Abstract
In oncology, liquid biopsy is used in the detection of next-generation analytes, such as tumor cells, cell-free nucleic acids and exosomes in peripheral blood and other body fluids from cancer patients. It is considered one of the most advanced non-invasive diagnostic systems to enable clinically relevant actions and implement precision medicine. Medical actions include, but are not limited to, early diagnosis, staging, prognosis, anticipation (lead time) and the prediction of therapy responses, as well as follow-up. Historically, the applications of liquid biopsy in cancer have focused on circulating tumor cells (CTCs). More recently, this analysis has been extended to circulating free DNA (cfDNA) and microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) associated with cancer, with potential applications for development into multi-marker diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic signatures. Liquid biopsies avoid some key limitations of conventional tumor tissue biopsies, including invasive tumor sampling, under-representation of tumor heterogeneity and poor description of clonal evolution during metastatic dissemination, strongly reducing the need for multiple sampling. On the other hand, this approach suffers from important drawbacks, i.e., the fragmentation of cfDNA, the instability of RNA, the low concentrations of certain analytes in body fluids and the confounding presence of normal, as well as aberrant DNAs and RNAs. For these reasons, the analysis of cfDNA has been mostly focused on mutations arising in, and pathognomonicity of, tumor DNA, while the analysis of cfRNA has been mostly focused on miRNA patterns strongly associated with neoplastic transformation/progression. This review lists some major applicative areas, briefly addresses how technology is bypassing liquid biopsy limitations, and places a particular emphasis on novel, PCR-free platforms. The ongoing collaborative efforts of major international consortia are reviewed. In addition to basic and applied research, we will consider technological transfer, including patents, patent applications and available information on clinical trials aimed at verifying the potential of liquid biopsy in cancer.
Keywords: liquid biopsy, circulating tumor cells, circulating free DNA, microRNA
1. The concept of liquid biopsy
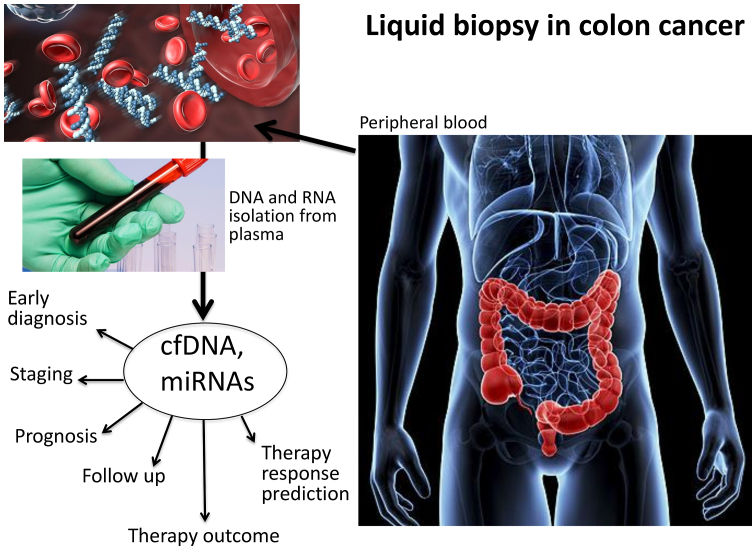
Liquid biopsy investigates circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and/or cell-free nucleic acids in the peripheral blood of cancer patients (Fig. 1) and is considered one of the most advanced non-invasive diagnostic systems with which to obtain key molecular information relevant to clinical decisions and the practice of precision medicine (1-5). Diagnostic actions include, but are not limited to, early diagnosis, staging, prognosis, the prediction of therapeutic responses, and follow-up during therapeutic intervention (5-13). Historically, the applications of liquid biopsy for the characterization of cancer patients have been focused on CTCs (1). Looking for CTCs in peripheral blood has generated a very large number of reports focusing on diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic management (6). The downstream characterization of CTCs, including the identification of possible therapeutic targets (e.g., mutations or other traits of aggressiveness) in this peculiar tumor cell subset not only has had a great impact on diagnosis and prognostication, but also has an impact on clinical protocols, charting the route to precision medicine (14-16). In this respect, an excellent example is colorectal cancer (CRC), one of the most frequent malignancies worldwide (17). As is known, the transformation of normal colonic epithelium into CRC is punctuated by the progressive accumulation of acquired genetic and epigenetic alterations deeply altering morphological parameters, cell growth potential and differentiation, and shutting down apoptosis. Recent basic and clinical research on CTCs in patients with CRC has underlined that the molecular detection of CTCs in peripheral blood is feasible, and their phenotypic characterization drives therapeutic protocols for tailored clinical interventions (18). Moreover, the real-time monitoring of CTCs in patients with CRC has been extensively applied for a better mechanistic understanding of the factors determining clinical outcome and the efficacy of therapeutic treatment, as well as the stability of therapeutic effects over time (18-21).
Figure 1.
Applications of liquid biopsy in colorectal cancer (CRC).
In addition to CTCs, the formal demonstration that free nucleic acids are present (although short-lived) in biological fluids (plasma being investigated by most authors), has led to the development of a large wealth of studies aimed at circulating DNA and RNA (22-24). This strategy, similar to CTC detection, allows for non-invasive diagnosis, and at the same time it represents a convenient method for directly interrogating tumor aberrations, addressing tumor heterogeneity and metastatic dissemination across multiple, longitudinally collected clinical specimens (6,7). On the other hand, this approach suffers from important drawbacks, i.e., the fragmentation of circulating free DNA (cfDNA), the instability of RNA, low analyte concentrations, and the confounding, variable presence of DNA and RNA from normal tissues and mutated cells from the hematopoietic compartment (clonal hematopoiesis) (25). Limitations notwithstanding, the analysis of cfDNA has successfully identified mutations arising in, and the pathognomonicity of, tumor DNA, while the analysis of circulating free RNA (cfRNA) has been mostly focused on miRNA patterns strongly associated with neoplastic transformation/progression (22). Examples of the detection of tumor cfDNA are presented in Table I (18-20,26-52), while examples of the detection of circulating miRNAs are presented in Table II (53-104).
Table I.
Selected examples of liquid biopsy based on the analysis of circulating free DNA (cfDNA).
| Title of the study | Tumor type | Assay | Major results | Authors/(Refs.) | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid biopsy in colon cancer: Comparison of different circulating DNA extraction systems following the absolute quantification of KRAS mutations using Intplex allele-specific PCR | Colon cancer | Intplex allele-specific and digital droplet PCR | Total cfDNA was significantly increased in cancer patients compared to healthy controls, with the highest yield in distant metastatic disease | Kloten et al (18) | 2017 |
| The prognostic value of simultaneous tumor and serum RAS/RAF mutations in localized colon cancer | Colon cancer | Droplet digital PCR technology | RAS and BRAF mutation in serum were strong independent prognostic factors in patients with colon cancer | Thomsen et al (19) | 2017 |
| Circulating free DNA as a biomarker and source for mutation detection in metastatic colorectal cancer | Colon cancer | Quantitative PCR | Tumor-specific KRAS mutations in plasma have prognostic value | Spindler et al (20) | 2015 |
| Multiplex picodroplet digital PCR to detect KRAS mutations in circulating DNA from the plasma of colorectal cancer patients | Colon cancer | Multiplex digital PCR (dPCR) | The study demonstrates the clinical utility of multiplex dPCR to screen for multiple mutations simultaneously with a sensitivity sufficient to detect mutations in circulating DNA obtained by non-invasive blood collection | Taly et al (26) | 2013 |
| Molecular detection of APC, KRAS, and p53 mutations in the serum of patients with colorectal cancer as circulating biomarkers | Colon cancer | PCR-single strand conformation polymorphism analysis (PCR-SSCP) followed by direct sequencing | Molecular detection of KRAS, and p53 gene mutations in circulating tumor DNA is a potential tool for early detection of postoperative recurrence/metastases and poor clinical outcome in patients with colorectal cancer | Wang et al (27) | 2004 |
| Changes in colorectal carcinoma genomes under anti-EGFR therapy identified by whole-genome plasma DNA sequencing | Colon cancer | Whole genome (WGS) sequencing | Whole genome sequencing of plasma of patients with colorectal cancer treated with anti-EGFR therapy unveils several copy number changes, including loss of the APC chromosomal 5q22 region and amplifications in known gene involved in the resistance to EGFR blockade such as MET, ERBB2 and KRAS | Mohan et al (28) | 2014 |
| Comparison of the SuperARMS and Droplet Digital PCR for Detecting EGFR Mutation in ctDNA From NSCLC Patients | Lung cancer | SuperARMS and Droplet Digital PCR | Super-ARMS and ddPCR share the similar accuracy for EGFR mutation detection in plasma biopsy, predicting the efficacy of EGFR-TKIs by detecting plasma EGFR status | Feng et al (29) | 2018 |
| An ultrasensitive method for quantitating circulating tumor DNA with broad patient coverage | Lung cancer | Cancer personalized profiling Deep sequencing (Capp-Seq) | Levels of ctDNA were highly associated with tumor volume and distinguished between residual disease and treatment-related imaging changes; measurement of ctDNA levels allowed for earlier response assessment than radiographic approaches | Newman et al (30) | 2014 |
| Identification of epigenetic aberrant promoter methylation in serum DNA is useful for early detection of lung cancer | Lung cancer | Methylation-specific PCR | Identification of promoter methylation of tumor suppressor genes in serum DNA may be useful for the early detection of lung cancer | Fujiwara et al (31) | 2005 |
| Cell-free DNA levels in plasma of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and inflammatory lung disease | Lung cancer | Real-time PCR | Significantly higher plasma cfDNA levels was found in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer than in subjects with chronic respiratory inflammation and healthy individuals | Szpechcinski et al (32) | 2015 |
| DREAMing: A simple and ultrasensitive method for assessing intratumor epigenetic heterogeneity directly from liquid biopsies | Lung cancer | DREAMing (Discrimination of Rare EpiAlleles by Melt) qPCR | The uses of semi-limiting dilution and precise melt curve analysis allow to distinguish and enumerate individual copies of epiallelic species at single-CpG-site resolution, providing facile and inexpensive ultrasensitive assessment of locus-specific epigenetic heterogeneity directly from liquid biopsies of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer | Pisanic et al (33) | 2015 |
| Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to monitor metastatic breast cancer | Breast cancer | Microfluidic digital PCR assay | Circulating tumor DNA is an informative, inherently specific, and highly sensitive biomarker of metastatic breast cancer | Dawson et al (34) | 2013 |
| Non-invasive analysis of acquired resistance to cancer therapy by sequencing of plasma DNA | Breast cancer | Exome sequencing | Exome-wide analysis of circulating tumor DNA could complement current invasive biopsy approaches to identify mutations associated with acquired drug resistance in advanced cancers | Murtaza et al (35) | 2013 |
| Detection of ESR1 mutations in plasma and tumors from metastatic breast cancer patients using next-generation sequencing | Breast cancer | Next-generation sequencing (NGS) | Results suggest the utility of NGS as a liquid biopsy for metastatic breast cancer patients and the potential to identify novel ESR1 mutations | Yanagawa et al (36) | 2017 |
| ESR1 Methylation: A Liquid Biopsy-Based Epigenetic Assay for the Follow-up of Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer Receiving Endocrine Treatment | Breast cancer | Methylation-specific qPCR | ESR1 methylation in plasma ctDNA showed a high concordance with ESR1 methylation in CTCs, suggesting a possible connection between CTCs and the origin of ctDNA | Mastoraki et al (37) | 2018 |
| Circulating tumor DNA to monitor treatment response and detect acquired resistance in patients with metastatic melanoma | Melanoma | Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) | Mutation-specific ddPCR was used to measure plasma concentrations of oncogenic BRAF and NRAS variants in metastatic melanoma. Tumor-associated ctDNA was detected in plasma of patients prior to treatment and lower circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) levels at this time point were significantly associated with response to treatment and prolonged progression-free survival | Gray et al (38) | 2015 |
| Quantitative assessment of BRAF V600 mutant circulating cell-free tumor DNA as a tool for therapeutic monitoring in metastatic melanoma patients treated with BRAF/MEK inhibitors | Melanoma | Allele-specific quantitative PCR (qPCR) | An increase of the BRAF V600mut ctDNA copy number and fraction, identified disease progression with high sensitivity and specificity | Schreuer et al (39) | 2016 |
| Pyrophosphorolysis-activated polymerization detects circulating tumor DNA in metastatic uveal melanoma | Melanoma | Bidirectional pyrophosphorolysis-activated polymerization (bi-PAP) real-time PCR | Bi-PAP assays detect and quantify ctDNA in patients with metastatic uveal melanoma | Madic et al (40) | 2012 |
| Personalized circulating tumor DNA biomarkers dynamically predict treatmen response and survival in gynecologic cancers | Ovarian cancer | Droplet digital PCR | The use of personalized ctDNA biomarkers in gynecologic cancers can identify the presence of the residual tumor | Pereira et al (41) | 2015 |
| Non-invasive identification and monitoring of cancer mutations by targeted deep sequencing of plasma DNA | Ovarian cancer | Tagged-amplicon deep sequencing (TAm-Seq) | TAm-Seq is a flexible and cost-effective platform for applications in non-invasive cancer genomics and diagnostics. This method can be used for high-throughput sequencing of plasma samples to identify and monitor levels of multiple cancer mutations in circulating DNA | Forshew et al (42) | 2012 |
| Cell-free DNA level as a prognostic biomarker for epithelial ovarian cancer | Ovarian cancer | Quantitative (real-time) PCR | The pre-operative serum cfDNA level of RAB25 may be a useful biomarker predicting survival outcomes in patients with advanced ovarian cancer | No et al (43) | 2012 |
| RASSF1A promoter methylation in high-grade serous ovarian cancer: A direct comparison study in primary tumors, adjacent morphologically tumor cell-free tissues and paired circulating tumor DNA | Ovarian cancer | Real-time methylation specific PCR (real-time MSP) and a methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting analysis (MS-HRMA) | RASSF1A promoter methylation provides significant prognostic information in HGSC patients | Giannopoulou et al (44) | 2017 |
| Cancer genome scanning in plasma: Detection of tumor-associated copy number aberrations, single-nucleotide variants, and tumor heterogeneity by massively parallel sequencing | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Shotgun massively parallel sequencing (MPS) | Genome wide profiling of copy number aberrations and point mutations in the plasma of the cancer patients was found | Chan et al (45) | 2013 |
| Methylation profiling of serum DNA from hepatocellular carcinoma patients using an Infinium Human Methylation 450 BeadChip | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Methylation, BeadChip, Hot-start PCR, Pyrosequencing | The methylation status of circulating DNA in hepatocellular cancer (HCC) may serve as a potential biomarker. BeadChip is useful tool for whole-genome serum DNA methylation screening in HCC | Zhang et al (46) | 2013 |
| The prognostic value of circulating plasma DNA level and its allelic imbalance on chromosome 8p in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Quantitative (real-time) PCR | Combination of circulating DNA and allelic imbalance at microsatellite D8S258 may predict the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma | Ren et al (47) | 2006 |
| Detecting circulating tumor DNA in hepatocellular carcinoma patients using droplet digital PCR is feasible and reflects intratumoral heterogeneity | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Droplet digital PCR | The DNAs from matched tumor and adjacent liver tissues or peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were sequenced to identify the origin of circulating mutants. ctDNA could be readily detected in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting hotspot mutations using ddPCR and might reflect intratumoral heterogeneity | Huang et al (48) | 2016 |
| Tumor-associated copy number changes in the circulation of patients with prostate cancer identified through whole-genome sequencing | Prostate cancer | Plasma-Seq | Shotgun DNA sequencing of plasma ctDNA is a potentially powerful tool for cancer detection, monitoring, and for studying tumor heterogeneity | Heitzer et al (49) | 2013 |
| Circulating tumor DNA genomics correlate with resistance to Abiraterone and Enzalutamide in prostate cancer | Prostate cancer | Whole-exome and deep targeted gene sequencing | A large randomized phase II trial, based on liquid biopsies in a patient population representative of clinical practice, demonstrated the impact of common genomic alterations on patient response to the most widely used therapies for advanced prostate cancer | Annala et al (50) | 2018 |
| Characterization of cell-free circulating DNA in plasma in patients with prostate cancer | Prostate cancer | Quantitative (real-time) PCR | The study suggests that ccfDNA integrity can be a useful biomarker to monitor prostate cancer progression, as the longer fragments are released of non-apoptotic cell death (for example necrosis) that is a frequent event in solid tumors | Delgado et al (51) | 2013 |
| Prognostic and therapeutic implications of circulating androgen receptor gene copy number in prostate cancer patients using droplet digital polymerase chain reaction | Prostate cancer | Droplet digital PCR | The study evaluates the circulating androgen receptor (AR) gene copy number (CN) control and prostate cancer serum samples. Poor prognosis in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) was predicted | Buelens et al (52) | 2017 |
Table II.
