Abstract
Aneuploidy seems to play not only a decisive role in embryonal development but also in tumorigenesis where chromosomal and genomic instability reflect a universal feature of malignant tumors. The cost of whole genome sequencing has fallen significantly, but it is still prohibitive for many institutions and clinical settings. No applied, cost-effective, and efficient technique has been introduced yet aiming at research to assess the ploidy status of all 24 different human chromosomes in interphases simultaneously, especially in single cells. Here, we present the selection of human probe DNA and a technique using multistep fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) employing four sets of six labeled FISH probes able to delineate all 24 human chromosomes in interphase cells. This full karyotype analysis approach will provide additional diagnostic potential for single cell analysis. The use of spectral imaging (SIm) has enabled the use of up to eight different fluorochrome labels simultaneously. Thus, scoring can be easily assessed by visual inspection, because SIm permits computer-assigned and distinguishable pseudo-colors to each probe during image processing. This enables full karyotype analysis by FISH of single-cell interphase nuclei.
Keywords: aneuploidy, chromosome enumeration, DNA probes, FISH, full karyotype analysis, interphase nuclei, spectral imaging
Introduction
Evaluating numerical abnormalities and structural aberrations of chromosomes by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) has been extensively carried out on cell metaphases and interphases since this technique has been introduced in the mid-1980s.1 Methodologies such as spectral karyotyping (SKY)2 or multiplex FISH3 and also comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)4 were able to effectively evaluate cytogenetic damage on metaphases across the whole genome. Nowadays, modern techniques such as high-resolution chip-based CGH arrays and next-generation sequencing (NGS), in particular massive parallel sequencing (MPS), are capable of evaluating a plethora of cytogenetic changes. For array CGH, segmental DNA copy number variations at kilobase-pair resolution can be detected,5 while MPS is capable of analyzing large parts of the genome by using shallow or low-pass whole genome sequencing when no coverage of the full genome is required, for example, for preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD).6
In the early 2000s, implantation rates had improved due to PGD aneuploidy screening by using commercially available chromosomal probe sets for single-cell analysis allowing the enumeration of up to 10 chromosomes with fluorescence filter-based evaluation. Thereby, more than half of the numerical abnormalities seen in abnormal embryos originating from nondisjunction of chromosomes during cell division were covered.7–10 Without a doubt, aneuploidy is the most common cause of chromosomal abnormalities in humans, leading to pregnancy loss.11,12 Hence, shifting from partial karyotype FISH analysis to genome sequencing in the last decade allowed for simultaneous testing of numerous genetic aberrations and abnormalities. This was also evident when looking at the biopsied specimens, shifting away from polar bodies or blastomeres toward the trophectoderm.13 In human embryos, multiple molecular mechanisms that may also be involved in cancer formation can lead to aneuploidy and chromosomal mosaicism, thus, to negative pregnancy outcomes; however, low-level mosaicism in human development may be a normal feature after all.14
Aneuploidy seems to also play a crucial role in cells of the extra-embryonal tissue that are important in implantation during early pregnancy and the formation of the placenta. These so-called invasive cytotrophoblasts (iCTB) showed different aneuploidy levels on the basis of their invasive behavior when assessed by using spectral imaging targeting six different chromosomes.15
Aneuploidy seems to play not only a decisive role in embryonal development but also in tumorigenesis where chromosomal and genomic instability reflect a universal feature of malignant tumors.16 It seems that the primary cause of pre-neoplastic/neoplastic genomic instability is the progression from stable diploid cells to unstable aneuploid cell species,17 making aneuploidy a useful marker of malignant transformation.18
Although the cost for sequencing the whole genome has fallen to around $1000 per analyzed genome,19 the price tag for equipment and material is quite high.20 Even though larger hospital trusts, major universities, and private biotech companies may have the funds to carry out high-throughput array chip methods and NGS on a daily basis, no applied, cost-effective, and efficient technique has been introduced yet aiming at research to assess the ploidy status of all 24 different human chromosomes in interphases simultaneously, especially in single cells. Improving the coverage of all the chromosomes and devising sophisticated, fast, and reliable methods to evaluate these single cells is favorable as not all of the possible numerical abnormalities can be currently assessed due to the limited number of available chromosome-specific probes and the limited number of suitable fluorochromes.21,22
Here, we present the selection of human probe DNA and a technique using multistep FISH employing four sets of six labeled FISH probes able to delineate all 24 human chromosomes in interphase cells. This full karyotype analysis approach will provide additional diagnostic potential for single-cell analysis.
Materials and Methods
Clone Selection and DNA Preparation
Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clones23 from the RP11 library (Invitrogen; Gaithersburg, MD) were chosen based on information available from the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) genome sequence database (http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway) and the U.S. National Institutes of Health, National Center for Biotechnology Information (NIH/NCBI) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mapview/map_search.cgi?taxid=9606). Comprehensive DNA sequence information as well as structural organization of these BACs can be found in the above-mentioned databases. The preparation of DNA from BAC clones has been described in detail before.24 Briefly, clones were cultured overnight in 10 ml Luria-Bertani (LB) medium containing 12.5 µg/ml chloramphenicol (Sigma; St. Louis, MO), and DNA was isolated using an alkaline lysis DNA extraction protocol.25 In addition to BAC clones (see Table 1 for a complete overview), bacterial plasmid clones from the Weier lab at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley, CA) have been used. For the isolation of plasmids from clones RMC16L006,26 pBS444/7, pBS864, pBS1131, pBS8B/9, pBS239′-5′, pBS609/51, 680TA-4, and W21R2-TA13, a commercial kit from Qiagen was used on an overnight LB culture containing 30 µg/ml ampicillin (RMC and pBS clones) or kanamycin (TA clones), respectively. Except for the RMC16L006 plasmid DNA, all other plasmid DNA has been employed as templates in PCR reactions. The final probe sets can be seen in Table 2.
Table 1.
