The molecular and crystal structures of 2-iodo benzamide and 2-iodo-N-phenylbenzamide are reported. In both crystals, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—I⋯π(ring) interactions stabilize the packing with additional C—H⋯π(ring) contacts found in the latter.
Keywords: crystal structure, benzamide, dimer, tetramer, hydrogen bonds, C—I⋯π(ring) interactions
Abstract
The title compounds, 2-iodobenzamide, C7H6INO (I), and 2-iodo-N-phenylbenzamide, C13H10INO (II), were both synthesized from 2-iodobenzoic acid. In the crystal structure of (I), N—H⋯O and hydrogen bonds form two sets of closed rings, generating dimers and tetramers. These combine with C—I⋯π(ring) halogen bonds to form sheets of molecules in the bc plane. For (II), N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds form chains along the a-axis direction, while inversion-related C—I⋯π(ring) contacts supported by C—H⋯π(ring) interactions generate sheets of molecules along the ab diagonal.
Chemical context
Aromatic amides can be found in a wide range of aromatic molecules and they also serve as intermediates in the production of many pharmaceutical compounds (Suchetan et al., 2016 ▸). Aromatic amides and N-aryl amides display a wide spectrum of pharmacological properties and are used as antibacterial (Ragavan et al., 2010 ▸), analgesic (Starmer et al., 1971 ▸), antiviral (Hu et al., 2008 ▸), anti-inflammatory (Kalgutkar et al., 2000 ▸) and anti-cancer (Pradidphol et al., 2012 ▸) agents. Furthermore, N-aryl amides are known to act as anti-tumor agents against a broad spectrum of human tumors (Abdou et al., 2004 ▸). In view of their potential importance, the title compounds (I) and (II) were synthesized and we report herein a comparison of their structures.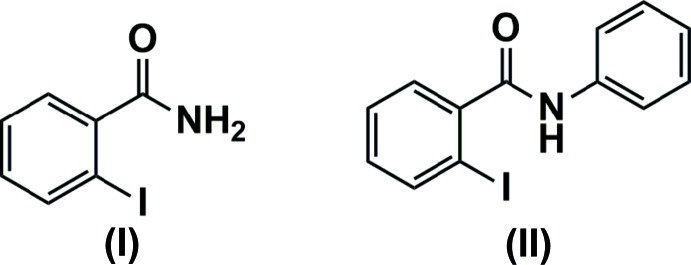
Structural commentary
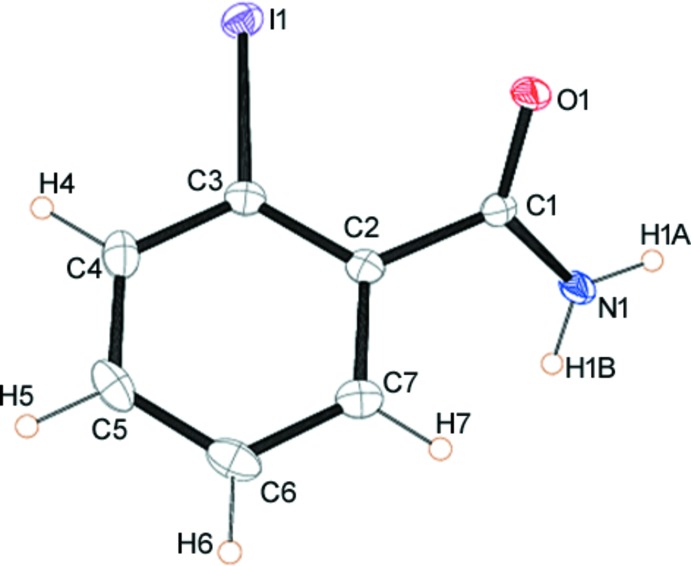
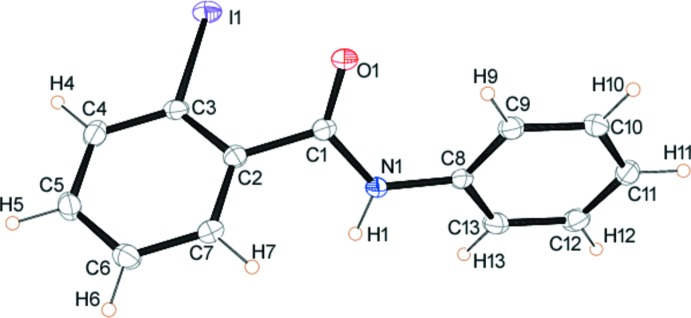