Selected examples of liquid biopsy based on the analysis of circulating microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs).
| Title of the study | Tumor type | Assay and target miRNAs | Major results | Authors/(Refs.) | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circulating miR-221 directly amplified from plasma is a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker of colorectal cancer and is correlated with p53 expression | Colon cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-221) | Plasma level of miR-221 is a potential biomarker for CRC. Furthermore, the elevated plasma miR-221 level is a significant prognostic factor for poor overall survival of patients with colorectal cancer | Pu et al (53) | 2010 |
| Serum miR-21 and miR-92a as biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer | Colon cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-21 and miR-92a) | Serum levels of miR-21 and miR-92a have potential impact for early detection of colorectal cancer. Furthermore, miR-92a is a prognostic parameter in patients with colorectal cancer | Liu et al (54) | 2013 |
| Circulating plasma miR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis | Colon cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-141) | Plasma miR-141 is a biomarker that complements carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) in detecting colon cancer with distant metastasis. Furthermore, high levels of miR-141 in plasma are associated with a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer | Cheng et al (55) | 2011 |
| Investigation of microRNA-155 as a serum diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer | Colon cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-155) | High serum miR-155 levels in patients with colorectal cancer has a significant impact on overall survival and progression-free survival. The detection of miR-155 levels in the serum may be considered a novel tumor biomarker for the diagnosis and assessment of the prognosis of colorectal cancer | Lv et al (56) | 2015 |
| Evaluation of miR-506 and miR-4316 expression in early and non-invasive diagnosis of colorectal cancer | Colon cancer | Eco real-time RT-PCR (miR-506, miR-4316) | A significant elevated expression of miR-506 and miR-4316 in patients with early-stage colorectal cancer is proposed as a diagnostic marker | Krawczyk et al (57) | 2017 |
| Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer | Colon cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-29a and miR-92a) | Plasma miR-29a and miR-92a levels have significant diagnostic impact for advanced colorectal cancer | Huang et al (58) | 2010 |
| Serum exosomal miR-4772-3p is a predictor of tumor recurrence in stage II and III colon cancer | Colon cancer | RNA sequencing and RT-qPCR (miR-4772-3p) | Reduced expression of serum exosomal miR-4772-3p is a prognostic biomarker for tumor recurrence in patients with stage II and stage III colon cancer | Liu et al (59) | 2016 |
| Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer | Colon cancer | miRNA microarray analysis and RT-qPCR (let-7a, miR-1229, miR-1246, miR-150, miR-21, miR-223 and miR-23a) | The serum exosomal levels of seven miRNAs were significantly higher in patients with primary colorectal cancer, even considering early stage disease, and were significantly downregulated after surgical resection of the tumors | Ogata-Kawata et al (60) | 2014 |
| Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: A potential marker for colorectal cancer screening | Colon cancer | RT-qPCR array (miR 17-3p, miR-135b, miR-92 and miR-222) | In the study, a panel of miRNAs were found to be upregulated both in plasma and tissue samples of patients with colorectal cancer | Ng et al (61) | 2009 |
| Serum microRNA panel as biomarkers for early diagnosis of colorectal adenocarcinoma | Colon cancer | MiRseq sequencing followed by (RT-qPCR) validation (miR-19a-3p, miR-223-3p, miR-92a-3p, and miR-422a) | A panel of four miRNA (miR-19a-3p, miR-223-3p, miR-92a-3p and miR-422a) with a high diagnostic accuracy of colorectal adenocarcinoma was identified. This miRNA panel could differentiate stage I/II colorectal adenocarcinoma from the controls | Zheng et al (62) | 2014 |
| Decreased plasma let-7c and miR-152 as non-invasive biomarker for non-small-cell lung cancer | Lung cancer | RT-qPCR (let-7c and miR-152) | The expression of let-7c and miR-152 in plasma was found to be downregulated patients in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and to be associated with the clinicopathological characteristics, such as histological classifications, differentiation status, lymph node metastasis and stage classifications | Dou et al (63) | 2015 |
| Decreased circulating miR-375: A potential biomarker for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer | Lung cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-375) | Plasma miR-375 levels in patients with NSCLC were significantly decreased. In addition, patients with metastatic NSCLC had a lower plasma miR-375 expression than those with non-metastatic NSCLC, and had worse overall survival rates | Yu et al (64) | 2014 |
| Digital PCR quantification of miRNAs in sputum for diagnosis of lung cancer | Lung cancer | Digital PCR and RT-qPCR (miR-31 and miR-210) | Combined quantification of miR-31 and miR-210 copy number by using digital PCR in sputum was demonstrated useful for lung cancer diagnosis | Li et al (65) | 2014 |
| Five microRNAs in plasma as novel biomarkers for screening of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer | Lung cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-20a, miR-145, miR-21, miR-223 and miR-221) | Five microRNAs (miR-20a, miR-145, miR-21, miR-223 and miR-221) were proposed as potential biomarkers for early-stage NSCLC | Geng et al (66) | 2014 |
| Serum microRNA signatures identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling predict survival of non-small-cell lung cancer | Lung cancer | Solexa sequencing and RT-qPCR (miR-486, miR-1, miR-30d and miR-499) | A panel of serum miRNAs was found altered by more than 5-fold between longer-survival and shorter-survival groups of lung cancer patients. The levels of four miRNAs (i.e., miR-486, miR-30d, miR-1 and miR-499) were significantly associated with overall survival | Hu et al (67) | 2010 |
| Early detection of lung adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers | Lung cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-21, miR-486, miR-375 and miR-200b) | In the sputum samples of lung adenocarcinoma patients, four miRNAs (miR-21, miR-486, miR-375 and miR-200b) were found able to distinguish patients with lung adenocarcinoma from normal subjects | Yu et al (68) | 2010 |
| High expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer | Lung cancer | miRNA microarray and RT-qPCR (miR-21) | Serum miR-21 was proposed as a biomarker for the diagnosis of NSCLC | Liu et al (69) | 2012 |
| A plasma miRNA signature for lung cancer early detection | Lung cancer | qPCR-based TaqMan microRNA arrays (miR-126, miR-145, miR-210, and miR-205-5p) | A panel of 30 miRNAs displayed a significant differential expression level in the plasma of patients with lung cancer with respect to the cancer-free controls. A selected plasma miRNA signature (miR-126, 145, 210 and 205-5p) was proposed for lung cancer detection | Leng et al (70) | 2017 |
| Direct serum assay for microRNA-21 concentrations in early and advanced breast cancer | Breast cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-21) | High circulating miR-21 concentrations were significantly. associated with visceral metastasis in a multivariate analysis of breast cancer patients that included standard clinicopathological prognostic factors | Asaga et al (71) | 2011 |
| Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer and healthy subjects | Breast cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-155) | Women with progesterone receptor-positive tumors had higher circulating miR-155 levels than tumors that were negative for these receptors | Zhu et al (72) | 2009 |
| Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for breast cancer | Breast cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-195 and Let-7a) | Cancer-specific miRNAs were detected and found to be significantly altered in the circulation of patients with breast cancer. Circulating levels of miR-195 and let-7a decreased in cancer patients post-operatively, to levels comparable with those of the control subjects | Heneghan et al (73) | 2010 |
| Aberrant plasma levels of circulating miR-16, miR-107, miR-130a and miR-146a are associated with lymph node metastasis and receptor status of breast cancer patients | Breast cancer | miRNA microarray profiling and RT-qPCR (miR-16, miR-107, miR-130a and miR-146a) | Differential concentrations of plasma miR-16, miR-107, miR-130a and miR-146a in different breast cancer subtypes were found, suggesting a potential role of these miRNAs in breast cancer biology and tumor progression | Stückrath et al (74) | 2015 |
| Diagnostic and prognostic microRNAs in the serum of breast cancer patients measured by droplet digital PCR | Breast cancer | Droplet digital PCR (miR-148b-3p, miR-652-3p and miR-10b-5p) | The serum levels of miR-148b-3p and miR-652-3p were significantly lower in the serum of breast cancer patients compared with the controls. In addition, higher serum levels of miR-10b-5p were associated with clinicobiological markers of a poor prognosis | Mangolini et al (75) | 2015 |
| A serum microRNA signature predicts tumor relapse and survival in triple-negative breast cancer patients | Breast cancer | Genome-wide serum miRNA expression and RT-qPCR analyses (miR-18b, miR-103, miR-107, and miR-652) | The study identified a four-miRNA signature (miR-18b, miR-103, miR-107 and miR-652) that predicted tumor relapse and overall survival for patients with triple-negative breast cancer | Kleivi Sahlberg et al (76) | 2015 |
| Comparison of a healthy miRNome with melanoma patient miRNomes: Are microRNAs suitable serum biomarkers for cancer? | Melanoma | miRNome and custom qPCR array (miR-3201 and miR-122-5p) | Results indicate a characteristic signatures with excellent prognostic scores only in patients with late-stage but not early-stage melanoma | Margue et al (77) | 2015 |
| Serum-based miRNAs in the prediction and detection of recurrence in melanoma patients | Melanoma | miRNA microarray and RT-qPCR (miR-15b, miR-150, miR-30d and miR-425) | The results of the study demonstrate that a panel of four serum miRNAs can improve melanoma patient stratification over stage | Fleming et al (78) | 2015 |
| A direct plasma assay of circulating microRNA-210 of hypoxia can identify early systemic metastasis recurrence in melanoma patients | Melanoma | RT-qPCR directly-in-plasma assay (RT-qPCR-DP) (miR-210) | A RT-qPCR-DP performed to detect cf-miR-210 demonstrated that cf-miR-210 expression was significantly higher in patients with metastatic melanoma versus the healthy donor controls | Ono et al (79) | 2015 |
| The prognostic and predictive value of melanoma-related microRNAs using tissue and serum: A microRNA expression analysis | Melanoma | TaqMan assays and Fluidigm Real-time PCR (miR-16, miR-211, miR-4487, miR-4706, miR-4731, miR-509-3p and miR-509-5p) | In a minimally-invasive blood test, a seven-miRNA panel (MELmiR-7) detected the presence of melanoma with high sensitivity and specificity | Stark et al (80) | 2015 |
| Serum microRNAs as biomarkers for recurrence in melanoma | Melanoma | RT-qPCR (miR-150, miR-15b, miR-199a-5p, miR-33a and miR-424) | A signature of five miRNAs successfully classified melanoma patients into high and low recurrence risk groups | Friedman et al (81) | 2012 |
| The circulating microRNA-221 level in patients with malignant melanoma as a new tumor marker | Melanoma | RT-qPCR (miR-221) | Patients with malignant melanoma had significantly higher miR-221 levels than the healthy controls. Furthermore, the miR-221 levels were significantly increased in patients with stage I-IV disease compared to those with melanoma in situ, and were associated with tumor thickness | Kanemaru et al (82) | 2011 |
| Identification of plasma microRNAs as new potential biomarkers with high diagnostic power in human cutaneous melanoma | Melanoma | RT-qPCR (miR-149-3p, miR-150-5p and miR-193a-3p) | Diagnostic impact of miRNAs was improved when considering the combination of miR-149-3p, miR-150-5p, and miR-193a-3p, discriminating between patients with melanoma and healthy controls | Fogli et al (83) | 2017 |
| A combination of circulating miRNAs for the early detection of ovarian cancer | Ovarian cancer | NGS miRNA sequencing followed by validation with RT-qPCR (let-7d-5p, miR-142-3p, miR-200a-3p, miR-26a-5p, miR-374a-5p, miR-766-3p, miR-130b-3p and miR-328-3p) | A novel predictive model was proposed based on a combination of 8 circulating serum miRNAs. This method was able to successfully distinguish patients with early-stage ovarian cancer from the healthy controls and those with benign tumors | Yokoi et al (84) | 2017 |
| Circulating miRNA landscape identifies miR-1246 as promising diagnostic biomarker in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma: A validation across two independent cohorts | Ovarian cancer | miRNA microarray and droplet digital PCR (miR-1246, miR-595 and miR-2278) | This study allowed the identification of circulating miRNAs with diagnostic relevance for high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) | Todeschini et al (85) | 2017 |
| Expression of serum miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-200c as candidate biomarkers in epithelial ovarian cancer and their association with clinicopathological features | Ovarian cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-200a and miR-200b, miR-200c) | The expression levels of miR-200a and miR-200c were found to be significantly associated with disease progression, while miR-200a overexpression was found be associated with tumor histology and the stage of epithelial ovarian cancer | Zuberi et al (86) | 2015 |
| Serum microRNA-145 as a novel biomarker in human ovarian cancer | Ovarian cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-145) | Serum miR-145 levels could discriminate patients with malignant ovarian cancer from the healthy controls | Liang et al (87) | 2015 |
| MicroRNA-200c and microRNA-141 as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for ovarian cancer | Ovarian cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-200c and miR-141) | The results of the study suggested that serum miR-200c and miR-141 were able to discriminate patients with ovarian cancer from healthy controls. In addition, miR-200c and miR-141 may be predictive biomarkers for the prognosis of ovarian cancer | Gao and Wu (88) | 2015 |
| Urinary microRNA-30a-5p is a potential biomarker for ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Ovarian cancer | miRNA microarray and RT-qPCR (miR-30a-5p) | Results indicated an increase in miR-30a-5p levels in the urine of patients with ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. In parallel, the inhibition of miR-30a-5p suppressed the malignant phenotypes of ovarian cancer in vitro | Zhou et al (89) | 2015 |
| Combining serum microRNA and CA-125 as prognostic indicators of preoperative surgical outcome in women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer | Ovarian cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-375, miR-34a-5p and miR-210) | The combination of serum miR-375, miR-210 and CA-125 can discriminate healthy versus patients with high-grade serous ovarian cancer. The combination of miR-34a-5p and CA-125 was the strongest predictor of completeness of surgical resection | Shah et al (90) | 2018 |
| Serum microRNA characterization identifies miR-885-5p as a potential marker for detecting liver pathologies | Hepatocellular carcinoma | qPCR-based TaqMan microRNA arrays (miR-885-5p) | miR-885-5p is significantly elevated in the sera of patients with liver pathologies, including hepatocellular carcinoma | Gui et al (91) | 2011 |
| MicroRNA-500 as a potential diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma | Hepatocellular carcinoma | RT-qPCR (miR-500) | An increased amount of miR-500 was found in the sera of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. In fact, miR-500 levels in the sera of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma returned to normal following surgical treatment | Yamamoto et al (92) | 2009 |
