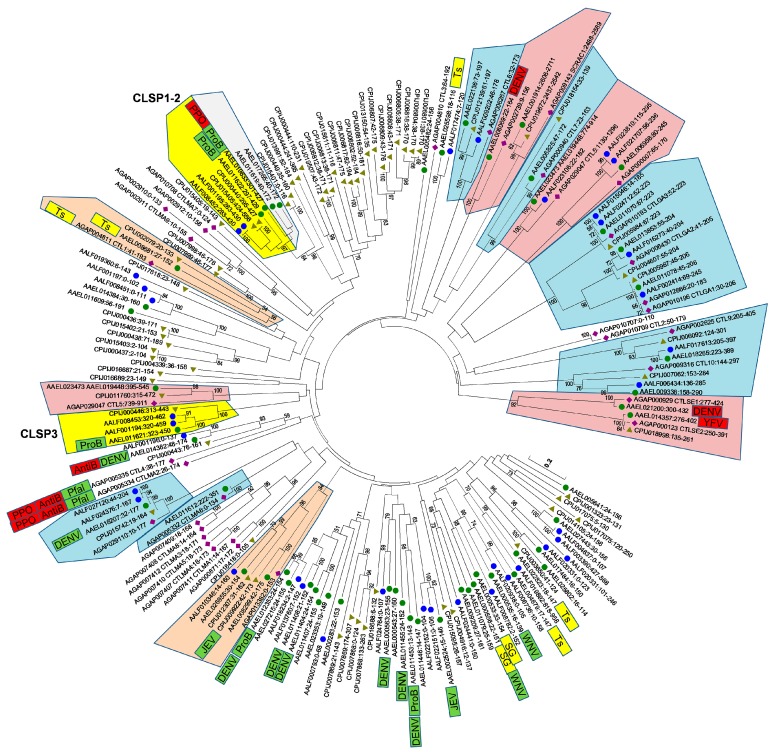
Figure 3.
Neighbor-joining tree based on alignment of 183 CTLDs extracted from A. aegypti (●), A. albopictus (●), C. quinquefasciatus (▲), and A. gambiae (♦) CTLD containing genes. Ambiguous positions were removed for each sequence pair; there were a total of 235 positions in the final dataset; branch support of more than 50% (1000 replicates) is indicated. Conserved clades containing CTLD-X (red) and CTLD-E (blue) members are indicated. Other highlighted clusters contain CTLD-SP (yellow) and CTLD-S proteins with both A. gambiae and A. aegypti orthologs with branch support over 50% (orange). Individual CTLDcps previously implicated as host (green) or resistance (red) factors for dengue virus (DENV), Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), West Nile encephalitis virus (WNV), P. falciparum (Pfal) bacteria (ProB/AntiB), or the prophenol oxidase response (PPO) are indicated, as are genes specifically expressed in the salivary glands (SG) and testes (Ts).