Abstract
The use of nucleic acid, DNA and RNA, based strategies to disrupt gene expression as a therapeutic is quickly emerging. Indeed, synthetic oligonucleotides represent a major component of emerging gene therapeutics. However, the efficiency and specificity of intracellular uptake for non-modified oligonucleotides is rather poor. Utilizing RNA based oligonucleotides as therapeutics is even more challenging to deliver, due to extremely fast enzymatic degradation of the RNAs. Like unmodified oligonucleotides, RNAs also get rapidly degraded in vivo and demonstrate large off-target binding events when they can reach and enter the desired target cells. One approach that holds much promise is the utilization of “click chemistry” to conjugate receptor or cell specific targeting molecules directly to the effector oligonucleotides. We discuss here the applications of the breakthrough technology of CuAAC “click-chemistry” and the immense potential in utilizing “click chemistry” in the development of new age targeted oligonucleotide therapeutics.
Keywords: Click Chemistry, siRNA, non-coding RNA, Protein conjugates
1. Introduction
Gene therapy is an emerging approach that targets intracellular nucleic acids, those DNA and RNAs, associated with human diseases. Synthetic oligonucleotides represent a major type of currently used gene therapeutics. However, the efficiency and specificity of intracellular uptake for non-modified oligonucleotides is poor, with the vast majority trafficking directly to the liver1. Utilizing RNA therapeutics are even more challenging to deliver, due to extremely fast enzymatic degradation of the RNAs. Like unmodified oligonucleotides, RNAs also get rapidly degraded in vivo and show large off-target binding even when they can reach and enter the desired target cells.
Clearly, creating a successful gene therapeutic is not limited to ensuring a successful base-pairing of a therapeutic to its target, but also ensuring stability and cell target specificity. Finding a suitable delivery carrier and enhancing the target specificity for gene therapeutics are both crucial key components required to advance oligonucleotide and RNA based therapeutics to a clinically relevant setting. Indeed, currently stability and receptor or cell targeting effectors can be added to both oligonucleotides and RNAs by conjugation with other biomolecules. Recent successful examples include oligonucleotide-lipid, oligonucleotide-carbohydrate and oligonucleotide-peptide conjugates (reviewed in2). An alternative to direct conjugations is the use of nanoparticles to shuttle therapeutic oligonucleotides with (in)organic polymers, small molecules and other biomolecules. The advantage of nanoassemblies is their relatively simple preparation compared to bioconjugation. However, nanoparticles formed by non-covalent interactions between molecules may inevitably prove to be unstable and require very fast delivery options, which are not available to date (reviewed in3).
Charged, chemically complex and sensitive biomolecules put limitations on the chemistry applied to link them. Click chemistry refers to a broad group of methods unified by the general concept of simple, biology-friendly and bioorthogonal procedures that conjugate molecules in a specific fashion. A breakthrough in click chemistry has been the development of copper-catalyzed click chemistry, CuAAC, by Sharpless, Finn et al. (2002). Rapidly after the discovery of CuAAC click-chemistry, the method was extended to the copper-free approach strain promoted click chemistry, or SPAAC, Diels-Alder, thiol-Michael click reactions. Today, several classical organic reactions have been modified to a “click” version. Each has its advantages and disadvantages and some can even be performed directly in live cells. With regards to gene therapy, CuAAC and SPAAC play a key role in creating decorated therapeutic DNA, RNA and their synthetic analogues, most of which have to date been evaluated in vitro (Figure 1). This is mainly due to the simplicity of the procedure, broad accessibility of the reagents and simple work up. However, new methods allow for the attachment of different modifications to one gene therapeutic, which potentially could be beneficial for in vivo applications. Indeed, a method to directly conjugate cell receptor targeted proteins, aptamers etc., to oligonucleotides or therapeutic RNAs could revolutionize oligonucleotide therapeutics.
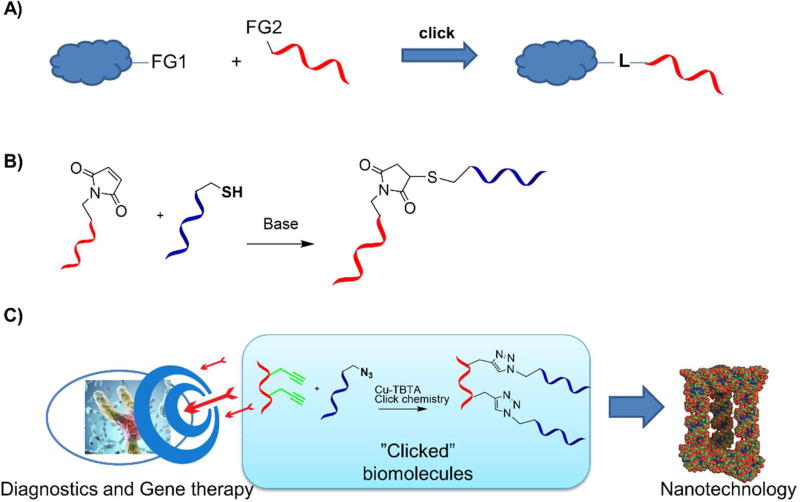
Figure 1.
Main principles of click chemistry (A), applications of “clicked” diagnostic tools, therapeutics and nanomaterials (B). FG1-2 = functional groups that are specific for bioconjugation and unreactive with other biological groups. L = linker.
