Abstract
Background
Culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections (CN PJI) have not been well studied, and due to the lack of consensus on PJI, especially with culture-negative infections, there are considerable uncertainties. Due to the challenging clinical issue of CN PJI the aim of this systematic review is to describe incidence, diagnosis, and treatment outcomes based on the current literature on CN PJI.
Hypothesis
The review is designed to assess the formal hypothesis that CN PJI of the hip and knee have a poorer outcome when compared with culture-positive ones.
Study Design
It is systematic review with level of evidence 3.
Methods
EMBASE, MEDLINE, and the Cochrane Library were searched electronically in January 2018. All studies regarding CN PJI of the hip or knee published in English or German with a minimum of 10 patients were included. Afterwards, the authors performed a descriptive analysis of diagnosis and treatment outcome.
Result
Eight studies were identified that met the inclusion criteria. The incidence of CN PJI in the hip or knee ranged from 7% to 42 %. The included studies were pooled to give an overall incidence rate estimate of 11 % [95% confidence interval (CI): 10-12] based on a random-effects model. The most common surgical intervention was the two-stage revision of prosthesis with 283 patients. Postoperatively, the majority of patients received vancomycin as the antibiotic treatment, alone or in combination with other antibiotics. The rate of succesfully treated infections varied from 85% to 95 % in all included studies. The two-stage exchange arthroplasty had the best outcome, based on the infection-free survival rate of 95%, five years after treatment.
Conclusions
We conclude that CN PJI have the same or even better results than culture-positive infections. Nonetheless, a standardized diagnostic protocol and evidence-based treatment strategies for CN PJI should be implemented for further studies.
1. Introduction
When performing arthroplasty of the hip or knee, periprosthetic joint infections are among the most serious complications after the procedure. 1% of all hip replacements and 2-3% of primary knee prostheses are affected [1, 2]. In the future, a rise in infections is likely due to an increase of implantations, increasing lifespans of patients and the resultant longer prostheses retention times.
Due to a lack of consensus on diagnosis and treatment of periprosthetic joint infections, especially culture-negative infections, there still seem to be considerable uncertainites. Different diagnostic protocols for detecting periprosthetic joint infections have been published, and hence there seems to be no standardized protocol being used across studies [3–13].
Moreover, comparisons of treatment outcomes are difficult to make, as the current evidence does not conclusively support a superior treatment strategy for periprosthetic joint infections.
The culture-negative periprosthetic joint infection is even more demanding in diagnosis and treatment, as without positive culture the uncertainty about the correct diagnosis of infection grows. Without knowing the causing microorganism, it is a challenge to determine the right treatment and choice of antibiotics for any patient. This is all the more difficult due to the sparse existing literature on the treatment and outcome of CN PJI.
This systematic review therefore aims to give an overview on the current database of studies concerning culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections of the hip and knee. The different diagnosis protocols and results after treatment were analyzed, and whether culture-negative infections really have a worse outcome when compared to culture-positive ones was evaluated.
2. Material and Methods
In January 2018 the authors conducted a systematic literature search of MEDLINE, EMBASE via OvidSP, and the Cochrane Library addressing culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections. To identify additional studies that possibly fit the criteria and had not been discovered via the electronic database search, the authors reviewed the bibliographies of the chosen studies and review articles. The systematic review has been reported in accordance with the PRISMA statement [14]. See Table 1 for search terms used.
Table 1.
Search strategy.
| Search # | Query |
|---|---|
| #1 | periprosthetic infection or periprosthetic joint infection or surgical wound infection or prosthesis-related infection |
|
| |
| #2 | knee arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty or knee replacement or knee prosthesis or arthroplasty, replacement, knee |
|
| |
| #3 | hip arthroplasty or total hip arthroplasty or hip replacement or hip prosthesis or arthroplasty, replacement, hip |
|
| |
| #4 | Culture negative OR culture |
|
| |
| #6 | #1 AND #2 AND #4 |
|
| |
| #7 | #1 AND #3 AND #4 |
Inclusion criteria comprised studies published in English or German, numbers of patients >10, and studies regarding culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections after arthroplasty of the knee or hip. Although two-stage exchange arthroplasty is the most widely performed procedure, all treatment strategies were included in the search. Studies with prosthetic joint infections of another region than knee or hip were excluded, as well as case reports, review articles, opinion of experts, and letters to the editors. The abstracts of the selected studies were screened. If they were found to be inadequate, the full text was evaluated to determine whether a study was eligible for inclusion. Two of the authors independently carried out the process described above. Lack of consensus was resolved by thorough discussion. A level of evidence based on The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery guidelines was then assigned to every article. Different variables for a comparative analysis of the outcome of each study were included in a data sheet (Table 2). A descriptive review of the variables, such as the infection control rate and outcome of the included studies, was drafted, and a comparison between all studies was performed. The included studies were pooled to give an overall incidence rate based on a random-effects model with 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity between the studies was assessed with a chi-square-test and quantified with I2 statistics. Publication bias was evaluated with funnel plot analysis.
