The 5-iodo- and 5-ethynyl-substituted dimethyl isophthalates show molecular frameworks with methyl carboxylate moieties being tilted or perfectly planar with respect to the benzene ring, respectively. Crystal structures feature a three- or two-dimensional supramolecular aggregation in the iodo and ethynyl derivatives, respectively, supported by C—H⋯I and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding as well as I⋯O and π–π interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, 5-substituted dimethyl isophthalates, I⋯O=C interaction, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯I hydrogen bonding, π–π stacking
Abstract
In dimethyl 5-iodoisophthalate, C10H9IO4, (I), the planes through the methyl carboxylate moieties are tilted with respect to the benzene ring, whereas the molecular framework of dimethyl 5-ethynylisophthalate, C12H10O4, (II), is perfectly planar. The crystal structure of (I) is stabilized by a three-dimensional supramolecular network comprising C—H⋯O=C hydrogen bonds, as well as I⋯O=C interactions. In the crystal of (II), the molecules are connected via C—Hethynyl⋯O=C hydrogen bonds to infinite strands. Moreover, π–π arene stacking interactions connect the molecular chains into two-dimensional supramolecular aggregates.
Chemical context
In recent years, the design of solid porous framework materials (MacGillivray, 2010 ▸; Furukawa et al., 2013 ▸; Eddaoudi et al., 2015 ▸) has become a very important topic in the field of supramolecular crystal engineering (Desiraju et al., 2011 ▸). Associated with it, so-called linker molecules featuring a geometrically rigid structure frequently being of linear, trigonal or tetrahedral shape and having carboxylic acid functions as terminal groups play a key role in building such systems (Lin et al., 2006 ▸; Hausdorf et al., 2009 ▸; Zheng et al., 2010 ▸). In the course of the synthesis of the respective linkers, the title compounds (I) and (II), both being 5-substituted dimethyl isophthalates, are much used intermediates. However, these compounds are not only synthetically significant but also show interesting structures in the crystalline state, as demonstrated herein.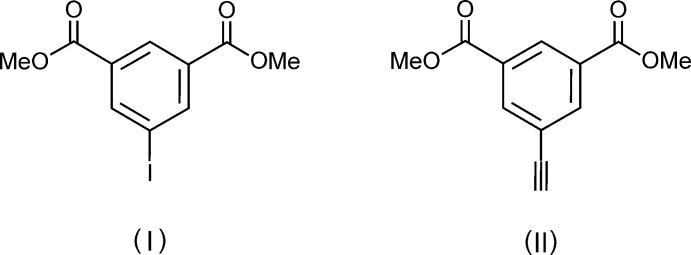
Structural commentary
The molecular structures of the title compounds, (I) and (II), are illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸ a and 1b, respectively. Taking into account experimental error, the bond distances within the isophthalate framework agree well with those found in the crystal structure of dimethyl isophthalate (Gallagher, 2012 ▸). Compound (I) crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Pna21 with one molecule in the asymmetric unit. The molecule adopts a twisted conformation with the mean planes defined by the methyl carboxylate moieties inclined at angles of 12.6 (2) and 6.0 (2)° with respect to the plane of the benzene ring. Compound (II) crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Pnma with the molecule located on a symmetry plane, i.e. the molecule is perfectly planar. However, the molecule adopts approximate C 2v symmetry with the atoms C2, C5, C11 and C12 lying on a non-crystallographic bisecting symmetry plane.
Figure 1.
Perspective view of the molecular structures of the title compounds, (a) (I) and (b) (II), with atom labelling. Anisotropic displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level.
