The title Schiff base compound displays a trans configuration with respect to the C=N bond, with the two benzene rings being inclined to each other by 31.90 (12)°.
Keywords: crystal structure, Schiff base, Hirshfeld surface analysis, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The title Schiff base compound, C17H16N2O6, has an E configuration with respect to the C=N bond, with a dihedral angle between the two benzene rings of 31.90 (12)°. There is an intramolecular O—H⋯Onitro hydrogen bond present forming an S(6) ring motif. In the crystal, molecules are linked by pairs of O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming inversion dimers enclosing an R
2
2(4) ring motif. The dimers are linked about an inversion centre by pairs of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, which enclose R
2
2(22) loops, forming chains propagating along the [10 ] direction. Hirshfeld surface analysis and fingerprint plots show enrichment ratios for the H⋯H, O⋯H and C⋯H contacts, indicating a high propensity of such interactions in the crystal. Both the nitro group and the CH3–CH2–O– group are positionally disordered.
] direction. Hirshfeld surface analysis and fingerprint plots show enrichment ratios for the H⋯H, O⋯H and C⋯H contacts, indicating a high propensity of such interactions in the crystal. Both the nitro group and the CH3–CH2–O– group are positionally disordered.
Chemical context
Schiff bases are an important class of compounds in the medicinal and pharmaceutical fields. They play a role in the development of coordination chemistry as they readily form stable complexes with most transition metals. These complexes show interesting properties, for e.g. their ability to reversibly bind oxygen, catalytic activity in hydrogenation of olefins and transfer of an amino group, photochromic properties, and complexing ability towards toxic metals (Karthikeyan et al., 2006 ▸; Khattab, 2005 ▸; Küçükgüzel et al., 2006 ▸). Recently, hydrazone Schiff base compounds (Cao, 2009 ▸; Zhou & Yang, 2010 ▸; Zhang et al., 2009 ▸) derived from the reaction of aldehydes with hydrazines have been shown to possess excellent biological activities, such as anti-bacterial, anti-convulsant, and antitubercular (Bernhardt et al., 2005 ▸; Armstrong et al., 2003 ▸). Herein, we report on the synthesis and crystal structure of the title Schiff base title compound, (E)-4-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-5-nitrobenzylidene)amino]benzoate. The Hirshfeld surface analysis was performed in order to visualize, explore and quantify the intermolecular interactions in the crystal lattice of the title compound.
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of the title Schiff base compound is illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸. The molecule has a trans or E configuration with respect to the C10=N1 double bond. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 31.90 (12)°. The C10=N1 bond length of 1.267 (3) Å confirms the azomethine bond formation. There is an intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond present involving the adjacent hydroxyl and nitro substituents on the C11–C16 benzene ring, forming an S(6) ring motif (Fig. 1 ▸ and Table 1 ▸).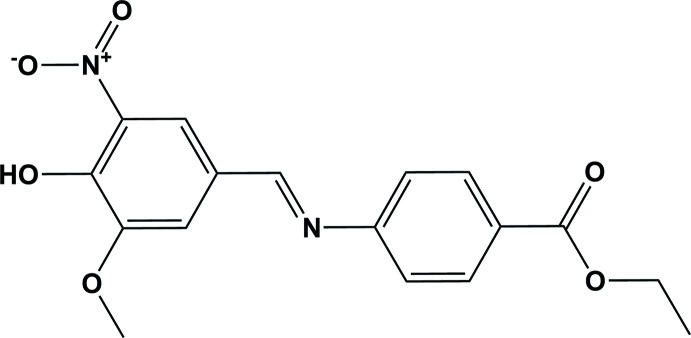
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond (Table 1 ▸) is shown as a dashed line. Only the major components of the disordered atoms (O3, O4, C1, C2 and O1) are shown.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H5A⋯O4 | 0.91 (4) | 1.73 (4) | 2.54 (2) | 146 (3) |
| O5—H5A⋯O4i | 0.91 (4) | 2.49 (4) | 3.23 (3) | 138 (3) |
| C12—H12⋯O2ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.471 (3) | 156 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, molecules are linked by pairs of O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming inversion dimers (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸). The dimers are linked by pairs of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, so forming chains propagating along [10 ]. Within the chains there are two ring motifs present, viz. R
2
2(4) and
]. Within the chains there are two ring motifs present, viz. R
2
2(4) and  (22), as illustrated in Fig. 2 ▸.