Shows a Complete Overview of BAC Clones and Bacterial Plasmid Clones Used.
| Locus | Probe Name | Clones/DNA | End Sequence 1 | End Sequence 2 | Full Sequence ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13q21.31 | OR7E156P | RP11-527N12 | — | — | AL354810 |
| RP11-282D7 | — | — | AL355609 | ||
| RP11-320N6 | — | — | AL359208 | ||
| RP11-67L17 | — | — | AL354774 | ||
| RP11-473M10 | — | — | AL445989 | ||
| RP11-394A14 | — | — | AL445238 | ||
| RP11-520F9 | — | — | AL355879 | ||
| RP11-205B18 | — | — | AL354736 | ||
| 14q13.3 | PAX9 | RP11-12H15 | B75808 | B75809 | — |
| RP11-150O18 | AQ378665 | AQ378667 | — | ||
| RP11-452H6 | AQ583099 | AQ583102 | — | ||
| RP11-381L10 | AQ532441 | AQ554647 | — | ||
| RP11-73H19 | AQ266602 | AQ266604 | — | ||
| RP11-49P15 | AQ051953 | AQ051955 | — | ||
| RP11-151J2 | AQ379285 | AQ379286 | — | ||
| RP11-410J4 | AQ549717 | — | — | ||
| 16qh, sat II | RMC16L006 | RMC16L006 | — | — | X06138 |
| 20p11.1–11.2 | SRCext | RP11-298O1 | AQ507400 | AQ507403 | — |
| RP11-465M13 | AQ636482 | — | — | ||
| RP11-192N1 | AQ412321 | AQ412322 | — | ||
| RP11-151C5 | AQ376308 | AQ376305 | — | ||
| RP11-451G10 | AQ583252 | AQ583256 | — | ||
| RP11-103B19 | AQ313159 | AQ313162 | — | ||
| RP11-467A7 | AQ637700 | AZ516714 | — | ||
| RP11-99B19 | AQ318386 | AQ318387 | — | ||
| RP11-76O8 | AQ266982 | AQ266948 | — | ||
| 21q22 | D21S167 | YAC 141G6 | — | — | X52289 |
| 22q11.22–q11.23 | BCR | RP11-357H16 | AZ518881 | AQ553050 | — |
| RP11-62K15 | AQ199674 | AQ199676 | — | ||
| RP11-164N13 | AQ380113 | AQ380117 | — | ||
| 15q25.3 | NTRK3ext | RP11-116G21 | AQ348695 | AQ348692 | — |
| RP11-113C11 | AQ344985 | AQ344986 | — | ||
| RP11-96B23 | AQ313684 | AQ313681 | — | ||
| RP11-114I9 | AQ344858 | AQ344856 | — | ||
| RP11-285I14 | — | — | AC011966 | ||
| RP11-427O16 | — | — | AC023844 | ||
| RP11-356B18 | — | — | AC009711 | ||
| RP11-247E14 | — | — | AC087593 | ||
| RP11-97O12 | — | — | AC013489 | ||
| 17cen, α-sat | 17cen | RP11-285M22 | — | — | AC131274 |
| 18cen, α-sat | 18cen | genomic DNA | — | — | M65181 |
| 19q13.2 | AXL | CTD-2052L21 | AQ270406 | AQ235108 | — |
| CTD-2288H11 | B98832 | — | — | ||
| CTD-2195C23 | — | — | — | ||
| CTD-2017C04 | — | — | — | ||
| CTD-2195B23 | — | — | AC011510 | ||
| CTD-2218D21 | AQ032786 | — | — | ||
| Xq21 | CYCL1 | RP11-422C9 | AQ553389 | AQ553391 | — |
| RP11-475A12 | AQ635998 | AQ636000 | — | ||
| RP11-14A18 | B76225 | B82244 | — | ||
| Yq12 | RP11-242E13 | RP11-242E13 | — | — | AC068123 |
| 1cen, α-sat | 1cen | genomic DNA | — | — | — |
| 2p16.1-15 | RELext | RP11-65A9 | AQ237129 | AQ237131 | — |
| RP11-139C21 | AQ382574 | AQ382578 | — | ||
| RP11-71D7 | AQ236987 | AQ267891 | — | ||
| RP11-373L24 | — | — | AC010733 | ||
| RP11-375M18 | AQ533441 | AQ551245 | — | ||
| RP11-418N22 | AQ550069 | AQ550072 | — | ||
| RP11-77P21 | AQ284573 | AQ284575 | — | ||
| RP11-477N2 | AQ637330 | AQ637326 | — | ||
| RP11-143D11 | — | — | AC092103 | ||
| 3q27.3 | BCL6 | RP11-567G11 | — | — | AC104635 |
| RP11-88P6 | — | — | AC018919 | ||
| RP11-211G3 | — | — | AC072022 | ||
| RP11-58M14 | AQ199229 | AQ199231 | — | ||
| RP11-120O8 | AQ350519 | AQ350515 | — | ||
| RP11-1E24 | B48349 | AQ312932 | — | ||
| 4q22.1 | TIGD2ext | RP11-502A23 | — | — | AC079141 |
| RP11-84C13 | — | — | AC104785 | ||
| RP11-173C9 | — | — | AC105388 | ||
| RP11-549C16 | — | — | AC093862 | ||
| RP11-15F14 | B76416 | B76417 | — | ||
| RP11-115D19 | — | — | AC097478 | ||
| RP11-67M1 | — | — | AC093759 | ||
| RP11-350B19 | — | — | AC105445 | ||
| RP11-176N15 | — | — | AC108038 | ||
| RP11-183D16 | — | — | AC093781 | ||
| 5q23.1 | 05BP1-S47 | RP11-23E11 | B86433 | B86434 | — |
| RP11-254M1 | AQ479016 | AQ479018 | — | ||
| RP11-464H3 | AQ586366 | AZ515952 | — | ||
| RP11-133L2 | AQ350910 | AQ350911 | — | ||
| RP11-59G17 | AQ194868 | AQ194864 | — | ||
| RP11-42O22 | AQ116158 | AQ046673 | — | ||
| RP11-185N19 | — | — | AC021224 | ||
| 12cen, α-sat | 12cen | 444/7 | — | — | G03348 |
| 6cen, α-sat | 6cen | 864 | — | — | G04505 |
| 7cen, α-sat | 7cen | 680TA-4 | — | — | AJ295152 |
| 8cen, α-sat | 8cen | 8B/9 | — | — | M64779 |
| 9cen, sat III | 9cen | W21R2-TA13 | — | — | X06137 |
| 10cen, α-sat | 10cen | 609/51 | — | — | X63622 |
| 11cen, α-sat | 11cen | 238′-5′ | — | — | M21452 |
Abbreviation: BAC, bacterial artificial chromosome.