Both compounds (I) and (II) crystallize with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Z′ = 1). The molecular structures of the molecules are shown in Figs. 1 ▸ and 2 ▸, respectively. In (I) the aromatic ring is inclined to the O1/C1/N1 plane of the amide by 44.37 (1)° whereas in (II) the two aromatic rings are almost orthogonal with an angle of 79.84 (6)° between them. The iodobenzene ring plane is inclined to the O1/C1/N1 amide plane by 52.01 (1)°, somewhat similar to the inclination found for (I), while the phenyl ring of the amide is inclined by 28.45 (5)° to this plane.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing the atom numbering with ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of (II) showing the atom numbering with ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
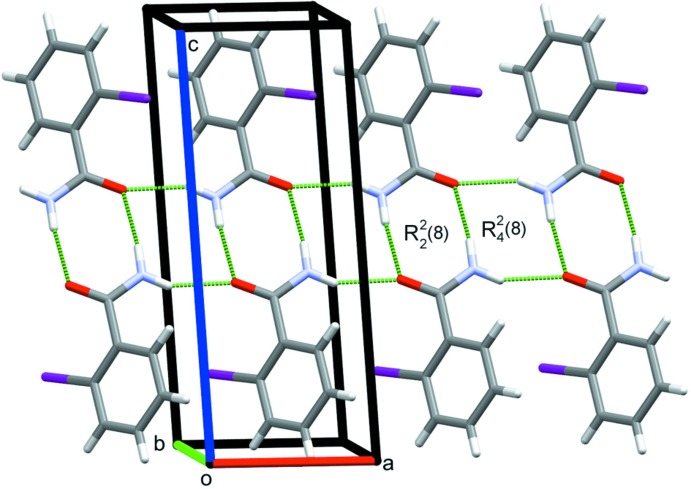
In the crystal structure of compound (I), strong classical N1—H1A⋯O1 and N1—H1B⋯O1 hydrogen bonds, Table 1 ▸, arrange the molecules in two linked sets of closed rings, forming both dimers with an 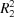 (8) graph-set motif and tetramers that enclose
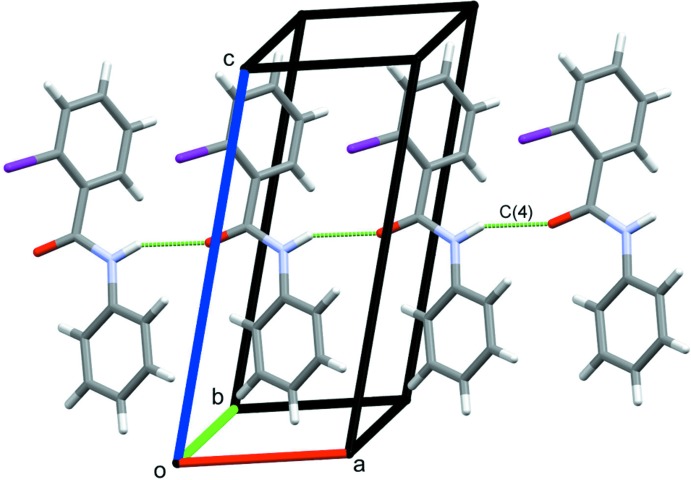
(8) graph-set motif and tetramers that enclose 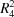 (8) rings (Etter et al., 1990 ▸). These contacts form chains of molecules along the a-axis direction (Fig. 3 ▸). In addition, C3—I1⋯Cg1 halogen bonds, Table 1 ▸, combine with the previously mentioned inversion dimers to generate sheets of molecules in the bc plane (Fig. 4 ▸).
(8) rings (Etter et al., 1990 ▸). These contacts form chains of molecules along the a-axis direction (Fig. 3 ▸). In addition, C3—I1⋯Cg1 halogen bonds, Table 1 ▸, combine with the previously mentioned inversion dimers to generate sheets of molecules in the bc plane (Fig. 4 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
Cg1 is the centroid of the C2–C7 phenyl ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.11 | 2.951 (2) | 164 |
| N1—H1B⋯O1ii | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.843 (2) | 154 |
| C3—I1⋯Cg1iii | 2.11 (1) | 3.99 (1) | 5.877 (2) | 148 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 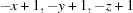 ; (ii)
; (ii) 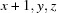 ; (iii)
; (iii) 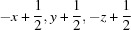 .
