Abstract
Frailty is defined as a state of increased vulnerability to poor resolution of homeostasis following stress, which increases the risk of adverse outcomes such as falls, delirium, and disability in the elderly. Recently in Japan, clinical practice guidelines (CPG) have recommended kampo treatment. We conducted a search for reports on Japanese CPG and kampo medicine in the treatment of symptoms in the elderly. The search was performed using the databases PubMed, Ichushi Web, J-Stage, Japan Medical Publishers Association, Medical Information Network Distribution Service, and CPG containing kampo products in Japan; reports from January 1st, 2012 to October 31st, 2017 were reviewed. Over the past 5 years, nine CPGs have recommended kampo treatment based on the evidence for improvement in skin symptoms, cough, gastro-intestinal dysfunction, urinary dysfunction, and dementia. Treatments with kampo medicine are performed depending on the coexistence of manifestations based on the original kampo concept, i.e., cognitive dysfunction and dementia with sarcopenia showing urinary disorder. Each kampo formula includes multiple crude drugs that have several pharmacological functions; these drugs include alkaloids, glycosides, and polysaccharides. Thus, kampo formula has an effect on multiple organs and coordinates the relationship between the brain, endocrine system, immune system, and skeletal muscles. Kampo treatment can be considered as supporting holistic medicine in elderly individuals with frailty.
Keywords: review, herbal medicine, kampo medicine, guidelines, geriatrics, elderly
Introduction
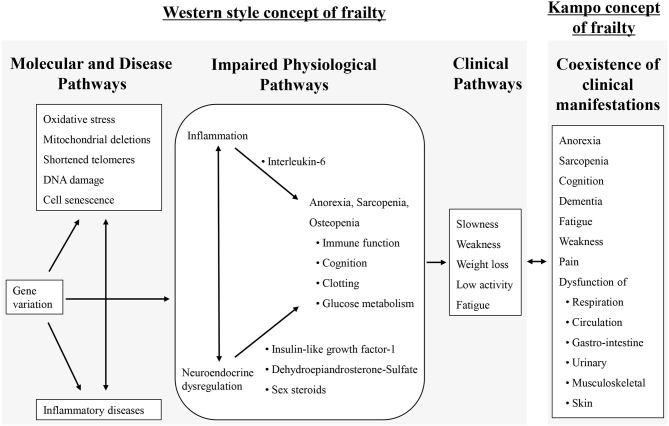
Frailty is defined as a state of increased vulnerability to poor resolution of homeostasis following stress, which increases the risk of adverse outcomes such as falls, delirium, and disability in the elderly (1–3). Frailty involves disorders in multiple inter-related physiological systems, including the brain, the endocrine system, the immune system, and the skeletal muscle, resulting in weight loss, exhaustion, low energy expenditure, slow gait speed, and weak grip strength (4). The left side of Figure 1 shows an overview of the hypothesized molecular, physiological, and clinical pathways involved in the pathogenesis of frailty (5). In addition to exercise intervention combined with nutrition, multifunctional pharmacological agents are probably required for preventing frailty.
Figure 1.
An overview of the hypothesized molecular, physiological, and clinical pathways involved in frailty and the kampo concept of frailty [adapted from (2, 5)].
In the super aged society in Japan, the percentage of the elderly population (aged over 65 years) is expected to exceed 30% in 2025 and reach 39.9% in 2060 (6). Frailty is one of the reasons for need of nursing care in the elderly, thus the medical, social, and economical correspondence has been a research focus. Traditional Japanese medicine (kampo) has been applied for the treatment of comorbid symptoms or disorder for the past 1500 years. Kampo medicine includes multiple crude drugs that have several pharmacological functions including alkaloids, glycoside, and polysaccharide (7). Thus, kampo medicine has an effect on multiple organs and coordinates the relationship between the brain, endocrine system, immune system, skeletal muscles, and the patients' emotional condition. The right side of the Figure 1 shows the kampo concept for frailty. We believe that concomitant use with western medicine and kampo medicine can contribute to management of patients with frailty. Evidence based on clinical studies has grown in the past two decades; and recently, in Japan, clinical practice guidelines (CPG) for symptoms in the elderly gave some recommendations for use of kampo medicine.
In this report, we review CPG regarding kampo and the evidence of the efficacy of kampo medicine in the treatment of the elderly. We also discuss the characteristics of the kampo concept.
Materials and methods
Literature search
We conducted data base searches for Japanese CPG and kampo medicine for the symptoms in elderlies in PubMed, Ichushi Web, J-Stage, Japan Medical Publishers Association, Medical Information Network Distribution Service, and Clinical Practice Guideline Containing Kampo products. The search was restricted to CPGs published between January 1st 2012 to October 31st 2017. We used the following search strategy: 1. CPG; 2. Kampo medicine; 3. Herbal medicine; 4. #1–3 in Japanese; 5. #1 OR #2 AND #3 OR; and 6. #4 OR #5.
Selection criteria
We included research articles published in English or Japanese that were related to CPG using kampo medicine. CPGs that mentioned the recommendation strength with quality of evidence and studies that included elderly subjects were selected. Physical therapy, massage therapy, acupuncture, and acupuncture-related techniques were excluded.
Data extraction
Eligible articles were categorized by two independent researchers (ST and SK). Specifically, information from the articles or CPGs was extracted and tabulated, and eligible CPG were classified according to the name of CPG, symptoms or diseases, clinical question, mention about quality of evidence, and recommendation strength.