Table 2.
Shows the Final Probe Set Used.
| Set | Locus | Position (Mbp) | Probe Type | Label | Color | Clone/Contig ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 13q21.31 | 62.520–63.638 | BAC pool of 8 BACs | Cy5 | IR1 | OR7E156P |
| I | 14q13.3 | 35.678–36.975 | BAC pool of 8 BACs | DEAC | aqua | PAX9 |
| I | 16qh, sat II | — | Plasmid | Cy5.5 | IR2 | RMC16L006 |
| I | 20q11.1–11.2 | 34.950–36.152 | BAC pool of 9 BACs | Sp.Red | red | SRCext |
| I | 21q22 | around 37.770 | PCR product | Sp.Green | green | D21S167 |
| I | 22q11.22/23 | 21.545–22.085 | BAC pool of 3 BACs | Sp.Orange | orange | BCR |
| II | 15q25.3–26.1 | 85.745–86.975 | BAC pool of 7 BACs | Sp.Orange | orange | NTRK3ext |
| II | 17cen, α-sat | — | PCR product | Sp.Red | red | 17cen |
| II | 18cen, α-sat | — | PCR product | Cy5.5 | IR2 | 18cen |
| II | 19q13.2 | around 46.500 | BAC pool of 6 BACs | Sp.Green | green | AXL |
| II | Xq21 | 82.447–82.915 | BAC pool of 3 BACs | Cy5 | IR1 | CYCL1 |
| II | Yq12 | 57.158–57.256 | Single BAC | DEAC | aqua | RP11-242E13 |
| III | 2p16.1–15 | 60.525–61.831 | BAC pool of 9 BACs | Sp.Red | red | RELext |
| III | 3q27.3 | 188.590–188.976 | BAC pool of 6 BACs | Sp.Green | green | BCL6 |
| III | 4q22.1 | 90.168–91.675 | BAC pool of 10 BACs | Sp.Orange | orange | TIGD2ext |
| III | 5q23.1 | 116.279–117.541 | BAC pool of 7 BACs | DEAC | aqua | 05BP1-S47 |
| III | 9cen, sat III | — | PCR product | Cy5.5 | IR2 | 9cen |
| III | 12cen, α-sat | — | PCR product | Cy5 | IR1 | 12cen |
| IV | 1cen, α-sat | — | PCR product | Cy5.5 | IR2 | 1cen |
| IV | 6cen, α-sat | — | PCR product | Sp.Green | green | 6cen |
| IV | 7cen, α-sat | — | PCR product | Sp.Red | red | 7cen |
| IV | 8cen, α-sat | — | PCR product | DEAC | aqua | 8cen |
| IV | 10cen, α-sat | — | PCR product | Sp.Orange | red | 10cen |
| IV | 11cen, α-sat | — | PCR product | Cy5 | IR1 | 11cen |
Abbreviations: BAC, bacterial artificial chromosome; DEAC, diethylaminocoumarin; Sp., Spectrum; IR, infrared.
It also gives an overview of the direct fluorescent labels for the four sets of chromosome-specific probes.
For PCR, 100 ng genomic DNA (Sigma), BAC or plasmid DNA was used as template for DNA amplification. PCR reactions (50 μl) were performed using 0.02 μl Taq Polymerase (Invitrogen) or JumpStart Taq polymerase (Sigma) in 1× PCR buffer (Invitrogen), 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM of each dNTP, and 0.6 mM of the forward and reverse primers (Qiagen; Alameda, CA). The chromosomes 1 and 6 alpha-satellite primers have been used as described previously.27 The generation of chromosome 17- and 18-specific probes has also been previously published.28 BlueScript primers WBS2 (ctc gga att aac cct cac taa agg) and WBS4 (gaa ttg taa tac gac tca cta tag) for the DNA amplification of alpha-satellite repeats were employed for chromosomes 8, 10, and 12. For chromosome 7 and 11, primers M13F/ M13R29 and WA8 (gat ggt agt agg ca[a/t] [c/g]t[c/a] aca gag) / WA9 (gat ggt agt agg cat c[a/c]c [a/c]aa g[a/t/c]a), respectively, have been used to amplify chromosome-specific DNA. For the amplification of chromosome 9- and 21-specific probe DNA, a single primer was in use for both, the satellite III primer W21R2 (caa acg tgc tca aag taa ggg aat g) and Jun15 (ccc aag ctt gca tgc gaa ttc), respectively. After an initial denaturation step of 2 min at 95C, 35 PCR cycles followed: denaturation at 95C for 40 sec, primer annealing at 54C for 1 min, and primer extension at 72C for 2.5 min. Ramp time was set to 30 sec for the first step followed by 1 min for the next two steps. A final step at 72C for 10 min concluded the PCR. PCR products were confirmed on a 2% agarose gel by applying 5 μl of the PCR reaction mixed with 1 μl of 0.4 g/ml sucrose solution.