.
Figure 3.
Chains of molecules of (I) along the a-axis direction, showing the dimers and tetramers formed by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Figure 4.
N—H⋯O and C—I⋯π(ring) contacts forming sheets of molecules of (I) in the bc plane.
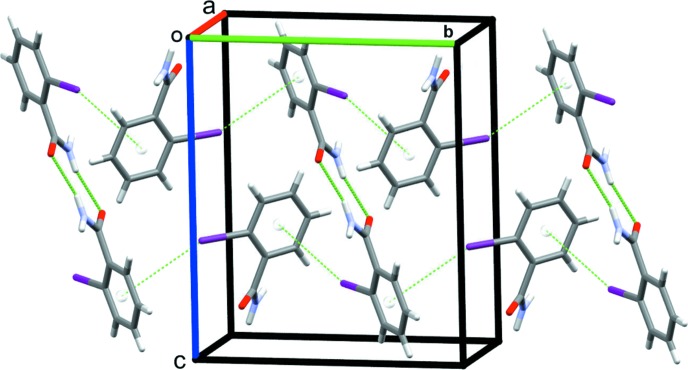
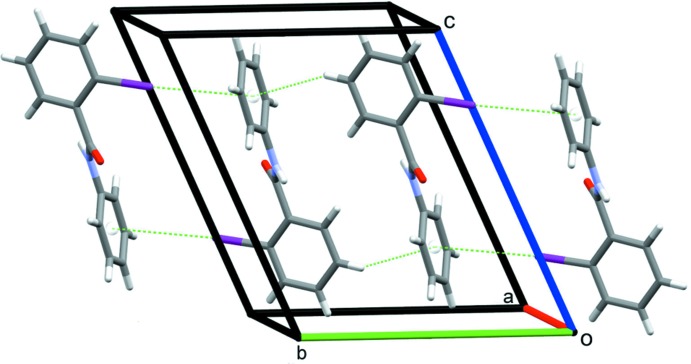
For compound (II), the absence of a second H atom on the N1 amine nitrogen atom limits the formation of classical hydrogen bonds to N1—H1⋯O1 contacts that generate C(4) molecular chains along the a-axis direction (Fig. 5 ▸, Table 2 ▸). Additional weak inversion-related C3—I1⋯Cg2 interactions (Table 2 ▸), in this instance also supported by C6—H6⋯Cg2 contacts that also lie about an inversion centre, form sheets of molecules along the ab diagonal (Fig. 6 ▸, Table 2 ▸).
Figure 5.
N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds forming chains of molecules of (II) along the a-axis direction.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
Cg2 is the centroid of the C8–C13 benzene ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.88 | 2.15 | 2.942 (2) | 150 |
| C3—I1⋯Cg2ii | 2.10 (1) | 3.83 (1) | 5.816 (2) | 156 (1) |
| C6—H6⋯Cg2iii | 0.95 | 2.81 | 3.627 (2) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 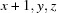 ; (ii)
; (ii) 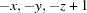 ; (iii)
; (iii) 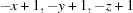 .
.
Figure 6.
C—I⋯π(ring) and C—H⋯π(ring) contacts generating sheets of molecules of (II) along the ab diagonal
Database survey
A search for the crystal structures of 2-iodobenzamide and 2-iodo-N-phenylbenzamide was carried out in the Cambridge Structural Database (Conquest Version 1.17; CSD Version 5.39, last update November 2017; Groom et al., 2016 ▸). Compound (I) was found to have been previously reported from film data (IBNZAM; Nakata et al., 1976 ▸), but there were no hits for compound (II). Four other related structures were observed: two fluorine-substituted 2-iodobenzamides, FAHSAK and FAHSIS (Nayak et al., 2012 ▸) and two nitro substituted 2-iodobenzamides, TAQBIX (Garden et al., 2005 ▸) and WAWMAJ (Wardell et al., 2005 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
The synthesis of the title compounds was carried out using a reported procedure (Jursic & Zdravkovski, 1993 ▸; Kavala et al., 2012 ▸; Mao et al., 2012 ▸). Single crystals for both compounds were grown by the slow evaporation method from dichloromethane and hexane (v/v 1:1) at low temperature for (I), whereas those for compound (II) were obtained from acetonitrile solvent at room temperature. The melting points of (I) and (II) are 398.2 and 419.6 K, respectively. Infra-red (IR) spectra confirm the presence of various functional groups as follows: compound (I) (cm−1): N—H = 3362, 3177, C=O = 1644, C=C = 1581–1470, ortho-substituted ring = 734; compound (II) (cm−1): N—H = 3235, Csp 2—H = 3037, C=O = 1646, C=C = 1536–1488, ortho-substituted ring = 752, N—H bending = 1597.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All H atoms were refined using a riding model with d(N—H) = 0.86 Å, U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(N) and d(C—H) = 0.93 Å, U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) for (I) and d(N—H) = 0.88 Å, U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(N) and d(C—H) = 0.95 Å, U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) for (II).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C7H6INO | C13H10INO |
| M r | 247.03 | 323.12 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n | Triclinic, P
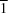
|
| Temperature (K) | 296 | 120 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 5.0531 (2), 11.4478 (5), 13.2945 (5) | 5.1225 (2), 10.4572 (4), 12.2167 (5) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 93.245 (1), 90 | 66.034 (2), 78.882 (2), 85.760 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 767.81 (5) | 586.76 (4) |
| Z | 4 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 4.10 | 2.71 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.23 × 0.22 × 0.21 | 0.23 × 0.22 × 0.21 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXII DUO | Bruker Kappa APEXII DUO |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.429, 0.456 | 0.546, 0.570 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 5827, 1504, 1461 | 13292, 2309, 2278 |
| R int | 0.021 | 0.018 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.617 | 0.617 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.014, 0.033, 1.16 | 0.017, 0.042, 1.08 |
| No. of reflections | 1504 | 2309 |
| No. of parameters | 92 | 145 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.45, −0.35 | 0.81, −0.48 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Deepak Chopra, IISER, Bhopal for the single-crystal X-ray data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
2-Iodobenzamide (I). Crystal data
| C7H6INO | F(000) = 464 |
| Mr = 247.03 | Dx = 2.137 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.0531 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 1504 reflections |
| b = 11.4478 (5) Å | θ = 2.3–26.0° |
| c = 13.2945 (5) Å | µ = 4.10 mm−1 |
| β = 93.245 (1)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 767.81 (5) Å3 | Plate, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.23 × 0.22 × 0.21 mm |
2-Iodobenzamide (I). Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII DUO diffractometer | 1504 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1461 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.021 |
| ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.429, Tmax = 0.456 | k = −14→11 |
| 5827 measured reflections | l = −15→16 |
2-Iodobenzamide (I). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.014 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0075P)2 + 0.6908P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.033 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| S = 1.16 | Δρmax = 0.45 e Å−3 |
| 1504 reflections | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
| 92 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0170 (5) |
2-Iodobenzamide (I). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2-Iodobenzamide (I). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | 0.14922 (2) | 0.55570 (2) | 0.18090 (2) | 0.01703 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.3073 (3) | 0.43218 (14) | 0.39426 (11) | 0.0177 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.7508 (3) | 0.44020 (16) | 0.41536 (14) | 0.0168 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.7438 | 0.4650 | 0.4762 | 0.020* | |
| H1B | 0.9018 | 0.4297 | 0.3900 | 0.020* | |
| C5 | 0.6303 (4) | 0.2793 (2) | 0.06578 (17) | 0.0219 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.6514 | 0.2473 | 0.0024 | 0.026* | |
| C6 | 0.7846 (4) | 0.23997 (19) | 0.14775 (17) | 0.0202 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.9113 | 0.1824 | 0.1396 | 0.024* | |
| C7 | 0.7504 (4) | 0.28652 (19) | 0.24225 (17) | 0.0165 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.8555 | 0.2598 | 0.2972 | 0.020* | |
| C2 | 0.5610 (4) | 0.37276 (18) | 0.25648 (15) | 0.0125 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.5297 (4) | 0.41830 (18) | 0.36086 (15) | 0.0125 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.4440 (4) | 0.3662 (2) | 0.07746 (16) | 0.0193 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.3416 | 0.3931 | 0.0219 | 0.023* | |
| C3 | 0.4101 (4) | 0.41317 (18) | 0.17218 (16) | 0.0138 (4) |
2-Iodobenzamide (I). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.01454 (9) | 0.01736 (10) | 0.01910 (10) | 0.00237 (5) | 0.00030 (5) | 0.00353 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0082 (7) | 0.0300 (9) | 0.0152 (8) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0019 (5) | −0.0026 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0094 (8) | 0.0280 (11) | 0.0132 (9) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0021 (6) | −0.0044 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0286 (12) | 0.0200 (11) | 0.0177 (12) | −0.0038 (9) | 0.0070 (9) | −0.0071 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0210 (11) | 0.0125 (11) | 0.0277 (12) | −0.0010 (9) | 0.0085 (9) | −0.0048 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0138 (9) | 0.0140 (10) | 0.0220 (11) | −0.0022 (8) | 0.0024 (8) | 0.0013 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0100 (9) | 0.0122 (10) | 0.0154 (10) | −0.0034 (7) | 0.0019 (7) | −0.0003 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0118 (9) | 0.0117 (9) | 0.0142 (10) | −0.0002 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0036 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0213 (10) | 0.0226 (12) | 0.0140 (11) | −0.0042 (9) | −0.0002 (8) | −0.0012 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0120 (9) | 0.0122 (10) | 0.0173 (11) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0005 (8) |
2-Iodobenzamide (I). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I1—C3 | 2.105 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.385 (3) |
| O1—C1 | 1.242 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.321 (3) | C7—C2 | 1.395 (3) |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1B | 0.8600 | C2—C3 | 1.398 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.379 (3) | C2—C1 | 1.499 (3) |
| C5—C4 | 1.384 (3) | C4—C3 | 1.389 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C1—N1—H1A | 120.0 | C7—C2—C3 | 118.20 (19) |
| C1—N1—H1B | 120.0 | C7—C2—C1 | 118.73 (18) |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 120.0 | C3—C2—C1 | 123.07 (18) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.2 (2) | O1—C1—N1 | 122.29 (19) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 | O1—C1—C2 | 121.37 (18) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 | N1—C1—C2 | 116.32 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.8 (2) | C5—C4—C3 | 120.0 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 |
| C6—C7—C2 | 121.1 (2) | C4—C3—C2 | 120.61 (19) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.4 | C4—C3—I1 | 117.38 (16) |
| C2—C7—H7 | 119.4 | C2—C3—I1 | 121.81 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.9 (3) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | −0.7 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.2 (3) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | −0.6 (3) |
| C6—C7—C2—C3 | −1.5 (3) | C5—C4—C3—I1 | 174.29 (16) |
| C6—C7—C2—C1 | 178.91 (18) | C7—C2—C3—C4 | 1.7 (3) |
| C7—C2—C1—O1 | −135.1 (2) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −178.75 (18) |
| C3—C2—C1—O1 | 45.3 (3) | C7—C2—C3—I1 | −172.99 (14) |
| C7—C2—C1—N1 | 43.5 (3) | C1—C2—C3—I1 | 6.6 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1—N1 | −136.1 (2) |
2-Iodobenzamide (I). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C2–C7 phenyl ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O1i | 0.86 | 2.11 | 2.951 (2) | 164 |
| N1—H1B···O1ii | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.843 (2) | 154 |
| C3—I1···Cg1iii | 2.11 (1) | 3.99 (1) | 5.877 (2) | 148 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (II) . Crystal data
| C13H10INO | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 323.12 | F(000) = 312 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.829 Mg m−3 |
| a = 5.1225 (2) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 10.4572 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 2309 reflections |
| c = 12.2167 (5) Å | θ = 1.9–26.0° |
| α = 66.034 (2)° | µ = 2.71 mm−1 |
| β = 78.882 (2)° | T = 120 K |
| γ = 85.760 (2)° | Plate, colorless |
| V = 586.76 (4) Å3 | 0.23 × 0.22 × 0.21 mm |
2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (II) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII DUO diffractometer | 2309 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2278 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.018 |
| ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.546, Tmax = 0.570 | k = −12→12 |
| 13292 measured reflections | l = −15→14 |
2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (II) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.017 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.042 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0207P)2 + 0.7193P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2309 reflections | Δρmax = 0.81 e Å−3 |
| 145 parameters | Δρmin = −0.48 e Å−3 |
2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (II) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (II) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | −0.30400 (3) | 0.03723 (2) | 0.77480 (2) | 0.01972 (6) | |
| O1 | −0.1224 (3) | 0.31161 (18) | 0.51921 (14) | 0.0233 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.3285 (3) | 0.2852 (2) | 0.49180 (16) | 0.0169 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.4668 | 0.2731 | 0.5279 | 0.020* | |
| C1 | 0.0875 (4) | 0.2939 (2) | 0.55727 (19) | 0.0161 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.0968 (4) | 0.2802 (2) | 0.68392 (19) | 0.0148 (4) | |
| C3 | −0.0677 (4) | 0.1861 (2) | 0.7861 (2) | 0.0156 (4) | |
| C4 | −0.0629 (4) | 0.1793 (2) | 0.9014 (2) | 0.0194 (4) | |
| H4 | −0.1751 | 0.1151 | 0.9704 | 0.023* | |
| C5 | 0.1069 (4) | 0.2670 (2) | 0.9157 (2) | 0.0206 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.1091 | 0.2632 | 0.9945 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | 0.2728 (4) | 0.3597 (2) | 0.8154 (2) | 0.0198 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.3893 | 0.4191 | 0.8255 | 0.024* | |
| C7 | 0.2685 (4) | 0.3657 (2) | 0.7005 (2) | 0.0169 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.3838 | 0.4289 | 0.6321 | 0.020* | |