Results
General aspects
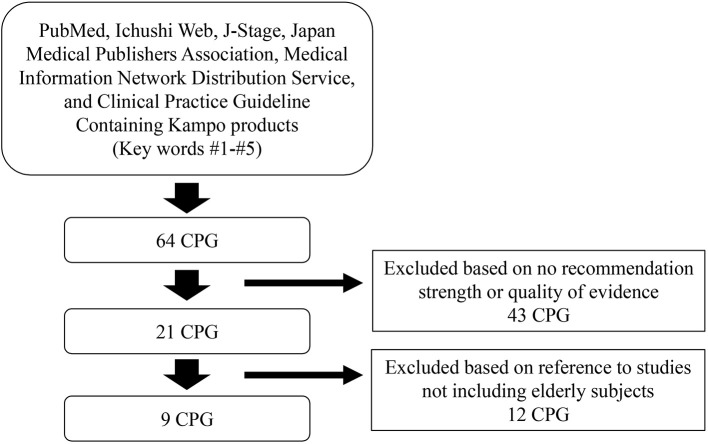
The review process flowchart is shown in Figure 2; and the eligible PCGs are shown in Table 1. Over the past 5 years, the following eligible nine CPGs have given some recommendations for kampo treatment based on the evidence for skin symptoms, allergy, cough, gastro-intestinal dysfunction, urinary dysfunction, and dementia: Clinical Practice Guideline for the Pruritus cutaneus universalis (8), Practical Guideline for the Management of Allergic Rhinitis in Japan (9), The Japanese Respiratory Society guidelines for management of cough (10), Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for GERD (11), Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Functional Dyspepsia (12), Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (13), Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for chronic constipation (14), Clinical guidelines for overactive bladder syndrome (15), and Practice Guideline for Dementia (16).
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the review process. CPG, clinical practice guideline.
Table 1.
Overview of CPGs included in the study.
| Clinical practice guideline | Clinical question | Symptom | Kampo medicine | Evidence (number of RCT including elderly subjects) | Recommendation | Publication year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Practice Guideline for the Pruritus cutaneus universalis | Is kampo medicine effective for pruritus? | Skin pruritus, Senile pruritus | tokiinshi, orengedokuto, goshajinkigan, hachimijiogan, rokumigan | At least one RCT (5) | Permit | 2012 | (7) |
| Practical Guideline for the Management of Allergic Rhinitis in Japan | What are the indications for effective kampo medicine treatment in patients with allergic rhinitis? | Allergic Rhinitis | shoseiryuto | Double-blind RCT (1) | Recommend | 2015 | (8) |
| The Japanese Respiratory Society guidelines for management of cough | What is a non-specific therapeutic agent for dry cough? | Dry cough | bakumondoto | At least one RCT (1) | Recommend | 2012 | (9) |
| What is a non-specific therapeutic agent for moist cough? | Moist cough | shoseiryuto | At least one RCT (1) | Recommend | |||
| Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for GERD 2015 (2nd Edition) | Identification of drug with additional gastro-intestinal regulation effect of or kampo medicine combined with proton pump inhibitor. | GERD (addition to PPI, refractory to PPI) | rikkunshito | Low quality of evidence (1) | Low recommendation | 2015 | (10) |
| Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Functional Dyspepsia | Is kampo medicine effective for Functional Dyspepsia? | Functional Dyspepsia | rikkunshito, (hangekobokuto) | High quality of evidence (2) | Low recommendation | 2014 | (11) |
| Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Irritable Bowel Syndrome | Is kampo medicine effective for Irritable Bowel Syndrome? | Irritable Bowel Syndrome | keishikashakuyakuto | Low quality of evidence (1) | Low recommendation | 2014 | (12) |
| Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for chronic constipation 2017 | Is kampo medicine effective for chronic constipation? | Chronic constipation | daiokanzoto, daikenchuto | Low quality of evidence (2) | Low recommendation | 2017 | (13) |
| Clinical guidelines for overactive bladder syndrome | Overactive bladder | goshajinkigan | Small scale RCT (1) | Recommend | 2015 | (14) | |
| Practice Guideline for Dementia 2017 | Patient indications for effective non-medication or medication for agitation. | Agitation | yokukansan | Low (1) | Suggest | 2017 | (15) |
| Patient indications for effective non-medication or medication for hallucinations and delusions. | Hallucinations, delusions | yokukansan | Low (0) | Suggest | |||
| How do you identify correspondence to dysphagia (including prevention for pneumonia)? | Correspondence to dysphagia (including prevention for pneumonia) | hangekobokuto | Very low (1) | Suggest | |||
| How do you respond in case of edema? (side effect) | Edema | yokukansan | Low (0) | Suggest | |||
| Is there treatment for behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia, and for the sleep behavior disorder associated with Lewy body disease, and the rem period? | Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia and the sleep behavior disorder symptom of patients with Lewy body disease | yokukansan | Low (0) | Suggest |
Randomized clinical trial involving elderly patients with each symptom introduced in the clinical practice guidelines
Skin symptoms
CPG for pruritus gave some recommendations (permission) for pruritus or dry skin based on some RCTs. Five RCTs for skin symptom were selected in the CPG focused on the elderly. Ohkawara et al. reported the efficacy and safety of orengedokuto or goshajinkigan for the symptom in senile pruritus (17). Orengedokuto (Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang) (18) or goshajinkigan (Niu-Che-Shen-Qi-Wan) (18) improved the subjective and objective symptom with no significant difference in the efficacy and safety as compared to Clemastine Fumarate that is potent and selective histamine H1 receptor antagonist. Iida et al. reported the efficacy of tokiinshi (Dang-Gui-Yin-Zi) (18) for moisture holding ability evaluated with a measurement device for the water content of the skin corneum in patients with senile pruritus (19). Tokiinshi significantly improved dry skin compared with no treatment. Ishioka et al. reported the efficacy of hachimijiogan (Ba-Wei-Di-Huang-Wan) (18) for the subjective symptom in patients with senile pruritus (20). Hachimijiogan improved the subjective symptom with no significant difference in efficacy compared to Ketotifen Fumarate that is selective histamine H1 receptor antagonist. In addition, Ishioka reported no significant difference in efficacy between hachimijiogan and rokumigan (Liu-Wei-Wan) (18) for treatment of subjective symptom in patients with senile pruritus (21). Ohkuma et al. reported that orengedokuto with tokiinshi, orengedokuto alone, or tokiinshi alone significantly improved the itchy symptom with no significant difference in efficacy compared with anti-histamine (22).
