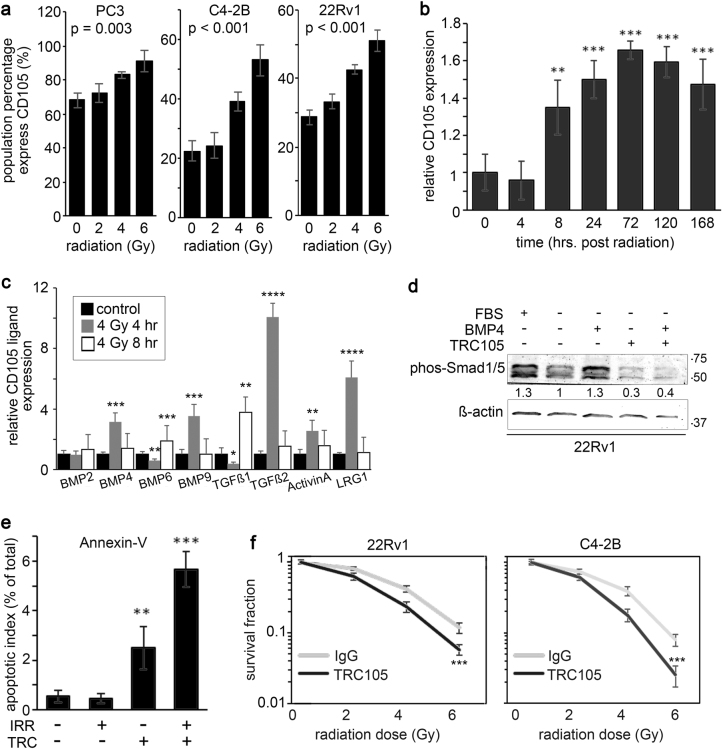
Fig. 1.
Radiation-induced CD105 expression in prostate cancer cells supports radio-resistance. a Cell surface CD105 expression was measured in cell lines at 72 h following a dose range of irradiation (0, 2, 4, or 6 Gy). b The durability of cell surface CD105 expression in 22Rv1 was determined 0, 0.5, 4, 8, 24, 48, 72, 120, and 168 h following 4 Gy irradiation. CD105 cell surface expression fold change was normalized to levels expressed prior to irradiation. c The mRNA expression of CD105 ligands was measured at 0, 4, and 8 h post radiation by rtPCR. Expression was normalized to GAPDH and to the 0 h time point. d Western blot for phosphorylated Smad1/5 was measured in 22Rv1 cells in the presence or absence of serum starvation and treatment with 50 ng/ml BMP4 or TRC105. β-actin expression served as the loading control. Molecular weight (kDa) is indicated. e Annexin-V expression was measured in 22Rv1 cells by FACS analysis 5 days following 4 Gy irradiation and treatment of IgG or TRC105. f Clonogenic assay was measured 10 days following irradiation of 22Rv1 and C4-2B cells in a dose range of 0–6 Gy in the presence of IgG or TRC105. Data are reported as a mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to control, unless otherwise indicated)