| Circulating microRNAs, miR-21, miR-122, and miR-223, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or chronic hepatitis | Hepatocellular carcinoma | RT-qPCR (miR-21, miR-122 and miR-223) | Results indicated that serum miR-21, miR-122 and miR-223 were elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or chronic hepatitis and these miRNAs have strong potential to serve as novel biomarkers for liver injury, but not specifically for hepatocellular carcinoma | Xu et al (93) | 2011 |
| Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma | Hepatocellular carcinoma | miRNA microarray analysis and RT-qPCR (miR-122, miR-192, miR-21, miR-223, miR-26a, miR-27a and miR-801) | A microRNA panel that provides a high diagnostic accuracy of hepatocellular carcinoma was described | Zhou et al (94) | 2011 |
| Serum microRNA profiles serve as novel biomarkers for HBV infection and diagnosis of HBV-positive hepatocarcinoma | Hepatocellular carcinoma | NGS microRNA sequencing followed by validation with TaqMan probe-based RT-qPCR (miR-23b, miR-423, miR-375, miR-23a and miR-342-3p) | The study demonstrates that serum miRNA profiles can serve as non-invasive biomarkers for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis | Li et al (95) | 2010 |
| Circulating miR-106b-3p, miR-101-3p and miR-1246 as diagnostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma | Hepatocellular carcinoma | RNAseq and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) (miR-106b-3p, miR-101-3p and miR-1246) | Circulating miR-101-3p, miR-106b-3p and miR-1246, either individually or in combination, exhibit a considerable potential value as diagnostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma | Moshiri et al (96) | 2018 |
| Combinations of serum prostate-specific antigen and plasma expression levels of let-7c, miR-30c, miR-141, and miR-375 as potential better diagnostic biomarkers for prostate cancer | Prostate cancer | Quantitative PCR (let-7c, miR-30c, miR-141 and miR-375) | Combinations of let-7c, miR-30c, miR-141, miR-375 and PSA obtained even better discrimination and could be more useful that prostate-specific antigen (PSA) alone as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for the screening of prostate cancer | Kachakova et al (97) | 2015 |
| Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer | Prostate cancer | miRNA microarray and RT-qPCR (miR-200b and miR-375) | miR-200b and miR-375 levels are increased in the serum of patients with metastatic prostate cancer compared with patients with localized disease | Bryant et al (98) | 2012 |
| Circulating microRNAs are associated with docetaxel chemotherapy outcome in castration-resistant prostate cancer | Prostate cancer | RT-qPCR microRNA array cards and RT-qPCR (miR-200 family and miR-17 family) | The study has identified selected circulating miRNAs, notably those of the miR-200 and miR-17 families, associated with PSA response and/or overall survival in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer | Lin et al (99) | 2014 |
| Circulating miRNAs 21 and 221 as biomarkers for early diagnosis of prostate cancer | Prostate cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-21 and miR-221) | The study showed that serum miR-21 and miR-221 levels may be used as specific non-invasive molecular biomarkers for prostate cancer diagnosis | Kotb et al (100) | 2014 |
| MicroRNA profiling in prostate cancer - the diagnostic potential of urinary miR-205 and miR-214 | Prostate cancer | RT-qPCR microRNA array cards and RT-qPCR (miR-205 and miR-214) | miR-205 and miR-214 levels are downregulated in prostate cancer and may serve as a potential non-invasive molecular biomarker for prostate cancer | Srivastava et al (101) | 2013 |
| Serum microRNA expression patterns that predict early treatment failure in prostate cancer patients | Prostate cancer | miRNA microarray and RT-qPCR (miR-103, miR-125b and miR-222) | Altered content of miR-103, miR-125b and miR-222 in the serum of patients with prostate cancer was found to be associated with the outcome of clinical treatment | Singh et al (102) | 2014 |
| A study on circulating microRNAs identifies a new potential biomarker panel to distinguish aggressive prostate cancer | Prostate cancer | RT-qPCR (miR-17, miR-192 and miR-181a) | The study demonstrates that a novel previously unreported circulating miRNA signature consisting of a combination of interacting miRNAs (miR-17/miR-192) and an independent miRNA (miR-181a) are capable of differentiating between aggressive and non-aggressive prostate cancer | Farran et al (103) | 2018 |
| Different levels of serum microRNAs in prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia: Evaluation of potential diagnostic and prognostic role | Prostate cancer | RT-qPCR (let-7c, let-7e, let-7i, miR-26a-5p, miR-26b-5p, miR-18b-5p and miR-25-3p) | let-7c, let-7e, let-7i, miR-26a-5p, miR-26b-5p, miR-18b-5p and miR-25-3p were able to discriminate between patients with prostate cancer from those harboring benign prostatic hyperplasia, both presenting altered PSA levels | Cochetti et al (104) | 2016 |
2. Analytes in plasma: Examples of biomedical applications
Molecular targets: Cancer genetic aberrations
One of the most robust evidence supporting the application value of liquid biopsies is the detection of circulating genomic aberrations, mainly mutations. The topic is extensive, and is the subject of a number of excellent reviews. Therefore, in this review, we focus on very specific examples, particularly in early-stage tumors. KRAS mutations are a case in point, since they serve as an actionable marker for EGFR blockade therapy, are highly prevalent, and have been thoroughly investigated. For instance, Brychta et al compared plasma and paired tumor samples from early-stage pancreatic cancer patients (105) by chip-based digital PCR. Their major aim was to identify selected KRAS codon 12 mutations (G12D, G12V and G12C) in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). Remarkably, circulating KRAS mutations were demonstrated in 72% of the patients, were associated with tumor burden, and were undetectable in the healthy controls. This study supports the use of liquid biopsy for early cancer diagnosis. Other studies focusing on KRAS mutations in ctDNA were reported by Kinusaga et al (pancreatic cancer) (106), Couraud et al (lung cancer) (107), Perez-Carbonell et al (CRC) (108) and Case et al (lymphoblastic leukemia) (109). Table I summarizes the applicative examples of liquid biopsy for the identification of oncogene mutations, including the detection of EGFR mutations in the blood of lung cancer patients, now approved by regulatory bodies. These assays are of outmost interest and exemplify the profound difference between non-invasive liquid biopsy and invasive tumor tissue biopsy. Tissue biopsy may not reflect the genomic profile of the tumor in its entirety due to intra-tumor heterogeneity, multiple foci poorly accessible to sampling, and/or changes occurring during tumor development and/or therapy. On the contrary, the non-invasive liquid biopsy of plasma, urine or saliva samples may more effectively recapitulate the mutational complexity of the many populations (cryptic and clinically evident) accounting for tumor burden in a given patient. This makes liquid biopsy particularly suitable to identify truncal aberrations that, when targeted, may result in a considerably greater systemic clinical benefit, as compared to targeting site-specific aberrations (Lin et al, 2015) (110).
Molecular targets: Gene methylation
A variation on the theme is to look at non-mutational events marking the cancer genome. Particularly relevant in this context is DNA methylation. It has been known for quite some time that tumor progression is associated with the abnormal methylation of cancer genes. Both hypomethylation and hypermethylation have been reported. Most often, the specific DNA hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes is observed in the context of widespread DNA hypomethylation. Since aberrant DNA methylation at specific promoter regions is a defined molecular feature of cancer, ctDNA methylation has been developed into a very promising molecular marker. DNA methylation is to date one of the preferred consensus circulating biomarkers in pre-symptomatic and symptomatic patients with CRC. This has been discussed by Warton et al (111) and by Mitchell et al (112), who have considered methylation-specific PCR assays as a novel approach for the assessment of low levels of DNA methylation in 29 regions of 17 genes. Eight differentially-methylated regions (DMRs) residing in the BCAT1, GRASP, IKZF1 and IRF4 genes, exhibited low positivity in the plasma of healthy subjects and high positivity (>59%) in ctDNA from colonoscopy-confirmed patients with CRC.
Molecular targets: Circulating microRNAs
MicroRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) are a family of small (19 to 25 nucleotides in length) non-coding RNAs which play important roles in controlling post-transcriptional gene expression. Regulatory miRNAs reduce protein synthesis through selective interactions with complementary sequences of target messenger RNAs (mRNAs) (113,114). Single or multiple mRNAs can be targeted at their 3′untranslated region (UTR), coding sequence (CDS), 5′UTR sequences, and it is calculated that >60% of human mRNAs are miRNA targets (114). The miRNA/mRNA interaction occurs at the level of RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and is associated with the repression of translation or mRNA degradation, depending on the levels of complementarity with nucleotide sequences on the target mRNAs (115-118). Since their discovery and first characterization, the number of human miRNAs identified and deposited in the miRBase databases (miRBase v.22, www.mirbase.org) has been steadily increasing and is now >2,500 (119,120). Research on miRNAs has confirmed the complexity of this expanding miRNA/RNA network (117-122).
Alterations in miRNA expression have been associated with different human diseases. The guided alteration of specific miRNAs may potentially lead to innovative therapeutic protocols (123,124). miRNAs function both as tumor promoters (oncomiRNAs and metastamiRNAs) and tumor suppressors (125,126), depending on their regulatory preference for oncoproteins with opposing influences on cancer cells. Based on this, it is unsurprising that circulating cell-free miRNAs have been actively investigated as liquid biopsy analytes. OncomiRNAs are abundant in several extracellular body fluids (127-132), where they are protected and stabilized by exosome-like structures and small intraluminal vesicles produced by a variety of cells (including cancer cells) (127). Hence, elevated levels of several miRNAs (including miR-221, miR-222, miR-141, miR-92a, miR-21, miR-155, miR-506 and miR4316, miR-4772 and miR-29a) are present in the blood from patients with CRC (53-62,133,134) and may contribute to the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with CRC (134). Furthermore, miRNAs may aid in the monitoring of therapeutic approaches. For instance, Ogata-Kawata et al reported that serum exosomal miRNA levels (let-7a, miR-1229, miR-1246, miR-150, miR-21, miR-223 and miR-23a) were higher in patients with CRC than in the controls, that this abnormally high levels were already detectable at early disease stages, and that they were significantly downregulated following surgical resection (60).
3. Technologies
In order to identify specific DNA mutations and quantify miRNA levels in plasma and other body fluids of cancer patients, several types of technologies for DNA/RNA analysis have been proposed. For cfDNA analysis, the golden standards are possibly quantitative PCR (qPCR) and digital PCR; however, several additional technologies have been proposed (Table I), such as polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) analysis (27), multiplex digital PCR (dPCR), allele-specific qPCR (18,39), whole genome sequencing (WGS) (28), cancer personalized profiling deep sequencing (Capp-Seq) (30), methylation-specific PCR (31,37,44), the Discrimination of Rare EpiAlleles by Melt qPCR (DREAMing) (33), bidirectional pyrophosphorolysis-activated polymerization (bi-PAP) real-time PCR (40) and tagged-amplicon deep sequencing (TAm-Seq) (42). For miRNA analysis, qPCR and reverse transcription (RT)-PCR (53-58), NGS RNA sequencing (63), miRNA microarray analysis (60) and digital PCR (65) are the most commonly used technologies (Table II).
A common step, and under many respects a complication of all the above-mentioned technologies, is the need to amplify the minute amounts of target analytes by an enzymatic reaction with DNA modifying enzymes, most often Taq polymerase and its derivatives. Biosensing platforms hold great promise for the simple and rapid detection of cfDNA and cfRNA (135), since they skip this time-consuming, analyte-dependent, PCR amplification step. Novel PCR-free biosensing approaches are able to detect KRAS and BRAF mutations in the serum of patients with lung cancer and melanoma (136).
Digital PCR (137) is based on the limiting dilution of DNA, and single molecule detection to identify and quantify the target mutated DNA in a given sample (138,139). This experimental approach is very useful for the identification of rare variants and in non-invasive diagnosis on peripheral blood, since only a small concentration of template is required for the analysis. Next generation sequencing (NGS) is a high throughput DNA sequencing technology which allows for the analysis, in a single reaction, a large variety of different DNA aberrations across multigene panels (140,141), although comprehensiveness may somewhat detract from sensitivity. Different commercial NGS platforms are available, such as Genome Analyzer and HiSeq 2000 (Illumina), HeliScope (Helicos BioSciences), SOLiD and Ion Torrent (Life Technologies), Roche/454 (Roche). In these instruments, templates, primers or polymerase enzymes are immobilized on a solid support or on microbeads before sequencing, allowing the process of millions of microreactions carried out in parallel on each spatially distinct template.
However, as already pointed out, several challenges are related to liquid biopsy, the most important of which is the amount of target molecules to be detected and quantified. As far as cfDNA detection is concerned, these target molecules are so diluted by normal DNA that existing sequencing methods, such as Sanger sequencing, were not considered sufficiently sensitive to detect tumor-associated DNA mutation. As shown in Table I, the most commonly used approach was based on mutation-specific PCR, a technology proven to exhibit sufficient specificity and sensitivity allowing for the detection of the weak tumor signal present in the patient's circulation. This technology may be associated with important drawbacks when the quantification of miRNAs is considered, suffering from biases in the template-to-product ratios of the amplified target sequences (141). In addition, differential RT efficiency on different miRNA targets may also introduce variability when miRNA patterning is considered. Once again, PCR-free detection strategies are of great interest (142,143).
4. Experimental model systems for technological validation
Liquid biopsy is a complex strategy requiring pre-analytical steps, post-analytical optimization, and the careful selection of optimal analytes for specific biological queries. In vivo model systems may be very useful in addressing and isolating these numerous individual variables (that are both technical and biological), and validate complex multi-step approaches. It is surprising, in this respect, that only few reports are available focusing on the use of animal models. For example, Garcia-Olmo et al directly compared the tumor ctDNA concentration and the number of circulating cancer cells in rats with xenograft tumors during the spread of CRC (144). Of note, they found that high ctDNA levels preceded the presence of CTCs. Rago et al (145) developed an elegant and highly sensitive qPCR test to quantify ctDNA by targeting LINE-1 in mouse xenografts, demonstrating that this experimental system enables the monitoring of systemic tumor burden and close examination of the therapeutic management on a variety of animal tumor models. These studies demonstrate the importance of ctDNA and how it intertwines with CTCs. In a more recent study, Thierry et al (146) evaluated the relative quantitative contributions of non-tumor, tumor and mutated ctDNA, as well as ctDNA integrity, in an animal model. In this case, they found differences between patients with CRC and nude mice xenografted with human colon cell lines, suggesting that further research is necessary to validate in vivo model systems based on mice xenografted with tumor cell lines.