| C8 | 0.3800 (4) | 0.2938 (2) | 0.37055 (19) | 0.0159 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.2215 (4) | 0.3717 (2) | 0.2855 (2) | 0.0180 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.0683 | 0.4185 | 0.3083 | 0.022* | |
| C10 | 0.2897 (4) | 0.3802 (2) | 0.1671 (2) | 0.0191 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.1821 | 0.4334 | 0.1089 | 0.023* | |
| C11 | 0.5124 (4) | 0.3123 (2) | 0.1323 (2) | 0.0203 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.5579 | 0.3190 | 0.0510 | 0.024* | |
| C12 | 0.6677 (4) | 0.2343 (2) | 0.2180 (2) | 0.0209 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.8204 | 0.1873 | 0.1952 | 0.025* | |
| C13 | 0.6024 (4) | 0.2245 (2) | 0.3364 (2) | 0.0192 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.7094 | 0.1703 | 0.3945 | 0.023* |
2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (II) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.01580 (8) | 0.01876 (9) | 0.02535 (9) | −0.00291 (5) | −0.00378 (6) | −0.00904 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0114 (7) | 0.0402 (10) | 0.0194 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | −0.0035 (6) | −0.0126 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0106 (8) | 0.0271 (10) | 0.0150 (9) | 0.0003 (7) | −0.0026 (7) | −0.0103 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0134 (10) | 0.0183 (10) | 0.0171 (10) | −0.0018 (8) | −0.0013 (8) | −0.0078 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0118 (9) | 0.0171 (10) | 0.0169 (10) | 0.0039 (8) | −0.0035 (8) | −0.0084 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0109 (9) | 0.0172 (10) | 0.0214 (11) | 0.0004 (8) | −0.0028 (8) | −0.0105 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0178 (10) | 0.0221 (11) | 0.0160 (10) | 0.0002 (8) | 0.0004 (8) | −0.0069 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0207 (11) | 0.0270 (12) | 0.0174 (10) | 0.0026 (9) | −0.0042 (8) | −0.0124 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0186 (10) | 0.0216 (11) | 0.0235 (11) | 0.0002 (8) | −0.0063 (9) | −0.0124 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0131 (10) | 0.0180 (10) | 0.0187 (10) | −0.0005 (8) | −0.0013 (8) | −0.0070 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0129 (9) | 0.0206 (10) | 0.0161 (10) | −0.0047 (8) | −0.0003 (8) | −0.0095 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0139 (10) | 0.0213 (11) | 0.0203 (11) | −0.0010 (8) | −0.0018 (8) | −0.0103 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0179 (10) | 0.0220 (11) | 0.0179 (10) | −0.0045 (8) | −0.0046 (8) | −0.0071 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0208 (11) | 0.0247 (11) | 0.0182 (10) | −0.0076 (9) | 0.0010 (8) | −0.0121 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0152 (10) | 0.0256 (12) | 0.0259 (12) | −0.0031 (9) | 0.0014 (9) | −0.0159 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0138 (10) | 0.0244 (11) | 0.0218 (11) | 0.0004 (8) | −0.0046 (8) | −0.0109 (9) |
2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (II) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I1—C3 | 2.104 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C1 | 1.225 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.354 (3) | C8—C13 | 1.392 (3) |
| N1—C8 | 1.420 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.394 (3) |
| N1—H1 | 0.8800 | C9—C10 | 1.388 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.505 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C7 | 1.395 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.388 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.399 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.387 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.388 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.390 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C12—C13 | 1.382 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.385 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C7 | 1.384 (3) | ||
| C1—N1—C8 | 126.37 (18) | C6—C7—C2 | 120.8 (2) |
| C1—N1—H1 | 116.8 | C6—C7—H7 | 119.6 |
| C8—N1—H1 | 116.8 | C2—C7—H7 | 119.6 |
| O1—C1—N1 | 124.4 (2) | C13—C8—C9 | 119.80 (19) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 121.64 (19) | C13—C8—N1 | 117.79 (19) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 113.98 (18) | C9—C8—N1 | 122.38 (19) |
| C7—C2—C3 | 118.70 (19) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.4 (2) |
| C7—C2—C1 | 119.60 (19) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.3 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.68 (18) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.3 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.61 (19) | C11—C10—C9 | 121.1 (2) |
| C4—C3—I1 | 117.07 (16) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.5 |
| C2—C3—I1 | 122.08 (15) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.7 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.3 (2) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.7 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.9 (2) | C12—C13—C8 | 120.1 (2) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C8—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C8—N1—C1—O1 | −0.6 (4) | C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.6 (3) |
| C8—N1—C1—C2 | 179.69 (19) | C3—C2—C7—C6 | −1.2 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—C7 | −127.2 (2) | C1—C2—C7—C6 | 177.16 (19) |
| N1—C1—C2—C7 | 52.6 (3) | C1—N1—C8—C13 | −152.1 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 51.1 (3) | C1—N1—C8—C9 | 29.9 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −129.1 (2) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −0.7 (3) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | 0.9 (3) | N1—C8—C9—C10 | 177.34 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −177.47 (19) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.1 (3) |
| C7—C2—C3—I1 | −173.28 (15) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.3 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—I1 | 8.4 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.4 (3) |
| I1—C3—C4—C5 | 174.51 (16) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 0.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.7 (3) | N1—C8—C13—C12 | −177.3 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.4 (3) |
2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (II) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 is the centroid of the C8–C13 benzene ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.88 | 2.15 | 2.942 (2) | 150 |
| C3—I1···Cg2ii | 2.10 (1) | 3.83 (1) | 5.816 (2) | 156 (1) |
| C6—H6···Cg2iii | 0.95 | 2.81 | 3.627 (2) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) −x, −y, −z+1; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Visvesvaraya Technological University grant . National Research Foundation grants 91995 and 96807. Durban University of Technology grant .
References
- Abdou, I. M., Saleh, A. M. & Zohdi, H. F. (2004). Molecules, 9, 109–116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2014). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Garden, S. J., Glidewell, C., Low, J. N., Skakle, J. M. S. & Wardell, J. L. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, o450–o451. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.-Y., Wan, Q.-Q., Yang, S., Song, B.-A., Bhadury, P. S., Jin, L.-H., Yan, K., Liu, F., Chen, Z. & Xue, W. (2008). J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 998–1001. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jursic, B. S. & Zdravkovski, Z. (1993). Synth. Commun. 23, 2761–2770.
- Kalgutkar, A. S., Marnett, A. B., Crews, B. C., Remmel, R. P. & Marnett, L. J. (2000). J. Med. Chem. 43, 2860–2870. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kavala, V., Wang, C.-C., Barange, D. K., Kuo, C.-W., Lei, P.-M. & Yao, C.-F. (2012). J. Org. Chem. 77, 5022–5029. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mao, W., Ning, M., Liu, Z., Zhu, Q., Leng, Y. & Zhang, A. (2012). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20, 2982–2991. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nakata, K., Tateno, T. & Sakurai, K. (1976). Mem. Osaka Kyoiku Univ. Ser. 3, 25, 61.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Nayak, S. K., Reddy, M. K., Chopra, D. & Guru Row, T. N. (2012). CrystEngComm, 14, 200–210.
- Pradidphol, N., Kongkathip, N., Sittikul, P., Boonyalai, N. & Kongkathip, B. (2012). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 49, 253–270. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ragavan, R. V., Vijayakumar, V. & Kumari, N. S. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 1173–1180. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Starmer, G., McLean, S. & Thomas, J. (1971). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 19, 20–28. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Suchetan, P. A., Suresha, E., Naveen, S. & Lokanath, N. K. (2016). Acta Cryst. E72, 819–823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wardell, J. L., Skakle, J. M. S., Low, J. N. & Glidewell, C. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, o634–o638. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018010162/sj5558IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report