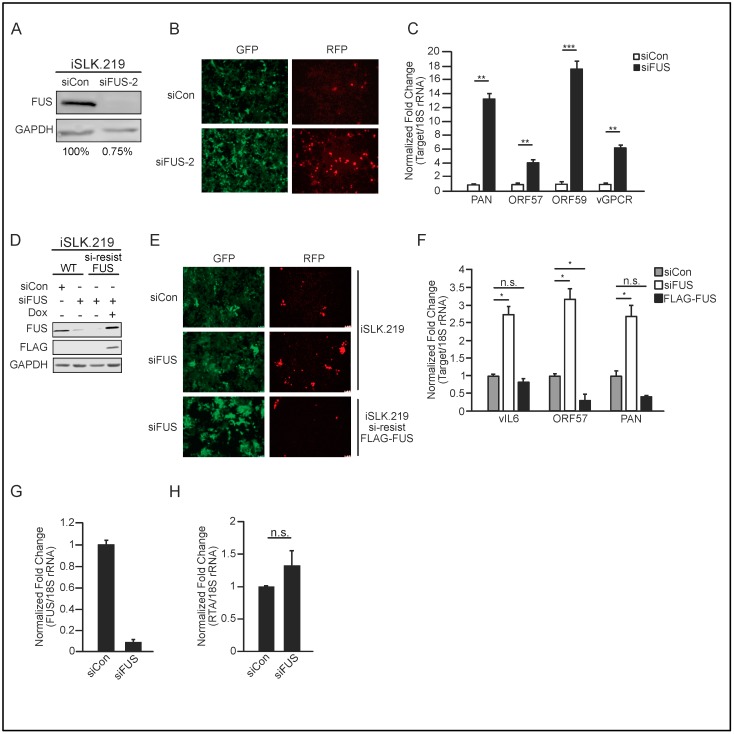
Figure 3.
Independent verification of FUS-siRNA specificity. (A) iSLK.219 cells were depleted of FUS with a second FUS-siRNA and induced with doxycycline for 48 h. Knockdown efficiency was determined by western blot analysis and is indicated beneath each lane. (B) Fluorescent microscopy, at 10× magnification, of iSLK.219 cells depleted of FUS in (A). (C) Quantification of viral gene expression in cells described in (A) by RT-qPCR. All samples were normalized to 18S and siCon set to 1. (D) Western blot analyses of protein extracts from WT iSLK.219 and iSLK.219 cells transduced with siRNA-resistant FLAG-tagged FUS. Cells were treated with either control or FUS-siRNA and induced for 48 h with doxycycline. (E) Fluorescent microscopy, at 10× magnification, of cells in (D). (F) RT-qPCR of viral gene expression in cells described in (D). All samples were normalized to 18S and siCon set to 1. (G) Uninfected iSLK control cells, which harbor the doxycycline-inducible RTA, were depleted of FUS with siRNA for 48 h, followed by doxycycline treatment for 24 h. FUS knockdown was determined by RT-qPCR. (H) Quantification of RTA mRNA levels from cells in (G). Student t test used to determine statistical significance * p ≤ 0.05. ** p ≤ 0.005. *** p ≤ 0.0005, n.s. not significant.