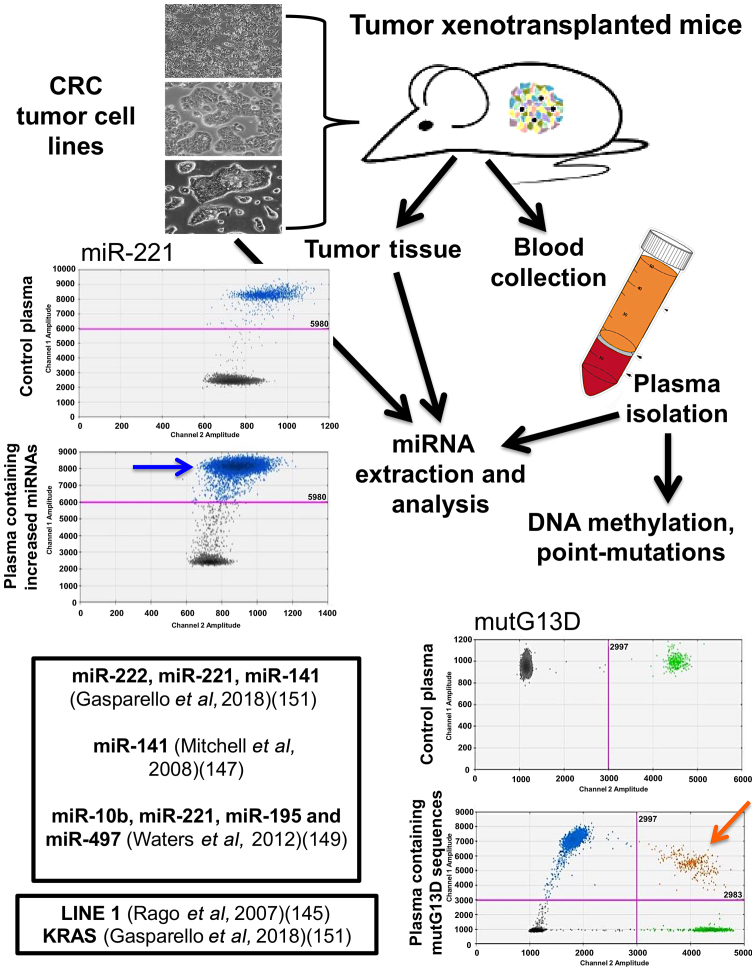
As for miRNAs, different independent studies have firmly demonstrated that miRNAs released into the circulation by tumor xenografts are distinct from 'background' mouse miRNAs. This is a key point, since pre-existing miRNAs present in mouse body fluids may be a powerful confounding parameter, possibly altering conclusions and implications of any circulating miRNA signature. In this respect, the use of laboratory mouse strains has the advantage that it sets a 'background' mouse miRNA pattern that is stable and easily quantifiable. Mitchell et al demonstrated that several miRNAs originating from xenografted human prostate cancer cells are present in the circulation (one of the most interesting being miR-141), and are readily measured in plasma, allowing a clear distinction between tumor-xenografted mice and controls (147). Selth et al (148) performed global miRNA profiling and identified a set of miRNAs exhibiting significantly altered serum levels in transgenic mice bearing prostate adenocarcinoma tumors. Among the most interesting miRNAs, they focused their attention on miR-141 and miR-375. Waters et al observed a complex miRNA dysregulation in the circulation of athymic nude mice subcutaneously injected with MDA-MB-231 cells. Some miRNAs (such as miR-10b) were undetectable in the circulation, some others (miR-195 and miR-497) were significantly decreased, the miR-221 content was not altered, and a positive correlation was observed between miR-497 and miR-195. That study highlighted the distinct roles of miRNAs in the circulation and in disease dissemination and progression, all of which may be candidates as molecular targets for diagnosis, as well as for systemic therapy (149). More recently, Greystoke et al developed a robust protocol that allowed for the specific profiling of human tumor miRNAs in microliters of tail vein plasma (150). In a recent study, Gasparello et al presented the analysis of KRAS variants and the content of miR-141, miR-221 and miR-222 in mice xenografted with colon cancer cell lines (151). These results support the existence of multiple, finely tuned (non-housekeeping) control gateways that selectively regulate the release/accumulation of distinct ctDNA and miRNA species in culture and tumor xenograft models (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
Study workflow on an in vivo model system to validate liquid biopsy protocols. Three human colorectal cancer cell lines can be selected as proxies of clinical cancers and cultured in vitro (top left panel) or used to establish tumor xenografts (top right panel). DNA and RNA can be isolated from cells, supernatants and tumor xenografts. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and microRNAs (miRNAs) can be isolated from blood plasma and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR), reverse transcription (RT)-ddPCR and RT-quantitative PCR (qPCR) can be performed to detect KRAS mutations and miRNA analysis. Examples of published studies are reported within the boxes. Blue and orange arrows indicate positive events associated with miR-221 and mutG13D content.
5. Specific biomedical applications
ctDNA and miRNAs find application in a variety of clinical cancer settings.
Early diagnosis
Liquid biopsy for early lung cancer detection has been reviewed by Hofman (152) and by Pérez-Ramírez et al (153). Coupled with thoracic imaging, liquid biopsy is a powerful diagnostic tool, and potentially provides surveillance recommendations for high-risk populations without a detectable nodule. In a study on patients with CRC, Bedin et al (154) examined a large cohort of patients with CRC in comparison to healthy subjects and patients with adenomatous lesions. In their study, the presence and integrity of plasma cfDNA and the methylation profile of two gene promoters were evaluated. The cfDNA concentration and cfDNA integrity were found to be increased in patients with CRC, and were associated with a poor prognosis. A lower extent of DNA methylation was observed in cfDNA as compared to tissue DNA.
With respect to alterations affecting cancer drivers, a high prevalence was previously described by Allenson et al of mutant KRAS in circulating exosome-derived DNA from patients with early-stage pancreatic cancer (155). One very interesting observation of their study was that exosomes from viable cancer cells may reflect a different biology than cfDNA shed from dying tissues, including normal tissues. The information that the analyzed ctDNA is derived from actively metabolizing cancer cells with invasive potential, and not from normal cells, is certainly a crucial issue for early diagnosis. In this respect, Allenson et al (155) observed that the size of ctDNA differs depending on whether it is released from necrotic and dying cells or from live cells. The former is contained in cfDNA, the latter is included in the exosome-DNA fraction. The conclusion of their study was that exosomes should be considered as distinct sources of tumor DNA that may be complementary to other liquid biopsy DNA sources. In addition, circulating mutant KRAS was found in a minority of healthy samples, suggesting that care should be exercised when proposing liquid biopsy as a broad cancer-screening method.
As far as miRNA-based early diagnosis, an interesting study by Shimomura et al employed a highly sensitive micro-array assay for the evaluation of serum miRNA expression profiles (156). In this large study, a total of 1,280 serum samples from patients with breast cancer were tested. In addition, 2836 serum samples were obtained from non-cancer controls, 451 from patients with other types of cancers, and 63 from patients with non-breast benign diseases. The expression of miRNAs was compared between breast cancer and non-breast cancer patients. The conclusion was that a set of five miRNAs (miR-1246, miR-1307-3p, miR-4634, miR-6861-5p and miR-6875-5p) discriminated breast cancer from healthy control and non-breast cancer patients.
Staging and prognosis
Schröck et al (157) presented a study on free-circulating methylated DNA for the diagnosis, staging and prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. In their study, the DNA methylation of two genes [short stature homeobox 2 (SHOX2) and septin (SepT9)] was quantified in plasma before treatment, and thereafter longitudinally during follow-up. The methylation levels were associated with the tumor and nodal category, and increased DNA methylation levels were associated with a shorter survival. On the whole, the data independently obtained in different laboratories support the hypothesis that the testing of DNA methylation in plasma is a powerful diagnostic tool for staging, risk stratification and disease monitoring. Patients with initially high biomarker levels may benefit from intensified treatment and surveillance. The marker-driven, timely detection of recurrent/metastatic disease may guide successive lines of treatment, thereby improving patient outcomes.
Therapeutic outcome
One example demonstrating the possible role of liquid biopsy in predicting therapeutic outcome has been reported by Quandt et al (158) who discussed how information obtained from liquid biopsies may contribute to the clinical decision-making process for cancer immunotherapy. This issue is of great interest since the application of immune checkpoint blockade over the past decade has revolutionized the treatment of a number of malignancies, leading to significantly improved survival. In this context, liquid biopsies are proposed to monitor treatment efficacy, acquired resistance to therapy and assign prognosis. A second example was published by Goodall et al (159) on cfDNA to guide prostate cancer treatment with poly(ADP)-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibition. They reported whole exome sequencing of serial cfDNA samples collected during the treatment of patients with prostate cancer with the PARP inhibitor, olaparib. Decreases in the cfDNA concentration were found to be associated with a favorable outcome. All tumor tissue somatic DNA repair mutations were detectable in cfDNA, and allelic frequencies of somatic mutations decreased selectively in responding patients. At disease progression, following response to olaparib, multiple sub-clonal aberrations and somatic mutations in DNA repair genes (BRCA2 and PALB2) emerged as mechanisms of resistance. These data support the role of liquid biopsies as predictive, prognostic, response and resistance biomarkers in prostate cancer.
Final considerations on the management of cancer patients, follow-up and treatment monitoring
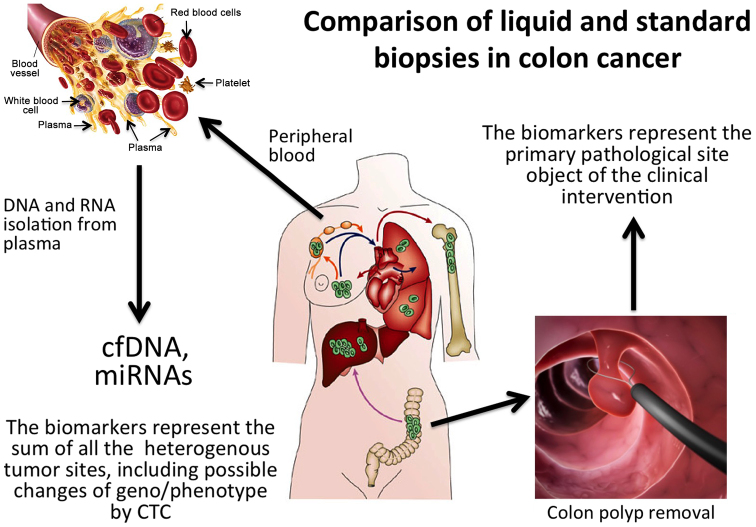
The results obtained thus far have indicated that liquid biopsy considerably affects systemic cancer therapy in metastatic cancer, due to the relevant information it provides to the medical oncologist. This is expected to improve key clinical parameters, such as patients overall survival and quality of life. This should be considered a major advantage of liquid biopsy (as outlined in Fig. 3), since the tissue biopsy of metastatic foci, is not only invasive, but is limited to certain locations, does not reflect clonal heterogeneity and multiple biopsies (even assuming they are feasible) may not be easily accepted, and may ingenerate doubts and contradictory diagnostic reports. Along this line, a droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) study by He et al (160) on 120 patients with a diverse EGFR mutational status supported an association between liquid biopsy and outcome. Of note, it was found that the mutant signature was stable and marked dynamic changes during the treatment allowing efficient and continuous disease profiling, which is expected to greatly facilitate the clinical decision-making process.
Figure 3.
Comparison of liquid and standard conventional tissue biopsies in colorectal cancer (CRC). Tissue biopsy samples single disease sites whereas liquid biopsy potentially samples all tumor sites, including circulating tumor cells.
6. PCR-free detection strategies
Despite the fact that the majority of the analytical technologies are based on PCR and RT-PCR (see the Technologies section above and Tables I and II), PCR-free methods have attracted great interest in biomedicine. In fact, several articles have been published dealing with PCR-free methods for the detection of point mutations. In addition to the already cited limitation of PCR-based approaches, the need for repeated steps involving heating and cooling is an important limitation of all the PCR-based technologies, particularly when the PCR steps for the amplification of nucleic acids are associated with procedures performed in microfluidic-based devices (143,161-164). Several alternative isothermal-amplification methods (which do not require thermal cycling) have been developed to overcome this limitation, including nucleic-acid-sequence-based polymerization (NASBA), loop-mediated amplification (LAMP), helicase-dependent amplification (HAD), rolling-circle amplification (RCA), recombinase-polymerase amplification (RPA) and multiple-displacement amplification (MDA) (142). Recently, isothermal circular-strand-displacement polymerization (ICSPD) has emerged as a novel and promising method for nucleic-acid amplification and detection (163). Finally, promising opportunities are offered by selected isothermal amplification approaches that are based on a simple design of the amplification process and can be integrated in microfluidic devices (142). Such methods allow for the minimization of potential sample contaminations and minimize the sample volume required for the analysis (143). In this respect, the direct detection of point mutations in non-PCR-amplified human genomic DNA has been recently demonstrated by surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPR-I). Attomolar concentrations of target genomic DNA have been detected, demonstrating the ultra-sensitivity of the new method and its potential application in several biomedical fields, including liquid biopsy methods (164).
7. Patents and clinical trials on liquid biopsy and ultrasensitive detection systems
Tables III (165-173) and IV (174-182) summarize patents and patent applications related to the development of liquid biopsy protocols in cancer diagnosis. It is of interest to go through the claims of these patents, as they reflect the consideration given to liquid biopsy by a large part of the scientific community. Several patents build on the concept that mutations of tumor-associated genes (present in cfDNA from body fluids) and/or miRNA profiles are prognostic (associated with outcome), and/or predictive (associated with susceptibility to specific treatments). Examples of patents related to cfDNA and miRNAs are numerous and have steadily increased over the years. In fact, CTC counts, and molecular signatures originating from or associated with CTCs have been shown to be associated with conventional cancer molecular genotyping in tissues.
Table III.
Examples of patents and patent applications on circulating free DNA (cfDNA) based liquid biopsy in oncology.
