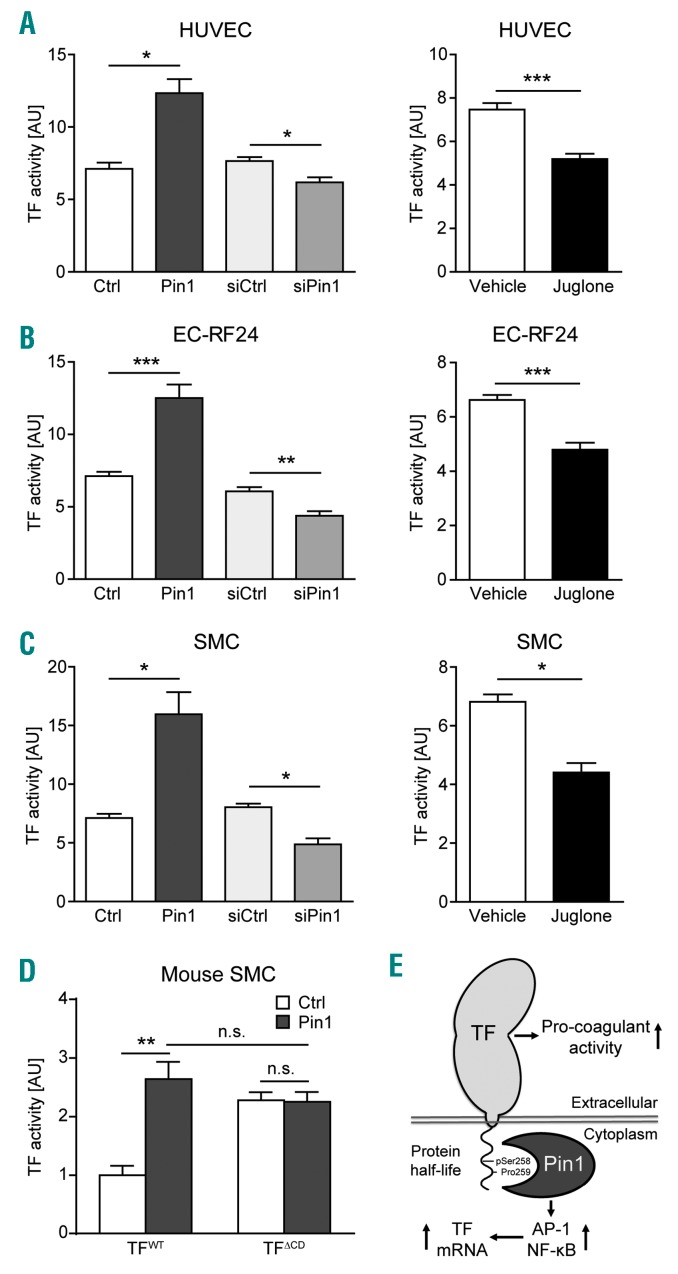
Figure 5.
Pin1 enhances Tissue Factor (TF) pro-coagulant activity via the twenty-amino acid cytoplasmic domain (TFCD). (A–C) Factor Xa generation as a measure of TF activity in human human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) (A), EC-RF24 cells (B), or smooth muscle cells (SMC) (C) after either overexpression or knockdown of Pin1 or treatment with the Pin1 inhibitor Juglone for 16 hours (hrs) followed by serum-starvation and treatment with ionomycin for 3 hrs (SMCs) or TNF-α for 16 hrs [EC-RF24 and endothelial cells (ECs)]. (D) Factor Xa generation as a measure of TF activity in mouse SMCs derived from wild-type mice (WT) or mice expressing TFΔCD from the endogenous TF gene locus after overexpression of Pin1 and stimulation with ionomycin for 3 hrs. (E) Summary of Pin1 effects on TF: Pin1 enhances the protein half-life and pro-coagulant activity of TF through interaction with the conserved pSer258-Pro259 motif in the TFCD and enhances the activity of the transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κB to increase TF gene expression. Data are shown as mean±Standard Error of Mean. P-values were calculated using two-tailed Student’s t-test (A–C) or two-way ANOVA (D). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. AU: arbitrary units.