Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by infestation of various body tissues by the encysted larvae of Echinococcosis granulosa, the tapeworm. The definitive host for the adult form is usually the dog, where the tapeworm lives in large numbers in the intestines. The disease is related to the inefficiency of environmental health and protective care and dealing with animals, which is prevalent in South America, Africa, Australia, the Mediterranean countries and the Middle East. Cerebral hydatid cysts are rare and comprise only 2% to 3% of all reported hydatid cysts. They constitute up to 3% to 4% of all intracranial space-occupying lesions.1–6 The parietal region is reported to be the most common location of cerebral hydatid cysts.1–3,7–14 On MR, the signal intensity of the cyst is isointense with cerebrospinal fluid on all pulse sequences. Variable amounts of septa can be observed. The MRI demonstrates the hydatid cyst as a spheral, thin-walled structure containing fluid with CSF imaging characters.8,14–16 Cerebral hydatid cysts are benign, slowly growing cysts. The lesions may remain asymptomatic until they are quite large.
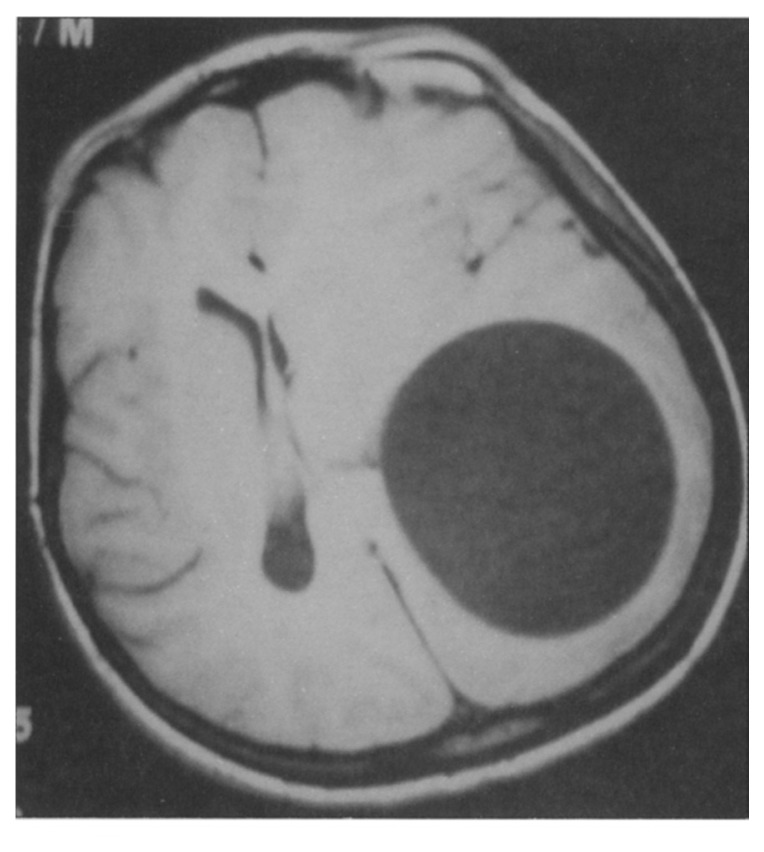
Figure 1.
T1-weighted axial image showing a cystic lesion with a well-defined border in the left parietal region and a markedly left-to-right midline shift
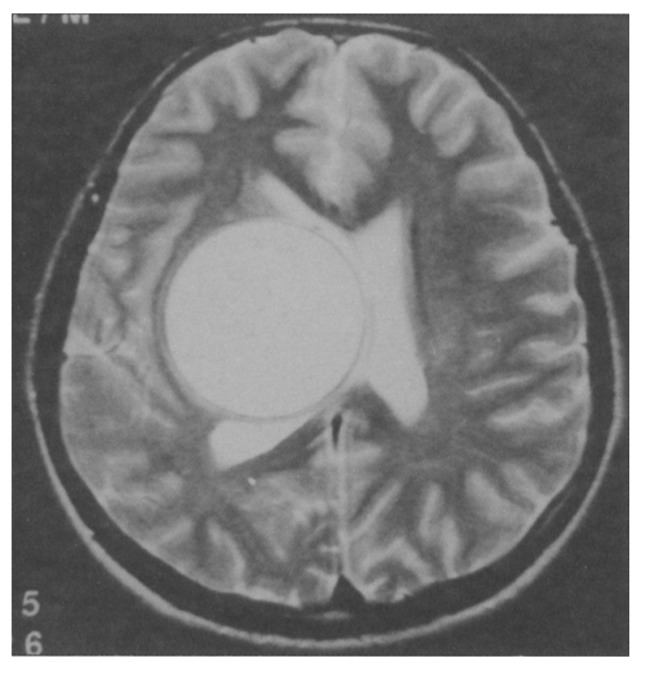
Figure 2.
T2-weighted axial image showing a gigantic right thalamic hydatid cyst causing displacement of the midline structures.