Supramolecular features
Infinite strands with the molecules connected via I⋯O=C interactions [I1⋯O3—C9(x −  , y +
, y +  , z − 1; D⋯A = 3.129 (2) (Desiraju & Steiner, 1999 ▸) (Politzer et al. 2007 ▸; Desiraju et al., 2013 ▸), represent the basic supramolecular aggregates of the crystal structure of (I). Association of the molecular strands by C—H⋯O=C type hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) (Desiraju & Steiner, 1999 ▸) and π–π stacking interactions [centroid–centroid distance = 4.149 (2) Å] (Tiekink & Zukerman-Schpector, 2012 ▸) generate a three-dimensional supramolecular network (Fig. 2 ▸). In the crystal structure of (II), the molecules are connected via Cethynyl—H⋯O=C bonds (Table 2 ▸) into infinite strands, which are further arranged into molecular sheets that extend parallel to the ac plane (Fig. 3 ▸). Furthermore, π–π arene interactions with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.566 (1) Å and a slippage of 1.325 Å between the interacting aromatic rings stabilize the crystal structure along the stacking axis of the molecular sheets.
, z − 1; D⋯A = 3.129 (2) (Desiraju & Steiner, 1999 ▸) (Politzer et al. 2007 ▸; Desiraju et al., 2013 ▸), represent the basic supramolecular aggregates of the crystal structure of (I). Association of the molecular strands by C—H⋯O=C type hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) (Desiraju & Steiner, 1999 ▸) and π–π stacking interactions [centroid–centroid distance = 4.149 (2) Å] (Tiekink & Zukerman-Schpector, 2012 ▸) generate a three-dimensional supramolecular network (Fig. 2 ▸). In the crystal structure of (II), the molecules are connected via Cethynyl—H⋯O=C bonds (Table 2 ▸) into infinite strands, which are further arranged into molecular sheets that extend parallel to the ac plane (Fig. 3 ▸). Furthermore, π–π arene interactions with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.566 (1) Å and a slippage of 1.325 Å between the interacting aromatic rings stabilize the crystal structure along the stacking axis of the molecular sheets.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8—H8A⋯O1i | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.257 (4) | 129 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 2.
Packing diagram of compound (I) viewed down the a axis. Dashed lines represent hydrogen-bonding interactions.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12—H12⋯O1i | 0.94 | 2.29 | 3.223 (1) | 172 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 3.
Packing excerpt of compound (II) viewed down the b axis. Dashed lines represent hydrogen-bonding interactions.
Database survey
The search in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.38, update May 2017; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for meta-substituted derivatives of dimethyl isophthalate excluding their metal complexes, solvates and salts gave 18 hits. None of these compounds represents a 5-halogen- and 5-alkynyl-substituted dimethyl isophalate. The parent compound, dimethyl isophthalate (CSD refcode GOHRUS; Gallagher & Mocilac, 2012 ▸) crystallizes in space group Pna21 with two conformationally similar molecules in the asymmetric unit. The independent molecules participate in different ways in non-covalent bonding. One of them is involved in the formation of linear strands with the molecules connected by C—Haryl⋯O=C bonds. Interstrand association is accomplished by π–π arene stacking. Molecules related by the twofold screw axis are also linked via C—Haryl⋯O=C bonding to form helical strands. In addition, these strands are stabilized by π–π stacking forces.