Allergy symptoms
CPG for nasal allergy recommended use of kampo medicine for perennial nasal allergy with a referred RCT. Baba et al. reported the efficacy and safety of shoseiryuto (Xiao-Qing-Long-Tang) (18) for perennial allergic rhinitis in a double-blind RCT including elderly subjects (23). The shoseiryuto group showed more moderate to high improvement than that of the placebo group, with statistical significance. Mild side effects were detected in both groups with no significant group-wise difference.
Cough symptoms
CPG for cough recommended use of kampo medicine for cough in the elderly with two referred RCTs focused on the elderly. Irifune et al. reported the efficacy of bakumondoto (Mai-Men-Dong-Tang) (18) for post-infectious prolonged cough in elderly patients (24). As compared to procaterol hydrochloride, bakumondoto with procaterol hydrochloride was more effective in treating post-infectious prolonged cough. Mukaida et al. reported the efficacy of bakumondoto for cough in elderly patients diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (25). Additional bakumondoto treatment was more effective than regular medication in suppressing the severity of cough.
Gastro-intestinal symptoms
CPG for Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Functional Dyspepsia (FD), Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), and chronic constipation gave weak recommendation for use of kampo medicine for these conditions with referred RCT. In a double-blind RCT including elderly patients, Tominaga et al. reported the efficacy of rikkunshito (Liu-Jun-Zi-Tang) (18) for patients with GERD who were refractory to treatment with proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) (26). Rikkunshito combined with PPI significantly decreased the frequency scale of the GERD symptoms' score, similar to the decrease seen on treatment with a double dose of PPI. Subgroup analysis showed that the patients of male sex or low body mass index showed more improvement compared with the other subgroups.
Harasawa et al. reported that the regular dose of rikkunshito significantly improved dysmotility-like dyspepsia than the low dose of rikkunshito in a double-blind RCT including elderly subjects (27). Arai et al. reported that there was a significant improvement in dyspeptic symptoms in patients treated with either rikkunshito or domperidone that is peripheral D2-like receptor antagonist, based on the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale score (28). The improvements of reflux and indigestion symptoms in patients treated with rikkunshito showed good correlations with the increased levels of acylated ghrelin.
Sasaki et al. reported the efficacy and safety of keishikasyakuyakuto (Gui-Zhi-Jia-Shao-Yao-Tang) (18) for functional abdominal pain of irritable bowel syndrome in a double-blind RCT including elderly subjects (29). Abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea significantly decreased after keishikasyakuyakuto administration, and the effect was superior to that of a placebo. Adverse effects of keishikasyakuyakuto were not significantly different from the placebo, suggesting the safety of keishikasyakuyakuto.
Miyoshi et al. reported the efficacy and safety of daiokanzoto (Da-Huang-Gan-Cao-Tang) (18) for constipation in a double-blind RCT including elderly subjects (30). Daiokanzoto was significantly effective for constipation compared to the placebo. There were no significant differences in safety between daiokanzoto and the placebo.
Horiuchi et al. reported the effect of daikenchuto (Da-Jian-Zhong-Tang) (18) in patients with chronic constipation in an RCT including elderly subjects (31). The addition of daikenchuto to sennoside resulted in significant improvement in bloating and abdominal pain and significant decrease in the gas volume score.
Urinary symptoms
CPG for overactive bladder syndrome gave weak recommendation for use of kampo medicine with a referred RCT (32). In an RCT including elderly patients, Nishizawa et al. reported the efficacy of goshajinkigan for patients with over active bladder compared with propiverine hydrochloride. During the 1-year observation period, propiverine hydrochloride significantly improved the symptom of over active bladder in the first month, however, goshajinkigan significantly improved the symptom of over active bladder after 2 months. The incidence of adverse event related to treatment with goshajinkigan was lower than that with propiverine hydrochloride.
Dementia and related symptoms
CPG for dementia and related symptom gave weak recommendation for use of kampo medicine with two referred RCTs. Mizukami et al. reported the effectiveness and safety of yokukansan (Yi-Gan-San) (18) for the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) in patients with dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease or Lewy bodies (33). The mean total of the Neuropsychiatric Inventory score used to evaluate BPSD were significantly improved by the additional yokukansan administration. Subscale analysis showed significant improvements in delusions, hallucinations, agitation/aggression, depression, anxiety, and irritability/lability. There were no serious adverse reactions. Iwasaki et al. examined the effect of hangekobokuto (Ban-Xia-Hou-Pu-Tang) (18) on swallowing reflex among the elderly (34). Compared to the placebo, hangekobokuto significantly improved time from the water injection to the onset of swallowing. Furthermore, substance P in the saliva of patients administered with hangekobokuto significantly increased. Based on the result, Iwasaki et al. reported that treatment with hangekobokuto reduced the risk of pneumonia and pneumonia-related mortality in elderly patients with dementia in an RCT with 12-month patients' follow-up (35).
Adverse effects
Adverse effects were not searched by the above steps. Additional hand searching for adverse effects showed that four CPG indicated the side effect of kampo medicine and introduce caution for using kampo medicine.
Guidelines for the management of hypertension 2014 (36) introduces the side effect of kampo medicine, western medicinal drugs, or health supplement that includes Glycyrrhiza. Glycyrrhiza includes glycyrrhizin which has potential to induce pseudo aldosteronism. If increase of blood pressure and/or hypokalemia are confirmed, withdrawing of suspicious products should be considered. In case it is difficult to stop use of the products, aldosterone antagonist can be prescribed.
Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma (37) introduces the side effect of crude drugs including aristolochic acid. Some studies indicated that aristolochic acid was associated with nephropathy, uropathy, or urothelial cancer. In Japan, crude drugs approved by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare do not include aristolochic acid, but patients can use imported drugs.
Consensus statement for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced lung injuries (38) introduced the side effect of kampo medicine, especially shosaikoto (Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang) (18), which can induce interstitial pneumonia in rare cases. The prevalence of shosaikoto-induced interstitial pneumonia is reported as under 0.1%, however, national survey reported the mortality rate of 10 in 100 cases of interstitial pneumonia induced by shosaikoto. If drug-induced interstitial pneumonia is expected, use of the suspected drug should be discontinued.
The guideline Japanese Society of Laboratory Medicine 2015 (39) introduced drug-induced edema, hypertension, and liver dysfunction. Comments for edema and hypertension induced by Glycyrrhiza were similar with prior comments in Guidelines for the management of hypertension 2014. Kampo medicine is one of the drugs that induce liver injury or hepatitis, therefore side effect correspondence is considered important.
Discussion
Interpretation of results
Nine CPG gave some recommendations for total 13 kampo medicines in treatment of the symptom in the elderly. Each kampo medicine includes multiple crude drugs which have several pharmacological functions; thus, kampo medicine affects multiple organs and coordinates the interrelation between the brain, endocrine system, immune system, and skeletal muscle in elderly patients.
Characteristics of kampo medicine introduced in CPGs
Table 2 show the over view of 13 kampo medicines introduced in CPG, its indications and components referred from STORK (40), and its characteristics in kampo theory. Kampo medicine have multiple effect on organs result in improving symptom.
Table 2.
Over view of 13 kampo medicines introduced in CPG, its indications and components referred from STORK (40), and its characteristics in kampo theory.
| Kampo medicine | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| orengedokuto | goshajinkigan | tokiinshi | hachimijiogan | rokumigan | shoseiryuto | bakumondoto | rikkunshito | keishikashakuyakuto | daiokanzoto | daikenchuto | yokukansan | hangekobokuto | ||
| Clinical manifestation of frailty according to the traditional concept | Anorexia | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | |||||||||
| Sarcopenia | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | |||||||||||
| Cognition | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | |||||||||||
| Dementia | ◦ | ◦ | ||||||||||||
| Fatigue | ◦ | ◦ | ||||||||||||
| Weakness | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ||||||||||
| Pain | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ||||||||||
| Dysfunction of | ||||||||||||||
| Respiration | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | |||||||||||
| Circulation | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ||||||||||
| Gastro-intestine | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ||||||||
| Urinary | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | |||||||||||
| Musculoskeletal | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | |||||||||||
| Skin | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | ◦ | |||||||||
| Indications | The relief of the following symptoms of those patients who have ruddy face with comparatively strong constitution, a touch of hot flushes, and a tendency to irritability: nose bleeding, hypertension, insomnia, neurosis, gastritis, alcoholic hangover, climacteric disturbance and automatic imbalance syndrome peculiar to women resembling climacteric disturbance, dizziness, palpitation, eczema or dermatitis and pruritus cutaneous | The relief of the following symptoms of those patients with decreased urine volume or polyuria sometimes having dry mouth who are easily fatigued and easily feel cold in the extremities: Leg pain, low back pain, numbness, blurred vision in old patients, pruritus, dysuria, frequent urination and edema | The relief of the following symptoms of those patients with oversensitivity to cold: Chronic eczema (with little exudation) and itching | The relief of the following symptoms of those patients with severe fatigue or malaise, decreased urinary output or increased urinary frequency, dry mouth, and alternate cold and hot feeling in the extremities: Nephritis, diabetes mellitus, impotence, sciatica, low back pain, beriberi, cystorrhea, prostatic hypertrophy and hypertension | The relief of the following symptoms of those patients with decreased urine volume or polyuria sometimes having dry mouth who are easily fatigued: Dysuria, frequent urination, edema and pruritus | Watery sputum, watery nasal discharge, nasal obstruction, sneezing, stridor, coughing, lacrimation in the following diseases: Bronchitis, bronchial asthma, rhinitis, allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, and common cold | The relief of the following symptoms: Coughing with a hard, obstructive sputum, bronchitis, and bronchial asthma | The relief of the following symptoms of those patients with weak stomach, loss of appetite and full stomach pit, and those who are easily fatigued, anemic and likely to have cold limbs: Gastritis, gastric atony, gastroptosis, maldigestion, anorexia, gastric pain, vomiting | The relief of the following symptoms of those patients with abdominal distension: Tenesmus alvi and abdominal pain | Constipation | The relief of abdominal cold feeling and pain accompanied by abdominal flatulence | The relief of the following symptoms of those patients with delicate constitution and nervousness: Neurosis, insomnia, night cry in children, and peevishness in children | The relief of the following symptoms of those patients who have depressed feelings and a feeling of foreign body in the throat and oesophagus and who sometimes have palpitation, dizziness, nausea, etc.: Anxiety neurosis, nervous gastritis, hyperemesis gravidarum, coughing, hoarseness, nervous oesophageal stricture, and insomnia | |
| Components of kampo medicine | JP Scutellaria Root | JP Rehmannia Root | JP Japanese Angelica Root | JP Rehmannia Root | JP Rehmannia Root | JP Pinellia Tuber | JP Ophiopogon Tuber | JP Atractylodes Lancea Rhizome | JP Peony Root | JP Rhubarb | JP Processed Ginger | JP Atractylodes Lancea Rhizome | JP Pinellia Tuber | |
| JP Coptis Rhizome | JP Achyranthes Root | JP Rehmannia Root | JP Cornus Fruit | JP Cornus Fruit | JP Processed Ginger | JP Brown Rice | JP Ginseng | JP Cinnamon Bark | JP Glycyrrhiza | JP Ginseng | JP Poria Sclerotium | JP Poria Sclerotium | ||
| JP Gardenia Fruit | JP Cornus Fruit | JP Tribulus Fruit | JP Dioscorea Rhizome | JP Dioscorea Rhizome | JP Glycyrrhiza | JP Pinellia Tuber | JP Pinellia Tuber | JP Jujube | JP Zanthoxylum Fruit | JP Cnidium Rhizome | JP Magnolia Bark | |||
| JP Phellodendron Bark | JP Dioscorea Rhizome | JP Peony Root | JP Alisma Rhizome | JP Alisma Rhizome | JP Cinnamon Bark | JP Jujube | JP Poria Sclerotium | JP Glycyrrhiz | JP Koi | JP Uncaria Hook | JP Perilla Herb | |||
| JP Plantago Seed | JP Cnidium Rhizome | JP Poria Sclerotium | JP Poria Sclerotium | JP Schisandra Fruit | JP Glycyrrhiza | JP Jujube | JP Ginger | JP Japanese Angelica Root | JP Ginger | |||||
| JP Alisma Tuber | JP Saposhnikovia Root and Rhizome | P Moutan Bark | JP Moutan Bark | JP Asiasarum Root | JP Ginseng | JP Citrus Unshiu Peel | JP Bupleurum Root | |||||||
| JP Poria Sclerotium | JP Polygonum Root | JP Cinnamon Bark | JP Peony Root | JP Glycyrrhiza | JP Glycyrrhiza | |||||||||
| JP Moutan Bark | JP Astragalus Root | JP Powdered Processed Aconite Root | JP Ephedra Herb | JP Ginger | ||||||||||
| JP Cinnamon Bark | JP Schizonepeta Spike | |||||||||||||
| JP Powdered Processed Aconite Root | JP Glycyrrhiza | |||||||||||||
JP, The Japanese Pharmacopoeia.
Orengedokuto, tokiinshi, goshajinkigan, hachimijiogan, and rokumigan were recommended in patients with skin symptom. In the kampo concept, orengedokuto is used to improve inflammation in skin and other organs and improve irritation. Therefore, it should be used in patients with reddish skin and worsening itchy symptom with irritation. Goshajinkigan, hachimijiogan, and rokumigan were categorized in similar kampo medicine. They have been used for dry skin, urinary disorder, and sarcopenia. These kampo medicine include crude drugs to moisturize the skin, strengthen the muscles, promote microcirculation, and control urination. Additional effects include the following: for tokiinshi, suppressing itchiness, for goshajinkigan, warming the body and improving edema and lumber pain, for hachimijiogan, controlling cold and hot feeling and improving edema, and for rokumigan, controlling hot feeling and improving edema. These kampo medicines can be selected depending on not only the skin condition but also cold/hot sensation and water balance. Kishida et al. reported that goshajinkigan suppressed sarcopenia via the IGF-1/insulin pathway, maintained the expression of mitochondrial-related transcription factors, and suppressed TNF-α in SAMP8 mice, indicating that goshajinkigan is a promising candidate for relief from sarcopenia (41). CPG and results from the study suggested that goshajinkigan can be applied for skin symptom with additional expected effect on sarcopenia.
Shoseiryuto was selected for use in patients with allergic rhinitis and cough. Bakumondoto was selected for use in patients with cough. These kampo medicines have opposite effects on water imbalance in the upper respiratory tract. Shoseiryuto can improve the occurrence of excess water in thin secretion, thus it is applied in cases with allergic rhinitis and cough with thin secretion. Shoseiryuto decreased the number of T-helper (Th) 2 cells and the level of interleukin-4. The Th1 cells were not altered (42). Since shoseiryuto does not affect the histamine H1 receptors, there are fewer side-effects such as sedation and drowsiness. On the other hand, bakumondoto can moisturize and improve the dryness and sensitivity of the upper respiratory tract epithelium. Thus, it is applied in case of dry cough without secretion after respiratory infection. Ophiopogonis Radix, another herb in bakumondoto, has anti-inflammatory activity; and its active components include ruscogenin and ophiopogonin D.
Rikkunshito was recommended for patients with PPI-refractory GEARD and FD. It supplies vital energy to the digestive organs and promotes peristalsis from the stomach to the intestine. Thus, this kampo medicine is more suitable for patients with fatigue, anorexia, and gastric hypomotility resulting in weight loss. A recent study reported that rikkunshito increased plasma ghrelin levels in humans and mice (43) and restored the decreased plasma ghrelin levels induced by serotonin release in rats.
Keishikashakuyakuto was recommended for irritable bowel syndrome. It can be applied for both diarrhea, constipation, and mix-type IBS. It can control contraction and expansion of the intestine, resulting in pain relief and control of the stool condition.
Daiokanzoto and daikenchuto were recommended for constipation. Daiokanzoto is applied for constipation in patients whose vital energy is sufficient; whereas, daikenchuto is applied for constipation in patients with low vital energy, and characteristics of low body weight and abdominal distention, because it includes the crude drug, ginseng, which can supply energy to the digestive function. Daikenchuto treats abdominal symptoms via enhancing the secretions of motilin (44), substance P (45), calcitonin gene-related peptide, and adrenomedullin (46, 47), and activating the transient receptor potential of the vanilloid receptor complex (48).
Yokukansan was recommended for patients with BPSD. It has been used for irritation and sleep disorder of children since ancient times. Recently, it has been applied for the symptom in elderly patients. With regard to the characteristics of yokukansan, it does not induce extrapyramidal symptoms, however, it controls the concentration of serotonin in the synaptic cleft via partial agonist action on the serotonin 1A receptor (49), downregulates expression of the serotonin 2A receptor (50), inhibits the release of glutamate resulting in a decreased concentration of glutamate at synaptic clefts in the brain, and promotes glutamate uptake by astrocytes (51–53).
Hangekobokuto was recommended for use in patients with dysphagia. It has been used for pharyngeal discomfort since ancient times. It can soothe sensation in the pharynx and improve swallowing and cough reflex. It is reported that hangekobokuto modulates cerebral levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline, and dopamine in mice (54).
There are some advantages in kampo treatment. As a super-aging society, the increased cost of medical insurance is a serious problem in Japan. The medical cost of kampo medicine is relatively lower than that of western medicine. This treatment can improve the target symptoms and contribute to holistic control of whole-body conditions, as mentioned above. Furthermore, kampo medicine has been applied for disease prevention and maintenance of quality of life since ancient times. Kampo medicine may contribute to health in elderly individuals. Based on these aspects, both CPG and research regarding kampo medicine for geriatric patients should be continued. The clinical application of kampo medicine has been performed depending on the patients' clinical history and physical sign. In this review, we demonstrated the present status of CPG involving kampo medicine for geriatrics. Clinical and basic research studies are currently on going. In future, more information on evidence-based detailed application will become available.
Limitation
A limitation of this review is that the target subjects of the RCT referenced in the CPG do not necessarily correspond to elderly patients. The articles cited in ref. (16–19, 22, 23) were limited in their study of elderly subjects. However, the articles cited in ref. (20, 21, 25–33) included elderly subjects as a portion of the study population. The number of RCTs with only elderly subjects was very small; thus, we included studies with elderly subjects as a portion of the study population. Despite this limitation, this review demonstrated the use of Japanese CPG and kampo medicine in the treatment of symptoms in elderly patients.
Conclusion
Japanese CPG gave some recommendation for use of kampo medicine for symptoms in the elderly. In the CPG, evidence related to kampo medicine for several symptoms is provided, and each kampo medicine includes multiple crude drugs that have multiple pharmacological functions. Thus, the treatment can be considered as holistic medicine which can lead to support of elderly patients with frailty.
Author contributions
ST designed the study, confirmed the CPG and articles, and wrote the manuscript. SK proof read the CPG and the manuscript. AK, MO, RA, and TI gave advice for the study design and manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
AK, MO, ST, and TI belong the Department of Kampo and Integrative Medicine, Tohoku University School of Medicine. The department received a grant from Tsumura, a Japanese manufacturer of Kampo medicine; however, the grant was used as per Tohoku University rules. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by our university's administration fund.
References
- 1.Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2001) 56:M146–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Walston J, Hadley EC, Ferrucci L, Guralnik JM, Newman AB, Studenski SA, et al. Research agenda for frailty in older adults: toward a better understanding of physiology and etiology: summary from the American Geriatrics Society/National Institute on Aging Research Conference on Frailty in Older Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2006) 54:991–1001. 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00745.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Eeles EM, White SV, O'Mahony SM, Bayer AJ, Hubbard RE. The impact of frailty and delirium on mortality in older inpatients. Age Ageing (2012) 41:412–6. 10.1093/ageing/afs021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Clegg A, Young J, Iliffe S, Rikkert MO, Rockwood K. Frailty in older people. Lancet (2013) 381:752–62. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62167-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hazzard WR, Blass JP, Halter JB, Ouslander JG, Tinetti ME. (eds). Principles of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; (2003). p. 1487–502. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Arai H, Ouchi Y, Toba K, Endo T, Shimokado K, Tsubota K, et al. Japan as the front-runner of super-aged societies: perspectives from medicine and medical care in Japan. Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2015) 15:673–87. 10.1111/ggi.12450 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Satoh H. Pharmacological characteristics of Kampo medicine as a mixture of constituents and ingredients. J Integr Med. (2013) 11:11–6. 10.3736/jintegrmed2013003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Satoh T, Yokozeki H, Katayama I, Murota H, Tokura Y, Boku N, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Pruritus cutaneus universalis [in Japanese]. Jpn J Dermatol. (2012) 122:267–80. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Okubo K, Kurono Y, Ichimura K, Enomoto T, Okamoto Y, Kawauchi H, et al. Practical Guideline for the Management of Allergic Rhinitis in Japan. Life Science Press; [in Japanese] (2015). [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kohno S, Okada K, Kadota J, Shioya T, Tanaka H, Tokuyama K, et al. The Japanese Respiratory Society Guidelines for Management of Cough. Medical Revew Co., Ltd. [in Japanese] (2012). [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kinoshita Y, Iwakiri K, Ashida K, Iwakiri R, Oshima T, Ohara S, et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for GERD 2015. 2nd ed. Nankodo Press; [in Japanese] (2015). [Google Scholar]
- 12.Miwa H, Kusano M, Arisawa T, Oshima T, Kato T, Joh T, et al. Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Functional Dyspepsia. Nankodo Press; [in Japanese] (2014). [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fukudo S, Kaneko H, Akiho H, Inamori M, Endo Y, Okumura T, et al. Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Nankodo Press; [in Japanese] (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Miwa H, Torii A, Maeda K, Akiho H, Araki Y, Iijima H, et al. Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Constipation 2017. Nankodo Press; [in Japanese] (2017). [Google Scholar]
- 15.Takeda M, Yokoyama O, Goto M, Homma Y, Asakura H, Yamanishi T, et al. Clinical Guidelines for Overactive Bladder Syndrome. 2nd ed. RichHill Medical Inc. [in Japanese] (2015). [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nakashima K, Tomimoto H, Aiba I, Akishita M, Kurita S, Iijima S, et al. Practice Guideline for Dementia 2017. Igaku-Shoin Ltd. [in Japanese] (2017). [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ohkawara A, Furuya K, Kurisu Y, Asada Y, Higashida T, Takeda K, et al. Experience with Orengedokuto (TJ-15) and Goshajinkigan (TJ-107) for the treatment of senile pruritus [in Japanese]. Nishinihon Hifuka (1991) 53:1234–41. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Appendix - Composition and Indications of 148 Ethical Prescriptions KAIM (The Journal of Kampo, Acupuncture, and Integrative Medicine) Special Edition - Current Kampo Medicine | November 2006, http://www.kaim.us/special_TOC.html)
- 19.Toshihiro I, Chiak N, Hiroyuki S. The effects of Toki-Inshi and a bath preparation containing licorice extract on patients with Senile Pruritus [in Japanese]. Kampo Med. (1996) 47:35–41. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ishioka T, Aoi R. Comparative evaluation of hachimijiogan and ketotifen fumarate on senile pruritus [in Japanese]. Shinyaku Rinsho (1992) 41:2603–8. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ishioka T. Comparative evaluation of Rokumigan and Hachimi-jiohgan on senile pruritus [in Japanese]. Ther Res. (1995) 16:1497–504. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ohkuma M. Treatment of pruritus by Chinese drugs [in Japanese]. J Med Pharm Soc WAKAN YAKU (1993)10:126–30. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Baba S, Takasaka T, Inamura N, Sato M, Suzuki S, Endo S, et al. Double-blind clinical trial of Sho-seiryu-to (TJ-19) for perennial nasal allergy [in Japanese]. Pract Otol. (1995) 88:389–405. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Irifune K, Hamada H, Ito R, Katayama H, Watanabe A, Kato A, et al. Antitussive effect of bakumondoto a fixed kampo medicine (six herbal components) for treatment of post-infectious prolonged cough: controlled clinical pilot study with 19 patients. Phytomedicine (2011) 18:630–3. 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.02.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mukaida K, Hattori N, Kondo K, Morita N, Murakami I, Haruta Y, et al. A pilot study of the multiherb Kampo medicine bakumondoto for cough in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Phytomedicine (2011) 18:625–9. 10.1016/j.phymed.2010.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tominaga K, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K, Fujiwara Y, Tanaka M, Shimoyama, et al. Rikkunshito improves symptoms in PPI-refractory GERD patients: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial in Japan. J Gastroenterol. (2012) 47:284–92. 10.1007/s00535-011-0488-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Harasawa S, Miyoshi A, Miwa T, Masamune O, Matsuo Y, Mori H, et al. Double-blind multicenter post-marketing clinical trial of TJ-43 TSUMURA Rikkunshi-to for the treatment of dysmotility-like dyspepsia [in Japanese]. Igaku Ayumi (1998) 187:207–29. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Arai M, Matsumura T, Tsuchiya N, Sadakane C, Inami R, Suzuki T, et al. Rikkunshito improves the symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia, accompanied by an increase in the level of plasma ghrelin. Hepatogastroenterology (2012) 59:62–6. 10.5754/hge11246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sasaki D, Uehara A, Hiwatashi N, Sekiguchi T, Nakahara A, Nakai Y, et al. Clinical efficacy of keishikashakuyakuto in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a multicenter collaborative randomized controlled study [in Japanese]. Rinsho Kenkyu (1998)75:1136–52. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miyoshi A, Masamune O, Fukutomi H, Mori H, Miwa T, Kojima K, et al. The clinical effects of TSUMURA Dai-Kanzo-To extract granules for ethical use (TJ-84) on constipation using double blind test [in Japanese]. Gastroenterology (1994) 18:299–312. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Horiuchi A, Nakayama Y, Tanaka N. Effect of traditional Japanese medicine, daikenchuto (TJ-100) in patients with chronic constipation. Gastroenterol Res. (2010) 3:151–5. 10.4021/gr219w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nishizawa Y, Nishizawa Y, Yoshioka F, Amakata Y, Nosaka S, Fushiki S, et al. Efficacy and safety of Chinese traditional medicine, Niu-Che-Shwn-Qi-Wan (Japanese name: goshajinki-gan) versus propiverine hydrochloride on health-related quality of life in patients with overactive bladder in prospective randomized comparative study [in Japanese]. Kampo New Ther. (2007) 16:131–42. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mizukami K, Asada T, Kinoshita T, Tanaka K, Sonohara K, Nakai R, et al. Randomized cross-over study of a traditional Japanese medicine (kampo), yokukansan, in the treatment of the behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2009) 12:191–9. 10.1017/S146114570800970X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Iwasaki K, Cyong JC, Kitada S, Niu K, Ohrui T, Okitsu R, et al. A traditional Chinese herbal medicine, banxia houpo tang, improves cough reflex of patients with aspiration pneumonia. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2002) 50:1751–2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Iwasaki K, Kato S, Monma Y, Niu K, Ohrui T, Okitsu R, et al. A pilot study of banxia houpu tang, a traditional Chinese medicine, for reducing pneumonia risk in older adults with dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2007) 55:2035–40. 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01448.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shimamoto K, Ando K, Ishimitsu T, Ito S, Ito M, Ito H, et al. Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension 2014. Life Science Publishing Co. Ltd. [in Japanese] (2014). [Google Scholar]
- 37.Oya M, Ichikawa T, Nishiyama H, Jinzaki M, Kamai T, Kawauchi A, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma. Medical Review Co., Ltd. [in Japanese] (2014). [Google Scholar]
- 38.Azuma A, Kanazawa M, Kameda H, Kusumoto M, Kubo K, Tsuruma A, et al. Consensus Statement for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Drug-Induced Lung Injuries Medical Review Co. Ltd., [in Japanese] (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Iinuma Y, Izuhara K, Koshiba T, Tanaka M, Higashida S, Toyama K, et al. Japanese Society of Laboratory Medicine Guideline 2015. Uchudo Yagi Bookstore Co. Ltd., [in Japanese] (2015). [Google Scholar]
- 40.Department of Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry and Narcotics (DPPN), National Institute of Health Sciences (NIHS) of Japan and National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Health and Nutrition (NIBIOHN). Standards of Reporting Kampo Products (STORK) http://mpdb.nibiohn.go.jp/stork/.
- 41.Kishida Y, Kagawa S, Arimitsu J, Nakanishi M, Sakashita N, Otsuka S, et al. Go-sha-jinki-Gan (GJG), a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, protects against sarcopenia in senescence-accelerated mice. Phytomedicine (2015) 22:16–22. 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.11.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ko E, Rho S, Cho C, Choi H, Ko S, Lee Y, et al. So-Cheong-Ryong-Tang, tradititional Korean medicine, suppresses Th2 lineage development. Biol Pharm Bull (2004) 27:739–43. 10.1248/bpb.27.739 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Matsumura T, Arai M, Yonemitsu Y, Maruoka D, Tanaka T, Suzuki T, et al. The traditional Japanese medicine Rikkunshito increases the plasma level of ghrelin in humans and mice. J Gastroenterol. (2010) 45:300–7. 10.1007/s00535-009-0166-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nagano T, Itoh H, Takeyama M. Effect of Dai-kenchu-to on levels of 3 brain-gut peptides (motilin, gastrin and somatostatin) in human plasma. Biol Pharm Bull. (1999) 22:1131–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kono T, Koseki T, Chiba S, Ebisawa Y, Chisato N, Iwamoto J, et al. Colonic vascular conductance increased by Daikenchuto via calcitonin gene-related peptide and receptoractivity modifying protein 1. J Surg Res. (2008) 150:78–84. 10.1016/j.jss.2008.02.057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kono T, Kaneko A, Hira Y, Suzuki T, Chisato N, Ohtake N, et al. Anticolitis and -adhesion effects of Daikenchuto via endogenous adrenomedullin enhancement in Crohn's disease mouse model. J Crohns Colitis (2010) 4:161–70. 10.1016/j.crohns.2009.09.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kono T, Omiya Y, Hira Y, Kaneko A, Chiba S, Suzuki T, et al. Daikenchuto (TU-100) ameliorates colon microvascular dysfunction via endogenous adrenomedullin in Crohn's disease rat model. J Gastroenterol. (2011) 46:1187–96. 10.1007/s00535-011-0438-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kikuchi D, Shibata C, Imoto H, Naitoh T, Miura K, Unno M. Intragastric Dai-Kenchu-To, a Japanese herbal medicine, stimulates colonic motility via transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 in dogs. Tohoku J Exp Med. (2013) 230:197–204. 10.1620/tjem.230.197 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Terawaki K, Ikarashi Y, Sekiguchi K, Nakai Y, Kase Y. Partial agonistic effect of yokukansan on human recombinant serotonin 1A receptors expressed in the membranes of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Ethnopharmacol. (2010) 127:306–12. 10.1016/j.jep.2009.11.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Egashira N, Iwasaki K, Ishibashi A, Hayakawa K, Okuno R, Abe M, et al. Repeated administration of Yokukansan inhibits DOI-induced head-twitch response and decreases expression of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) 2A receptors in the prefrontal cortex. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol Psychiatry (2008) 32:1516–20. 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.05.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Takeda A, Itoh H, Tamano H, Yuzurihara M, Oku N. Suppressive effect of Yokukansan on excessive release of glutamate and aspartate in the hippocampus of zinc-deficient rats. Nutr Neurosci. (2008) 11:41–6. 10.1179/147683008X301414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Takeda A, Tamano H, Itoh H, Oku N. Attenuation of abnormal glutamate release in zinc deficiency by zinc and Yokukansan. Neurochem Int. (2008) 53:230–5. 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.07.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kawakami Z, Ikarashi Y, Kase Y. Glycyrrhizin and its metabolite 18 beta-glycyrrhetinic acid in glycyrrhiza, a constituent herb of yokukansan, ameliorate thiamine deficiency-induced dysfunction of glutamate transport in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. (2010) 626:154–8. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.09.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kaneko A, Cho S, Hirai K, Okabe T, Iwasaki K, Nanba Y, et al. Hange-koboku-to, a Kampo medicine, modulates cerebral levels of 5-HT (5-hydroxytryptamine), NA (noradrenaline) and DA (dopamine) in mice. Phytother Res. (2005) 19:491–5. 10.1002/ptr.1669 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]