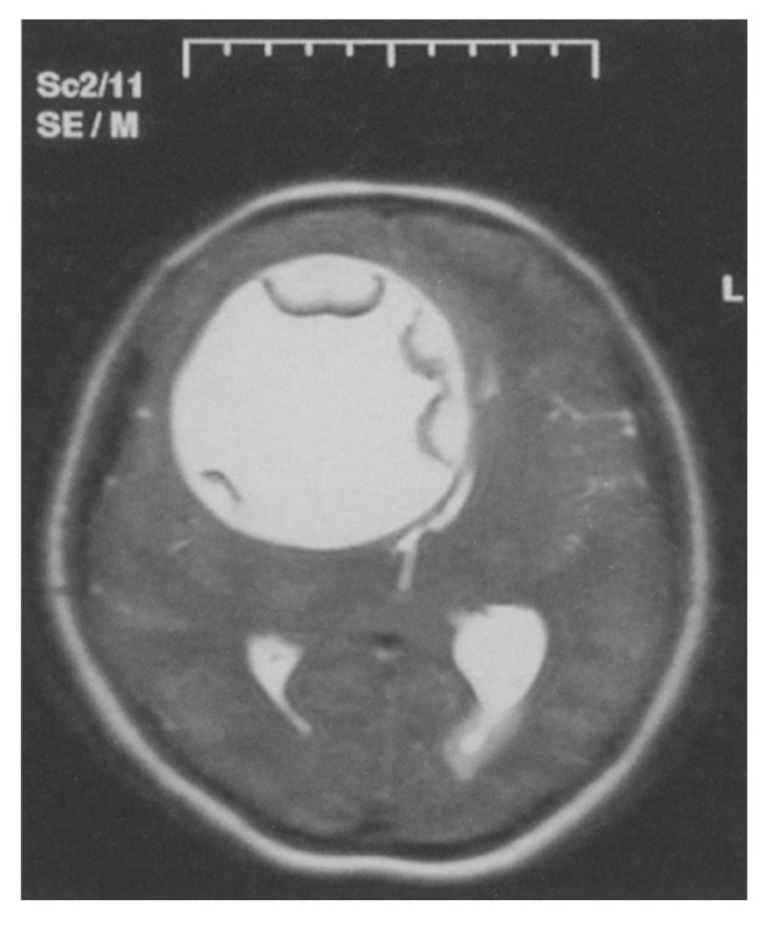
Figure 3.
T2-weighted axial MR image showing a gigantic right frontotemporoparietal hydatic cyst causing displacement of the midline structures.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ayres MC, Dewey IM, German WS. Cerebral Hydatidosis. J Neurosurg. 1963;20:371–377. doi: 10.3171/jns.1963.20.5.0371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ciurea AV, Vasilescu G, Nuteanu L, Carp N. Cerebral hydatid cyst in children. Experience of 27 cases. Child’s Nerv Syst. 1995;11:679–685. doi: 10.1007/BF00262230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dew HR. Primary cerebral hydatid disease. Aust N Z J Surg. 1995;24:261–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1955.tb05089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ersahin Y, Mutluer S, Guzelbag E. Intracranial hydatid cysts in children. Neurosurgery. 1993;33:219–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Krajewski R, Stelmasiak Z. Cerebral hydatid cyst in children. Child’s Nerv Syst. 1991;7:154–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00776712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Özek M. Complications of central nervous system hydatid disease. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1994;20:84–91. doi: 10.1159/000120770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Carrea R, Dowling E, Jr, Guevara JA. Surgical treatment of hydatid cysts of the central nervous system in pediatric age (Dowling’s technique) Childs Brain. 1975;1:4–21. doi: 10.1159/000119553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Çataltepe O, Çolak A, Özcan OE, Özgen T. Intracranial hydatid cysts: experience with surgical treatment in 120 patients. Neurochirurgia. 1992;35:108–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Turgut M. Intracranial hydatidozis in Turkey: Its clinical presentation, diagnostic studies surgical management, and outcome. A review of 276 cases. Neurosurg Rev. 2001;24:200–208. doi: 10.1007/s101430100168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kaya U, Özden B, Turker K, Tarcan B. Intracranial hydatid cysts. Study of 17 cases. Neurosurg. 1975;42:580–584. doi: 10.3171/jns.1975.42.5.0580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kurtsoy A, Öktem S, Koç K, Akdemir H, Menkü A. Successful surgical treatment of a thalamic hydatid cyst with contralateral transcallosal approach. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1999;31:96–99. doi: 10.1159/000028840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Menkü A, Kulaksýzoglu O, Tucer B, Kurtsoy A, Akdemir H. Successful surgical excision of a gigantic cerebral hydatid cyst: Case report. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2004;47:61–64. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-812435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Öktem IS, Akdemir H, Pasoglu A, Kurtsoy A, Selçuklu A. Hydatid cyst of the posterior fossa: A case report. Erciyes Tip Dergisi. 1994;16:303–306. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shamam OEI, Amer T, Atta MA. Magnetic resonance imaging of simple and infected hydatid cysts of the brain. Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2001;19:965–974. doi: 10.1016/s0730-725x(01)00413-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sahin-Akyar G. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings in cerebral hydatid disease. Radiography. 2002;8:251–258. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tüzün M, Altinörs N, Arda IS, Hekimoglu B. Cerebral hydatid CT and MR findings. Journal of Clinical Imaging. 2002;26:353–357. doi: 10.1016/s0899-7071(02)00449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]