Here in honor of one of the founders of “click chemistry”, Professor M.G. Finn’s 60th birthday, we review the current applications of click chemistry, CuAAC in particular the generation of new oligonucleotides and their nanoassemblies as therapeutic modalities.
2. Emerging targets in gene therapy and use of synthetic biomolecules
Therapeutic oligonucleotide strategies are promising owing to the fact they are designed a priori to be specific towards their target, with minimal off-target effects4. As such, targeting a single gene or RNA species with an oligonucleotide is thought to be a more effective approach in various diseases where drug approaches have shown reduced or limited efficacy. However, limitations in delivering these molecules to the host, as well as identifying their distribution and target efficiency into target cells in a multicellular environment, have hampered the progression of these strategies into the clinic. Click chemistry provides a promising approach to generate oligonucleotides that can be delivered into target cells safely and with a high efficiency. Current strategies are in their infancy and have to date been mainly proof-of-concept. Most research to date focuses on different delivery strategies and visualization strategies of oligonucleotides being delivered into their cellular targets.
Recent studies have used click-chemistry to mediate the construction of nanoparticles that are loaded with their oligonucleotide cargo for efficient delivery into cells5–6. O’Brien et al., developed a new method called “SnapFect” using a nucleic acid complex with a bio-orthogonal group and a modified cell surface to recognize and deliver the oligonucleotide complex into the cell7. This strategy had minimal toxicity, few steps, was highly efficient and is compatible with siRNA, CRISPR and microfluidic technology. The authors also found that this method is amendable to work in stem and primary cells. Other authors have developed moieties that may help to control gene silencing in vivo. Harun et al., developed siRNA molecules conjugated to a poly(N-isoproprylacylamide) moiety that behaves as a coil-globule that changes its conformation with heat, with an optimal conformation at 35 °C8. The conformation results in accessibility of the siRNA to the RNA induced silencing complex. The authors tested the thermo-responsive siRNA conjugate and found that they were able to induce gene silencing at higher temperatures8.
Immunotherapy is a promising strategy in cancer therapy, and has shown recent success with the use of oncolytic viruses and CAR-T cell therapies. However, these strategies are expensive. As such, the use of other chemical adjuvants, such as cytokines, small oligonucleotides, or cancer antigens may be a more cost effective approach, despite their limited success to date.9 One innovative approach recently developed cell lines to express chemically modified glycan carrying azide moieties, which subsequently allowed the cells to be clicked with different adjuvants, including ODNs. These cells were found to be able to stimulate macrophages in vitro, and when injected into mice, resulted in significantly smaller tumor sizes, than the control cells. Additionally, when mice were re-challenged with unmodified cells, no new tumors developed, suggesting broad protection from immune system targeting of the tumor9.
Click chemistry approaches have been developed and effectively used to conjugate fluorescent molecules, 5’ caps, lipids, polysaccharides and peptides to RNA molecules10. Further, “click chemistry” has been developed as a strategy to circularize RNA10. Others have found using ”click chemistry” that bio-conjugating mRNA with different polyamines at the 5’cap, increased formation of poly-ion complexes (PICs) and their binding to initiation factor 4E to increase translational efficiency of the mRNA target in vitro11. These technologies may help to better understand gene regulation and result in the development of smarter strategies that have discreet and specific effects on their intended targets, by visualizing where these siRNA conjugates are delivered to in vivo and by using the most relevant moieties to obtain the best siRNA conjugates to effectively deliver and target the appropriate cells for treatment. Other uses of click-chemistry have been to develop better labelling of RNA in vitro and in vivo to better profile RNA populations in distinct cellular populations.12–13 Furthermore, click chemistry has also been shown to be an effective tool to analyze the transport of stem cells to different locations14–15 and has been used to understand the molecular dynamics and potential heterogeneity in drug activity in vivo16.
While progressive steps have been made in creating better deliverable molecules for gene therapy, few studies have been focused on a specific disease using an RNA-conjugate to mediate a positive medical outcome. The current strategies suggest that using the tool-box that click-chemistry affords, creating or redeveloping old strategies with new moieties for better delivery, enhanced uptake, and increased specificity into target cells, may result in new pathways for gene therapy. Indeed, research by our group(s) has focused largely on the use of peptide moieties that have shown to have great potential in overcoming the cell membrane to deliver its siRNA cargo to effect gene silencing for both HIV17 and cholesterol regulation18.