(22), as illustrated in Fig. 2 ▸.
Figure 2.
Crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the a axis. The O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (see Table 1 ▸) are shown as dashed lines. Only the major components of the disordered atoms (O3, O4, C1, C2 and O1) are shown.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.39, update May 2018; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for ethyl-4-(benzylideneamino)benzoate yielded five hits, while a search for the 2-methoxy-4-[(phenylimino)methyl]phenol skelton gave 25 hits. The most significant structure among these results is that of ethyl-4-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)amino]benzoate (APAMUB; Ling et al., 2016 ▸). The only difference between APAMUB and the title compound is the presence of a nitro group in the title compound. The two benzene rings in APAMUB are inclined to each other by 24.58 (8)° compared to 31.90 (12)° in the title compound. The crystal packing of the two compounds is significantly different. In APAMUB, molecules are linked by O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming chains along [010]. The chains are linked by C—H⋯π and offset π–π interactions, resulting in the formation of layers parallel to (10 ). In the title compound there are only O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds present; no C—H⋯π nor offset π–π interactions are present.
). In the title compound there are only O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds present; no C—H⋯π nor offset π–π interactions are present.
Hirshfeld surface analysis
Hirshfeld surfaces and their associated two-dimensional (2D) fingerprint plots (Soman et al., 2014 ▸) have been used to quantify the various intermolecular interactions in the title compound. The Hirshfeld surface of a molecule is mapped using the descriptor d norm, which encompasses two factors: one is d e, representing the distance of any surface point nearest to the internal atoms; another one is d i, representing the distance of the surface point nearest to the exterior atoms and also with the van der Waals radii of the atoms (Dalal et al., 2015 ▸). The Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over d norm (range of −0.502–1.427 a.u.) are displayed in Fig. 3 ▸. The dominant interactions between the oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) atoms can be observed in the Hirshfeld surface as the red areas in Fig. 4 ▸. Other visible spots in the Hirshfeld surfaces correspond to C⋯H and H⋯H contacts.
Figure 3.
Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over d norm for the title compound.
Figure 4.
2D fingerprint plots and relative contributions of the atom pairs to the Hirshfeld surface of the title compound.
The intermolecular interactions of the title compound, strongly evidenced by the 2D fingerprint plots from the Hirshfeld surface, are shown in Fig. 4 ▸. The H⋯H interactions (36.9%) are relatively high compared to the other bonding interactions of the total Hirshfeld surface area. However, it is lower than the H⋯H interactions (47.4%) in the crystal of ethyl-4-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)amino]benzoate (APAMUB; Ling et al., 2016 ▸). The percentage contributions of the other contacts in the title compound to the total Hirshfeld surface are as follows: O⋯H/H⋯O (29.8%), C⋯H/H⋯C (13.7%), N⋯H/H⋯N (2.8%), C⋯N/N⋯C (2.2%), C⋯C (4.6%), C⋯O/O⋯C (5.6%), O⋯N/N⋯O (1.0%). Such a visual analysis for intermolecular interactions is coherent with those indicated by the X-ray diffraction results, with the O⋯H/H⋯O (29.8%) interactions being the most significant after the H⋯H interactions (36.9%).
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound was synthesized by the reaction of a 1:1 molar ratio of ethyl-4-aminobenzoate (0.151 mg) and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde (0.134 mg) in an acetic acid solution (10 ml). The reaction mixture was refluxed for 6 h. The solid product formed during refluxing was filtered, washed with methanol and dried over anhydrous calcium chloride in a vacuum desiccator (yield 75%, m.p. 505 K). Brown block-like crystals of the title compound were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution in DMSO.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The hydroxyl H atom was located in a difference-Fourier map and freely refined. The C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined as riding: C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C-methyl) and 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms. Atoms O3 and O4 of the nitro group are disordered with a refined occupancy ratio of O3/O3′ = O4/O4′ = 0.64 (12):0.36 (12). Atoms O1, C2 and C1 of the ethyl benzoate group are also disordered with a refined occupancy ratio of O1/O1′ = C2/C2′ = C1/C1′ = 0.65 (3): 0.35 (3).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C17H16N2O6 |
| M r | 344.32 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 4.7565 (3), 11.3377 (9), 15.7590 (13) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 70.415 (4), 87.230 (4), 85.238 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 797.73 (11) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.11 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.15 × 0.10 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXIII CMOS |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.684, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 27199, 3642, 2484 |
| R int | 0.049 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.650 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.061, 0.176, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 3642 |
| No. of parameters | 279 |
| No. of restraints | 148 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.30, −0.22 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018009465/su5450sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018009465/su5450Isup3.hkl
CCDC reference: 1852926
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C17H16N2O6 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 344.32 | F(000) = 360 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.433 Mg m−3 |
| a = 4.7565 (3) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 11.3377 (9) Å | Cell parameters from 9528 reflections |
| c = 15.7590 (13) Å | θ = 3.6–27.4° |
| α = 70.415 (4)° | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 87.230 (4)° | T = 296 K |
| γ = 85.238 (4)° | Block, brown |
| V = 797.73 (11) Å3 | 0.15 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXIII CMOS diffractometer | 3642 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2484 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.049 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.684, Tmax = 0.746 | k = −14→14 |
| 27199 measured reflections | l = −20→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.061 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.176 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0654P)2 + 0.6845P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.005 |
| 3642 reflections | Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3 |
| 279 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 148 restraints | Extinction correction: (SHELXL2018; Sheldrick, 2015b), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.045 (8) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| O1 | −0.444 (3) | 0.8211 (8) | 0.6197 (8) | 0.067 (3) | 0.65 (3) |
| C1 | −0.573 (3) | 0.8426 (17) | 0.7583 (10) | 0.096 (4) | 0.65 (3) |
| H1A | −0.720338 | 0.841550 | 0.802321 | 0.144* | 0.65 (3) |
| H1B | −0.426110 | 0.779408 | 0.785013 | 0.144* | 0.65 (3) |
| H1C | −0.497179 | 0.923524 | 0.737445 | 0.144* | 0.65 (3) |
| C2 | −0.688 (2) | 0.8170 (10) | 0.6822 (7) | 0.0457 (19) | 0.65 (3) |
| H2A | −0.835749 | 0.880321 | 0.653798 | 0.055* | 0.65 (3) |
| H2B | −0.764188 | 0.735211 | 0.701695 | 0.055* | 0.65 (3) |
| O1' | −0.490 (3) | 0.8195 (11) | 0.6094 (9) | 0.031 (2) | 0.35 (3) |
| C1' | −0.563 (4) | 0.864 (2) | 0.7540 (12) | 0.055 (4) | 0.35 (3) |
| H1A' | −0.678101 | 0.843919 | 0.808005 | 0.083* | 0.35 (3) |
| H1B' | −0.368939 | 0.840230 | 0.769233 | 0.083* | 0.35 (3) |
| H1C' | −0.585013 | 0.953027 | 0.722506 | 0.083* | 0.35 (3) |
| C2' | −0.652 (6) | 0.796 (3) | 0.6957 (15) | 0.064 (5) | 0.35 (3) |
| H2A' | −0.849502 | 0.819587 | 0.682424 | 0.077* | 0.35 (3) |
| H2B' | −0.633848 | 0.707008 | 0.729060 | 0.077* | 0.35 (3) |
| C3 | −0.3156 (5) | 0.7161 (2) | 0.61512 (16) | 0.0395 (6) | |
| C4 | −0.1133 (5) | 0.7365 (2) | 0.53762 (15) | 0.0360 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.0617 (6) | 0.6365 (3) | 0.53244 (17) | 0.0510 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.052119 | 0.558702 | 0.577298 | 0.061* | |
| C6 | 0.2516 (6) | 0.6501 (3) | 0.46139 (17) | 0.0517 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.368657 | 0.581337 | 0.458992 | 0.062* | |
| C7 | 0.2706 (5) | 0.7644 (2) | 0.39378 (15) | 0.0352 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.0976 (6) | 0.8652 (2) | 0.39978 (18) | 0.0502 (7) | |
| H8 | 0.110938 | 0.943380 | 0.355718 | 0.060* | |
| C9 | −0.0955 (6) | 0.8518 (2) | 0.47027 (18) | 0.0475 (7) | |
| H9 | −0.213650 | 0.920337 | 0.472518 | 0.057* | |
| C10 | 0.5352 (5) | 0.6934 (2) | 0.29175 (15) | 0.0375 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.443589 | 0.619824 | 0.316787 | 0.045* | |
| C11 | 0.7498 (4) | 0.6990 (2) | 0.22091 (14) | 0.0338 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.8139 (5) | 0.5934 (2) | 0.19733 (15) | 0.0364 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.719860 | 0.521090 | 0.225004 | 0.044* | |
| C13 | 1.0217 (5) | 0.5963 (2) | 0.13136 (15) | 0.0360 (5) | |
| C14 | 1.1643 (5) | 0.7032 (2) | 0.08737 (15) | 0.0355 (5) | |
| C15 | 1.0965 (5) | 0.8105 (2) | 0.11319 (14) | 0.0342 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.8937 (5) | 0.8077 (2) | 0.17850 (15) | 0.0353 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.850675 | 0.878663 | 0.194993 | 0.042* | |
| C17 | 1.2144 (6) | 1.0171 (3) | 0.09638 (19) | 0.0529 (7) | |
| H17A | 1.023098 | 1.052175 | 0.086809 | 0.079* | |
| H17B | 1.340280 | 1.078339 | 0.061842 | 0.079* | |
| H17C | 1.255566 | 0.993340 | 0.159176 | 0.079* | |
| N1 | 0.4682 (4) | 0.78390 (19) | 0.32058 (13) | 0.0379 (5) | |
| N2 | 1.0868 (5) | 0.4819 (2) | 0.11024 (15) | 0.0501 (6) | |
| O2 | −0.3425 (5) | 0.61540 (19) | 0.67179 (14) | 0.0630 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.931 (7) | 0.396 (2) | 0.138 (2) | 0.065 (4) | 0.64 (12) |
| O4 | 1.297 (6) | 0.4818 (19) | 0.061 (2) | 0.068 (4) | 0.64 (12) |
| O3' | 0.979 (12) | 0.387 (3) | 0.157 (4) | 0.063 (7) | 0.36 (12) |
| O4' | 1.259 (8) | 0.475 (3) | 0.050 (2) | 0.062 (5) | 0.36 (12) |
| O5 | 1.3628 (4) | 0.71443 (18) | 0.02210 (12) | 0.0485 (5) | |
| H5A | 1.380 (7) | 0.637 (3) | 0.016 (2) | 0.066 (10)* | |
| O6 | 1.2501 (4) | 0.90927 (16) | 0.06865 (12) | 0.0452 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.079 (5) | 0.058 (3) | 0.074 (5) | −0.024 (3) | 0.050 (4) | −0.036 (3) |
| C1 | 0.125 (8) | 0.095 (7) | 0.088 (7) | −0.070 (6) | 0.036 (6) | −0.048 (5) |
| C2 | 0.049 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.049 (3) | −0.007 (2) | 0.021 (3) | −0.014 (2) |
| O1' | 0.031 (4) | 0.026 (4) | 0.030 (4) | 0.000 (3) | 0.007 (3) | −0.005 (3) |
| C1' | 0.064 (7) | 0.066 (8) | 0.044 (7) | −0.001 (7) | 0.024 (6) | −0.034 (5) |
| C2' | 0.072 (8) | 0.061 (7) | 0.061 (7) | −0.009 (6) | 0.037 (6) | −0.027 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0415 (13) | 0.0415 (13) | 0.0378 (13) | −0.0099 (10) | 0.0089 (10) | −0.0160 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0380 (12) | 0.0384 (12) | 0.0344 (12) | −0.0077 (9) | 0.0082 (10) | −0.0158 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0599 (17) | 0.0441 (14) | 0.0375 (13) | 0.0080 (12) | 0.0107 (12) | −0.0027 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0563 (16) | 0.0460 (14) | 0.0403 (14) | 0.0194 (12) | 0.0108 (12) | −0.0047 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0434 (13) | 0.0326 (11) | −0.0037 (9) | 0.0058 (9) | −0.0143 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0608 (17) | 0.0346 (12) | 0.0506 (15) | −0.0049 (11) | 0.0260 (13) | −0.0116 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0523 (15) | 0.0356 (12) | 0.0531 (15) | −0.0022 (11) | 0.0217 (12) | −0.0160 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0329 (12) | 0.0426 (13) | 0.0349 (12) | −0.0024 (9) | 0.0080 (9) | −0.0114 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0287 (11) | 0.0413 (12) | 0.0293 (11) | 0.0005 (9) | 0.0045 (9) | −0.0101 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0362 (12) | 0.0373 (12) | 0.0319 (11) | −0.0038 (9) | 0.0089 (9) | −0.0075 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0390 (12) | 0.0364 (12) | 0.0322 (11) | −0.0003 (9) | 0.0070 (9) | −0.0123 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0310 (11) | 0.0443 (13) | 0.0298 (11) | −0.0031 (9) | 0.0070 (9) | −0.0116 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0328 (11) | 0.0396 (12) | 0.0293 (11) | −0.0060 (9) | 0.0023 (9) | −0.0100 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0335 (11) | 0.0405 (12) | 0.0330 (11) | −0.0009 (9) | 0.0020 (9) | −0.0146 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0652 (18) | 0.0472 (15) | 0.0487 (15) | −0.0164 (13) | 0.0091 (13) | −0.0175 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0330 (10) | 0.0450 (11) | 0.0355 (10) | −0.0024 (8) | 0.0090 (8) | −0.0144 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0594 (14) | 0.0436 (12) | 0.0463 (13) | −0.0056 (10) | 0.0210 (11) | −0.0163 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0736 (14) | 0.0533 (12) | 0.0516 (12) | −0.0069 (10) | 0.0272 (10) | −0.0067 (9) |
| O3 | 0.091 (8) | 0.052 (4) | 0.058 (7) | −0.029 (5) | 0.032 (6) | −0.024 (4) |
| O4 | 0.070 (6) | 0.050 (4) | 0.090 (8) | −0.009 (4) | 0.042 (6) | −0.038 (4) |
| O3' | 0.087 (12) | 0.043 (5) | 0.062 (13) | −0.018 (6) | 0.034 (10) | −0.022 (6) |
| O4' | 0.076 (9) | 0.066 (9) | 0.054 (9) | −0.022 (6) | 0.038 (6) | −0.036 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0520 (11) | 0.0497 (11) | 0.0465 (10) | −0.0119 (8) | 0.0250 (8) | −0.0211 (9) |
| O6 | 0.0486 (10) | 0.0433 (9) | 0.0445 (10) | −0.0126 (8) | 0.0152 (8) | −0.0156 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C3 | 1.314 (8) | C8—C9 | 1.383 (3) |
| O1—C2 | 1.481 (8) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.464 (12) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C10—N1 | 1.267 (3) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C10—C11 | 1.465 (3) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C11—C12 | 1.375 (3) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C11—C16 | 1.406 (3) |
| O1'—C3 | 1.359 (10) | C12—C13 | 1.394 (3) |
| O1'—C2' | 1.484 (13) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C1'—C2' | 1.476 (17) | C13—C14 | 1.392 (3) |
| C1'—H1A' | 0.9600 | C13—N2 | 1.450 (3) |
| C1'—H1B' | 0.9600 | C14—O5 | 1.343 (3) |
| C1'—H1C' | 0.9600 | C14—C15 | 1.415 (3) |
| C2'—H2A' | 0.9700 | C15—O6 | 1.357 (3) |
| C2'—H2B' | 0.9700 | C15—C16 | 1.370 (3) |
| C3—O2 | 1.203 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.485 (3) | C17—O6 | 1.425 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.373 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C9 | 1.386 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.380 (3) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | N2—O3' | 1.220 (13) |
| C6—C7 | 1.381 (3) | N2—O3 | 1.220 (9) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | N2—O4 | 1.239 (9) |
| C7—C8 | 1.378 (3) | N2—O4' | 1.239 (12) |
| C7—N1 | 1.422 (3) | O5—H5A | 0.91 (4) |
| C3—O1—C2 | 119.9 (8) | C7—C8—C9 | 121.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.5 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.5 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C8—C9—C4 | 120.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C8—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C4—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | N1—C10—C11 | 123.2 (2) |
| C1—C2—O1 | 104.4 (10) | N1—C10—H10 | 118.4 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 110.9 | C11—C10—H10 | 118.4 |
| O1—C2—H2A | 110.9 | C12—C11—C16 | 119.85 (19) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 110.9 | C12—C11—C10 | 118.3 (2) |
| O1—C2—H2B | 110.9 | C16—C11—C10 | 121.8 (2) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.9 | C11—C12—C13 | 119.1 (2) |
| C3—O1'—C2' | 108.6 (15) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.5 |
| C2'—C1'—H1A' | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12 | 120.5 |
| C2'—C1'—H1B' | 109.5 | C14—C13—C12 | 122.3 (2) |
| H1A'—C1'—H1B' | 109.5 | C14—C13—N2 | 120.63 (19) |
| C2'—C1'—H1C' | 109.5 | C12—C13—N2 | 117.1 (2) |
| H1A'—C1'—H1C' | 109.5 | O5—C14—C13 | 125.9 (2) |
| H1B'—C1'—H1C' | 109.5 | O5—C14—C15 | 116.3 (2) |
| C1'—C2'—O1' | 115.1 (16) | C13—C14—C15 | 117.70 (19) |
| C1'—C2'—H2A' | 108.5 | O6—C15—C16 | 125.9 (2) |
| O1'—C2'—H2A' | 108.5 | O6—C15—C14 | 113.86 (18) |
| C1'—C2'—H2B' | 108.5 | C16—C15—C14 | 120.2 (2) |
| O1'—C2'—H2B' | 108.5 | C15—C16—C11 | 120.9 (2) |
| H2A'—C2'—H2B' | 107.5 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| O2—C3—O1 | 123.4 (5) | C11—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| O2—C3—O1' | 123.2 (6) | O6—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O2—C3—C4 | 123.5 (2) | O6—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1—C3—C4 | 112.8 (5) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1'—C3—C4 | 112.8 (6) | O6—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 118.9 (2) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.4 (2) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C4—C3 | 122.8 (2) | C10—N1—C7 | 118.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.7 (2) | O3—N2—O4 | 125 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | O3'—N2—O4' | 119 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | O3'—N2—C13 | 118 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.0 (2) | O3—N2—C13 | 119.8 (14) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | O4—N2—C13 | 115.5 (13) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.5 | O4'—N2—C13 | 122.7 (19) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 118.3 (2) | C14—O5—H5A | 103 (2) |
| C8—C7—N1 | 118.7 (2) | C15—O6—C17 | 117.55 (18) |
| C6—C7—N1 | 123.0 (2) | ||
| C3—O1—C2—C1 | 102.5 (12) | C11—C12—C13—N2 | 178.6 (2) |
| C3—O1'—C2'—C1' | 106 (2) | C12—C13—C14—O5 | −178.7 (2) |
| C2—O1—C3—O2 | −16.7 (18) | N2—C13—C14—O5 | 1.8 (4) |
| C2—O1—C3—C4 | 168.9 (11) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.4 (4) |
| C2'—O1'—C3—O2 | 16.1 (18) | N2—C13—C14—C15 | −178.1 (2) |
| C2'—O1'—C3—C4 | −171.3 (13) | O5—C14—C15—O6 | −1.5 (3) |
| O2—C3—C4—C5 | −3.1 (4) | C13—C14—C15—O6 | 178.4 (2) |
| O1—C3—C4—C5 | 171.2 (8) | O5—C14—C15—C16 | 179.2 (2) |
| O1'—C3—C4—C5 | −175.7 (8) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.9 (3) |
| O2—C3—C4—C9 | 176.5 (3) | O6—C15—C16—C11 | −179.2 (2) |
| O1—C3—C4—C9 | −9.2 (9) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.0 (3) |
| O1'—C3—C4—C9 | 3.9 (8) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.5 (3) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | −0.2 (4) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | 179.1 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 179.4 (3) | C11—C10—N1—C7 | −175.8 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.0 (5) | C8—C7—N1—C10 | −149.9 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 1.0 (4) | C6—C7—N1—C10 | 32.9 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | 178.2 (3) | C14—C13—N2—O3' | 172 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −1.7 (4) | C12—C13—N2—O3' | −7 (4) |
| N1—C7—C8—C9 | −179.1 (2) | C14—C13—N2—O3 | −168 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C4 | 1.5 (4) | C12—C13—N2—O3 | 12 (2) |
| C5—C4—C9—C8 | −0.5 (4) | C14—C13—N2—O4 | 9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C9—C8 | 179.9 (3) | C12—C13—N2—O4 | −170 (2) |
| N1—C10—C11—C12 | 177.4 (2) | C14—C13—N2—O4' | −4 (3) |
| N1—C10—C11—C16 | −1.3 (4) | C12—C13—N2—O4' | 177 (3) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.0 (3) | C16—C15—O6—C17 | 5.0 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −178.7 (2) | C14—C15—O6—C17 | −174.3 (2) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.0 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H5A···O4 | 0.91 (4) | 1.73 (4) | 2.54 (2) | 146 (3) |
| O5—H5A···O4i | 0.91 (4) | 2.49 (4) | 3.23 (3) | 138 (3) |
| C12—H12···O2ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.471 (3) | 156 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Science and Engineering Research Board grant SB/FT/CS-058/2013 to K. Balasubramani and P. Sivajeyanthi.
References
- Armstrong, C. M., Bernhardt, P. V., Chin, P. & Richardson, D. R. (2003). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 1145–1156.
- Bernhardt, P. V., Chin, P., Sharpe, P. C., Wang, J. C. & Richardson, D. R. (2005). J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 10, 761–777. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2016). SAINT, APEX3, XPREP and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cao, G.-B. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dalal, J., Sinha, N., Yadav, H. & Kumar, B. (2015). RSC Adv. 5, 57735–57748.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, M. S., Prasad, D. J., Poojary, B., Bhat, K. S., Holla, B. S. & Kumari, N. S. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14, 7482–7489. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Khattab, S. N. (2005). Molecules, 10, 1218–1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Küçükgüzel, G., Kocatepe, A., De Clercq, E., Şahin, F. & Güllüce, M. (2006). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 41, 353–359. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ling, J., Kavuru, P., Wojtas, L. & Chadwick, K. (2016). Acta Cryst. E72, 951–954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Soman, R., Sujatha, S., De, S., Rojisha, V. C., Parameswaran, P., Varghese, B. & Arunkumar, C. (2014). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 2653–2662.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-J., Yin, L.-Z., Wang, D.-C., Deng, X.-M. & Liu, J.-B. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.-S. & Yang, T. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018009465/su5450sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018009465/su5450Isup3.hkl
CCDC reference: 1852926
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