DNA Labeling and FISH
Using a commercially available kit (BioPrime Kit; Invitrogen; Gaithersburg, MD), random priming was employed to label all the BAC, plasmid, and PCR-derived probe DNA. After initial testing employing indirect labels,30–32 the random priming process was slightly modified to incorporate various fluorochrome dUTPs into the probe DNA: Cy5-dUTP and Cy5.5-dCTP (Amersham; Arlington Heights, IN), diethylaminocoumarin (DEAC)-dUTP (PerkinElmer; Waltham, MA) as well as SpectrumGreen-dUTP, SpectrumRed-dUTP, and SpectrumOrange-dUTP (Vysis, Abbott Molecular Inc; Des Plaines, IL). Regarding the four sets of chromosome-specific probes, Table 2 gives also an overview of their direct fluorescent labels.
For FISH, labeled probe DNA is mixed with blocking DNA and concentrated via precipitation in ethanol. Salmon sperm DNA is added to block nonspecific binding of the probe, and human Cot-1 DNA is added to block repetitive DNA sequences in the probes from binding to sites spread throughout several chromosomes/loci. The desired combination of labeled probe is mixed using 2–5 μl of each individual probe, depending on intensity of signal, as previously described.15
This is then combined with 1 μl of human Cot-1 DNA (1 mg/ml, Invitrogen), 1 μl of salmon sperm DNA (10 mg/ml; Invitrogen), and 7 μl of the hybridization master mix (78.6% formamide, 14.3% dextran sulfate in 1.43×SSC, pH 7.0; 20× SSC is 3 M sodium chloride, 300 mM tri-sodium citrate) and thoroughly mixed and denatured at 76C for 10 min. The hybridization mixture was then pre-annealed by incubating at 37C for 30 min (allowing the Cot-1 DNA to anneal to non-chromosome-specific DNA repeats on the probes). In parallel, the metaphase slides prepared from phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-stimulated peripheral blood lymphocytes from a karyotypically normal male31 were denatured for 3 min at 76C in 70% formamide/2× SSC, pH 7.0, dehydrated in 70%, 85%, and 100% ethanol for 2 min each, and allowed to air-dry. The hybridization mixture was then carefully applied to the slides, covered with a 22×22 mm2 coverslip, and sealed with rubber cement. Slides were incubated overnight in a moist chamber at 37C. After removing rubber cement and the coverslips, the slides were washed in 0.1× SSC at 43C for 2 min, then, when biotin or digoxigenin labels have been used, incubated in PNM blocking reagent (5% nonfat dry milk powder [NestléCarnation; Wilkes-Barre, PA], 1% Nonidet-P40 [Sigma], 1% sodium azide [Sigma], 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 8.0) for 10 min at room temperature. Bound probes were detected with fluorescein-conjugated avidin (avidin DCS; Vector Laboratories Inc.; Burlingame, CA) and rhodamine-labeled anti-digoxigenin antibodies (Roche Diagnostics; Indianapolis, IN). In the case of direct-labeled probes, no immuno-detection step was necessary. Finally, after a last wash in PN or 2×SSC, the slides were mounted with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, 0.5 µg/ml; Calbiochem; La Jolla, CA) in antifade solution.32,33
Image Acquisition and Analysis
Fluorescence microscopy was performed on a Zeiss Axioskop microscope equipped with a SKY filter set (ChromaTechnology; Brattleboro, VT) for simultaneous observation of SKY suitable fluorochromes and also a DAPI filter (ChromaTechnology) for the detection of the counterstain. Images were collected using a cooled CCD camera (CCD-1300DS; VDS Vosskühler; Osnabrück, Germany).24 Further processing and printing of the images were done using the image processing software Adobe Photoshop (Adobe Systems Inc.; San Jose, CA).
Results
Our probe sets have been constructed by choosing the most suitable probe DNA and fluorochrome so that each chromosome-specific probe within its set provides specificity and similar high efficiency. The probes used (see Tables 1 and 2 for a complete overview) are either locus-specific or repeat-specific (targeting alpha-satellites or satellite III). They are labeled with the following fluorescent labels: DEAC (excitation wavelength: 432 nm / emission wavelength: 472 nm, light blue), SpectrumGreen (497 nm / 524 nm, green), SpectrumOrange (559 nm / 588 nm, orange), SpectrumRed (592 nm / 612 nm, red), Cy5 (649 nm / 666 & 670 nm, infrared), and Cy5.5 (675 nm / 694 nm, infrared).
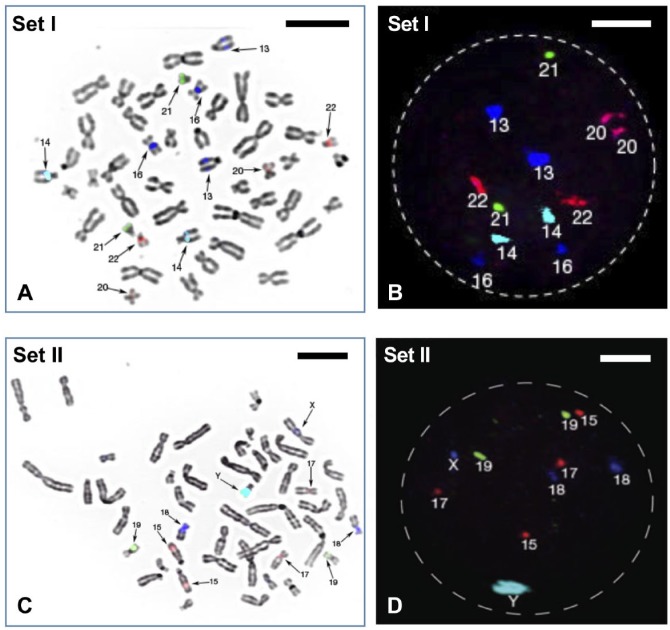
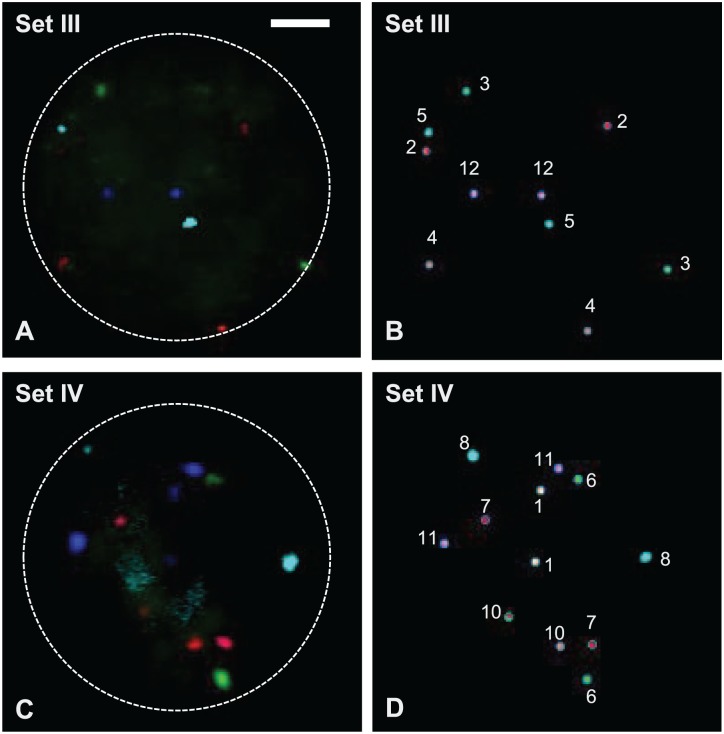
Sets I and II detect chromosomes 13, 14, 16, 20, 21, and 22 as well as of chromosomes 15, 17, 18, 19, X, and Y, respectively (Fig. 1) according to their fluorochrome labels (Fig. 2), whereas sets III and IV are able to evaluate the rest of the chromosomes for the full karyotype by detecting chromosomes 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 12 as well as chromosomes 1, 6, 7, 8, 10, and 11, respectively (Fig. 3). All the signals produced in metaphases and interphases by FISH are unambiguous, strong, and do not cross-hybridize to other chromosomes (Figs. 1 and 3). The exception was chromosome 9 in set III (Fig. 3), which did produce a strong signal when tested for itself but was rather dim when co-hybridized with the rest of set III probes.
Figure 1.
(A) FISH probe set I (see Table 2) hybridized on one metaphase spread from normal male lymphocyte and (B) one interphase nucleus. Computer-assigned pseudo-colors can be seen showing two copies each of chromosomes 13, 14, 16, 20, 21, and 22. (C) FISH probe set II (see Table 2) hybridized on one metaphase spread from normal male lymphocyte and (D) one interphase nucleus. It showed two copies each of chromosomes 15, 17, 18, 19, and one copy of chromosome X and Y. Scale bars A and C = 5 µm; B and D = 2.5 µm. Abbreviation: FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization.
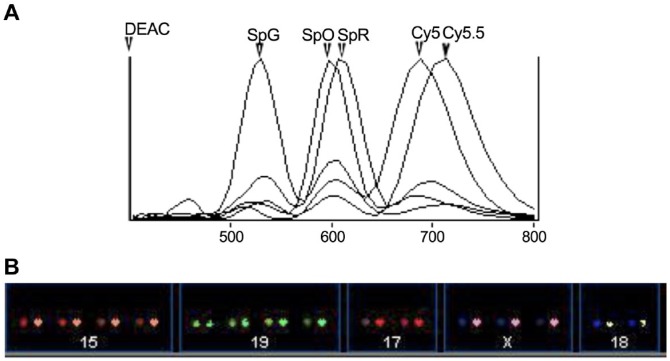
Figure 2.
(A) The emission spectra of DEAC, Spectrum Green, Spectrum Orange, Spectrum Red, Cy5, and Cy5.5 can be seen in this graph. (B) By using the distinguished emission spectra of these fluorochromes saved in a classified file, the SKY system can easily identify individual chromosomes and create a karyotype. This is an example of an abnormal female cell hybridized with probe set II showing four copies each of chromosomes 15 and 19, three copies of chromosome X, and two copies each of chromosomes 17 and 18. Abbreviations: DEAC, diethylaminocoumarin; SKY, spectral karyotyping.
Figure 3.
(A) FISH probe set III (see Table 2) hybridized on one normal male interphase nucleus (RGB colors). (B) The corresponding classified image from SKY system (pseudo-colors) showed two copies each of chromosomes 2, 3, 4, 5, and 12. The chromosome 9-Cy5.5 probe developed in-house showed weak hybridization signals and was not detected by the SKY system. (C) FISH probe set IV (see Table 2) hybridized on one normal male interphase nucleus (RGB colors). (D) The corresponding classified image from SKY system (pseudo-colors) showed two copies each of chromosomes 1, 6, 7, 8, 10, and 11. Scale bar = 2.5 µm. Abbreviations: FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; SKY, spectral karyotyping; RGB, red green blue.
Discussion
Detection techniques for assessing numerical abnormalities and other cytogenetic aberrations often utilize cost-effective and rapid classical staining methods such as Giemsa staining for karyotyping, but also molecular diagnostic tools such as FISH and its multiple variations for a quick, robust, and reliable detection of genetic damage. During the last decade, methodology development has been progressing toward a full karyotype analysis34; however, adjusting probe sets, that is, probe target and fluorochrome label, rapidly to particular needs in the laboratory is still quite difficult. Using BAC clones as a source of probe DNA for FISH is cheap and effective28,35,36 and, in contrast, allows the analysis of the whole genome37,38 for cytogenetic diagnoses. However, this metaphase-specific approach cannot be used for analysis of single cells per se, as they are likely to be in an interphase stage.
Although several bright chromosome-specific DNA repeat probes have been prepared and cloned by our labs in previous years,30,39 the approach does not work for all human chromosomes. The acrocentric chromosomes 13 and 21, for example, share a high level of homologous sequences, which is found heteromorphic in some individuals.40 The BAC approach41 has advantages for complete chromosome enumeration in interphase cells. During preparation of this manuscript, Ioannou et al. demonstrated this, using BAC clones from Roswell Park Cancer Institute RP11 library. We decided to combine preexisting DNA repeat probes with optimized BAC contigs, which were identified using bioinformatics22,42 to obtain optimal specificity and brightness (Table 2).
Now, combining the versatility of BACs and preexisting repeat probes with a wide repertoire of different fluorochromes, together with the use of the SKY system, resulted in a cost-effective, flexible, and reliable methodology to detect four sets of six probes in interphase nuclei (see Figs. 1 and 3). Incorporating consecutive hybridization steps (cell recycling) considerably increased the diagnostic range of existing FISH technologies.43
Sequential multilocus interphase FISH is one strategy where chromosome-specific (locus-specific and alpha-centromeric) FISH probes have been hybridized sequentially to the same cell, initially done in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded histological sections from tumor tissues.44 The use of spectral imaging (SIm) has enabled up to eight different fluorochrome labels (with emission spectra from 450–1000 nm) simultaneously.45 The scoring can be easily assessed by visual inspection, because SIm permits computer-assigned and distinguishable pseudo-colors to each probe during image processing.2 This leads to the full karyotype analysis by FISH of single-cell interphase nuclei like those of iCTBs in placental cell analysis (data not shown in this publication).
The benefits of combing sets of single copy DNA probes with separate sets of DNA repeat probes that contain super-bright signals in sequential hybridizations may raise concerns of DNA loss in repeated cycles of denaturation, hybridization, and wash steps. The approach presented here does not eliminate potential problems associated with DNA losses, but optimized BAC contigs and plasmids targeting highly reiterated DNA repeat sequences consistently lead to brighter signals, thus, reducing the negative effect of said losses.
As seen in Fig. 3, the flexibility of choosing probe DNA and fluorochromes may have an unforeseen negative consequence, as chromosome 9 showed a very dim signal that was below the threshold of detection for the SKY system, even though the same probe resulted in good strong signals when tested individually. Hence, either cell-type or donor differences as well as the interaction of DNA probes with each other within a set could lead to a less prominent or even a very dim and almost not visible signal. Thus, quality control when tailoring such probe sets to work in particular cell types is imperative.
In this article, we present the development of a probe collection made up of four sets of six labeled chromosome-specific FISH probes that can easily be modified toward three sets of eight probes using far-infrared fluorochromes such as Cy7. These have been arranged so that the first two sets detect the most prevalent numerical abnormalities observed in human embryos, and the last two sets fill in the gap toward a full karyotype analysis. The generation of these probe sets shows the full potential of BAC/plasmid clones, which can be rapidly selected and tailored for specific genetic screening applications. The strong signal intensities from these repeat-rich probes, and the labeling methodology employed, allow reduction in the costs for a single hybridization event by approximately 10-fold over conventional FISH.
In a clinical PGD setting, there is no apparent reason to do further analysis using multiple FISH probe sets after determining an abnormal ploidy status such as trisomy 13; however, if information on all 24 different chromosomes for individual embryos, that is, the discarded chromosomally abnormal embryos, can be collected, this could be very important information for early embryo development, and this information may be useful for future clinical diagnosis. Also, with regard to array and NGS analysis in a clinical PGD setting, 250–500 ng of DNA, an equivalent of about 35,000–70,000 cells, would be required for analysis. This entails that if there is only a limited number of cells (i.e., blastocytes), whole genome amplification will have to be applied, increasing time and cost but also errors.46 As our 24-probe set was originally developed for and applied to score all 24 chromosomes in placental iCTBs, we have found that at least 75% of the male invasive CTBs have gained extra copies of chromosomes with the most common gains being acrocentric chromosomes. Also, most of the iCTBs did not have the same karyotype (unpublished data). The probes that have been developed and tested are typically very useful to do full karyotyping on the few interphase cells, such as cancer stem cells, fetal cells in maternal blood, or heterogeneous cells with different karyotypes.
The set of 4×6 chromosome-enumerating FISH probes has been initially developed in-house to study invasive placental cells and to aid in PGD due to the fact that only some commercial probes are available as enumeration sets with a maximum of four different colors. There are many clinical applications for DNA probe sets like the ones described here, that is, prenatal analysis of aneuploidy. But, for example, if one wishes to study malignant mesothelioma, the panel would include a probe for ERBB2.47 Similarly, overexpression due to potential amplification of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene in squamous carcinoma cell lines might include an EGF receptor-specific DNA probe.48 Hence, it is very conceivable that our set of probes, original or modified, could find a use in other studies, such as in tumor cytogenetic evaluations or chromosome analysis in genotoxicology and mutagenesis, or whenever quick chromosome analysis of numerical abnormalities in interphase cells is required.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author Contributions: All authors have contributed to this article as follows: H-UGW, JFW, and BO designed the study; AB and H-UGW created and optimized the DNA probes using bacterial artificial chromosomes (BAC), plasmids, and PCR; AB, CFH, AAP, and JFW optimized fluorescent labels and carried out fluorescence in situ hybridization and spectral imaging as well as analysis of single probes and set of probes; and AB, BO, H-UGW, and JFW drafted the manuscript; and all authors have read and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Authors’ Note: This document was prepared as an account of work sponsored by the U.S. government. While this document is believed to contain correct information, neither the U.S. government, nor any agency thereof, nor The Regents of the University of California, nor any of their employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, or assumes any legal responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, apparatus, product, or process disclosed, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference herein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by its trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the U.S. government or any agency thereof, or The Regents of the University of California. The views and opinions of authors expressed herein do not necessarily state or reflect those of the U.S. government or any agency thereof or The Regents of the University of California.
Funding: The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants CA-88258, HD-045736, and ND-044313, and a grant from the Director, Office of Energy Research, Office of Health and Environmental Research, U.S. Department of Energy, under contract DE-AC02-05CH11231. A.B. was supported in part by a grant from the University of California Discovery Program (BIO03-10414 to JF). J.F. was supported by NIH grant HD-041425.
ORCID iD: B O’Brien  https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7024-2337
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7024-2337
Contributor Information
Adi Baumgartner, Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences, University of California, San Francisco, California; Life Sciences Division, E.O. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California; Biomedical Science, School of Health Sciences, York St John University, York, United Kingdom.
Christy Ferlatte Hartshorne, Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences, University of California, San Francisco, California.
Aris A. Polyzos, Life Sciences Division, E.O. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California
Heinz-Ulrich G. Weier, Life Sciences Division, E.O. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California.
Jingly Fung Weier, Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences, University of California, San Francisco, California; Dermatopathology Service, University of California, San Francisco, California; Life Sciences Division, E.O. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California.
Ben O’Brien, Life Sciences Division, E.O. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California; Department of Perioperative Medicine, St Bartholomew’s Hospital & Barts Heart Centre, London, United Kingdom; Outcomes Research Consortium, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio.
Literature Cited
- 1. Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray JW. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83:2934–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Schrock E, du Manoir S, Veldman T, Schoell B, Wienberg J, Ferguson-Smith MA, Ning Y, Ledbetter DH, Bar-Am I, Soenksen D, Garini Y, Ried T. Multicolor spectral karyotyping of human chromosomes. Science. 1996;273:494–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Speicher MR, Gwyn Ballard S, Ward DC. Karyotyping human chromosomes by combinatorial multi-fluor FISH. Nat Genet. 1996;12:368–75. doi: 10.1038/ng0496-368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Kallioniemi A, Kallioniemi OP, Sudar D, Rutovitz D, Gray JW, Waldman F, Pinkel D. Comparative genomic hybridization for molecular cytogenetic analysis of solid tumors. Science. 1992;258:818–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Le Scouarnec S, Gribble SM. Characterising chromosome rearrangements: recent technical advances in molecular cytogenetics. Heredity (Edinb). 2012;108:75–85. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2011.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Deleye L, Dheedene A, De Coninck D, Sante T, Christodoulou C, Heindryckx B, Van den Abbeel E, De Sutter P, Deforce D, Menten B, Van Nieuwerburgh F. Shallow whole genome sequencing is well suited for the detection of chromosomal aberrations in human blastocysts. Fertil Steril. 2015;104:1276–85 e1271. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.07.1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Baart EB, Martini E, Van Opstal D. Screening for aneuploidies of ten different chromosomes in two rounds of FISH: a short and reliable protocol. Prenat Diagn. 2004;24:955–61. doi: 10.1002/pd.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Baart EB, Van Opstal D, Los FJ, Fauser BC, Martini E. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of two blastomeres from day 3 frozen-thawed embryos followed by analysis of the remaining embryo on day 5. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:685–93. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Bahce M, Escudero T, Sandalinas M, Morrison L, Legator M, Munne S. Improvements of preimplantation diagnosis of aneuploidy by using microwave hybridization, cell recycling and monocolour labelling of probes. Mol Hum Reprod. 2000;6:849–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Munne S, Magli C, Bahce M, Fung J, Legator M, Morrison L, Cohert J, Gianaroli L. Preimplantation diagnosis of the aneuploidies most commonly found in spontaneous abortions and live births: XY, 13, 14, 15, 16, 18, 21, 22. Prenat Diagn. 1998;18:1459–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Hassold T, Hall H, Hunt P. The origin of human aneuploidy: where we have been, where we are going. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16(Spec No. 2):R203–8. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Simpson JL. Causes of fetal wastage. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2007;50:10–30. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0b013e31802f11f6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Treff NR, Zimmerman RS. Advances in preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic disease and aneuploidy. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2017;18:189–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091416-035508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. McCoy RC. Mosaicism in preimplantation human embryos: when chromosomal abnormalities are the norm. Trends Genet. 2017;33:448–63. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2017.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Weier JF, Hartshorne C, Nguyen HN, Baumgartner A, Polyzos AA, Lemke KH, Zeng H, Weier HU. Analysis of human invasive cytotrophoblasts using multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization. Methods. 2013;64:160–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Todorovic-Rakovic N. Genome-based versus gene-based theory of cancer: possible implications for clinical practice. J Biosci. 2011;36:719–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Duesberg P, Fabarius A, Hehlmann R. Aneuploidy, the primary cause of the multilateral genomic instability of neoplastic and preneoplastic cells. IUBMB Life. 2004;56:65–81. doi: 10.1080/15216540410001667902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Alaizari NA, Sperandio M, Odell EW, Peruzzo D, Al-Maweri SA. Meta-analysis of the predictive value of DNA aneuploidy in malignant transformation of oral potentially malignant disorders. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018;47(2):97–103. doi: 10.1111/jop.12603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Hayden EC. Technology: the $1,000 genome. Nature. 2014;507:294–5. doi: 10.1038/507294a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Liehr T. What about the real costs of next generation sequencing (NGS) in human genetic diagnostics? https://atlasofscience.org/what-about-the-real-costs-of-next-generation-sequencing-ngs-in-human-genetic-diagnostics/.
- 21. Lemke KH, Weier JF, Weier HG, Lawin-O’Brien AR. High performance DNA probes for perinatal detection of numerical chromosome aberrations. Adv Tech Biol Med. 2015;3:155. doi: 10.4172/2379-1764.1000155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Hsu JH, Zeng H, Lemke KH, Polyzos AA, Weier JF, Wang M, Lawin-O’Brien AR, Weier HU, O’Brien B. Chromosome-specific DNA repeats: rapid identification in silico and validation using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;14:57–71. doi: 10.3390/ijms14010057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Shizuya H, Birren B, Kim UJ, Mancino V, Slepak T, Tachiiri Y, Simon M. Cloning and stable maintenance of 300-kilobase-pair fragments of human DNA in Escherichia coli using an F-factor-based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:8794–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Weier HU, Tuton TB, Ito Y, Chu LW, Lu CM, Baumgartner A, Zitzelsberger HF, Weier JF. Molecular cytogenetic characterization of chromosome 9-derived material in a human thyroid cancer cell line. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006;114:284–91. doi: 10.1159/000094215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Birnboim HC, Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;7:1513–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Moyzis RK, Albright KL, Bartholdi MF, Cram LS, Deaven LL, Hildebrand CE, Joste NE, Longmire JL, Meyne J, Schwarzacher-Robinson T. Human chromosome-specific repetitive DNA sequences: novel markers for genetic analysis. Chromosoma. 1987;95:375–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Dunham I, Lengauer C, Cremer T, Featherstone T. Rapid generation of chromosome-specific alphoid DNA probes using the polymerase chain reaction. Hum Genet. 1992;88:457–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Baumgartner A, Weier JF, Weier HU. Chromosome-specific DNA repeat probes. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006;54:1363–70. doi: 10.1369/jhc.6A6974.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. O’Shaughnessy JB, Chan M, Clark K, Ivanetich KM. Primer design for automated DNA sequencing in a core facility. Biotechniques. 2003;35:112–6, 118–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Fung J, Hyun W, Dandekar P, Pedersen RA, Weier HU. Spectral imaging in preconception/preimplantation genetic diagnosis of aneuploidy: multicolor, multichromosome screening of single cells. J Assist Reprod Genet. 1998;15:323–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Fung J, Weier HU, Pedersen RA. Detection of structural and numerical chromosome abnormalities in interphase cells using spectral imaging. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001;49:797–8. doi: 10.1177/002215540104900616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Weier HU, Wang M, Mullikin JC, Zhu Y, Cheng JF, Greulich KM, Bensimon A, Gray JW. Quantitative DNA fiber mapping. Hum Mol Genet. 1995;4:1903–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Weier HU, Rhein AP, Shadravan F, Collins C, Polikoff D. Rapid physical mapping of the human trk protooncogene (NTRK1) to human chromosome 1q21-q22 by P1 clone selection, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and computer-assisted microscopy. Genomics. 1995;26:390–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Turner K, Fowler K, Fonseka G, Griffin D, Ioannou D. Multicolor detection of every chromosome as a means of detecting mosaicism and nuclear organization in human embryonic nuclei. Panminerva Med. 2016;58:175–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Lu CM, Kwan J, Baumgartner A, Weier JF, Wang M, Escudero T, Munne S, Zitzelsberger HF, Weier HU. DNA probe pooling for rapid delineation of chromosomal breakpoints. J Histochem Cytochem. 2009;57:587–97. doi: 10.1369/jhc.2009.953638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Weier HU, Ito Y, Kwan J, Smida J, Weier JF, Hieber L, Lu CM, Lehmann L, Wang M, Kassabian HJ, Zeng H, O’Brien B. Delineating chromosomal breakpoints in radiation-induced papillary thyroid cancer. Genes (Basel). 2011;2:397–419. doi: 10.3390/genes2030397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Voullaire L, Slater H, Williamson R, Wilton L. Chromosome analysis of blastomeres from human embryos by using comparative genomic hybridization. Hum Genet. 2000;106:210–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Wells D, Delhanty JD. Comprehensive chromosomal analysis of human preimplantation embryos using whole genome amplification and single cell comparative genomic hybridization. Mol Hum Reprod. 2000;6:1055–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Weier HU, Kleine HD, Gray JW. Labeling of the centromeric region on human chromosome 8 by in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1991;87:489–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Weier HU, Gray JW. A degenerate alpha satellite probe, detecting a centromeric deletion on chromosome 21 in an apparently normal human male, shows limitations of the use of satellite DNA probes for interphase ploidy analysis. Anal Cell Pathol. 1992;4:81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Ioannou D, Meershoek EJ, Thornhill AR, Ellis M, Griffin DK. Multicolour interphase cytogenetics: 24 chromosome probes, 6 colours, 4 layers. Mol Cell Probes. 2011;25:199–205. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2011.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Zeng H, Weier JF, Wang M, Kassabian HJ, Polyzos AA, Baumgartner A, O’Brien B, Weier HU. Bioinformatic tools identify chromosome-specific DNA probes and facilitate risk assessment by detecting aneusomies in extra-embryonic tissues. Curr Genomics. 2012;13:438–45. doi: 10.2174/138920212802510510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Harrison CJ, Gibbons B, Yang F, Butler T, Cheung KL, Kearney L, Dirscherl L, Bray-Ward P, Gregson M, Ferguson-Smith M. Multiplex fluorescence in situ hybridization and cross species color banding of a case of chronic myeloid leukemia in blastic crisis with a complex Philadelphia translocation. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2000;116:105–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Walch A, Bink K, Hutzler P, Bowering K, Letsiou I, Zitzelsberger H, Braselmann H, Stein H, Hofler H, Werner M. Sequential multilocus fluorescence in situ hybridization can detect complex patterns of increased gene dosage at the single cell level in tissue sections. Lab Invest. 2001;81:1457–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Weier JF, Ferlatte C, Baumgartner A, Jung CJ, Nguyen HN, Chu LW, Pedersen RA, Fisher SJ, Weier HU. Molecular cytogenetic studies towards the full karyotype analysis of human blastocysts and cytotrophoblasts. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006;114:302–11. doi: 10.1159/000094218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Sho S, Court CM, Winograd P, Lee S, Hou S, Graeber TG, Tseng HR, Tomlinson JS. Precision oncology using a limited number of cells: optimization of whole genome amplification products for sequencing applications. BMC Cancer. 2017;17:457. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3447-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Horvai AE, Li L, Xu Z, Kramer MJ, Jablons DM, Treseler PA. Malignant mesothelioma does not demonstrate overexpression or gene amplification despite cytoplasmic immunohistochemical staining for c-Erb-B2. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003;127:465–9. doi: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Yamamoto T, Kamata N, Kawano H, Shimizu S, Kuroki T, Toyoshima K, Rikimaru K, Nomura N, Ishizaki R, Pastan I, Gamou S, Shimizu N. High incidence of amplification of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in human squamous carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1986;46:414–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]