Synthesis and crystallization
Compounds (I) and (II) were synthesized following literature procedures. This involves a diazotization/iodination reaction of dimethyl 5-aminoisophthalate (Mazik & König, 2006 ▸) to give compound (I). Subsequent reaction of (I) with 2-methylbut-3-yne-2-ol (MEBYNOL) using a Pd-catalysed Sonogashira coupling procedure (Doucet & Hierso, 2007 ▸; Rafael & Carmen, 2007 ▸) yielded the corresponding blocked acetylenic diester as an intermediate (Hauptvogel et al., 2011 ▸). Removal of the 2-hydroxypropyl blocking group was undertaken using sodium hydride in toluene and quenching with water to result in the title compound (II) (Havens & Hergenrother, 1985 ▸; Hauptvogel et al., 2011 ▸).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. Hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model with C—H distances of 0.94–0.98 Å and U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C-methyl) or U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C10H9IO4 | C12H10O4 |
| M r | 320.07 | 218.20 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P n a21 | Orthorhombic, P n m a |
| Temperature (K) | 143 | 223 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 7.7483 (2), 19.3451 (6), 7.2338 (2) | 10.1206 (5), 6.6219 (4), 16.3658 (8) |
| V (Å3) | 1084.29 (5) | 1096.80 (10) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 2.94 | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.30 × 0.22 × 0.15 | 0.54 × 0.12 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD area detector | Bruker APEXII CCD area detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.472, 0.666 | 0.948, 0.990 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 22794, 2909, 2806 | 12397, 1292, 932 |
| R int | 0.026 | 0.033 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.684 | 0.638 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.015, 0.038, 1.05 | 0.039, 0.110, 1.03 |
| No. of reflections | 2909 | 1292 |
| No. of parameters | 139 | 87 |
| No. of restraints | 1 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.47, −0.44 | 0.17, −0.18 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 1255 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) | – |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.004 (8) | – |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732Isup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732IIsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
1,3-Dimethyl 1-iodocyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (I). Crystal data
| C10H9IO4 | Dx = 1.961 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 320.07 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pna21 | Cell parameters from 5755 reflections |
| a = 7.7483 (2) Å | θ = 3.0–33.7° |
| b = 19.3451 (6) Å | µ = 2.94 mm−1 |
| c = 7.2338 (2) Å | T = 143 K |
| V = 1084.29 (5) Å3 | Irregular, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.30 × 0.22 × 0.15 mm |
| F(000) = 616 |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-iodocyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (I). Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD area detector diffractometer | 2806 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.026 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a) | θmax = 29.1°, θmin = 1.1° |
| Tmin = 0.472, Tmax = 0.666 | h = −10→10 |
| 22794 measured reflections | k = −26→26 |
| 2909 independent reflections | l = −9→9 |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-iodocyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (I). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.015 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.019P)2 + 0.3689P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.038 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.47 e Å−3 |
| 2909 reflections | Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3 |
| 139 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 1255 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: −0.004 (8) |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-iodocyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (I). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component twin. |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-iodocyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (I). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | 0.81504 (2) | 0.66115 (2) | 0.83115 (6) | 0.02386 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.5202 (3) | 0.54751 (11) | 0.1864 (3) | 0.0327 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.3831 (3) | 0.63417 (11) | 0.0411 (3) | 0.0260 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.4971 (3) | 0.87789 (10) | 0.2029 (3) | 0.0281 (5) | |
| O4 | 0.6557 (3) | 0.89701 (11) | 0.4576 (3) | 0.0282 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.5514 (4) | 0.66267 (12) | 0.2993 (4) | 0.0190 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.5347 (3) | 0.73272 (14) | 0.2585 (4) | 0.0198 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.479369 | 0.746965 | 0.147720 | 0.024* | |
| C3 | 0.5994 (3) | 0.78152 (14) | 0.3805 (3) | 0.0194 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.6796 (3) | 0.76086 (15) | 0.5445 (4) | 0.0206 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.723931 | 0.794439 | 0.627770 | 0.025* | |
| C5 | 0.6940 (3) | 0.69088 (15) | 0.5850 (4) | 0.0207 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.6295 (4) | 0.64128 (15) | 0.4637 (4) | 0.0209 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.638485 | 0.593502 | 0.492478 | 0.025* | |
| C7 | 0.4856 (4) | 0.60819 (14) | 0.1721 (4) | 0.0223 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.3221 (5) | 0.58545 (18) | −0.0951 (5) | 0.0330 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.418544 | 0.571014 | −0.173823 | 0.049* | |
| H8B | 0.232932 | 0.607288 | −0.171341 | 0.049* | |
| H8C | 0.273509 | 0.544937 | −0.032593 | 0.049* | |
| C9 | 0.5768 (3) | 0.85636 (11) | 0.3323 (8) | 0.0214 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.6363 (5) | 0.97101 (16) | 0.4293 (5) | 0.0338 (7) | |
| H10A | 0.688803 | 0.984036 | 0.311034 | 0.051* | |
| H10B | 0.693716 | 0.995947 | 0.529896 | 0.051* | |
| H10C | 0.513396 | 0.982919 | 0.427800 | 0.051* |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-iodocyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (I). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.02804 (8) | 0.02336 (8) | 0.02019 (8) | −0.00006 (6) | −0.00121 (12) | 0.00381 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0500 (14) | 0.0174 (10) | 0.0308 (12) | 0.0032 (9) | −0.0060 (10) | −0.0006 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0300 (11) | 0.0187 (10) | 0.0293 (11) | 0.0017 (8) | −0.0066 (9) | −0.0048 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0347 (12) | 0.0194 (10) | 0.0301 (11) | 0.0027 (9) | −0.0082 (9) | 0.0019 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0382 (12) | 0.0165 (9) | 0.0299 (11) | −0.0011 (8) | −0.0073 (9) | −0.0004 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0216 (11) | 0.0183 (10) | 0.017 (2) | 0.0009 (9) | 0.0020 (10) | −0.0004 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0196 (12) | 0.0190 (12) | 0.0209 (11) | 0.0022 (10) | 0.0042 (10) | 0.0019 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0191 (11) | 0.0183 (11) | 0.0208 (13) | 0.0013 (9) | 0.0025 (9) | 0.0012 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0217 (13) | 0.0191 (13) | 0.0211 (12) | −0.0014 (10) | 0.0017 (10) | −0.0012 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0224 (13) | 0.0217 (13) | 0.0181 (12) | 0.0022 (10) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0017 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0242 (13) | 0.0183 (12) | 0.0201 (12) | 0.0016 (10) | 0.0024 (11) | 0.0013 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0256 (13) | 0.0197 (12) | 0.0217 (13) | −0.0011 (10) | 0.0035 (11) | −0.0011 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0409 (19) | 0.0257 (15) | 0.0323 (15) | 0.0005 (13) | −0.0088 (13) | −0.0075 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0218 (10) | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0250 (10) | −0.0001 (8) | 0.0096 (18) | −0.002 (2) |
| C10 | 0.0453 (19) | 0.0174 (14) | 0.0387 (19) | 0.0014 (13) | −0.0064 (15) | −0.0021 (12) |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-iodocyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (I). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I1—C5 | 2.093 (3) | C3—C4 | 1.398 (4) |
| O1—C7 | 1.209 (3) | C3—C9 | 1.499 (4) |
| O2—C7 | 1.335 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.390 (4) |
| O2—C8 | 1.443 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| O3—C9 | 1.196 (5) | C5—C6 | 1.393 (4) |
| O4—C9 | 1.347 (5) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| O4—C10 | 1.454 (4) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.393 (3) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C6 | 1.398 (4) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| C1—C7 | 1.489 (4) | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.386 (4) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| C7—O2—C8 | 115.7 (2) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.4 |
| C9—O4—C10 | 115.7 (3) | O1—C7—O2 | 124.0 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.5 (3) | O1—C7—C1 | 124.0 (3) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 121.8 (3) | O2—C7—C1 | 112.1 (2) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 117.7 (2) | O2—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.7 (3) | O2—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.2 | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.2 | O2—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.4 (3) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C9 | 117.9 (3) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C9 | 121.7 (3) | O3—C9—O4 | 123.9 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.5 (3) | O3—C9—C3 | 125.3 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.2 | O4—C9—C3 | 110.7 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.2 | O4—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.6 (3) | O4—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—I1 | 118.9 (2) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—I1 | 120.5 (2) | O4—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.2 (3) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.4 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.3 (4) | C8—O2—C7—O1 | −4.1 (4) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −179.4 (2) | C8—O2—C7—C1 | 176.3 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.6 (4) | C2—C1—C7—O1 | 168.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C9 | −179.3 (3) | C6—C1—C7—O1 | −12.7 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.1 (4) | C2—C1—C7—O2 | −12.5 (4) |
| C9—C3—C4—C5 | 178.5 (3) | C6—C1—C7—O2 | 166.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.1 (4) | C10—O4—C9—O3 | 1.1 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—I1 | 179.86 (19) | C10—O4—C9—C3 | −177.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.7 (4) | C2—C3—C9—O3 | 5.3 (5) |
| I1—C5—C6—C1 | −179.1 (2) | C4—C3—C9—O3 | −173.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.3 (4) | C2—C3—C9—O4 | −176.1 (3) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 179.4 (2) | C4—C3—C9—O4 | 5.3 (4) |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-iodocyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (I). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C8—H8A···O1i | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.257 (4) | 129 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+1, z−1/2.
1,3-Dimethyl 1-ethynylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (II). Crystal data
| C12H10O4 | Dx = 1.321 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 218.20 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pnma | Cell parameters from 2950 reflections |
| a = 10.1206 (5) Å | θ = 2.4–23.1° |
| b = 6.6219 (4) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 16.3658 (8) Å | T = 223 K |
| V = 1096.80 (10) Å3 | Column, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.54 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| F(000) = 456 |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-ethynylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (II). Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD area detector diffractometer | 932 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.033 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a) | θmax = 27.0°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Tmin = 0.948, Tmax = 0.990 | h = −12→12 |
| 12397 measured reflections | k = −8→5 |
| 1292 independent reflections | l = −20→19 |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-ethynylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (II). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.110 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0486P)2 + 0.2932P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1292 reflections | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 87 parameters | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-ethynylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (II). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-ethynylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (II). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| O1 | 1.25864 (13) | 0.2500 | 0.40733 (10) | 0.0552 (4) | |
| O2 | 1.08848 (14) | 0.2500 | 0.32081 (9) | 0.0519 (4) | |
| O3 | 1.15356 (16) | 0.2500 | 0.70802 (10) | 0.0759 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.94247 (15) | 0.2500 | 0.74402 (9) | 0.0617 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.98919 (18) | 0.2500 | 0.60451 (11) | 0.0339 (4) | |
| C2 | 1.08100 (18) | 0.2500 | 0.54143 (12) | 0.0350 (4) | |
| H2 | 1.1718 | 0.2500 | 0.5536 | 0.042* | |
| C3 | 1.03958 (18) | 0.2500 | 0.46063 (12) | 0.0339 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.90505 (19) | 0.2500 | 0.44325 (12) | 0.0361 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.8767 | 0.2500 | 0.3886 | 0.043* | |
| C5 | 0.81192 (17) | 0.2500 | 0.50582 (12) | 0.0348 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.85496 (18) | 0.2500 | 0.58682 (12) | 0.0340 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.7929 | 0.2500 | 0.6296 | 0.041* | |
| C7 | 1.0392 (2) | 0.2500 | 0.68995 (13) | 0.0428 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.9818 (3) | 0.2500 | 0.82935 (14) | 0.0791 (9) | |
| H8A | 1.0203 | 0.1202 | 0.8431 | 0.119* | 0.5 |
| H8B | 0.9050 | 0.2740 | 0.8634 | 0.119* | 0.5 |
| H8C | 1.0465 | 0.3558 | 0.8385 | 0.119* | 0.5 |
| C9 | 1.1418 | 0.2500 | 0.3949 | 0.039 | |
| C10 | 1.1813 | 0.2500 | 0.2530 | 0.067 | |
| H10A | 1.1353 | 0.2149 | 0.2030 | 0.101* | 0.5 |
| H10B | 1.2505 | 0.1519 | 0.2633 | 0.101* | 0.5 |
| H10C | 1.2202 | 0.3832 | 0.2474 | 0.101* | 0.5 |
| C11 | 0.67260 (19) | 0.2500 | 0.48649 (12) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.5604 (2) | 0.2500 | 0.47022 (14) | 0.0532 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.4700 | 0.2500 | 0.4571 | 0.064* |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-ethynylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (II). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0293 (8) | 0.0828 (11) | 0.0536 (10) | 0.000 | 0.0049 (7) | 0.000 |
| O2 | 0.0409 (9) | 0.0783 (11) | 0.0364 (8) | 0.000 | 0.0066 (7) | 0.000 |
| O3 | 0.0329 (9) | 0.1475 (18) | 0.0473 (10) | 0.000 | −0.0079 (8) | 0.000 |
| O4 | 0.0362 (9) | 0.1153 (14) | 0.0336 (8) | 0.000 | −0.0026 (7) | 0.000 |
| C1 | 0.0294 (10) | 0.0371 (10) | 0.0352 (11) | 0.000 | −0.0006 (8) | 0.000 |
| C2 | 0.0257 (9) | 0.0385 (10) | 0.0408 (11) | 0.000 | −0.0029 (8) | 0.000 |
| C3 | 0.0295 (10) | 0.0338 (9) | 0.0385 (11) | 0.000 | 0.0023 (8) | 0.000 |
| C4 | 0.0343 (11) | 0.0404 (10) | 0.0334 (10) | 0.000 | −0.0020 (9) | 0.000 |
| C5 | 0.0275 (9) | 0.0379 (10) | 0.0389 (11) | 0.000 | −0.0002 (8) | 0.000 |
| C6 | 0.0276 (9) | 0.0398 (10) | 0.0347 (11) | 0.000 | 0.0011 (8) | 0.000 |
| C7 | 0.0299 (11) | 0.0568 (12) | 0.0416 (12) | 0.000 | −0.0013 (9) | 0.000 |
| C8 | 0.0550 (16) | 0.151 (3) | 0.0315 (13) | 0.000 | −0.0049 (12) | 0.000 |
| C9 | 0.034 | 0.043 | 0.039 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 |
| C10 | 0.063 | 0.098 | 0.041 | 0.000 | 0.018 | 0.000 |
| C11 | 0.0341 (11) | 0.0558 (12) | 0.0319 (10) | 0.000 | 0.0003 (9) | 0.000 |
| C12 | 0.0340 (12) | 0.0849 (17) | 0.0409 (13) | 0.000 | −0.0041 (10) | 0.000 |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-ethynylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (II). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C9 | 1.1998 (14) | C4—C5 | 1.392 (3) |
| O2—C9 | 1.3272 (15) | C4—H4 | 0.9400 |
| O2—C10 | 1.4544 (14) | C5—C6 | 1.395 (3) |
| O3—C7 | 1.195 (3) | C5—C11 | 1.445 (3) |
| O4—C7 | 1.319 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9400 |
| O4—C8 | 1.452 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.389 (3) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.389 (3) | C8—H8C | 0.9700 |
| C1—C7 | 1.487 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.387 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9400 | C10—H10C | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.391 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.166 (3) |
| C3—C9 | 1.4925 (18) | C12—H12 | 0.9400 |
| C9—O2—C10 | 115.75 (10) | O3—C7—O4 | 123.6 (2) |
| C7—O4—C8 | 116.19 (18) | O3—C7—C1 | 124.21 (19) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.96 (18) | O4—C7—C1 | 112.23 (17) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 118.13 (17) | O4—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 121.91 (17) | O4—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.42 (17) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.8 | O4—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.8 | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.39 (18) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C9 | 118.53 (15) | O1—C9—O2 | 123.76 (10) |
| C4—C3—C9 | 122.09 (16) | O1—C9—C3 | 124.12 (11) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.83 (18) | O2—C9—C3 | 112.12 (9) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.6 | O2—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.6 | O2—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.18 (17) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C11 | 119.98 (18) | O2—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C11 | 120.84 (17) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.21 (17) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.9 | C12—C11—C5 | 179.5 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.9 | C11—C12—H12 | 180.0 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.000 (1) | C8—O4—C7—O3 | 0.000 (1) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | 180.000 (1) | C8—O4—C7—C1 | 180.000 (1) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.000 (1) | C2—C1—C7—O3 | 0.000 (1) |
| C1—C2—C3—C9 | 180.000 (1) | C6—C1—C7—O3 | 180.000 (1) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.000 (1) | C2—C1—C7—O4 | 180.000 (1) |
| C9—C3—C4—C5 | 180.000 (1) | C6—C1—C7—O4 | 0.000 (1) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.000 (1) | C10—O2—C9—O1 | 0.000 (1) |
| C3—C4—C5—C11 | 180.000 (1) | C10—O2—C9—C3 | 180.000 (1) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.000 (1) | C2—C3—C9—O1 | 0.000 (1) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 180.000 (1) | C4—C3—C9—O1 | 180.000 (1) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.000 (1) | C2—C3—C9—O2 | 180.000 (1) |
| C11—C5—C6—C1 | 180.000 (1) | C4—C3—C9—O2 | 0.000 (1) |
1,3-Dimethyl 1-ethynylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,3-dicarboxylate (II). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C12—H12···O1i | 0.94 | 2.29 | 3.223 (1) | 172 |
Symmetry code: (i) x−1, y, z.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft grant DFG Priority Program 1362.
References
- Bruker (2014). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Desiraju, G. R., Ho, P. S., Kloo, L., Legon, A. C., Marquardt, R., Metrangolo, P., Politzer, P., Resnati, G. & Rissanen, K. (2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 85, 1711–1713.
- Desiraju, G. R. & Steiner, T. (1999). In The Weak Hydrogen Bond. Oxford University Press.
- Desiraju, G. R., Vittal, J. J. & Ramanan, A. (2011). Crystal Engineering. Singapore: World Scientific Publications.
- Doucet, H. & Hierso, J. C. (2007). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 834–871. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Eddaoudi, M., Sava, D. F., Eubank, J. F., Adil, K. & Guillerm, V. (2015). Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 228–249. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Furukawa, H., Cordova, K. E., O’Keeffe, M. & Yaghi, O. M. (2013). Science, 341, 1230444. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, C. F. & Mocilac, P. (2012). CSD Communication (Refcode GOHRUS). CCDC, Cambridge, England.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hauptvogel, I. M., Seichter, W. & Weber, E. (2011). Supramol. Chem. 23, 398–406.
- Hausdorf, S., Seichter, W., Weber, E. & Mertens, F. O. R. L. (2009). Dalton Trans. pp. 1107–1113. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Havens, S. J. & Hergenrother, P. M. (1985). J. Org. Chem. 50, 1863–1865.
- Lin, X., Jia, J., Zhao, X., Thomas, K. M., Blake, A. J., Walker, G. S., Champness, N. R., Hubberstey, P. & Schröder, M. (2006). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 7358–7364. [DOI] [PubMed]
- MacGillivray, L. R. (2010). Metal-Organic Frameworks. Hoboken: Wiley.
- Mazik, M. & König, A. (2006). J. Org. Chem. 71, 7854–7857. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P., Lane, P., Concha, M. C., Ma, Y. & Murray, J. S. (2007). J. Mol. Model. 13, 305–311. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rafael, C. & Carmen, N. (2007). Chem. Rev. B107, 874–922.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008a). SADABS. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008b). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Tiekink, E. R. T. & Zukerman-Schpector, J. (2012). In The Importance of Pi-Interactions in Crystal Engineering. Frontiers in Crystal Engineering. Chichester: Wiley.
- Zheng, B., Liang, Z., Li, G., Huo, Q. & Liu, Y. (2010). Cryst. Growth Des. 10, 3405–3409.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732Isup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732IIsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901800912X/zl2732IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