| Patent or patent application/(Refs.) | Date | Title | Inventors (location) | Original assignee or co-assignee | Short description (claims) | Validity, significance and biomedical applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9255926B2 (165) | February 9, 2016 | Hematopoietic cell phenotyping using circulating cell-free markers | Albitar M (Coto De Caza, CA, USA) | Quest Diagnostics Investments LLC (Wilmington, DE, USA) | This invention provides methods or classifying clusters of differentiation (CD) marker phenotype for hematopoietic cancer cells using multiple circulating cell-free CD markers in body fluid. Furthermore, treatment and disease progression can be monitored by measuring the levels of CD and other markers in body fluids | A method for predicting survival or remission duration in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) |
| EP2426217A1 (166) | March 7, 2012 | Analytical methods for cell free nucleic acids and applications | Thierry A (Saint Clement, France) and Molina F (Les Matelles, France) | Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) (Paris, France) | This invention is based on an in vitro method for detecting cell free nucleic acids, preferably circulating free DNA (cfDNA) in a body fluid sample from an individual or a patient, wherein the method comprises the step of accurately and sensitively determining the concentration of cell free nucleic acid in the sample and/or the index of integrity and/or the determination of the presence of genetic polymorphisms (SNPs) or mutations). The invention also encompasses a method to discriminate body fluid individuals where cfDNA are highly released | A method for diagnosis, prognosis a pathological or physiological state, such as the presence of a tumor or tumor progression in a patient, or a theranostic method comprising i) determining said pathological or physiological state in a patient, including the assessment of the progression of a tumor or metastatic cancer; and ii) monitoring the efficacy of a cancer treatment in a patient |
| US9062350B2 (167) | June 23, 2015 | Method of mutation detection in blood cell-free DNA using primer extension (PE) and PCR | Platica O (New York, NY, USA) | US Department of Veterans Affairs (Washington, DC, USA) | A method for detecting mutations in blood cell-free DNA, including providing a serum sample, isolating DNA, amplifying the DNA by PCR, subjecting the PCR product to primer extension (PE), separating the PE reaction product and identifying the mutation by gel electrophoresis. In order to improve accuracy and sensitivity, the PE reaction can be carried out using a primer that blocks the extension of the wild or non-mutated sequence | The method includes the following major steps: i) Subjecting the serum sample to whole genome DNA amplification; ii) amplifying the DNA by a first PCR; iii) re-amplifying a portion of the reaction product by a second PCR by using specific reverse primers; iv) subjecting the reaction product to primer extension (PE); and v) separating the final reaction product and identifying mutation by gel electrophoresis or chemiluminescence |
| US7718364B2 (168) | May 18, 2010 | DNA markers for management of cancer | Hoon DSB (Los Angeles, CA, USA) and Taback B (Santa Monica, CA, USA) | John Wayne Cancer Institute (Santa Monica, CA, USA) | A method is provided for assessing allelic losses and hypermethylation of genes in the CpG tumor promoter region on specific chromosomal regions in cancer patients, including patients with melanoma, neuroblastoma breast, colorectal and prostate cancer. The method relies on the evidence that free DNA and the hypermethylation of genes in the CpG tumor promoter region may be identified in the bone marrow, serum, plasma and tumor tissue samples of cancer patients | A method of detecting DNA markers in a sample, comprising: i) Providing a cell-free bone marrow sample from a subject; and ii) detecting one or more DNA markers in the sample, wherein the DNA markers are indicative of LOH or DNA hypermethylation, or the DNA markers are indicative of DNA mutation in KRAS or BRAF gene |
| EP2483426A4 (169) | April 10, 2013 | Method for analysis of DNA methylation profiles of cell-free circulating DNA in bodily fluids | Cortese R and and Petronis A | Centre for Addiction and Mental Health | This invention regards a variety of methods and compositions for obtaining epigenetic information, such as DNA methylation patterns, through the preparation, amplification and analysis of Methylome libraries. In several aspects of the present invention, there are methods based on methylation-dependent enrichment or depletion of genomic DNA isolated from cellular and cell-free sources. In additional embodiments, there are methods and compositions for single-step high throughput preparations of Methylome libraries | Genomic regions that are actively expressed within cells are often found to be hypomethylated in the promoter and upstream coding regions. By contrast, downstream regions are typically kept hypermethylated in actively transcribed genes, but become hypomethylated in cancer. On the other hand, the hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes has been associated with the development of many forms of cancer |
| US20140303008A1 (170) | October 9, 2014 | Colorectal cancer associated circulating nucleic acid biomarkers | Schutz E (Göttingen, Germany), Beck J (Göttingen, Germany) and Urnovitz H (San Jose, CA, USA) | Chronix Biomedical | The methods consists of detecting biomarkers in body fluids of patients with colorectal cancer. The proposed biomarkers are polynucleotide fragments, e.g., DNA fragments, that are present at an elevated level in blood, e.g., in a serum or plasma sample, of a colorectal cancer patient in comparison to the level in blood, e.g., a serum or plasma sample, obtained from a normal individual who does not have colorectal cancer | This invention provides methods and reagents for diagnosing colorectal cancer that are based on the detection of biomarkers in the circulating nucleic acids from a patient to be evaluated |
| WO2016168844A1 (171) | October 20, 2016 | Quality assessment of circulating cell-free DNA using multiplexed droplet digital PCR | Murtaza M and Contente-Cuomo T | The Translational Genomics Research Institute | This invention provides a method of determining integrity and/or quantity of cfDNA in a biological sample. The present invention also provides methods for generating a library with the cfDNA for sequencing and analysis | This invention provides methods for the diagnosis of cancer that are based on the release of cfDNA from the patient to be evaluated |
| WO2006128192A2 (172) | November 30, 2006 | Use of free circulating DNA for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of cancer | Hoon DSB, Umetani N and Sunami E | John Wayne Cancer Institute | This invention provides a method to determine the sequence integrity of circulating DNA using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), microarrays, probes by blotting, or gel electrophoresis based, colorimetric detection assays such as ELISA, chemiluminescence methods, digital detection, and mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF). The methylation integrity of the circulating DNA may be detected and quantified, e.g., using quantitative analysis of methylated alleles (QAMA), qPCR, gel electrophoresis, microarrays, mass spectrometry, digital detection, or colorimetric based methods The total amount of the circulating DNA is indicated by the amount of ALUs and LINEs | The method comprises identifying a subject suffering from or at risk for developing cancer, obtaining a body fluid sample from the subject, and determining the sequence integrity of circulating DNA. The body fluid sample may be, a sample of serum, plasma, urine, saliva, bone marrow, lymphatic fluid, lacrimal fluid, serous fluid, peritoneal fluid, pleural fluid, ductal fluid from breast, gastric juice, or pancreatic juice. A cancer may be a breast cancer, colorectal cancer, periampullary cancer, melanoma, prostate cancer, gastric cancer, leukemia/lymphoma, renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, neural-derived tumor, head and neck cancer, lung cancer, or sarcoma |
| US20160053301A1 (173) | February 25, 2016 | Methods for quantitative genetic analysis of cell free DNA | Raymond CK, Lim LP and Armour CD | Clearfork Bioscience Inc., Resolution Bioscience Inc. | The invention provides a method for the genetic analysis of individuals that reveals both the genetic sequences and chromosomal copy number of targeted and specific genomic loci in a single assay. The present invention further provides methods for the sensitive and specific detection of target gene sequences and gene expression profiles. The key objective of the method is performing a quantitative genetic analysis of one or more target genetic loci in the cfDNA library clones. | The cfDNA is isolated from a biological sample selected from the group consisting of: amniotic fluid, blood, plasma, serum, semen, lymphatic fluid, cerebral spinal fluid, ocular fluid, urine, saliva, stool, mucous, and sweat. The analyzed genetic lesion comprises a genomic rearrangement that fuses the 3′ coding region of the ALK gene to another gene (for example the EML4 gene) |
For instance, in EP2426217A1 (166) a method is described for detecting cell free nucleic acids, preferably cfDNA in a body fluid sample from an individual or a patient. A general claim, present in many other similar patent applications, relates to a method that comprises the step of accurately and sensitively determining the concentration of cell free nucleic acids in the sample and/or the index of integrity of said cell free nucleic acid and/or the determination of the presence of genetic polymorphisms [such as known single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or mutations]. The invention encompasses also a method to discriminate body fluid individuals where cfDNA are highly released. The majority of the approaches described in Table III have been validated on a variety of body fluids (urine, saliva, serum, plasma, bone marrow, lymphatic fluid, lacrimal fluid, serous fluid, peritoneal fluid, pleural fluid, ductal fluid from breast, gastric juice, or pancreatic juice) and cancers [breast cancer, CRC, periampullary cancer, melanoma, prostate cancer, gastric cancer, leukemia/lymphoma, renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), neural-derived tumor, head and neck cancer, lung cancer, or sarcoma]. In addition to SNPs and tumor-associated mutations (presented in EP2426217A1, US7718364B2, WO2016168844A1 and US20160053301A1) (166,168,171,173), another interesting marker is DNA methylation. In US7718364B2 (168), a method is provided for assessing allelic losses and the hypermethylation of genes in the CpG tumor promoter region on specific chromosomal regions in patients suffering from melanoma, neuroblastoma, breast, colorectal and prostate cancer. The method is based on the evidence that free DNA and hyper-methylation of genes in the CpG tumor promoter region may be identified in the bone marrow, serum, plasma and tumor tissue samples of cancer patients. Table III lists examples of patents and patent applications focusing on cfDNA analysis in the body fluids of cancer patients.
As far as miRNAs are concerned, US8216784B2 (175) and EP2806273B1 (176) deal with cancer-derived microvesicle-associated miRNAs as a diagnostic marker for the detection of cancer. The method is based on the analysis of one or more miRNAs selected from a group comprising miR-21, miR-141, miR-200a, miR-200b, miR-200c, miR-203, miR-205 and miR-214. The method can be applied to a variety of biologicals, including milk, blood, serum, plasma, ascites, cyst fluid, pleural fluid, peritoneal fluid, cerebral spinal fluid, tears, urine, saliva, sputum, or combinations thereof. EP3011058A1 (178) is an example of patents focusing on total miRNA analysis. In addition, in this case, a shortlist of candidate miRNAs is provided, such as the combination of miR-365, miR-425, miR-143, miR-133a, miR-15a and miR-18a. The alteration in the level of the miRNA in the test sample (such as serum, plasma, or whole blood), relative to the level of a corresponding miRNA in a control sample, is indicative of the subject either having, or being at risk of developing, cancer, or the response of a subject to any treatment for the cancer. Further examples of miRNAs identified as cancer biomarkers are shown in Table IV.
Table IV.
Examples of patents and patent applications on circulating microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) for non-invasive liquid biopsy in oncology.
| Patent or patent application/(Refs.) | Date | Title | Inventors | Original assignee or co-assignee | Short description (claims) | Validity, significance and biomedical applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9896683B2 (174) | February 20, 2018 | Isolating circulating microRNA (miRNA) | Ambros V, Lee R and Fusco AP | Firefly Bioworks University of Massachusetts (UMass) | Methods for isolating circulating small RNAs, e.g., miRNAs from plasma samples, e.g., that involve the use of an alkaline phenol:chloroform extraction, and methods of use thereof, including for the detection, prognosis, and/or monitoring of disease in a subject | The methods include providing a first sample comprising plasma or serum of the human subject; detecting a level of one or more circulating miRNAs; providing a second sample comprising plasma or serum at a second time point; detecting a level of the one or more circulating miRNAs in the second sample using the same method; and comparing the level of the miRNA in the first sample to the level of the miRNA in the second sample |
| US8216784B2 (175) | July 10, 2012 | Cancer-derived microvesicle-associated microrna as a diagnostic marker | Taylor DD and Gercel-Taylor C | University Of Louisville Research Foundation, Inc. | A method for assessing the presence of one or more microRNAs in microvesicles, comprising isolating a population of cancer-derived microvesicles from a biological sample using a microvesicle surface marker, isolating microRNA from said population of cancer-derived microvesicles and determining a presence of one or more microRNAs in said cancer-derived microvesicles | The method can be applied to a variety of biological including milk, blood, serum, plasma, ascites, cyst fluid, pleural fluid, peritoneal fluid, cerebral spinal fluid, tears, urine, saliva, sputum, or combinations thereof. The method is based on the analysis of one or more microRNAs selected from the group consisting of miR-21, miR-141, miR-200a, miR-200b, miR-200c, miR-203, miR-205 and miR-214 |
| EP2806273B1 (176) | September 6, 2017 | Exosome-associated microRNA as a diagnostic marker | Taylor DD and Gercel-Taylor C | University of Louisville Research Foundation, Inc. | A method is described for assessing the presence of one or more microRNAs in microvesicles, comprising isolating a population of microvesicles from a biological sample using a microvesicle surface marker, isolating microRNA from said population of microvesicles and determining a presence of one or more microRNAs in said microvesicles | As one example, ovarian cancer remains the sixth most common type of cancer affecting women worldwide, causing approximately 125,000 deaths annually. Since long-term survival has not altered significantly over the past few decades, the best prospects for further improvement of ovarian cancer survival reside in early diagnosis |
| US20130324589A1 (177) | December 5, 2013 | Methods for Diagnosing Pancreatic Cancer Using MicroRNAs | Croce CM, Calin GA and Volinia S | Ohio State University | Described herein are methods for diagnosing pancreatic cancer using miRNAs | Also described are methods and compositions for the diagnosis and treatment of solid cancers. Methods of identifying inhibitors of tumorigenesis are also provided |
| EP3011058A1 (178) | April 27, 2016 | Circulating microRNA based cancer biomarkers | Ditzel H and Kodahl AR | Syddansk Universitet | A method of diagnosing whether a subject has, or is at risk of developing cancer, such as breast cancer or colorectal cancer, or monitoring the progression or regression of said cancer in a subject. The method comprises measuring the level of at least one miR-365, miR-425, miR-143, miR-133a, miR-15a, and miR-18a, such as the combination of miR-365, miR-425, miR-143, miR-133a, miR-15a and miR-18a | The alteration in the level of the miRNA in the test sample (such as serum, plasma, or full blood), relative to the level of a corresponding miRNA in a control sample, is indicative of the subject either having, or being at risk for developing, cancer, or respond to any treatment of the cancer |
| EP3138926A3 (179) | April 5, 2017 | MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer | Croce CM | The Ohio State University Research Foundation | The present invention provides novel methods for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer using at least one miR selected from miR-200b, miR-141, miR-199a, miR-140, miR-145 and miR-125b, miR-200c | The invention also provides methods of identifying anti-ovarian cancer agents and a kit for detecting ovarian cancer |
| EP2944700B1 (180) | October 18, 2017 | Plasma microRNAs for the detection of early colorectal cancer | Gironella I Cos M, Lonzano-Salvatella JJ, Castells I Garangou A and Giraldez MM | Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBEREHD) | The method comprises the following steps: i) Measuring an overall expression pattern or level of miRNAs obtained from one or more biological samples (wherein at least those miRNAs are miR18a and optionally miR19a and miR19b and miR15b); ii) comparing the overall expression pattern of miRNAs from the biological sample of the subject suspected of suffering from advanced colorectal adenomas or colorectal neoplasia with the overall expression pattern of the miRNAs from a biological sample of a normal subject | The present invention refers to a method for the diagnosis or detection of advanced colorectal adenomas and optionally colorectal neoplasia in a subject |
| US9388470B2 (181) | July 12, 2016 | Serum or plasma microRNA as biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer | Zhang C, Zeng K, Zhang J, Ba Y, Chen X and Li H | Micromedmark Biotech Co. Ltd. | The present invention provides non-small cell lung cancer markers and the use thereof in diagnosing and monitoring diseases in vitro. The non-small cell lung cancer markers include at least one of the 26 selected detectable mature miRNAs existing stably in human serum or plasma. The invention also provides probe combinations, a kit and biochip for detecting the non-small cell lung cancer markers | The method in the present invention enables extensive detection spectrum, high sensitivity, low cost, convenient sample taking and preservation; it can be applied the general survey of disease, solves issues with the low specificity and sensitivity encountered with previous single markers, and significantly increases the clinical detection rate of diseases |
| US8603744B2 (182) | December 10, 2013 | Methods for diagnosing breast cancer using MicroRNAs | Croce CM, Calin GA and Volinia S | Ohio State University | The alteration (e.g., an increase, a decrease) in the level of the miRNA is indicative of the subject either having, or being at risk for developing, a solid cancer. At least one miRNA measured in the test sample is selected from the group consisting of miR-21, miR-17-5p, miR-191, miR-29b-2, miR-223, miR-128b, miR-199a-1, miR-24-1, miR-24-2, miR-146, miR-155, miR-181b-1, miR-20a, miR-107, miR-32, miR-92-2, miR-214, miR-30c, miR-25, miR-221, miR-106a and combinations thereof | The present invention provides novel methods and compositions for diagnosis and treatment of solid cancers. The solid cancer can be any cancer that arises from organs and solid tissues, such as stomach cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer or prostate cancer |
Liquid biopsy is implemented (and is technologically tested) in several ongoing clinical trials (Tables V and VI) (183-204). For instance, NCT02639832 (183) is focused on the presence of tumor-derived CTCs or ctDNA using an investigational medical device known as the LiquidBiopsy. Using the LiquidBiopsy platform, recovered cells or DNA can also be investigated to obtain genetic information that may be useful to physicians for treating and understanding disease. The LiquidBiopsy device is able to purify the tiny numbers of tumor cells or ctDNA in blood. Even if a tumor is too small to be found by other means, such as an X-ray, it is possible that ctDNA or CTCs may be found in the blood. Genetic information can then be recovered from these cells or DNA to identify genetic alterations that are related to abnormal growth in a tumor. The proponents claim that this will potentially allow researchers to study tumor cells or tumor DNA from a blood sample instead of a biopsy sample, and may influence cancer diagnosis, treatment and drug selection in the future. In NCT02784639 (195) a method is employed which simultaneously allows the determination of three parameters: The specific quantification of tumor-derived ccfDNA, the ccfDNA fragmentation index and SNP or point mutation detection. The evaluation and validation of the method will be performed by determining the KRAS/BRAF mutational status prior to anti-EGFR therapy in patients with CRC. The protocol will detect the six most frequent KRAS mutations in CRC (G12D, G12V, G13D, G12S, G12C and G12A) and BRAF V600E. The goal of this multicenter prospective study is to validate, and ultimately translate in routine clinical practice, the use of plasma analysis of cfDNA for the determination of KRAS mutation status in patients with CRC. Table V lists several examples of ongoing clinical trials based on the analysis of cfDNA in breast, lung, colorectal, stomach, gastric and pancreatic cancers, HCC, non-Hodgkin lymphoma and melanoma.
Table V.