Table 2.
| Author | Li H et al. | Choi HR et al. | Ibrahim MS et al. | Huang R et al. | Berbari EF et al. | Malekzadeh D et al. | Kim YH et al. | Kim YH et al. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Two-stage revisions for culture-negative infected total knee arthroplasties: A five-year outcome in comparison with one-stage and two-stage revisions for culture-positive cases. | Periprosthetic joint infection with negative culture results: Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome. | Two-stage revision for the culture-negative infected total hip arthroplasty. | Culture-negative periprosthetic joint infection does not preclude infection control. | Culture-negative Prosthetic Joint Infection. | Prior Use of Antimicrobial Therapy is a Risk Factor for Culture-negative Prosthetic Joint Infection. | Comparison of infection control rates and clinical outcomes in culture-positive and culture-negative infected total-knee arthroplasty. | The outcome of infected total knee arthroplasty: culture-positive versus culture-negative. |
|
| ||||||||
| Year | 2017 | 2013 | 2017 | 2012 | 2007 | 2010 | 2015 | 2015 |
|
| ||||||||
| Country | Netherlands | United States | UK | United States | United States | United States | Korea | Korea |
|
| ||||||||
| LoE | III | III | III | III | III | III | III | III |
|
| ||||||||
| Study design | Retrospective | Retrospective | Prospective | Retrospective | Retrospective | Retrospective | Retrospective | Retrospective |
|
| ||||||||
| Study Type | Case-Control study | Case-Control study | Case-Control study | Case-Control study | Cohort study | Case-Control study | Case-Control study | Case-Control study |
|
| ||||||||
| Treatment interval | 2003-2014 | 2000-2009 | 2007-2012 | 2000-2007 | 1990-1999 | 1985-2000 | 2001-2008 | 1991-2008 |
|
| ||||||||
| Total number of cases | 129 | 175 | - | 295 | 897 | 1413 | 242 | 191 |
|
| ||||||||
| Prevalence of CN cases % | 14.2 | 23 | - | 16.3 | 7 | 10.5 | 42.1 | 26.7 |
|
| ||||||||
| Hip % | - | 50 | 100 | 43.8 | 45 | 50 | - | - |
|
| ||||||||
| Knee % | 100 | 50 | - | 56.2 | 55 | 50 | 100 | 100 |
|
| ||||||||
| FU in months, median | 55.6 | 52 | 60 | 47 | 36-60 | 56 | 127.2 | 127.2 |
|
| ||||||||
| Risk factors | - | (1) prior use of antibiotics (2) referral from elsewhere (3) age |
(1) prior use of antibiotics (within 3 months) | (1) prior use of antibiotics (in 64%) (2) prolonged wound drainage after index arthroplasty (residual confounder) |
- | - | ||
|
| ||||||||
| Debridement n | - | 11 | - | 12 | 12 | 18 | 56 | 28 |
|
| ||||||||
| 1-stage n | 3 | 5 | 8 | - | - | |||
|
| ||||||||
| 2-stage n | 18 | 23 | 50 | 33 | 34 | 56 | 46 | 23 |
|
| ||||||||
| Permanent resection n | - | - | - | 8 | 34 | - | - | |
|
| ||||||||
| Other therapy | 6 | - | - | 1 | 19 | - | - | |
|
| ||||||||
| Antibiotic treatment after diagnosis % | Vancomycin 33 Vancomycin + Ceftriaxone 33 Others 34 | Vancomycin 70; Others 30 | - | Vancomycin 81; Cephalosporins 10; Others 9 | Cephalosporins 82; Vancomycin 12; Others 6 | Cefazolin 69; Vancomycin 13; Others/None 18 | Vancomycin 85; Others 15 | Vancomycin 86; Others 14 |
|
| ||||||||
| Successful treatment in % | 88,9 | 85 | 94 | - | - | - | 95 | 95 |
|
| ||||||||
| Overall infection free survival rate % 1.) 3-year 2.) 5-year |
- | - | 1.) - 2.) 94 |
73 | - | 1.) - 2.) 67 |
- | - |
|
| ||||||||
| I&D infection free survival rate % 1.) 3-year 2.) 5-year |
- | - | - | 50 | 1.) - 2.) 71 |
78 | 57 | 61 |
|
| ||||||||
| 2-Stage infection free survival rate % 1.) 3-year 2.) 5-year |
1.) 75 2.) 95 |
- | - | 58 | 1.) - 2.) 94 |
1.) 87 2.) 79 |
83 | 83 |
|
| ||||||||
| 1-Stage infection free survival rate % 1.) 3-year 2.) 5-year |
- | - | - | 100 | - | - | - | - |
|
| ||||||||
| Resection arthroplasty infection free survival rate % 1.) 3-year 2.) 5-year |
- | - | - | - | 1.) 51 | 1.) 49 2.) 43 |
- | - |
|
| ||||||||
| Outcome | With combined or broad-spectrum antibiotics, two-stage revision showed comparable outcome in satisfaction rates, reinfections rates and cumulative survival rates at 5-year Follow-up with CP PJI patients. | The success rate of infection control was higher in the CN group, which suggests that CN may not necessarily be a negative prognostic factor for PJI. | - | The overall infection control rate was similar between CP and CN PJI cases (both 73%). | The outcome of CN PJI is similar to the outcome of PJI due to known pathogens. | The demographics and outcome of CP and CN PJI patients were similar (free of treatment failure at 2 years 79% and 75%). | The infection control rates and clinical outcomes were not different between CP and CN groups (overall infection control rates 90% and 95%). | Overall rates of infection control, successful treatment, and functional outcomes were not different between the CP and CN groups (overall infection control rates 90% and 95%). |
3. Results
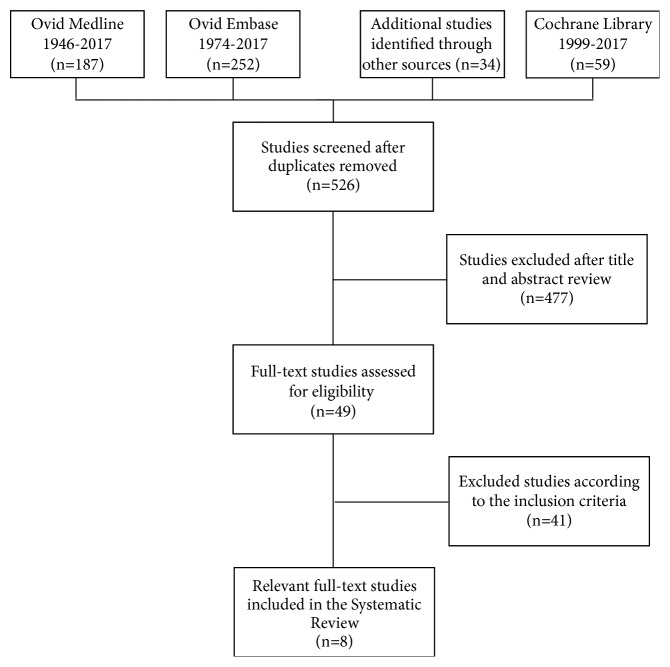
A flow chart of our literature research was created using the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Flow chart.
532 potential studies matching our inclusion criteria were identified via the search strategy and manual screening of the bibliographies of relevant studies. We excluded 477 studies after reviewing title and abstract. This left 49 full-text studies to be assessed for eligibility. Finally, 8 papers were selected for inclusion in our systematic review and meta-analysis [15–22].
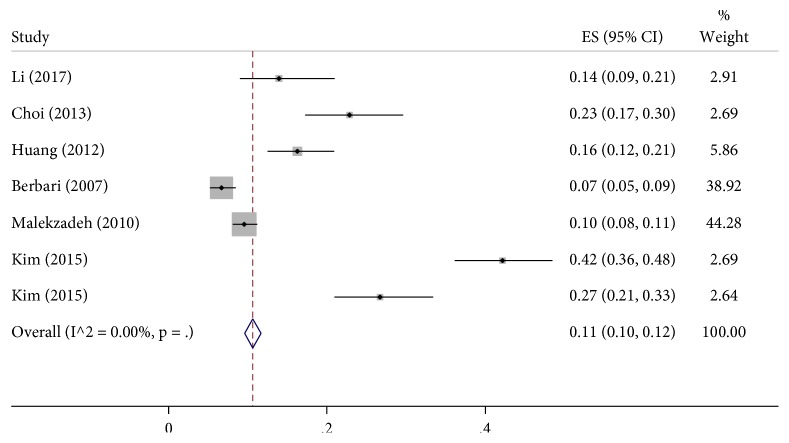
Table 2 shows short summaries of the results of all included studies. All studies have retrospective character and lower quality, with level III of evidence based on The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery guidelines. All studies were published between 2007 and 2017. The incidence rate of culture-negative periprosthetic infections in the hip or knee ranged from 7% to 42 % with a total number of all included patients being 3,342. Of these, 504 were culture-negative (Figure 2). The included studies were pooled to give an overall incidence rate estimate of 11 % [95% confidence interval (CI): 10-12] based on a random-effects model (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
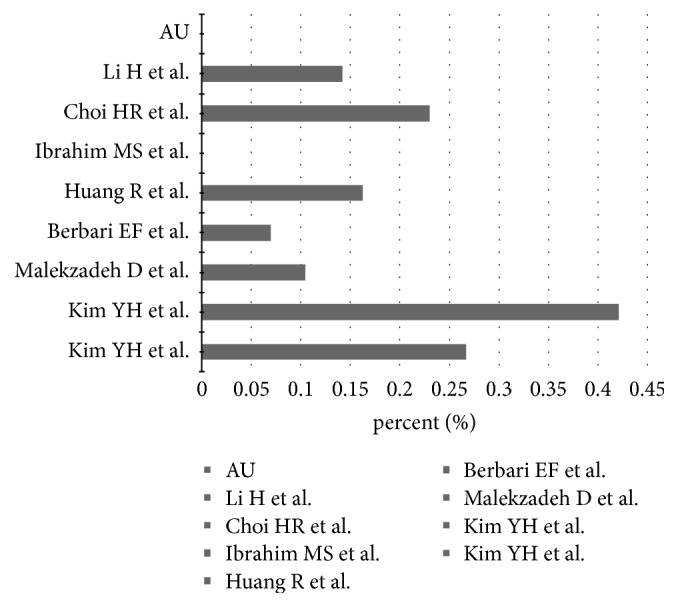
Range of incidence of CN PJI.
Figure 3.
Rates of incidence for culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections of the hip and the knee. Summary estimates for the incidence of CN PJI were calculated using random-effects models with 95% confidence interval (CI). An I2 value (statistical heterogeneity) of 0.00% indicates a low variability in intrastudy differences in the overall effect size.
Funnel plot analysis of included studies assessing the overall incidence of CN PJI revealed a publication bias (Figure 4). 36% of all included culture-negative cases were periprosthetic hip infections, and 64% were prosthetic knee infections. A total number of 137 patients were treated for irrigation and debridement with retention of the prosthesis, 16 patients with one-stage exchange arthroplasty, 42 with permanent resection of the joint, and 26 patients with other treatment options like chronic antibiotic suppression. The two-stage revision of prosthesis was the most common surgical intervention with a total number of 283 patients. The studies differ in the diagnostic protocols used to identify culture-negative infections. Often the diagnostic criteria of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society [8] are used as a reference. To better compare the included studies, a graphic was created (Figure 5).
Figure 4.
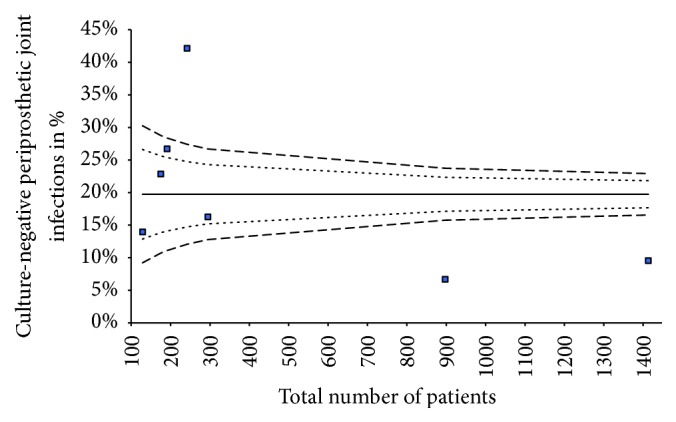
Funnel plot analyses.
Figure 5.
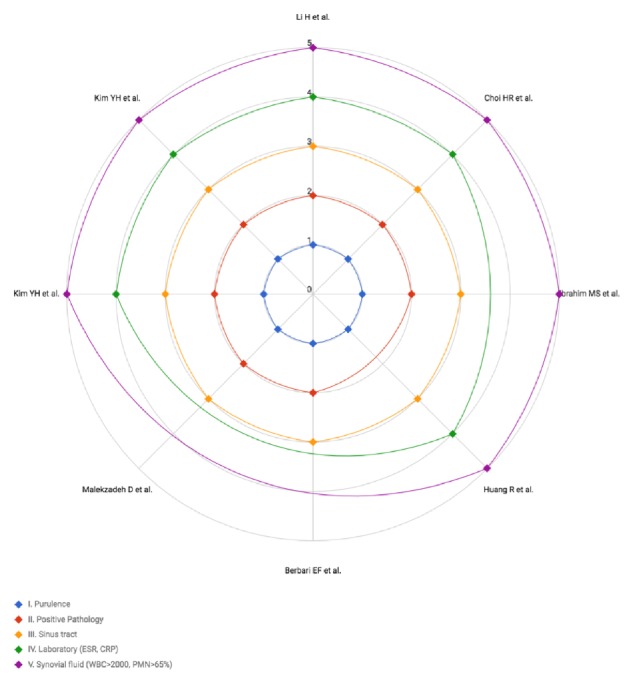
Definition of diagnosis of culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections.
As a postoperative antibiotic, vancomycin was used to treat most of the patients in the included studies, either alone or in combination with other antibiotics. In the studies of Berbari et al. and Malekzadeh et al. cephalosporins were more commonly used to eliminate a periprosthetic joint infection. The relevant studies documented prior use of antibiotics as a risk factor for culture-negative periprosthetic infections.
The included studies define a successful treatment with variable parameters [15–22]. Intersections of the parameters are illustrated in the following graphic, excluding Li et al. as the study did not specify parameters (Figure 6).
Figure 6.
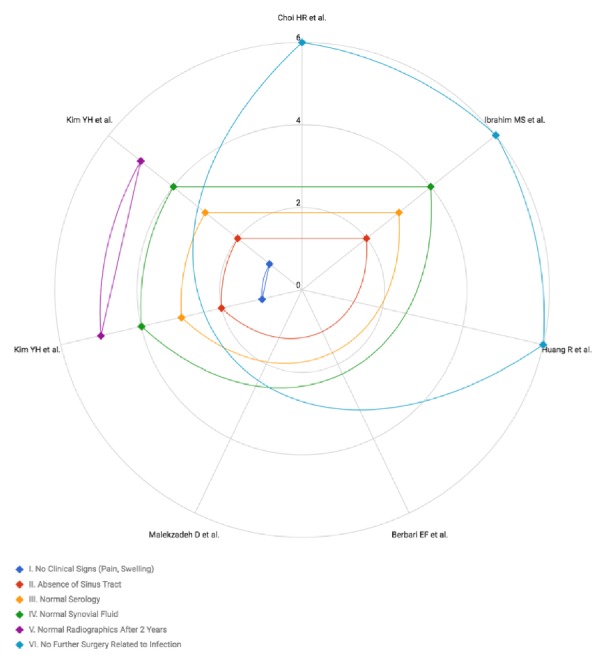
Definition of successful treatment.
The rate of successful treated infections varied from 85% to 95 % in all included studies. The majority of studies observe infection-free survival rates in 3-year and 5-year time-intervals. The overall infection-free survival rate ranged from 67% to 94%. The two-stage exchange arthroplasty has the best outcome with regard to the infection-free survival rate with rates up to 95% five years after treatment. When comparing the outcomes of culture-negative periprosthetic infections with those of culture-positive periprosthetic infections, all studies came to the conclusion that culture-negative infections have the same or, in the study of Choi et al., even better results than culture-positives.
4. Discussion
Periprosthetic joint infections are serious complications that may occur after joint replacement. The incidence ranges from 2% to 3% in primary knee [1, 2] and 1% to 4% in primary hip replacement [2, 24]. In this systematic review, the incidence rate of CN PJI ranged from 7% to 42% [15–22] with a pooled incidence rate of 11%.
The aim of this study is to identify the relevant studies on culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections from the hip and knee and to analyze the reported incidences, diagnostic protocols, and treatment outcomes.
Treating a periprosthetic infection even when the causing organism is known is challenging in itself and a topic of the current investigations [25–29]. When there is no identification of the causing pathogen it is certainly an even bigger challenge. A culture-negative infection is still a subject of controversy because of a lack of literature for a consistent diagnostic protocol and optimal treatment recommendations. Because there are no consistent diagnostic parameters, a comparison between the studies is complicated. While reviewing the literature, the authors found different classifications for the diagnosis of a periprosthetic joint infection (Table 3).
Table 3.
| Parameter | MSIS criteria | AAOS | Philadelphia Consensus | Parvizi et al. | Aggarwal et al. [3] | Zimmerli et al. | Trampuz et al. | Tohtz et al. [11] | Atkins et al. | Portillo et al. | Shanmugasundaram et al. [9] | Müller et al. | Spangehl et al. [10] | Tohtz et al. | Aggarwal et al. | Shanmugasundaram et al. | Spangehl et al. | Charité (modified from Zimmerli) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sinus tract or abscess | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Pain or poor functional status | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| Erythema or swelling | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||
| Pus | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| Early loosening | x | |||||||||||||||||
| Labor | ||||||||||||||||||
| CRP | x (>10mg/L) |
x | x (>10mg/L) |
x (>10mg/L) |
x (>10mg/L) |
x (>0,5mg/dl) |
x (>10mg/L) |
x (>10mg/L) |
x (>10mg/L) |
x (>10mg/L) |
x | |||||||
| ESR | x (>30mm/h) |
x | x (>30mm/h) |
x (>30mm/h) |
x (>30mm/h) |
x | x (>30mm/h) |
x (>30mm/h) |
x (>30mm/h) |
x (>30mm/h) |
x | |||||||
| Leucocytes | x (>10.000/ul) |
x (>12.000/ul) |
x (>10.000/ul) |
|||||||||||||||
| Histology | ||||||||||||||||||
| Acute infection | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||
| Acute infection (Type II or III according to Krenn/Morawietz) |
x | x | x (>2) |
|||||||||||||||
| Granulocytes/HPF | x (>5) |
x (>5) |
x (1-10) |
x (≥10 ) |
x (≥2 ) |
x (>5) |
x (≥10 ) |
x (≥2 ) |
x (>5) |
x (>2) |
x (≥10 ) |
x (>5) |
||||||
| Microbiology | ||||||||||||||||||
| ≥2 culture-positive samples | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x (≥3) |
x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||
| 1 culture-positive sample | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| 1 culture-positive sample (high virulent germ) |
x | x | ||||||||||||||||
| Sonication | ||||||||||||||||||
| ≥ 50 colonies/ml | ||||||||||||||||||
| Synovial flood | ||||||||||||||||||
| Leucocytes | x (>1.100 cells/ul) |
x | x (>1.100 cells/ul) |
x | x (>1.700 cells/ul) |
x (>1.700 cells/ul) |
x (>1.700 cells/ul) |
x | x | |||||||||
| Granulocytes | x (>64%) |
x | x (>64%) |
x | x (>65%)) |
x (>65%)) |
x (>65%)) |
x | x | |||||||||
| Pus | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||
| Culture positive | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| Main criteria | ||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary criteria |
A consistent usage from one classification, separated from the author, joint, or location of the study was not recognizable. Renz and Trampuz et al. published a diagnostic protocol following the international recommendations for usage in further studies to make comparisons between studies and results more reliable (Table 4). In the case that the pathogen cannot be identified, there are three additional parameters to confirm the periprosthetic joint infection.
Table 4.
Diagnostic parameters for CN PJI [23].
| Test | Criteria | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical features | Sinus tract (fistula) or purulence around prosthesisa | 20-30% | 100% |
|
| |||
| Leukocyte count in synovial fluid b | >2000/ul leucocytes or >70% granulocytes (PMN) | ≈90% | ≈95% |
|
| |||
| Periprosthetic tissue histology c | Inflammation (≥23 granulocytes per 10 high-power fields) | 73% | 95% |
|
| |||
| Microbiology | Microbial growth in: (i) synovial fluid or (ii) ≥2 tissue samplesd or (iii) sonication fluid (>50 CFU/ml)e |
45-75% 60-80% 80-90% |
95% 92% 95% |
aMetal-on-metal bearing components can simulate pus (≪pseudopus≫), leukocyte count is usually normal (visible is metal debris)
bLeukocyte count can be high without infection in the first 6 weeks after surgery, in rheumatic joint disease (including crystalopathy), periprosthetic fracture or luxation.
Leukocyte count should be determined within 24 h after aspiration by microscopy or automated counter; clotted specimens are treated with 10 μl hyaluronidase
cClassification after Krenn and Morawietz: PJI corresponds to type 2 or type 3
dFor highly virulent organisms (e.g. S. aureus, streptococci, E. coli) or patients under antibiotics, already one positive sample confirms infection
eUnder antibiotics, for S. aureus and anaerobes, <50 CFU/ml can be significant
Reasons for culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections are not definitely resolved. They could include inappropriate diagnostic tools for rare organisms such as mycobacterium, fungi, and others like Brucella or Coxiella burnetti that are difficult to identify using routine methods [15, 16, 30]. The most common risk factor in our systematic review for culture-negative infection was the prior use of antibiotics [15, 18, 22] which can compromise the sensitivity of routinely used diagnostic laboratory tests. For this reason, Della Valle et al. in the clinical practice guideline of American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons recommends that the antimicrobial treatment be interrupted at least two weeks before aspiration [5]. To increase the detection rate of the low-virulence microorganisms multiple samples (minimum 3) should be taken, and an adequate growth time of at least 14 days [2, 31] should be allowed. Emphasis is placed on new diagnostic tools for improving the sensitivity and specifying for diagnosis of culture-negative prosthetic joint infections, while reducing the number of false-negative results. Trampuz et al. demonstrated the importance of sonication of prostheses in improving diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infections of the knee and the hip, since this method attains more sensitivity than conventional periprosthetic-tissue culture, particularly in patients with prior antibiotic treatment [31]. The most common molecular biological technique is the polymerase chain reaction to detect the causing microorganism [32, 33]. Even unusual species like fungal periprosthetic joint infections could be detected with a selective medium and an increased incubation time [34]. The analyses of the synovial fluid with new biomarkers are currently validated in clinical studies [2]. The alpha-defensin test shows especially good results in detecting a periprosthetic joint infection [2, 35, 36], but it is yet to be validated in larger studies. Next-generation sequencing has recently gained attention and is a topic of current investigations to evaluate the accuracy in identifying causing microorganisms in periprosthetic joint infections, especially in culture-negative infections [37].
The outcome of PJI is determined by the choice of surgical treatment. There are different treatment strategies, including irrigation, debridement, and retention of the prosthesis, one-stage exchange arthroplasty, or two-stage exchange of the prosthesis. The choice of the optimal treatment must be made jointly by orthopedic surgeons and experienced infectologists in accordance with the type of infection and patient's condition.
The largest amount of data in the literature is focused on the two-stage exchange arthroplasty, since this is still considered the gold standard with the lowest reinfection rates, from 0% to 36% [29, 38–44], and best functional outcomes [45–49]. But studies researching the one-stage exchange arthroplasty have also found similar reinfection rates, from 2% to 40% [27, 42, 45, 50–54]. In our systematic review most patients with culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections were treated with two-stage exchange arthroplasty, followed by 4-6 weeks of antibiotic treatment. The two-stage exchange has the highest infection-free survival rate up to 95% after five years of follow-up and a success rate ranging from 70% up to 100%. Of the included studies none recommended one-stage exchange as the first treatment option.
The included studies used different parameters to define a successful treatment. To evaluate and compare the outcome after treatment, a consistent definition of a successful treatment should be determined to enable a reliable comparison between different studies and treatment options.
As was the case regarding the surgical treatment of PJI, there is no consensus in the literature about a standardized protocol for antibiotic usage, especially not in CN PJI. Vancomycin was the antibiotic used to treat most of the patients in our included studies after surgery, either alone or in combination with other antibiotics. Choi et al. reported that high-dosage vancomycin has a better outcome in CN PJI. The rising usage of vancomycin in culture-negative infections may also be encouraged by an increasing number of MRSA infections [13]. Besides the antibiotic agent, the duration of parental and oral antibiotic treatment is another uncertain topic in the published literature, and no treatment protocol has yet been established. Trampuz et al. therefore developed a antimicrobial treatment based on international references [23] (Table 5).
Table 5.
Antimicrobial treatment in CN PJI [23].
| Microorganism | Antibiotic a | Dose b | Route |
|---|---|---|---|
| (red: difficult-to-treat) | (check pathogen susceptibility before) | (italic font: renal adjustment needed) | |
| Culture-negative | Ampicillin/sulbactamc | 3 × 3 g | i.v. |
| for 2 weeks, followed by: | |||
| Rifampind + Levofloxacin | 2 × 450 mg | p.o. | |
| 2 × 500 mg | p.o. |
a Total duration of therapy: 12 weeks, usually 2 weeks intravenously, followed by oral route.
bLaboratory testing 2x weekly: leukocytes, CRP, creatinine/eGFR, liver enzymes (AST/SGOT and ALT/SGPT). Dose-adjustment according to renal function and body weight (<40/> 100kg).
c Penicillin allergy of NON-type 1 (e.g., skin rash): cefazolin (3 × 2 g i.v.). In case of anaphylaxis (= type 1 allergy such as Quincke's edema, bronchospasm, and anaphylactic shock) or cephalosporin allergy, vancomycin (2 × 1 g i.v.) or daptomycin (1 × 8 mg/kg i.v.).
Ampicillin/sulbactam is equivalent to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (3 × 2.2 g i.v.).
d Rifampin is administered only after the new prosthesis is implanted. Add it already to intravenous treatment as soon as wounds are dry and drains removed; in patients aged >75 years, rifampin is reduced to 2 × 300 mg p.o.
Our systematic review has several limitations. First of all, the included studies are based on level III evidence and retrospective in design, which leads to a limited validity of the results of our study. Secondly, only studies published in English or German were selected, resulting in a selective presentation of included studies and results. Only eight studies that met all inclusion criteria were assessed. This led to a small sample size of patients, resulting in restricted validity of our findings. Furthermore, this only allowed us to perform a descriptive analysis of the data. Due to the small sample size, statistical methods used in the meta-analysis to summarize the results are statistically insignificant. With a low heterogeneity in the incidence rates provided by the studies we included, referral bias possibly affects the results. The possibility of not having retrieved all relevant information published on CN PJI should also be considered as one of the limitations of our study. Further, due to the lack of literature which deals with CN PJI and because of publications focusing only on positive results treating CN PJI, a publication bias is likely. Additionally, the included studies did not utilize a standardized treatment protocol (e.g., different surgeons and operative standards, interval between stages, spacer, antibiotic treatment, and duration), which made a direct comparison of their results difficult. The descriptive analysis could not address the functional status after treatment in the selected studies because of missing information in the primary studies.
When the microorganism is confirmed, treatment outcomes are well documented in the literature. However, treatment outcome of culture-negative PJI is only reported in a few studies. In all eight studies included in this systematic review, the clinical outcome and infection control rates are similar to CP PJI groups or have even higher rates of successful treatments [16]. At the same time, when assessing the treatment success of CN PJI, one should consider the relatively short follow-up of the included studies.
Also one of the recently published articles comparing the outcome of culture-negative to culture-positive periprosthetic joint infections Kang et al. came to the conclusion that CN PJI can be treated successfully and can even show a better outcome regarding clinical course [55].
In conclusion, a culture-negative status may not be a negative prognostic factor for treatment outcome. One clearly significant factor is the appropriate selection of the surgical and antimicrobial treatment according to the type of infection, including additional factors like comorbidities, status of the patient, and operative risk for the patient. To increase the validity of the conclusions in further studies, prospectively designed studies of culture-negative PJI should implement a standardized diagnostic protocol and evidence-based treatment strategies for culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections. This will significantly increase the commensurability and thus yield more tangible recommendations.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support from the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Open Access Publication Fund of Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin.
Appendix
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- 1.Corvec S., Portillo M. E., Pasticci B. M., Borens O., Trampuz A. Epidemiology and new developments in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. The International Journal of Artificial Organs. 2012;35(10):923–934. doi: 10.5301/ijao.5000168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Renz N., Trampuz A. Periprothetische Infektionen: aktueller Stand der Diagnostik und Therapie. Orthopädie & Rheuma. 2015:18–20. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aggarwal V. K., Bakhshi H., Ecker N. U., Parvizi J., Gehrke T., Kendoff D. Organism profile in periprosthetic joint infection: pathogens differ at two arthroplasty infection referral centers in Europe and in the United States. The Journal of Knee Surgery. 2014;27(5):399–406. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1364102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Atkins BL., Athanasou N., Deeks JJ., Crook DWM., Simpson H., Peto TEA., et al. Prospective evaluation of criteria for microbiological diagnosis of prosthetic-joint infection at revision arthroplasty. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 1998;36:2932–2939. doi: 10.1128/jcm.36.10.2932-2939.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Della Valle C., Parvizi J., Bauer T. W., et al. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons clinical practice guideline on: the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infections of the hip and knee. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. 2011;93(14):1355–1357. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.9314EBO. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Parvizi J., Gehrke T. Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Proceedings of the International Consensus Meeting on Periprosthetic Joint Infection; 2013; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Parvizi J., Ghanem E., Sharkey P., Aggarwal A., Burnett R. S. J., Barrack R. L. Diagnosis of infected total knee: Findings of a multicenter database. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2008;466(11):2628–2633. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0471-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Parvizi J., Zmistowski B., Berbari E. F., et al. New definition for periprosthetic joint infection: from the workgroup of the musculoskeletal infection society. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2011;469(11):2992–2994. doi: 10.1007/s11999-011-2102-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shanmugasundaram S., Ricciardi B. F., Briggs T. W. R., Sussmann P. S., Bostrom M. P. Evaluation and Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infection-an International, Multicenter Study. HSS Journal. 2014;10(1):36–44. doi: 10.1007/s11420-013-9366-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Spangehl M. J., Masri B. A., O'Connell J. X., Duncan C. P. Prospective analysis of preoperative and intraoperative investigations for the diagnosis of infection at the sites of two hundred and two revision total hip arthroplasties. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. 1999;81(5):672–683. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199905000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tohtz S. W., Müller M., Morawietz L., Winkler T., Perka C. Validity of frozen sections for analysis of periprosthetic loosening membranes. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2010;468(3):762–768. doi: 10.1007/s11999-009-1102-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Trampuz A., Perka C., Borens O. Prosthetic joint infection: New developments in diagnosis and treatment. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift. 2013;138(31-32):1571–1573. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1343280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zimmerli W., Trampuz A., Ochsner P. E. Current concepts: prosthetic-joint infections. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2004;351:1645–1654. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra040181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Moher D., Liberati A., Tetzlaff J., Altman D. G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. British Medical Journal. 2009;339, article b2535 doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Berbari E. F., Marculescu C., Sia I., et al. Culture-negative prosthetic joint infection. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2007;45(9):1113–1119. doi: 10.1086/522184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Choi H.-R., Kwon Y.-M., Freiberg A. A., Nelson S. B., Malchau H. Periprosthetic joint infection with negative culture results: Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome. The Journal of Arthroplasty. 2013;28(6):899–903. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2012.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Huang R., Hu C.-C., Adeli B., Mortazavi J., Parvizi J. Culture-negative periprosthetic joint infection does not preclude infection control hip. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2012;470(10):2717–2723. doi: 10.1007/s11999-012-2434-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ibrahim M. S., Twaij H., Haddad F. S. Two-stage revision for the culture-negative infected total hip arthroplasty. The Bone & Joint Journal. 2018;100-B(1_Supple_A):3–8. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.100B1.BJJ-2017-0626.R1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kim Y.-H., Kulkarni S. S., Park J.-W., Kim J.-S., Oh H.-K., Rastogi D. Comparison of infection control rates and clinical outcomes in culture-positive and culture-negative infected total-knee arthroplasty. Journal of Orthopaedics. 2015;12:S37–S43. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2015.01.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kim Y.-H., Park J.-W., Kim J.-S., Kim D.-J. The outcome of infected total knee arthroplasty: culture-positive versus culture-negative. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery. 2015;135(10):1459–1467. doi: 10.1007/s00402-015-2286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li H., Ni M., Li X., Zhang Q., Li X., Chen J. Two-stage revisions for culture-negative infected total knee arthroplasties: A five-year outcome in comparison with one-stage and two-stage revisions for culture-positive cases. Journal of Orthopaedic Science. 2017;22(2):306–312. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2016.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Malekzadeh D., Osmon D. R., Lahr B. D., Hanssen A. D., Berbari E. F. Prior use of antimicrobial therapy is a risk factor for culture-negative prosthetic joint infection. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2010;468(8):2039–2045. doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1338-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Trampuz A., Renz N. Pocket Guide to Diagnosis Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) PRO-IMPLANT foundation; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Janz V., Wassilew G. I., Hasart O., Tohtz S., Perka C. Improvement in the detection rate of PJI in total hip arthroplasty through multiple sonicate fluid cultures. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 2013;31(12):2021–2024. doi: 10.1002/jor.22451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kunutsor S. K., Whitehouse M. R., Lenguerrand E., et al. Re-infection outcomes following one- and two-stage surgical revision of infected knee prosthesis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(3) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151537.e0151537 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kurd M. F., Ghanem E., Steinbrecher J., Parvizi J. Two-stage exchange knee arthroplasty: does resistance of the infecting organism influence the outcome? Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2010;468(8):2060–2066. doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1296-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lindberg-Larsen M., Jorgensen C. C., Bagger J., Schroder H. M., Kehlet H. Revision of infected knee arthroplasties in Denmark. Acta Orthopaedica. 2016;87(4):333–338. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2016.1148453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Masters J. P. M., Smith N. A., Foguet P., Reed M., Parsons H., Sprowson A. P. A systematic review of the evidence for single stage and two stage revision of infected knee replacement. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2013;14, article no. 222 doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-14-222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mortazavi S. M. J., Vegari D., Ho A., Zmistowski B., Parvizi J. Two-stage exchange arthroplasty for infected total knee arthroplasty: predictors of failure. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2011;469(11):3049–3054. doi: 10.1007/s11999-011-2030-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Million M., Bellevegue L., Labussiere A.-S., et al. Culture-negative prosthetic joint arthritis related to coxiella burnetii. American Journal of Medicine. 2014;127(8):786–e10. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Trampuz A., Piper K. E., Jacobson M. J., et al. Sonication of removed hip and knee prostheses for diagnosis of infection. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2007;357(7):654–663. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa061588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Achermann Y., Eigenmann K., Ledergerber B., et al. Factors associated with rifampin resistance in staphylococcal periprosthetic joint infections (PJI): A matched case-control study. Infection. 2013;41(2):431–437. doi: 10.1007/s15010-012-0325-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Portillo M. E., Salvadó M., Sorli L., et al. Multiplex PCR of sonication fluid accurately differentiates between prosthetic joint infection and aseptic failure. Infection. 2012;65(6):541–548. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2012.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jakobs O., Schoof B., Klatte T. O., et al. Fungal periprosthetic joint infection in total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review. Orthopedic Reviews. 2015;7(1) doi: 10.4081/or.2015.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Frangiamore S. J., Gajewski N. D., Saleh A., Farias-Kovac M., Barsoum W. K., Higuera C. A. α-Defensin Accuracy to Diagnose Periprosthetic Joint Infection-Best Available Test? The Journal of Arthroplasty. 2016;31(2):456–460. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2015.09.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Maurer T. Die Diagnostik bei Infektionen des Bewegungsapparates. Infektionen des Bewegungsapparates: Grundlagen, Prophylaxe, Diagnostik und Therapie. 2015;2:68–93. Auflage. Schweiz: Gesellschaft für Orthopädie und Traumatologie (swiss orthopaedics), Gesellschaft für Infektiologie (Swiss Society for Infectious Diseases) [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tarabichi M., Shohat N., Goswami K., et al. Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. 2018;100(2):147–154. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.17.00434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Babis G. C., Zahos K. A., Tsailas P., Karaliotas G. I., Kanellakopoulou K., Soucacos P. N. Treatment of stage III-A-1 and III-B-1 periprosthetic knee infection with two-stage exchange arthroplasty and articulating spacer. Journal of Surgical Orthopaedic Advances . 2008;17(3):173–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Emerson R. H., Jr., Muncie M., Tarbox T. R., Higgins L. L. Comparison of a static with a mobile spacer in total knee infection. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2002;(404):132–138. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200211000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ghanem M., Zajonz D., Bollmann J., Geissler V., Prietzel T., Moche M. DGPW 5:Doc12. Doc12: Outcome of total knee replacement following explantation and cemented spacer therapy. GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW; 2016. GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gooding C. R., Masri B. A., Duncan C. P., Greidanus N. V., Garbuz D. S. Durable infection control and function with the PROSTALAC spacer in two-stage revision for infected knee arthroplasty. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2011;469(4):985–993. doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1579-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Haddad F. S., Sukeik M., Alazzawi S. Is Single-stage Revision According to a Strict Protocol Effective in Treatment of Chronic Knee Arthroplasty Infections? Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2015;473(1):8–14. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3721-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Meek R. M. D., Masri B. A., Dunlop D., et al. Patient satisfaction and functional status after treatment of infection at the site of a total knee arthroplasty with use of the PROSTALAC articulating spacer. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. 2003;85(10):1888–1892. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200310000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pelt C. E., Grijalva R., Anderson L., Anderson M. B., Erickson J., Peters C. L. Two-stage revision TKA is associated with high complication and failure rates. Advances in Orthopedics. 2014:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2014/659047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Goksan S. B., Freeman M. A. R. One-stage reimplantation for infected total knee arthroplasty. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (British Volume) 1992;74(1):78–82. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.74B1.1732271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Park S.-J., Song E.-K., Seon J.-K., Yoon T.-R., Park G.-H. Comparison of static and mobile antibiotic-impregnated cement spacers for the treatment of infected total knee arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics. 2010;34(8):1181–1186. doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0907-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shaikh A. A., Ha C.-W., Park Y.-G., Park Y.-B. Two-stage approach to primary TKA in infected arthritic knees using intraoperatively molded articulating cement spacers. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2014;472(7):2201–2207. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3545-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Vasso M., Del Regno C., Corona K., D’Apolito R., Schiavone Panni A. Articulated spacer provides long-term knee improvement after two-stage reimplantation. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 2016;24(10):3100–3105. doi: 10.1007/s00167-016-4238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Villanueva-Martínez M., Ríos-Luna A., Pereiro J., Fahandez-Saddi H., Villamor A. Hand-made articulating spacers in two-stage revision for infected total knee arthroplasty: good outcome in 30 patients. Acta Orthopaedica. 2008;79(5):674–682. doi: 10.1080/17453670810016704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Buechel F. F., Femino F. P., D'Alessio J. Primary exchange revision arthroplasty for infected total knee replacement: a long-term study. American journal of orthopedics (Belle Mead, N.J.) 2004;33(4):190–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jenny J.-Y., Barbe B., Gaudias J., Boeri C., Argenson J.-N. High infection control rate and function after routine one-stage exchange for chronically infected TKA knee. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2013;471(1):238–243. doi: 10.1007/s11999-012-2480-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tibrewal S., Malagelada F., Jeyaseelan L., Posch F., Scott G. Single-stage revision for the infected total knee replacement: Results from a single centre. The Bone & Joint Journal. 2014;96(6):759–764. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.96B6.33086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.VonFoerster G., Klüber D., Käbler U. Mid- to long-term results after treatment of 118 cases of periprosthetic infections after knee-joint replacement using one-stage revision arthroplasty. Orthopäde. 1991;20:244–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zahar A., Kendoff D. O., Klatte T. O., Gehrke T. A. Can Good Infection Control Be Obtained in One-stage Exchange of the Infected TKA to a Rotating Hinge Design? 10-year Results. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2016;474(1):81–87. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4408-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kang J., Shin E., Roh T., Na Y., Moon K. H., Park J. Long-term clinical outcome of two-stage revision surgery for infected hip arthroplasty using cement spacer. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery. 2018;26(1) doi: 10.1177/2309499017754095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]