3. Growing role of click chemistry in the development of gene therapeutics
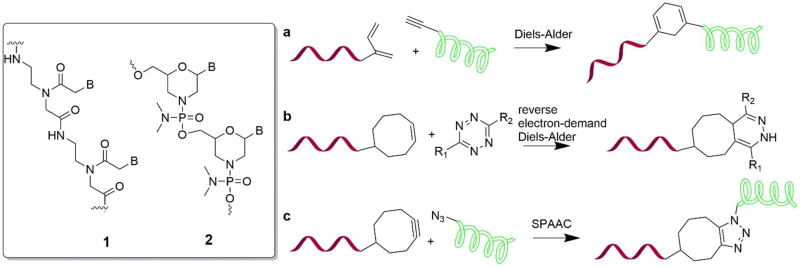
Since the first reports on click chemistry for gene therapeutics,19–20 the original CuAAC approach has been extended by alternative chemical strategies. Wiessler et al., explored the Diels Alder click chemistry for therapeutic peptide nucleic acids (PNA; Figure 2)21. Several groups have demonstrated that PNA conjugates created by click chemistry have advantageous delivery properties compared to unconjugated precursors. In one body of work, Pipkort et al., applied a similar approach to Diels Alder click, for cell-specific fluorescence imaging using PNA probes.22 Using modular PNA probes allowed for the combination of the imaging and therapeutic activities in one PNA molecule. The mRNA product of the cysteine protease cathepsin B (CtsB) gene was imaged and simultaneously degraded using the peptide-PNA conjugate. The degradation was completed by adding a cleavage site to the CtsB complementary PNA probe. Further, Wojciechowska et al., used click chemistry to make cell penetrating peptide (CPP) attached to PNA for atherosclerosis treatment, although the affinity to target hSTAT1 mRNA was demonstrated only in vitro23. The toxicity of PNA has been reported by several groups24–25, however it is not commented on in the aforementioned PNA click papers.
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of PNA (1), morpholino (2); Diels Alder (a)26, reverse electron-demand Diels-Alder (b) and SPAAC (c) for oligonucleotide-peptide conjugation.
For therapeutic applications, there is a need for purification from any residual copper that can be left in the product of the CuAAC reaction. This is particularly important when cell penetrating and other peptides are clicked, due to the high affinity of amino acids to copper27–28. One approach is the use of Tangential flow filtration (TFF) purification that yields hundreds of grams of clicked biomolecules without any sign of toxicity in cells or in vivo29. Another strategy is using a copper-free click reaction. Wang et al., used SPAACto modify DNA with diverse functionalities30. SPAAC has advantages of high reaction rate at ultramild conditions when the two molecules to be reacted have no steric hindrance. However, the rate of SPAAC can be lower compared to CuAAC when clicking longer peptides (> 20 amino acids) to oligonucleotides31.
Phosphorodiamidite morpholino oligonucleotides (PMO) conjugated with cell-penetrating peptides exhibit a high potential for application as therapeutics for Duchenne muscular dystrophy32. Conjugates were initially screened using a selection of peptide conjugates (SELPEPCON) procedure and then the best hits were tested in cells. The SELPEPCON procedure is beneficial for the selection of bioactive peptides that suggest the possibility of crossing the blood-brain barrier through the conjugates and simultaneously being time and cost effective for therapeutic screening32.
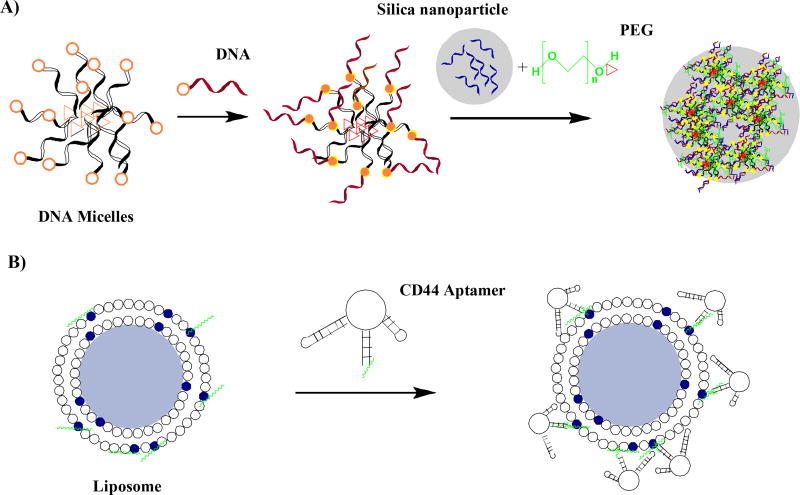
Since the late 2000s, most studies on click chemistry for gene therapy have used nanomaterials, being beneficial for the delivery and activity of gene therapeutics. Ghosh and Hamilton developed thermosensitive dendrimers based on G-quadruplex forming CG rich sequences33. They used different metal ion concentrations to drive the assembly which was confirmed by imaging. DNA-microcapsules prepared by Cavaleri et al. contained the hydrophobic core built from a poly N-isopropylacrylamide (PNIPAM) polymer and reactive “click” domains34. The products were decorated with DNA and poly ethylene glycol (PEG) and showed higher stability that the analogues that did not contain the PNIPAM hydrophobic core (Figure 3A).
Figure 3.
Oligonucleotide nanomaterials as gene therapeutics. Functionalization of DNA-Polymer (A) microcapsules;34 and (B) Liposomes functionalized with CD44 Aptamer35.
Clicking cargos for gene therapeutics is another recent approach. Alshaer et al., functionalized liposomes with an anti-CD44 aptamer via a thiol-maleimide click reaction, for selective targeting of cancer cells – Fig. 3 B)35. Uptake was proven in two CD44(+) human cancer cell lines, lung cancer A549 and breast cancer MDA-MB-231. A new cyclodextrin derivative CD-PLLD, consisting of a beta-cyclodextrin core and poly-L-lysine dendron, efficiently delivered siRNA encoding plasmid to cancer HNE-1 cells36. Simultaneously, a docetaxel was delivered. This star-shaped copolymer of cyclodextrin showed high activity, better blood compatibility and also lower cytotoxicity compared to the controls. It is exciting that clicked modified cyclodextrins have also been found to be capable of siRNA delivery to neurons37. Furthermore, low toxicity and high stability in serum has been confirmed for these vectors.
As to the specificity, additional modifications such as LNA are helpful to decrease off-target binding27. Decorating DNA with several peptide units resulted in improved stability and target recognition specificity of antisense oligonucleotides that target BRAF V600E oncogene. The CuAAC method gave good yields of double-labelled products as well. A “clickable” LNA variant has been suggested for miRNA targeting within LNA/DNA probes38. Besides often-applied sugar modification and terminal attachment by click chemistry, nucleobases can be modified by click chemistry as well. This is often applied when using clickable triphosphates (TPPs), due to better yields upon enzymatic incorporation than for sugar-modified TPPs. Also, the modification can be done post-synthetically with a broad range of azides. Xiong et al., applied 8-aza-7-deazaguanine oligonucleotides to create branched Y-shaped DNA39. Annealing of branched DNA with complementary oligonucleotides yielded well defined nanostructures. Selective target recognition was also confirmed by in vitro assays.
In the last decade, focus has shifted from DNA to RNA therapeutics. As for DNA and its analogues, chemical modifications are compulsory for RNA therapeutics to increase stability in vivo and to ensure the specific delivery and intracellular uptake. Recent studies show that conjugation of therapeutic siRNA with fatty acids and carbohydrate residues benefit the therapeutic performance of RNA (RNA-galnac and RNA-fa papers40–42). For these molecules, maleimide and N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) chemistry is being used. Most methods are developed for DNA conjugation and do not meet the additional requirement of mild conditions needed for RNA modification. Growing applications in RNA therapy stimulate rapid development of bioconjugation methods that allow RNA labelling in high yields and purity43–44(Figure 5).
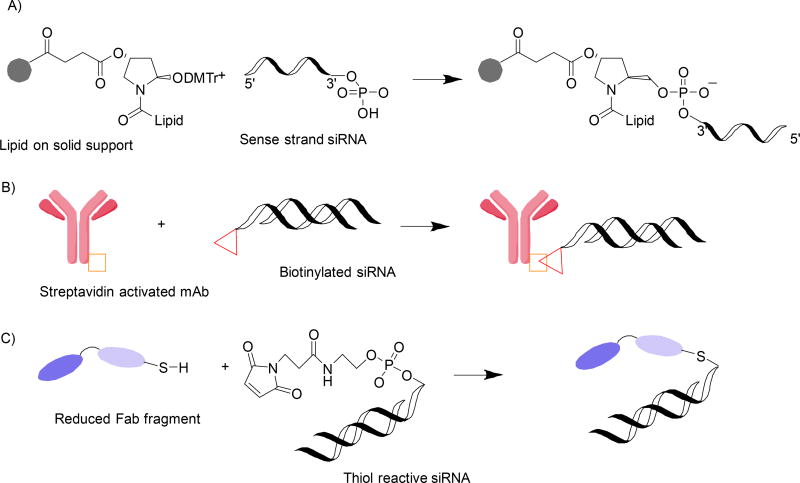
Figure 5.
Approaches of “clicked” therapeutic RNA. siRNA conjugate with lipophilic molecule on a solid CPG support A);45 Biotinylated siRNA conjugated with streptavidin activated monoclonal antibody B);46 Thiol-reactive siRNA conjugated with reduced Fab fragment C)47.
4. Comparison of “clicked” gene therapeutics to alternatives
Although much progress has been made on the click chemistry of therapeutic oligonucleotides and their delivery vesicles, critical points that need to be addressed are their potential toxicity and possibility to scale-up production. TFF purification, which has been mentioned previously, is a good way to scale up the CuAAC reaction29. Moreover, as has been described by Jones et al., click modification can affect the uptake pathway for therapeutics30. Trafficking determines the fate of a therapeutic inside the cell. Therefore, tracking studies are crucial to get structure-activity relationships for conjugates. Lastly, reducing the price of gene therapy is of crucial importance48.
The performance of available clicked therapeutics vs. alternative therapies is summarized in Table 1. Recently, Costales et al., compared clicked small molecule drugs with oligonucleotides49. They showed that morpholino-oligonucleotides had superior specificity in vivo when targeting myotonic dystrophy type 2 (DM2) associated gene alterations. Especially, therapeutic poly-oligonucleotides assembled on site had superior activity when compared to small molecule drugs. In addition, conjugation with CPPs was found to dramatically enhance the therapeutic performance of PMOs used to target exon skipping in the mouse mdx model50.
Table 1.