Clinical trials focusing on circulating tumor cells and/or circulating free DNA (cfDNA).
| ClinicalTrials.gov identifier/(Refs.) | Start date | Title | Sponsors, collaborators and investigators (location) | Short description | Condition(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02639832 (183) | First received: December 10, 2015; Last updated: August 8, 2016 | A pilot surveillance study to monitor Natural Killer Cells and Circulating Tumor Cells in women with previously treated non-metastatic triple negative breast cancer and women with previously treated non-metastatic breast cancer with a confirmed BRCA miitntinn | Sponsor: Cynvenio Biosystems, Inc. (Westlake Village, CA, USA) | The purpose was to test blood for the presence of tumor derived Triple-negative breast circulating tumor cells (CTCs) or circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) cancer using an investigational medical device. This LiquidBiopsy® device is able to purify low numbers of tumor cells or low amounts of ctDNA in the blood. Even if a tumor is too small to be found by other means such as an x-ray, it is possible that ctDNA or CTCs may be found in the blood. Genetic information can then be recovered from these cells or DNA to look for genetic changes that are related to the abnormal growth in a tumor. This will potentially allow researchers to study tumor cells or tumor DNA from a blood sample instead of a biopsy sample. This may influence cancer diagnosis, treatment and drug selection in the future | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| NCT02626039 (l84) | First received: October 15, 2015; Last updated: March 9, 2017 | Characterization & comparison of drugable mutations in primary and metastatic tumors, CTCs and cfDNA in MBC patients | Sponsor: Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañon; Principal investigator: Martín M (Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañon, Madrid, Spain) | In the study, it is hypothesized that breast cancer métastasés and Metastatic breast primary tumors can harbor different genomic profiles related to cancer genomic regions of interest in a clinically relevant proportion of metastatic breast cancer patients. Furthermore, the genomic aberrations found in the metastatic breast cancer tissue can also be detected in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and cfDNA. The study will evaluate whether CTCs and cfDNA would be convenient, non-invasive, easily accessible sources of genomic material for the analysis of mutations and other genomic aberrations | Metastatic breast cancer |
| NCT02186236 (185) | First received: July 7, 2014; Last updated: September 27, 2016 | Detection of oncogenic tumor mutations in the urine and blood of lung and colorectal cancer patients | Sponsor: Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center; Collaborator: Trovagene, Inc. ; Principal investigator: Yu H (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center | The purpose of the study is to determine whether gene mutations Lung cancer; can be found in the urine or blood of patients with lung cancer and colorectal cancer the urine of patients with colorectal cancer. The study is based on gene mutations that are only found in lung and colorectal cancer cells, but not in normal cells. In the study, a plasma-based assay is applied to determine the presence of EGFR mutation in CTC and in cfDNA | Lung cancer; colorectal cancer |
| NCT02788084 (186) | First received: May 25, 2016; Last updated: June 27, 2017 | Development of a tissue-based & cell free DNA next-generation sequencing workflow | Sponsor: Alberta Health Services, Calgary; Principal investigator: Mähe E (FRCPC; Calgary Laboratory Services, University of Calgary) | In the study, blood samples will be prospectively collected scheduled follow-up and if the primary objectives of this study are met, the presence of cfDNA and the impact of variation on clinical outcomes will be assessed. A next generation sequencing (NGS) workflow will be developed for the mutation profiling of cfDNA specimens. The major issue is to calculate the proportion of cases in a test series of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (BNHL) with somatic mutations or immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH) gene rearrangements. Participant data will be collected, and clinical outcomes will be assessed to determine the effect of mutation profiles on outcomes over a two-year follow-up | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| NCT02883517 (187) | First received: August 25, 2016; Last updated: February 23, 2017 | Cell-free circulating DNA in primary cutaneous lymphomas | ^ Sponsor: University Hospital, Bordeaux; Principal Investigator: Pham-Ledard A (University Hospital, Bordeaux, France) | This study is based on the concept that liquid biopsies allowing the detection of tumor mutation in plasma have been validated in nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. The purpose of the study is to evaluate the possibility to detect cell-free circulating tumor DNA in primary cutaneous lymphomas, using a highly sensitive method (digital PCR), combined with a next generation sequencing panel of the tumor sample | Lymphoma, large B-cell |
| NCT02887612 (188) | First received: May 14, 2016; Last updated: January 17, 2018 | ctDNA for prediction of relapse in gastric cancer | Sponsor: Sun Yat-sen University; Principal Investigator: Xu R (Sun Yat-sen University) | By monitoring the serum ctDNA mutational profile using NGS, the present clinical trial aims to elucidate the association between the serum ctDNA status and the prognosis of patients with early and intermediate-stage gastric cancer upon surgical treatment, and to explore the possibility of clinical utility of serum ctDNA as a clinical index to predict post-operative relapse. Furthermore, by comparing the molecular profiles of patients with different prognosis, it will be possible to identify molecular markers related to the prognosis of gastric cancer | Stomach neoplasms |
| NCT02738593 (189) | First received: April 6, 2016; Last updated: April 14,2016 | Detection Cell Free DNA in lung cancer patients | :Sponsor: Sun Yat-Sun University Cancer Center (Guangzhou, China); Principal investigator: Zhang L (Sun University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China) | The study is based on next generation sequencing as the most sensitive and specific method to examine gene mutation and diversion. Eligible patients receiving 3rd generation EGFR-TKIs (AZD9291 and AVITINIB) were enrolled in this study. Tumor tissue sample within 6 months, and 10 ml peripheral blood samples were collected at baseline. Following treatment initiation, 10 ml peripheral blood would be collected at every image testing time point until disease progression. Blood samples will be draw using EDTA tube and centrifuged within 2 h and store at −80°C in a refrigerator. NGS testing will cover target genes of non-small cell lung cancer | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| NCT02610218 (190) | First received: November 18, 2015; Last updated: October 31, 2017 | Liquid biopsy in monitoring the therapeutic efficacy of targeted therapy in advanced/meta-static gastric cancer | Sponsor: Peking University (Beijing, China) | The study is undertaken in patients with both histologically HER2-positive and -negative advanced/metastatic gastric cancer. Peripheral blood samples are collected from the patients for cfDNA and CTC analysis (before therapy, at the time that the patients achieve the optimal response and when they suffer progressive disease). The enumeration of CTCs, as well as the detection of HER2 expression will be achieved via the integrated subtraction enrichment (SET) and immunostaining-fluorescence in situ hybridization (iFISH) platform. Furthermore, for the genomic analysis, the enriched single CTC will be isolated for single-cell targeted sequencing. While for cfDNA analysis, extracted DNA from plasma will be directly subjected to targeted sequencing. The association of the HER2 status on CTCs and the HER2 amplification in cfDNA to the therapeutic response will be evaluated. Moreover, genetic variations associated with resistance in HER2-targeted therapy will be also studied based on the genomic data from sequencing of CTC and cfDNA | Gastric cancer |
| NCT02872779 (191) | First received: August 16, 2016; Last updated: August 22, 201 | Correlation between circulating tumour markers early variations and 7 clinical response in first line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (COCA-MACS) | Sponsor: University Hospital, Rouen (Rouen, France); Principal investigator: Gangloff A (University Hospital, Rouen, Rouen, France) | The aim of the present study is to evaluate, in a prospective cohort of patients treated with systemic IV chemotherapy (5-fluorouracil +/− oxaliplatin +/− irinotecan) +/− targeted therapy as first line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer, the correlation between early variations of circulating tumor markers including CEA, circulating tumor DNA and total cell free DNA, and the 3-month objective response as defined in the RECIST 1.1 guideline | Metastatic colorectal cancer |
| NCT02443948 (192) | First received: March 19, 2015; Last updated: February 14, 2017 | Circulating cell-free tumor DNA in the plasma of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) | Sponsor: Fondazione del Piemonte per l'Oncologia | This study is based on the fact that cf-DNA may become an efficient marker of the mutational GIST status and disease itself. On this basis, this trial aims to evaluate whether tumor DNA carrying mutations (for KIT, PDGFRa, BRAF, RAS and SDH) can be detected and quantified in the plasma of patients with GISTs, either with active disease or during follow-up, and whether detection can be associated with the disease status | Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) |
| NCT02133222 (193) | First received: April 30, 2014; Last updated: October 21, 2016 | Circulating cell-free DNA in metastatic melanoma patient: Mutational analyses in consecutive measurement before and after chemotherapy ÍAMMAM) | Sponsor: Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nice (Nice, France); Principal investigator: Long-Mira E (CHU de Nice, Nice, France) | In recent years, BRAF and KIT have become established therapeutic targets in patients with melanoma showing activating mutations in these oncogenes. However, it is crucial that genetic mutations present in the melanoma lesions are identified if the investigators are to design tailormade therapies for individual patients. The aim of the study is to determine the mutational status in circulating DNA in patients with melanoma metastatic, with the Sequenom Mass Array, a next generation sequencing technology. Results obtained before and after treatment will be comnared with the nrimarv tumor 2enotvne | Metastatic (Stage IV) melanoma |
| NCT02934984 (194) | First received: October 13, 2016; Last updated: October 17, 2016 | Circulating cell-free tumor DNA (ctDNA) in pancreatic cancer | Sponsor: Samsung Medical Center (Seoul, Republic of Korea) | In this study, ctDNA of patients with pancreatic cancer who underwent surgery will be collected, and it will be evaluated whether peripheral ctDNA can aid in the early screening of cancer recurrence. The genomic signature of ctDNA will be determined to evaluate the association between ctDNA and the clinical outcome of cancer patients | Pancreatic cancer |
| NCT02784639 (195) | First received: May 24, 2016; Last updated: August 3, 2016 | Comparison of KRAS/BRAF mutational status with conventional techniques and plasma samples analysis | Sponsor: Y chou M (Institut régional du Cancer de Montpellier, Montpellier, France); Principal investigator: Y chou M (Institut régional du Cancer de Montpellier, Montpellier, France) | In this study, a method is employed which simultaneously allows the determination of three parameters: The specific quantification of tumor-derived ccfDNA, the ccfDNA fragmentation index, and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) or point mutation detection. The evaluation and validation of the method will be performed by determining the KRAS/BRAF mutational status before anti-EGFR therapy in patients with colorectal cancer. The protocol will detect the six more frequent KRAS mutations in CRC (G12D, G12V, G13D, G12S, G12C and G12A) and the BRAF V600E. The goal of this multicenter prospective study is to validate, and ultimately translate into routine clinical practice, the use of plasma analysis of cfDNA for the determination of KRAS mutation status in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer | Colorectal cancer |
| NCT02036216 (196) | First received: January 7,2014; Last updated: January 14, 2014 | Circulating cell-free DNA as a predictive biomarker for hepatocelluar carcinoma | Sponsor: Peking Union Medical College Hospital (Beijing, China); Collaborator: Stanford University; Principal investigator: Mao Y (Peking Union Medical College Hospital (Beijing, China) | This study is based on technologies exhibiting high sensitivity and specificity detection developed at the Stanford Genome Technology Center. Some cfDNA characteristic changes, such as pl61NK4A, RTL, RASSF1A, LINE-1 and GSTP1, will be examined in hepatocellular carcinoma, since studies have shown that cfDNA level is associated with 1 intrahepatic and extra-hepatic metastasis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. In the study, these characteristic changes in cfDNA and primary tumor lesions will be investigated. The possible applications in early diagnosis, treatment monitoring and prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma will be evaluated | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| NCT02791217 (197) | First received: May 30, 2016; Last updated: June 6, 2016 | Identification of hematological malignancies and therapy predication using microRNAs as a diagnostic tool | Sponsor: Assuta Medical Center; Collaborator: Laniado Hospital | The objective of the trial is related to the early diagnosis of very aggressive hematological malignancies as an essential approach for improving prognosis and increasing survival rates. The early diagnosis is based on the analysis of circulating miRNAs, considering that current diagnostic methods have various limitations, such as insufficient sensitivity, specificity, require time-consuming and costly approaches, and a high level of expertise, limiting applications in clinical contexts. Thus, the development of novel biomarkers (miRNAs) for the early detection and relapse of hematological malignancies is desirable. The approach is based on the readily-made detection of miRNAs in small-volume samples using specific and sensitive quantitative PCR | Lymphoma, B-Cell; follicular lymphoma; Hodgkin lymphoma; multiple myeloma |
| NCT02928627 (198) | First received: October 7, 2016; Last updated: October 25, 2017 | Clinical significance of hepatic and circulating microRNAs miR-221 and miR-222 in hepatocellular carcinoma | Sponsor: University of Aberdeen; Collaborator: Robert Gordon University; Principal investigator: Soggiu F (NHS Grampian) | It has been shown that miRNAs play a role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma, but it is unknown whether these molecules can be used as markers for diagnosis and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. In particular, the miRNAs miR-221 and miR-222 are dysregulated in tumor tissues in approximately 80% of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. The aim of this study is to evaluate whether these two miRNAs are expressed not only in tumor tissues, but also in blood from cancer patients, and in different amounts compared to circulating levels in healthy individuals. The possible association between tumor tissue and blood levels will also be evaluated | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| NCT02964351 (199) | First received: November 8, 2016; Last updated: November 16, 2016 | MicroRNA profiles identification in adenocarcinoma prostate cancer | Sponsor: Assuta Medical Center; Principal investigator: Goldberg N (Assuta Medical Center) | The main objective of the study is to determine whether an association exists between circulating miRNAs associated with prostate cancer métastasés to bones and to lymph nodes, analyzed by positron emission computed (PET) imaging. miRNA profiles will be assessed by using nano-string technology validated by real-time PCR | Prostate carcino-sarcoma |
| NCT01541800 (200) | First received: February 24, 2012; Last updated: February 5, 2016 | Circulating microRNAs as disease markers in pediatric cancers | Sponsor: Ann & Robert H Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago; Principal investigator: Lulla R (Ann & Robert H Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago) | This study is aimed to evaluate the presence of miRNAs in the blood f and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with central nervous system tumors, leukemia and lymphoma who are currently being treated with & chemotherapy and are undergoing blood draws, lumbar punctures and/or reservoir taps for routine clinical care | Leukemia; lymphoma; central nervous system |
Table VI.
Clinical trials focusing on circulating miRNA detection in cancer diagnostics.
| ClinicalTrials.gov identifier/(Refs.) | History | Title | Sponsors, collaborators and investigators (location) | Short description | Condition(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02791217 (197) | First received: May 30, 2016; Last updated: June 6, 2016 | Identification of hematological malignancies and therapy predication using microRNAs as a diagnostic tool | Sponsor: Assuta Medical Center; Collaborator: Laniado Hospital | The objective of the trial is related to the early diagnosis of very aggressive hematological malignancies as an essential approach for improving prognosis and increasing survival rates. The early diagnosis is based on the analysis of circulating miRNAs, considering that current diagnostic methods have various limitations, such as insufficient sensitivity, specificity, require time-consuming and costly approaches, and a high level of expertise, limiting applications in clinical contexts. Thus, the development of novel biomarkers (miRNAs) for the early detection and relapse of hematological malignancies is desirable. The approach is based on the readily-made detection of miRNAs in small- volume samples using specific and sensitive quantitative PCR | Lymphoma, B-Cell; follicular lymphoma; Hodgkin lymphoma; multiple myeloma |
| NCT02928627 (198) | First received: October 7, 2016; Last updated: October 25, 2017 | Clinical significance of hepatic and circulating microRNAs miR-221 and miR-222 in hepato- cellular carcinoma | Sponsor: University of Aberdeen; Collaborator: Robert Gordon University; Principal investigator: Soggiu F (NHS Grampian) | It has been shown that miRNAs play a role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma, but it is unknown whether these molecules can be used as markers for diagnosis and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. In particular, the miRNAs miR-221 and miR-222 are dysregulated in tumor tissues in approximately 80% of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. The aim of this study is to evaluate whether these two miRNAs are expressed not only in tumor tissues, but also in blood from cancer patients, and in different amounts compared to circulating levels in healthy individuals. The possible association between tumor tissue and blood levels will also be evaluated | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| NCT02964351 (199) | First received: November 8, 2016; Last updated: November 16, 2016 | MicroRNA profiles identification in adenocarcinoma prostate cancer | Sponsor: Assuta Medical Center; Principal investigator: Goldberg N (Assuta Medical Center) | The main objective of the study is to determine whether an association exists between circulating miRNAs associated with prostate cancer metastases to bones and to lymph nodes, analyzed by positron emission computed (PET) imaging. miRNA profiles will be assessed by using nano-string technology validated by real-time PCR | Prostate carcino- sarcoma |
| NCT01541800 (200) | First received: February 24, 2012; Last updated: February 5, 2016 | Circulating microRNAs as disease markers in pediatric cancers | Sponsor: Ann & Robert H Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago; Principal investigator: Lulla R (Ann & Robert H Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago) | This study is aimed to evaluate the presence of miRNAs in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with central nervous system tumors, leukemia and lymphoma who are currently being treated with chemotherapy and are undergoing blood draws, lumbar punctures and/or reservoir taps for routine clinical care | Leukemia; lymphoma; central nervous system |
| NCT02065908 (201) | First received: February 15, 2014; Last updated: December 8, 2016 | Circulating microRNA as biomarker of cardiotoxicity in breast cancer | Sponsor: West Pomeranian Cancer Center; Collaborator: Pomeranian Medical University Szczecin; Principal investigator: Dąbek B (West Pomeranian Cancer Center) | In the proposed project, the investigators will assess whether changes in expression of selected circulating miRNAs in serum could comprise a sensitive and specific biomarker of cardiotoxicity in cancer patients treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy | Breast cancer |
| NCT02812680 (202) | First received: June 14, 2016; Last updated: January 5, 2018 | The utility of circulating tumour cells and plasma microRNA in esophageal adenocarcinoma | Sponsor: University Health Network (Toronto, ON, Canada); Principal investigator: Darling GE (University Health Network (Toronto, ON, Canada) | The goal of this project is to assess the use of circulating miRNAs and circulating tumor cells (CTC) as biomarkers of cancer and predictive markers for neoadjuvant therapy | Esophageal cancer |
| NCT01612871 (203) | First received: June 4, 2012; Last updated: March 5, 2018 | Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers of hormone sensitivity in breast cancer (MIRHO) | Sponsor: Institut Claudius Regaud; Principal investigator: Dalencr F (Institut Claudius Regaud) | This is a biomedical and prospective study of the interventional type, conducted in women with metastatic invasive breast cancer or locally advanced breast cancer and for which treatment with tamoxifen or anti- aromatase (first line hormone therapy for metastatic breast cancer) is indicated. The main objective of this pilot study is to evaluate the feasibility to detect in the circulating blood of patients the presence of the fifteen miRNAs described in preclinical studies as possibly involved in hormone resistance/sensitivity | Breast cancer |
| NCT01722851 (204) | First received: October 24, 2012; Last updated: August 10, 2017 | Circulating miRNAs. ICORG 10-11, V2 | Sponsor: Cancer Trials Ireland | The main objective of the study is to identify a panel of circulating miRNA markers which could help to identify patients with breast cancer who are most likely to respond well to neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy, and indeed serve as an overall prognostic factor and stratify patients into risk categories which would further guide their management. A suitable panel of markers would show significant changes in expression level in good-responders whilst little or no change would be observed in miRNA expression in non-responders | Breast cancer |
As regards clinical trials related to miRNAs, one example is NCT02928627 (198), which is focused on miRNAs, such as miR-221 and miR-222, that are both dysregulated in the tumor tissues in approximately 80% of patients with HCC. The aim of that study was to evaluate whether these two miRNAs are overexpressed not only in tumor tissues, but also in the blood of cancer patients. An association between tumor tissue and blood levels will also be evaluated. Table VI lists additional examples of ongoing clinical trials in breast, esophageal and prostate cancer, HCC, lymphoma and leukemias.
8. International Networks focusing on liquid biopsy
The interest in non-invasive tumor diagnosis by liquid biopsy is demonstrated by several international projects supported by public funding. A few selected examples (LIQBIOPSENS, CANCER-ID, PRECISE, BILOBA and ULTRAPLACAD) are reported in the following sections irrespectively of their success in terms of delivered products (manuscripts, validated protocols and platforms, or patents).
LIQBIOPSENS (Reliable Novel Liquid Biopsy technology for early detection of CRC)
This Horizon-2020 project is based on a reliable novel liquid biopsy technology for the early detection of CRC using multidisciplinary approaches involving microelectronics, microfluidics, nanomaterials and genomics. The overall aim of LIQBIOPSENS is the further development and validation in real settings of a novel diagnostic platform for the early and rapid detection of ctDNA and their KRAS and BRAF mutations associated with CRC through blood samples. This sensitive (in the zM range) assay includes 27 KRAS and BRAF mutations, to be simultaneously analyzed. Other main features of LIQBIOPSENS are reliability, low-cost and short analysis time. Furthermore, a user-friendly and flexible interface is provided. Among the participants are DestiNA Genomics Ltd. (UK); the Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas, Greece; the Servicio Andaluz del Salud, Spain; BEABLE SL, Spain; Université Catholique de Louvain, Belgium and Sistemas Genomicos SL, Spain (http://liqbiopsens.com).
CANCER-ID (cancer treatment and monitoring through the identification of CTCs and tumor-related nucleic acids in blood)
This is a newly formed European consortium funded by the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) with currently 33 partners from 13 countries aiming at the establishment of standard protocols for, and the clinical validation of, blood-based biomarkers. It brings together experts from academic and clinical research, innovative small-to-medium sized enterprises (SMEs), diagnostics companies and the pharmaceutical industry, thus providing a unique setting for establishing clinical utility of liquid biopsy. The academic leads of the CANCER-ID consortium are Professor Klaus Pantel, Head of the Department of Tumor Biology at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany, and Professor Leon Terstappen, Head of the Department of Medical Cell Biophysics at the University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands. The lead companies of the CANCER-ID consortium are Bayer HealthCare and Silicon Biosystems, A Menarini Group Company (http://www.cancer-id.eu).
PRECISE (Personalized Engine for Cancer Integrative Study and Evaluation)
This project is an Horizon-2020 pilot project that combines hypothesis-driven strategies with data-driven analysis in a novel mathematical and computational methodology for the integration of genomic, epigenetic, transcriptomic, proteomic and clinical data with the goal of risk-stratifying patients and suggesting personalized therapeutic interventions. As far as motivation is concerned, the PRECISE project is based on the concept that, despite their great promise, high-throughput technologies in cancer research have often failed to translate to major therapeutic advances in clinical practice. One challenge has been tumor heterogeneity, where multiple competing subclones co-exist within a single tumor. Genomic heterogeneity renders it difficult to identify all driving molecular alterations, and thus results in therapies that only target subsets of aggressive tumor cells. Another challenge lies in the integration of multiple types of molecular data into mathematical disease models that can make actionable clinical statements. PRECISE aims to develop predictive computational technology that can exploit molecular and clinical data to improve our understanding of disease mechanisms and to inform clinicians about optimized strategies for therapeutic intervention. The Precise project will focus on two urgent clinical needs in prostate cancer: i) Distinguishing the many indolent tumors from the minority of lethal ones; and ii) providing rationally selected treatment options for patients with advanced disease (http://www.precise-project.eu).
BILOBA (Bloch electromagnetic surface wave biosensors for early cancer diagnosis)
BILOBA is a collaborative project funded by the European Commission through its Seventh Framework Program. The major goal of the project is to explore, design and set-up systems optimized for analytical sensing, associated with the development of a corresponding analytical instrument. For this purpose, the immobilization protocols and biochemical assays have been established to ensure an optimized binding site density at the surface of SPR sensors and to enable the detection of the target biomarkers. Furthermore, a fluidic system has been developed for handling the aqueous analyte solutions ensuring a high signal-to-noise ratio and robust results even in the case of ultralow concentrations. The BILOBA multifunctional point-of-care platform is expected to be capable of performing real-time cancer biomarker detection in a tandem configuration. The BILOBA project consists of 9 participants from different European countries, including the Department of Basic and Applied Sciences for Engineering (Università degli Studi di Roma 'La Sapienza', Rome, Italy); the Department of Applied Sciences and Technology (Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy); Fraunhofer Gesellschaft, Munich, Germany; the Department of Materials (Imperial College London, London, UK), the Department of Oncology (Università degli Studi di Torino, Torino, Italy); Labor Srl, Rome, Italy; Biotray SAS, Lyon, France; Horiba Jobin Yvon SAS, Paris, France; KDS Radeberg GmbH, Dresden, Germany (http://www.biloba-project.eu/).
ULTRAPLACAD (ULTRAsensitive PLAsmonic devices for early CAncer Diagnosis)
With respect to the issue of the detection of cfDNA and miRNAs in tumor liquid biopsies, the highly multidisciplinary ULTRAPLACAD project relies on two advanced plasmonic biosensor technologies: i) Plasmon-enhanced fluorescence spectroscopy imaging (PEFSI); and ii) nanostructure-enhanced surface plasmon resonance imaging (NESPRI). Plasmonic methods have already been shown to be useful for biomedical applications for the analysis of nucleic acid analytes in real samples (including human blood) with a limit of detection (LOD) from low femtomolar to attomolar concentrations (162,205,206). In the ULTRAPLACAD project, novel plasmonic structures will be delivered based on surface plasmon modes supported by continuous metallic films and arrays of metallic nanoparticles. Those structures hold the potential for a breakthrough enhancement of sensitivity. Moreover, this method will be implemented in an innovative compact biosensor device based on an integration of key optical elements for the excitation and collecting of fluorescence light directly on the sensor chip. The SPRI approach is based on the detection of target analytes through biomolecular binding-induced refractive index changes. In the ULTRAPLACAD project, an SPRI platform based on the diffraction coupling of light into surface plasmons will be developed, in order to increase sensitivity and limit the signal-to-noise ratios. With respect to the proposed diagnostic model systems, KRAS and BRAF mutations are considered, since they are routinely assessed in genomic DNAs from surgically removed lesions of colorectal carcinoma, breast cancer, melanoma and other tumors. As far as miRNA target sequences are concerned, miR-221, miR-222, miR-141, miR-155, miR-21, let-7a and miR-16 are considered, since these miRNA molecules are available in circulating exosomes, and could mark tumor aggressiveness. ULTRAPLACAD is the only project in which ctDNAs, miRNAs and proteins, e.g., the three major analyte classes, are combined in a single detection platform (www.ultraplacad.eu).
9. Conclusions
The liquid biopsy of cancer is mainly based on the analysis of CTCs and/or cell-free nucleic acids in the peripheral blood of cancer patients, as well as in other body fluids suitable for diagnostic assessment. Among these, cerebrospinal fluid for tumors of the central nervous system, saliva for tumors affecting the head and neck, pleural effusion in the case of respiratory tract cancers and urine for urinary tract cancers. At present, liquid biopsy should be considered one of the most advanced non-invasive diagnostic systems suitable for performing key clinically relevant actions possibly leading to precision medicine. Historically, the applications of liquid biopsy for the characterization of cancer patients have been focused on CTCs. More recently, this analysis has been extended to cfDNA and miRNAs, demonstrated to be associated with cancer, with potential applications in early diagnosis, staging, prognosis, prediction of therapeutic responses, therapeutic outcome, and follow-up during therapeutic intervention. Liquid biopsy measures alterations in gene structure, regulation and expression that are the hallmarks of cancer. These analytes include nucleotide variants, promoter methylation, copy number variations of specific genes, chromosomal rearrangements, mutations affecting transcription, splicing and RNA maturation, translational efficiency and differences in miRNA signatures. The analysis of all these parameters can be approached by a variety of technological platforms. Moreover, the great interest of liquid biopsy is that this approach avoids certain key issues associated with invasive surgical biopsy. These include, but are not limited to: i) A static representation of the tumor pathology strictly limited to the tumor tissue sampling; ii) ethical and practical issues preventing repeated tissue biopsy; iii) tumor heterogeneity, particularly during progression and metastatic dissemination (making multiple sampling necessary); iv) easier patient monitoring by non-invasive analytical procedures (i.e., liquid biopsy). Therefore, despite the fact that the liquid biopsy approach suffers from important drawbacks (fragmentation of cfDNA, instability of RNA, low yield of isolated samples to be analyzed and variable presence of normal DNA and RNA) this approach is generally deemed of great interest for future applications, patent development and clinical trials. These will ultimately verify the potential of liquid biopsy in cancer. It is not expected that liquid biopsy will replace surgical biopsy; however, it will probably complement within a few years the information routinely obtained by excisional, incisional, surgical and needle biopsies, becoming a tool of choice for the dynamic monitoring of patients during clinical treatment and during the long-term surveillance of their health status.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CRC
colorectal cancer
- HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
- CTCs
circulating tumor cells
- cfDNA
circulating free DNA
- cfRNA
circulating free RNA
- miRNA or miR
microRNA
- UTR
untranslated region
- CDS
coding sequence
- RISC
RNA-induced silencing complex
- PCR
polymerase-chain reaction
- RT
reverse transcription
- qPCR
quantitative PCR
- ddPCR
droplet digital PCR
- WGS
whole genome sequencing
- NGS
next generation sequencing
- SPR-I
surface plasmon resonance imaging
- SNPs
single nucleotide polymorphisms
Funding
This study was supported by the European Union (EU) Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme (GA #633937, project ULTRAsensitive PLAsmonic devices for early CAncer Diagnosis (ULTRAPLACAD), and by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) (IG #13575 to RG, IG# 14204 and IG #19052 to PG). MA is the recipient of an AIRC, Nuvenia Fellowship id. 19503.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
All authors were involved in the conception of the study, and revised and approved the final manuscript. All authors take the responsibility for publishing this review paper. AF, PG, GS and RG performed the literature search, wrote the manuscript, and critically analyzed the existing knowledge; AF and RG designed the figures; AF, MA, JG and RG have ideated and drew the tables; AF, JG and RG were involved in the acquisition of data and in the analysis of patents and clinical trials; JG and MA significantly contributed to editing the manuscript; PG, DAS, GS and RG significantly contributed to the analyses of international networks focusing on liquid biopsy. AF, PG, DAS, GS and RG were significantly involved in the drafting of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
DAS is the Editor-in-Chief for the journal, but had no personal involvement in the reviewing process, or any influence in terms of adjudicating on the final decision, for this article.
References
- 1.Heitzer E, Auer M, Ulz P, Geigl JB, Speicher MR. Circulating tumor cells and DNA as liquid biopsies. Genome Med. 2013;5:73. doi: 10.1186/gm477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bettegowda C, Sausen M, Leary RJ, Kinde I, Wang Y, Agrawal N, Bartlett BR, Wang H, Luber B, Alani RM, et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:224ra24. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Domínguez-Vigil IG, Moreno-Martínez AK, Wang JY, Roehrl MHA, Barrera-Saldaña HA. The dawn of the liquid biopsy in the fight against cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;9:2912–2922. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Breitbach S, Tug S, Helmig S, Zahn D, Kubiak T, Michal M, Gori T, Ehlert T, Beiter T, Simon P. Direct quantification of cell-free, circulating DNA from unpurified plasma. PloS One. 2014;9:e87838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Heitzer E, Ulz P, Geigl JB. Circulating tumor DNA as a liquid biopsy for cancer. Clin Chem. 2015;61:112–123. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2014.222679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yang M, Forbes ME, Bitting RL, O'Neill SS, Chou PC, Topaloglu U, Miller LD, Hawkins GA, Grant SC, DeYoung BR, et al. Incorporating blood-based liquid biopsy information into cancer staging: Time for a TNMB system. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:311–323. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kleppe M, Levine RL. Tumor heterogeneity confounds and illuminates: Assessing the implications. Nat Med. 2014;20:342–344. doi: 10.1038/nm.3522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Diehl F, Schmidt K, Choti MA, Romans K, Goodman S, Li M, Thornton K, Agrawal N, Sokoll L, Szabo SA, et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat Med. 2008;14:985–990. doi: 10.1038/nm.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Leon SA, Shapiro B, Sklaroff DM, Yaros MJ. Free DNA in the serum of cancer patients and the effect of therapy. Cancer Res. 1977;37:646–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Burz C, Pop VV, Buiga R, Daniel S, Samasca G, Aldea C, Lupan I. Circulating tumor cells in clinical research and monitoring patients with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2018;9:24561–24571. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sozzi G, Conte D, Mariani L, Lo Vullo S, Roz L, Lombardo C, Pierotti MA, Tavecchio L. Analysis of circulating tumor DNA in plasma at diagnosis and during follow-up of lung cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4675–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Spindler KL, Pallisgaard N, Vogelius I, Jakobsen A. Quantitative cell-free DNA, KRAS, and BRAF mutations in plasma from patients with metastatic colorectal cancer during treatment with cetuximab and irinotecan. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:1177–1185. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Perkins G, Yap TA, Pope L, Cassidy AM, Dukes JP, Riisnaes R, Massard C, Cassier PA, Miranda S, Clark J, et al. Multi-purpose utility of circulating plasma DNA testing in patients with advanced cancers. PloS One. 2012;7:e47020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ignatiadis M, Lee M, Jeffrey SS. Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA: Challenges and opportunities on the path to clinical utility. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:4786–4800. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Krebs MG, Hou JM, Ward TH, Blackhall FH, Dive C. Circulating tumour cells: Their utility in cancer management and predicting outcomes. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2010;2:351–365. doi: 10.1177/1758834010378414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Millner LM, Linder MW, Valdes R., Jr Circulating tumor cells: a review of present methods and the need to identify heterogeneous phenotypes. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2013;43:295–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kuipers EJ, Spaander MC. Personalized screening for colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:391–392. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kloten V, Rüchel N, Brüchle NO, Gasthaus J, Freudenmacher N, Steib F, Mijnes J, Eschenbruch J, Binnebösel M, Knüchel R, et al. Liquid biopsy in colon cancer: Comparison of different circulating DNA extraction systems following absolute quantification of KRAS mutations using Intplex allele-specific PCR. Oncotarget. 2017;8:86253–86263. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Thomsen CEB, Appelt AL, Andersen RF, Lindebjerg J, Jensen LH, Jakobsen A. The prognostic value of simultaneous tumor and serum RAS/RAF mutations in localized colon cancer. Cancer Med. 2017;6:928–936. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Spindler KL, Pallisgaard N, Andersen RF, Brandslund I, Jakobsen A. Circulating free DNA as biomarker and source for mutation detection in metastatic colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0108247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hardingham JE, Grover P, Winter M, Hewett PJ, Price TJ, Thierry B. Detection and clinical significance of circulating tumor cells in colorectal cancer-20 years of progress. Mol Med. 2015;21:S25–S31. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2015.00149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Veldore VH, Choughule A, Routhu T, Mandloi N, Noronha V, Joshi A, Dutt A, Gupta R, Vedam R, Prabhash K. Validation of liquid biopsy: Plasma cell-free DNA testing in clinical management of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Auckl) 2018;9:1–11. doi: 10.2147/LCTT.S147841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Anfossi S, Babayan A, Pantel K, Calin GA. Clinical utility of circulating non-coding RNAs - an update. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018 May 21; doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0035-x. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Izzotti A, Carozzo S, Pulliero A, Zhabayeva D, Ravetti JL, Bersimbaev R. Extracellular MicroRNA in liquid biopsy: Applicability in cancer diagnosis and prevention. Am J Cancer Res. 2016;6:1461–1493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Coombs CC, Zehir A, Devlin SM, Kishtagari A, Syed A, Jonsson P, Hyman DM, Solit DB, Robson ME, Baselga J, et al. Therapy-related clonal hematopoiesis in patients with non-hematologic cancers is common and associated with adverse clinical outcomes. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21:374–382e4. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.07.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Taly V, Pekin D, Benhaim L, Kotsopoulos SK, Le Corre D, Li X, Atochin I, Link DR, Griffiths AD, Pallier K, et al. Multiplex picodroplet digital PCR to detect KRAS mutations in circulating DNA from the plasma of colorectal cancer patients. Clin Chem. 2013;59:1722–1731. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2013.206359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang JY, Hsieh JS, Chang MY, Huang TJ, Chen FM, Cheng TL, Alexandersen K, Huang YS, Tzou WS, Lin SR. Molecular detection of APC, K-ras, and p53 mutations in the serum of colorectal cancer patients as circulating biomarkers. World J Surg. 2004;28:721–726. doi: 10.1007/s00268-004-7366-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mohan S, Heitzer E, Ulz P, Lafer I, Lax S, Auer M, Pichler M, Gerger A, Eisner F, Hoefler G, et al. Changes in colorectal carcinoma genomes under anti-EGFR therapy identified by whole-genome plasma DNA sequencing. PLoS Genet. 2014;10:e1004271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Feng WN, Gu WQ, Zhao N, Pan YM, Luo W, Zhang H, Liang JM, Yang J, Deng YM. Comparison of the SuperARMS and Droplet Digital PCR for detecting EGFR mutation in ctDNA from NSCLC patients. Transl Oncol. 2018;11:542–545. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.02.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Newman AM, Bratman SV, To J, Wynne JF, Eclov NC, Modlin LA, Liu CL, Neal JW, Wakelee HA, Merritt RE, et al. An ultrasensitive method for quantitating circulating tumor DNA with broad patient coverage. Nat Med. 2014;20:548–554. doi: 10.1038/nm.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fujiwara K, Fujimoto N, Tabata M, Nishii K, Matsuo K, Hotta K, Kozuki T, Aoe M, Kiura K, Ueoka H, et al. Identification of epigenetic aberrant promoter methylation in serum DNA is useful for early detection of lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:1219–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Szpechcinski A, Chorostowska-Wynimko J, Struniawski R, Kupis W, Rudzinski P, Langfort R, Puscinska E, Bielen P, Sliwinski P, Orlowski T. Cell-free DNA levels in plasma of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and inflammatory lung disease. Br J Cancer. 2015;113:476–483. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pisanic TR, 2nd, Athamanolap P, Poh W, Chen C, Hulbert A, Brock MV, Herman JG, Wang TH. DREAMing: A simple and ultrasensitive method for assessing intratumor epigenetic heterogeneity directly from liquid biopsies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:e154. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dawson SJ, Tsui DW, Murtaza M, Biggs H, Rueda OM, Chin SF, Dunning MJ, Gale D, Forshew T, Mahler-Araujo B, et al. Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to monitor metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1199–209. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1213261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Murtaza M, Dawson SJ, Tsui DW, Gale D, Forshew T, Piskorz AM, Parkinson C, Chin SF, Kingsbury Z, Wong AS, et al. Non-invasive analysis of acquired resistance to cancer therapy by sequencing of plasma DNA. Nature. 2013;497:108–112. doi: 10.1038/nature12065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yanagawa T, Kagara N, Miyake T, Tanei T, Naoi Y, Shimoda M, Shimazu K, Kim SJ, Noguchi S. Detection of ESR1 mutations in plasma and tumors from metastatic breast cancer patients using next-generation sequencing. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017;163:231–240. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4190-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mastoraki S, Strati A, Tzanikou E, Chimonidou M, Politaki E, Voutsina A, Psyrri A, Georgoulias V, Lianidou E. ESR1 Methylation: A liquid biopsy-based epigenetic assay for the follow-up of patients with metastatic breast cancer receiving endocrine treatment. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:1500–1510. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gray ES, Rizos H, Reid AL, Boyd SC, Pereira MR, Lo J, Tembe V, Freeman J, Lee JH, Scolyer RA, et al. Circulating tumor DNA to monitor treatment response and detect acquired resistance in patients with metastatic melanoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6:42008–42018. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schreuer M, Meersseman G, Van Den Herrewegen S, Jansen Y, Chevolet I, Bott A, Wilgenhof S, Seremet T, Jacobs B, Buyl R, et al. Quantitative assessment of BRAF V600 mutant circulating cell-free tumor DNA as a tool for therapeutic monitoring in metastatic melanoma patients treated with BRAF/MEK inhibitors. J Transl Med. 2016;14:95. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0852-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Madic J, Piperno-Neumann S, Servois V, Rampanou A, Milder M, Trouiller B, Gentien D, Saada S, Assayag F, Thuleau A, et al. Pyrophosphorolysis-activated polymerization detects circulating tumor DNA in metastatic uveal melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:3934–3941. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pereira E, Camacho-Vanegas O, Anand S, Sebra R, Catalina Camacho S, Garnar-Wortzel L, Nair N, Moshier E, Wooten M, Uzilov A, et al. Personalized Circulating Tumor DNA Biomarkers dynamically predict treatment response and survival in gynecologic cancers. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0145754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Forshew T, Murtaza M, Parkinson C, Gale D, Tsui DW, Kaper F, Dawson SJ, Piskorz AM, Jimenez-Linan M, Bentley D, et al. Noninvasive identification and monitoring of cancer mutations by targeted deep sequencing of plasma DNA. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:136ra68. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.No JH, Kim K, Park KH, Kim YB. Cell-free DNA level as a prognostic biomarker for epithelial ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:3467–3471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Giannopoulou L, Chebouti I, Pavlakis K, Kasimir-Bauer S, Lianidou ES. RASSF1A promoter methylation in high-grade serous ovarian cancer: A direct comparison study in primary tumors, adjacent morphologically tumor cell-free tissues and paired circulating tumor DNA. Oncotarget. 2017;8:21429–21443. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chan KC, Jiang P, Zheng YW, Liao GJ, Sun H, Wong J, Siu SS, Chan WC, Chan SL, Chan AT, et al. Cancer genome scanning in plasma: Detection of tumor-associated copy number aberrations, single-nucleotide variants, and tumoral heterogeneity by massively parallel sequencing. Clin Chem. 2013;59:211–224. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2012.196014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zhang P, Wen X, Gu F, Deng X, Li J, Dong J, Jiao J, Tian Y. Methylation profiling of serum DNA from hepatocellular carcinoma patients using an Infinium Human Methylation 450 BeadChip. Hepatol Int. 2013;7:893–900. doi: 10.1007/s12072-013-9437-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ren N, Qin LX, Tu H, Liu YK, Zhang BH, Tang ZY. The prognostic value of circulating plasma DNA level and its allelic imbalance on chromosome 8p in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006;132:399–407. doi: 10.1007/s00432-005-0049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Huang A, Zhang X, Zhou SL, Cao Y, Huang XW, Fan J, Yang XR, Zhou J. Detecting circulating tumor DNA in hepatocellular carcinoma patients using Droplet Digital PCR is feasible and reflects intratumoral heterogeneity. J Cancer. 2016;7:1907–1914. doi: 10.7150/jca.15823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Heitzer E, Ulz P, Belic J, Gutschi S, Quehenberger F, Fischereder K, Benezeder T, Auer M, Pischler C, Mannweiler S, et al. Tumor-associated copy number changes in the circulation of patients with prostate cancer identified through whole-genome sequencing. Genome Med. 2013;5:30. doi: 10.1186/gm434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Annala M, Vandekerkhove G, Khalaf D, Taavitsainen S, Beja K, Warner EW, Sunderland K, Kollmannsberger C, Eigl BJ, Finch D, et al. Circulating tumor DNA genomics correlate with resistance to Abiraterone and Enzalutamide in prostate cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:444–457. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Delgado PO, Alves BC, Gehrke Fde S, Kuniyoshi RK, Wroclavski ML, Del Giglio A, Fonseca FL. Characterization of cell-free circulating DNA in plasma in patients with prostate cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:983–986. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0634-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Buelens S, Claeys T, Dhondt B, Poelaert F, Vynck M, Yigit N, Thas O, Ost P, Vandesompele J, Lumen N, et al. Prognostic and therapeutic implications of circulating androgen receptor gene copy number in prostate cancer patients using Droplet Digital polymerase chain reaction. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;16:197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2017.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pu XX, Huang GL, Guo HQ, Guo CC, Li H, Ye S, Ling S, Jiang L, Tian Y, Lin TY. Circulating miR-221 directly amplified from plasma is a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker of colorectal cancer and is correlated with p53 expression. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:1674–1680. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Liu GH, Zhou ZG, Chen R, Wang MJ, Zhou B, Li Y, Sun XF. Serum miR-21 and miR-92a as biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:2175–2181. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0753-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H, Schetter AJ, Nykter M, Harris CC, Chen K, Hamilton SR, Zhang W. Circulating plasma miR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lv ZC, Fan YS, Chen HB, Zhao DW. Investigation of microRNA-155 as a serum diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:1619–1625. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Krawczyk P, Powrózek T, Olesiński T, Dmitruk A, Dziwota J, Kowalski D, Milanowski J. Evaluation of miR-506 and miR-4316 expression in early and non-invasive diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2017;32:1057–1060. doi: 10.1007/s00384-017-2814-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W, Du X. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:118–126. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Liu C, Eng C, Shen J, Lu Y, Takata Y, Mehdizadeh A, Chang GJ, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Li Y, Chang P, et al. Serum exosomal miR-4772-3p is a predictor of tumor recurrence in stage II and III colon cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:76250–76260. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ogata-Kawata H, Izumiya M, Kurioka D, Honma Y, Yamada Y, Furuta K, Gunji T, Ohta H, Okamoto H, Sonoda H, et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9:e92921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, Lam EK, Shin VY, Yu J, Poon TC, Ng SS, Sung JJ. Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: A potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut. 2009;58:1375–1381. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.167817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Zheng G, Du L, Yang X, Zhang X, Wang L, Yang Y, Li J, Wang C. Serum microRNA panel as biomarkers for early diagnosis of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;111:1985–1992. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Dou H, Wang Y, Su G, Zhao S. Decreased plasma let-7c and miR-152 as noninvasive biomarker for non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:9291–9298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Yu H, Jiang L, Sun C, Li Guo L, Lin M, Huang J, Zhu L. Decreased circulating miR-375: A potential biomarker for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Gene. 2014;534:60–65. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.10.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Li N, Ma J, Guarnera MA, Fang H, Cai L, Jiang F. Digital PCR quantification of miRNAs in sputum for diagnosis of lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140:145–150. doi: 10.1007/s00432-013-1555-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Geng Q, Fan T, Zhang B, Wang W, Xu Y, Hu H. Five microRNAs in plasma as novel biomarkers for screening of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Respir Res. 2014;15:149. doi: 10.1186/s12931-014-0149-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hu Z, Chen X, Zhao Y, Tian T, Jin G, Shu Y, Chen Y, Xu L, Zen K, Zhang C, et al. Serum microRNA signatures identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling predict survival of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1721–1726. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.9342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Yu L, Todd NW, Xing L, Xie Y, Zhang H, Liu Z, Fang H, Zhang J, Katz RL, Jiang F. Early detection of lung adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2870–2878. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, Ma LN, Zhou SQ, Wang YK, Zeng F, Zhou JH, Zhang YK. High expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2012;29:618–626. doi: 10.1007/s12032-011-9923-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Leng Q, Lin Y, Jiang F, Lee CJ, Zhan M, Fang H, Wang Y, Jiang F. A plasma miRNA signature for lung cancer early detection. Oncotarget. 2017;8:111902–111911. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Asaga S, Kuo C, Nguyen T, Terpenning M, Giuliano AE, Hoon DS. Direct serum assay for microRNA-21 concentrations in early and advanced breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2011;57:84–91. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2010.151845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhu W, Qin W, Atasoy U, Sauter ER. Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer and healthy subjects. BMC Res Notes. 2009;2:89. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-2-89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney KJ, Newell J, Kerin MJ. Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 2010;251:499–505. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181cc939f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Stückrath I, Rack B, Janni W, Jäger B, Pantel K, Schwarzenbach H. Aberrant plasma levels of circulating miR-16, miR-107, miR-130a and miR-146a are associated with lymph node metastasis and receptor status of breast cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2015;6:13387–13401. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Mangolini A, Ferracin M, Zanzi MV, Saccenti E, