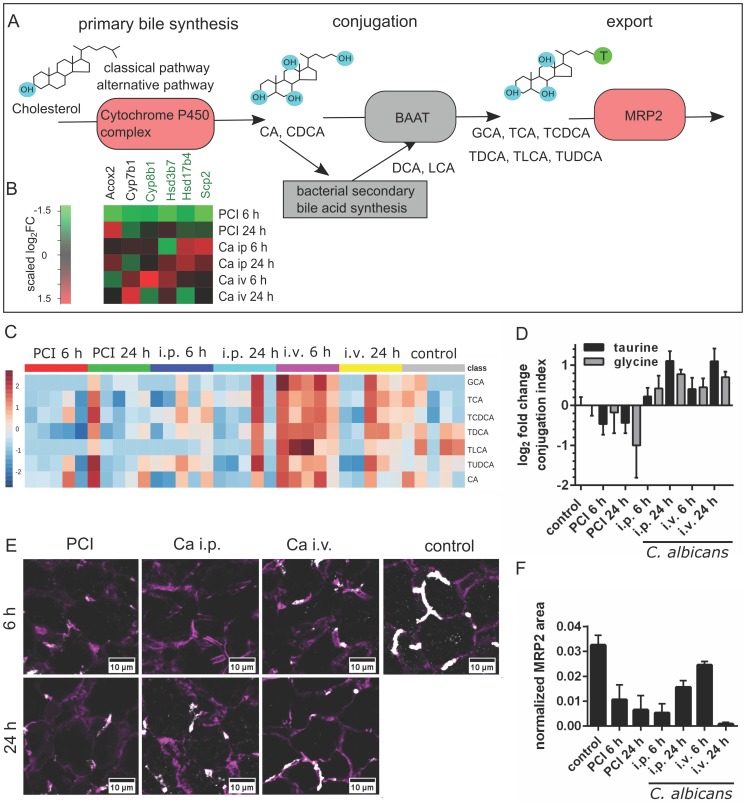
Figure 5.
Bile acid synthesis, conjugation and secretion are distinct for PCI and Candida infection. (A) Schematic outline of bile synthesis, conjugation and export. CA: cholic acid; CDCA: chenodeoxycholic acid; DCA: deoxycholic acid; LCA: lithocholic acid; GCA: glycocholic acid; TCA: taurocholic acid; TCDCA: taurochenodeoxycholic acid; TDCA: taurodeoxycholic acid; TLCA: taurolithocholic acid; TUDCA: tauroursodeoxycholic acid; BAAT: bile acid-CoA:amino acid n-acyltransferase. (B) Genes involved in primary bile synthesis are overall downregulated; genes downregulated in all groups are marked by a green gene symbol. A heat map shows scaled relative changes within the downregulation. (C) Relative change in conjugated and unconjugated bile acids and (D) respective conjugation index of bile acids. (E) Immunostaining of MRP2 in liver tissue (white). MRP2 is localized at the cell membrane and linked to the cytoskeleton (F-actin, purple). (F) Quantification of MRP2-stained areas and overlap areas with F-actin (Figure S6) at 20x magnification depict the loss of membrane-associated MRP2 protein leading to cholestasis.