Performance metrics of “clicked” gene therapeutics compared to other methods.
| # | Oligonucleotide/ small molecule |
Mechanism of action/Target |
Modification | Stability in biofluids |
Specificity | Uptake efficacy |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MO-DM2 | Antisense/r(CCUG) repeat expansion | morpholino | ++ | +++ | ++ | 49 |
| 2 | PMO-CPP | antisense | morpholino | nd | nd | +++ | 50 |
| 3 | P-gp siRNA | siRNA/reducing Pgp expression in breast cancer | “Clicked” triblock copolymer, natural siRNA | + | ++ | +++ | 51 |
| 4 | CD206-siRNA | siRNA/macrophage targeted delivery | Micelle mannosylation by click | ++ | +++ | +++ | 52 |
| 5 | LW6 | HIV-1 α supressing | Click with a fluorophore | nd | nd | +++ | 53 |
| 6 | D/Gal | Induced gene expression/cancer cell | Clicked galactose | nd | ++ | ++ | 54 |
| 7 | ADC | anti-CD22 antibody with doxorubicin/lymph oma cancer cell | - | ++ | +++ | +++ | 55 |
+ Moderate, ++ High, +++ Very high
Multidrug resistance is an issue that blocks the use of available small molecule drugs49. It was shown that using siRNA and ULANAR PS antisense/siRNA makes cancer cells more permeable and reduces resistance. Wu et al., proposed a novel copolymer decorated with folic acid and siRNA for breast cancer treatment51. Co-delivery with doxorubicin resulted in suppression of tumor growth while maintaining rather low toxicity on other tissues. In another work was reported that multidrug resistance could be reversed using click polymer/iMDR1-pDNA complex nanoparticles56. This approach could become useful in breast cancer and other solid tumor treatments in cases when conventional therapy is not working and to reduce the toxicity.
Macrophages could be targeted by siRNA via click mannosylated polymeric micelles52. Being involved in cancer and atherosclerosis pathology, macrophages represent an important therapeutic target. CD206 (mannose receptor) is primarily expressed on macrophages which ensured specific delivery of mannose-decorated siRNA micelles. Up to a 13-fold higher siRNA concentration was found in the macrophages compared to CD206 negative control cells which supports the high specificity of the approach. The authors underline that this approach is general and can be adopted for click functionalization with other target ligands to direct siRNA delivery52.
Main competitors to gene therapeutics remain small molecule drugs53. Small molecules have the advantage of well controlled chemical composition and low cost. However, many of them suffer from poor water solubility and high toxicity. Additionally, cells often become resistant to small molecule drugs, via mutagenesis57. It is worth noting that the therapeutic action of these drugs can be improved by click chemistry as well53–54. The drugs can be used in mixed formulations with siRNA,51 or they can be covalently conjugated to antibodies and nucleic acids including aptamers55.
Lastly, the synthesis of biodegradable polymers is an exciting approach that could solve the issue of drug clearance from the blood stream. Zhao et al., prepared disulfide - containing copolymers and showed that they are useful for gene delivery58.
5. Conclusions
In summary, click chemistry finds a growing amount of applications in the development of gene therapeutics and is now being applied for direct oligonucleotide modification, cargo functionalization or the preparation of nucleotide variants at the nucleoside level. Click chemistry on DNA is relatively well established, whereas RNA modification by click chemistry requires further improvements. The sensitivity of unmodified RNA to chemical reagents and enzymes puts a high demand on the conditions for modifications.
Among prepared molecules, peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates and oligonucleotide nanomaterials show the best therapeutic performance. It is exciting that observations to date suggest gene therapeutics can reverse drug resistance from virus and solid tumors. Delivery and intracellular uptake remain the rate-limiting step, but this issue plagues all therapeutic developments. However, it is convincing from recent developments described in this review that these two issues can be successfully overcome using appropriate design and conjugation strategies.
Compared with small molecule drugs, the high cost of synthetic oligonucleotides and peptides is another obstacle for gene therapy application. Nevertheless, given the rapid development in oligonucleotide and peptide syntheses and the low cost of click chemistry reagents, the overall therapeutic price is bound to fall as the field progresses.
Recent discoveries in RNA biology also provide new targets for clicked therapeutics. Examples are miRNA and lncRNA59–62. Following the development of new clickable nucleosides, nucleotides and oligonucleotide modification reagents, targeting regulatory RNAs is an exciting new direction that might bring new advances to the field of synthetic gene therapeutics.
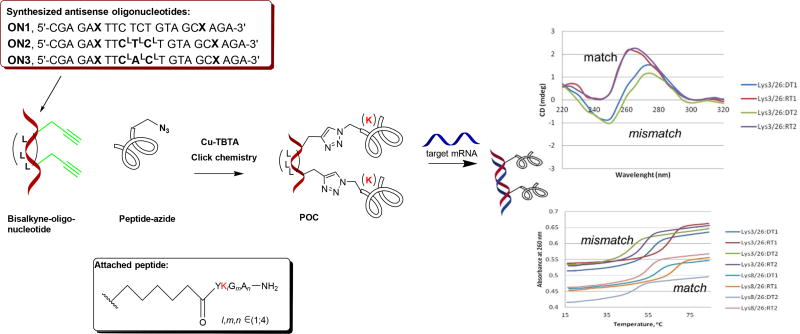
Figure 4.
Specific recognition of BRAF RNA by internally clicked peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates (POCs)27
Acknowledgments
Funding. KA, MT, JU and AC acknowledge Villum Foundation (grant no. 13152) for financial support. KVM acknowledges support by NIAID PO1 AI099783-01 and R01 AI111139-01.
Literature cited
- 1.Geary RS, Norris D, Yu R, Bennett CF. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and cell uptake of antisense oligonucleotides. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;87:46–51. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gooding M, Malhotra M, Evans JC, Darcy R, O'Driscoll CM. Oligonucleotide conjugates - Candidates for gene silencing therapeutics. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016;107:321–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.07.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zagorovsky K, Chou LY, Chan WC. Controlling DNA-nanoparticle serum interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(48):13600–13605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610028113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lorenzer C, Dirin M, Winkler A-M, Baumann V, Winkler J. Going beyond the liver: Progress and challenges of targeted delivery of siRNA therapeutics. Journal of Controlled Release. 2015;203:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Awino JK, Gudipati S, Hartmann AK, Santiana JJ, Cairns-Gibson DF, Gomez N, Rouge JL. Nucleic Acid Nanocapsules for Enzyme-Triggered Drug Release. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2017;139(18):6278–6281. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b13087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Han J, Wang X, Liu L, Li D, Suyaola S, Wang T, Baigude H. “Click” chemistry mediated construction of cationic curdlan nanocarriers for efficient gene delivery. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2017;163:191–198. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.O’Brien PJ, Elahipanah S, Rogozhnikov D, Yousaf MN. Bio-Orthogonal Mediated Nucleic Acid Transfection of Cells via Cell Surface Engineering. ACS Central Science. 2017;3(5):489–500. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.7b00132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Che Harun NF, Takemoto H, Nomoto T, Tomoda K, Matsui M, Nishiyama N. Artificial Control of Gene Silencing Activity Based on siRNA Conjugation with Polymeric Molecule Having Coil–Globule Transition Behavior. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 2016;27(9):1961–1964. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mongis A, Piller F, Piller V. Coupling of Immunostimulants to Live Cells through Metabolic Glycoengineering and Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 2017;28(4):1151–1165. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Warminski M, Kowalska J, Jemielity J. Synthesis of RNA 5′-Azides from 2′-O-Pivaloyloxymethyl-Protected RNAs and Their Reactivity in Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition Reactions. Organic Letters. 2017;19(13):3624–3627. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b01591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Uchida H, Itaka K, Uchida S, Ishii T, Suma T, Miyata K, Oba M, Nishiyama N, Kataoka K. Synthetic Polyamines to Regulate mRNA Translation through the Preservative Binding of Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4E to the Cap Structure. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2016;138(5):1478–1481. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b11726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nguyen K, Fazio M, Kubota M, Nainar S, Feng C, Li X, Atwood SX, Bredy TW, Spitale RC. Cell-Selective Bioorthogonal Metabolic Labeling of RNA. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2017;139(6):2148–2151. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b11401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Akbalik G, Langebeck-Jensen K, Tushev G, Sambandan S, Rinne J, Epstein I, Cajigas I, Vlatkovic I, Schuman EM. Visualization of newly synthesized neuronal RNA in vitro and in vivo using click-chemistry. RNA Biology. 2017;14(1):20–28. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1251541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yoon HI, Yhee JY, Na JH, Lee S, Lee H, Kang S-W, Chang H, Ryu JH, Lee S, Kwon IC, Cho YW, Kim K. Bioorthogonal Copper Free Click Chemistry for Labeling and Tracking of Chondrocytes In Vivo. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 2016;27(4):927–936. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee S, Yoon HI, Na JH, Jeon S, Lim S, Koo H, Han S-S, Kang S-W, Park S-J, Moon S-H, Park JH, Cho YW, Kim B-S, Kim SK, Lee T, Kim D, Lee S, Pomper MG, Kwon IC, Kim K. In vivo stem cell tracking with imageable nanoparticles that bind bioorthogonal chemical receptors on the stem cell surface. Biomaterials. 2017;139:12–29. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.05.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tyler DS, Vappiani J, Caneque T, Lam EYN, Ward A, Gilan O, Chan Y-C, Hienzsch A, Rutkowska A, Werner T, Wagner AJ, Lugo D, Gregory R, Ramirez Molina C, Garton N, Wellaway CR, Jackson S, MacPherson L, Figueiredo M, Stolzenburg S, Bell CC, House C, Dawson S-J, Hawkins ED, Drewes G, Prinjha RK, Rodriguez R, Grandi P, Dawson MA. Click chemistry enables preclinical evaluation of targeted epigenetic therapies. Science. 2017;356(6345):1397–1401. doi: 10.1126/science.aal2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Turner AM, Ackley AM, Matrone MA, Morris KV. Characterization of an HIV-targeted transcriptional gene-silencing RNA in primary cells. Hum Gene Ther. 2012;23(5):473–83. doi: 10.1089/hum.2011.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Matsui M, Sakurai F, Elbashir S, Foster DJ, Manoharan M, Corey DR. Activation of LDL receptor expression by small RNAs complementary to a noncoding transcript that overlaps the LDLR promoter. Chem Biol. 2010;17(12):1344–55. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.10.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.von Maltzahn G, Ren Y, Park JH, Min DH, Kotamraju VR, Jayakumar J, Fogal V, Sailor MJ, Ruoslahti E, Bhatia SN. In vivo tumor cell targeting with"click" nanoparticles. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19(8):1570–8. doi: 10.1021/bc800077y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lutz JF, Zarafshani Z. Efficient construction of therapeutics, bioconjugates, biomaterials and bioactive surfaces using azide-alkyne "click" chemistry. Advanced drug delivery reviews. 2008;60(9):958–70. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wiessler M, Waldeck W, Pipkorn R, Kliem C, Lorenz P, Fleischhacker H, Hafner M, Braun K. Extension of the PNA world by functionalized PNA monomers eligible candidates for inverse Diels Alder Click Chemistry. International journal of medical sciences. 2010;7(4):213–23. doi: 10.7150/ijms.7.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pipkorn R, Wiessler M, Waldeck W, Hennrich U, Nokihara K, Beining M, Braun K. Improved synthesis strategy for peptide nucleic acids (PNA) appropriate for cell-specific fluorescence imaging. International journal of medical sciences. 2012;9(1):1–10. doi: 10.7150/ijms.9.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wojciechowska M, Ruczynski J, Rekowski P, Alenowicz M, Mucha P, Pieszko M, Miszka A, Dobkowski M, Bluijssen H. Synthesis and hybridization studies of a new CPP-PNA conjugate as a potential therapeutic agent in atherosclerosis treatment. Protein and peptide letters. 2014;21(7):672–8. doi: 10.2174/0929866521666140320102034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Narenji H, Gholizadeh P, Aghazadeh M, Rezaee MA, Asgharzadeh M, Kafil HS. Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs): currently potential bactericidal agents. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie. 2017;93:580–588. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Taskova M, Mantsiou A, Astakhova K. Synthetic Nucleic Acid Analogues in Gene Therapy: An Update for Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates. Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology. 2017 doi: 10.1002/cbic.201700229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kozma E, Demeter O, Kele P. Bio-orthogonal Fluorescent Labelling of Biopolymers through Inverse-Electron-Demand Diels-Alder Reactions. Chembiochem. 2017;18(6):486–501. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201600607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Taskova M, Madsen CS, Jensen KJ, Hansen LH, Vester B, Astakhova K. Antisense Oligonucleotides Internally Labeled with Peptides Show Improved Target Recognition and Stability to Enzymatic Degradation. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 2016 doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Maegawa Y, Mochizuki S, Miyamoto N, Sakurai K. Gene silencing using a conjugate comprising Tat peptide and antisense oligonucleotide with phosphorothioate backbones. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters. 2016;26(4):1276–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Raja K, McDonald R, Tuck S, Rodriguez R, Milley B, Traquina P. One-pot synthesis, purification, and formulation of bionanoparticle-CpG oligodeoxynucleotide hepatitis B surface antigen conjugate vaccine via tangential flow filtration. Bioconjug Chem. 2007;18(2):285–8. doi: 10.1021/bc060118q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang R, He A, Ramu E, Falck JR. Correction: Studies towards asymmetric synthesis of 4(S)-11-dihydroxydocosahexaenoic acid (diHDHA) featuring cross-coupling of chiral stannane under mild conditions. Organic & biomolecular chemistry. 2015;13(7):2196. doi: 10.1039/c5ob90015h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lou C, Martos-Maldonado MC, Madsen CS, Thomsen RP, Midtgaard SR, Christensen NJ, Kjems J, Thulstrup PW, Wengel J, Jensen KJ. Peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates as nanoscale building blocks for assembly of an artificial three-helix protein mimic. Nature communications. 2016;7:12294. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.O'Donovan L, Okamoto I, Arzumanov AA, Williams DL, Deuss P, Gait MJ. Parallel synthesis of cell-penetrating peptide conjugates of PMO toward exon skipping enhancement in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nucleic acid therapeutics. 2015;25(1):1–10. doi: 10.1089/nat.2014.0512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ghosh PS, Hamilton AD. Supramolecular dendrimers: convenient synthesis by programmed self-assembly and tunable thermoresponsivity. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 2012;18(8):2361–5. doi: 10.1002/chem.201103051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cavalieri F, Postma A, Lee L, Caruso F. Assembly and functionalization of DNA-polymer microcapsules. ACS nano. 2009;3(1):234–40. doi: 10.1021/nn800705m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Alshaer W, Hillaireau H, Vergnaud J, Ismail S, Fattal E. Functionalizing Liposomes with anti-CD44 Aptamer for Selective Targeting of Cancer Cells. Bioconjug Chem. 2015;26(7):1307–13. doi: 10.1021/bc5004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Liu T, Xue W, Ke B, Xie MQ, Ma D. Star-shaped cyclodextrin-poly(l-lysine) derivative co-delivering docetaxel and MMP-9 siRNA plasmid in cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(12):3865–72. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.O'Mahony AM, Godinho BM, Ogier J, Devocelle M, Darcy R, Cryan JF, O'Driscoll CM. Click-modified cyclodextrins as nonviral vectors for neuronal siRNA delivery. ACS chemical neuroscience. 2012;3(10):744–52. doi: 10.1021/cn3000372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Okholm A, Kjems J, Astakhova K. Fluorescence detection of natural RNA using rationally designed "clickable" oligonucleotide probes. RSC Advances. 2014;4(86):45653–45656. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Xiong H, Leonard P, Seela F. Construction and assembly of branched Y-shaped DNA: "click" chemistry performed on dendronized 8-aza-7-deazaguanine oligonucleotides. Bioconjug Chem. 2012;23(4):856–70. doi: 10.1021/bc300013k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kaczmarek JC, Kowalski PS, Anderson DG. Advances in the delivery of RNA therapeutics: from concept to clinical reality. Genome medicine. 2017;9(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13073-017-0450-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Huang Y. Preclinical and Clinical Advances of GalNAc-Decorated Nucleic Acid Therapeutics. Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids. 2017;6:116–132. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2016.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nishina K, Unno T, Uno Y, Kubodera T, Kanouchi T, Mizusawa H, Yokota T. Efficient in vivo delivery of siRNA to the liver by conjugation of alpha-tocopherol. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy. 2008;16(4):734–40. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jeong JH, Mok H, Oh YK, Park TG. siRNA conjugate delivery systems. Bioconjug Chem. 2009;20(1):5–14. doi: 10.1021/bc800278e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhang HM, Su Y, Guo S, Yuan J, Lim T, Liu J, Guo P, Yang D. Targeted delivery of anti-coxsackievirus siRNAs using ligand-conjugated packaging RNAs. Antiviral Res. 2009;83(3):307–16. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wolfrum C, Shi S, Jayaprakash KN, Jayaraman M, Wang G, Pandey RK, Rajeev KG, Nakayama T, Charrise K, Ndungo EM, Zimmermann T, Koteliansky V, Manoharan M, Stoffel M. Mechanisms and optimization of in vivo delivery of lipophilic siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(10):1149–57. doi: 10.1038/nbt1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.AnChiu C, Xian W, Moss CF. Flying in silence: Echolocating bats cease vocalizing to avoid sonar jamming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008;105(35):13116–13121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804408105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sugo T, Terada M, Oikawa T, Miyata K, Nishimura S, Kenjo E, Ogasawara-Shimizu M, Makita Y, Imaichi S, Murata S, Otake K, Kikuchi K, Teratani M, Masuda Y, Kamei T, Takagahara S, Ikeda S, Ohtaki T, Matsumoto H. Development of antibody-siRNA conjugate targeted to cardiac and skeletal muscles. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society. 2016;237:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.06.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dalakas MC. Gene therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: balancing good science, marginal efficacy, high emotions and excessive cost. Therapeutic advances in neurological disorders. 2017;10(8):293–296. doi: 10.1177/1756285617717155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Costales MG, Rzuczek SG, Disney MD. Comparison of small molecules and oligonucleotides that target a toxic, non-coding RNA. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters. 2016;26(11):2605–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.04.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Burki U, Keane J, Blain A, O'Donovan L, Gait MJ, Laval SH, Straub V. Development and Application of an Ultrasensitive Hybridization-Based ELISA Method for the Determination of Peptide-Conjugated Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Oligonucleotides. Nucleic acid therapeutics. 2015;25(5):275–84. doi: 10.1089/nat.2014.0528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Sun C, Wu J, Tang J. Reversing of multidrug resistance breast cancer by co-delivery of P-gp siRNA and doxorubicin via folic acid-modified core-shell nanomicelles. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces. 2016;138:60–9. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.11.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Yu SS, Lau CM, Barham WJ, Onishko HM, Nelson CE, Li H, Smith CA, Yull FE, Duvall CL, Giorgio TD. Macrophage-specific RNA interference targeting via "click", mannosylated polymeric micelles. Molecular pharmaceutics. 2013;10(3):975–87. doi: 10.1021/mp300434e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kim BS, Lee K, Jung HJ, Bhattarai D, Kwon HJ. HIF-1alpha suppressing small molecule, LW6, inhibits cancer cell growth by binding to calcineurin b homologous protein 1. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2015;458(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sakashita M, Mochizuki S, Sakurai K. Hepatocyte-targeting gene delivery using a lipoplex composed of galactose-modified aromatic lipid synthesized with click chemistry. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry. 2014;22(19):5212–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Li X, Fang T, Boons GJ. Preparation of well-defined antibody-drug conjugates through glycan remodeling and strain-promoted azide-alkyne cycloadditions. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2014;53(28):7179–82. doi: 10.1002/anie.201402606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gao Y, Chen L, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Li Y. Reversal of multidrug resistance by reduction-sensitive linear cationic click polymer/iMDR1-pDNA complex nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2011;32(6):1738–47. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lambert G, Estevez-Salmeron L, Oh S, Liao D, Emerson BM, Tlsty TD, Austin RH. An analogy between the evolution of drug resistance in bacterial communities and malignant tissues. Nature reviews. Cancer. 2011;11(5):375–82. doi: 10.1038/nrc3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zhao N, Roesler S, Kissel T. Synthesis of a new potential biodegradable disulfide containing poly(ethylene imine)-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymer cross-linked with click cluster for gene delivery. International journal of pharmaceutics. 2011;411(1–2):197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.03.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Renganathan A, Felley-Bosco E. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer and Therapeutic Potential. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. 2017;1008:199–222. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-5203-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Saayman SM, Ackley A, Burdach J, Clemson M, Gruenert DC, Tachikawa K, Chivukula P, Weinberg MS, Morris KV. Long Non-coding RNA BGas Regulates the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy. 2016;24(8):1351–7. doi: 10.1038/mt.2016.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sastre B, Canas JA, Rodrigo-Munoz JM, Del Pozo V. Novel Modulators of Asthma and Allergy: Exosomes and MicroRNAs. Frontiers in immunology. 2017;8:826. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kayhanian H, Smyth EC, Braconi C. Emerging molecular targets and therapy for cholangiocarcinoma. World journal of gastrointestinal oncology. 2017;9(7):268–280. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v9.i7.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]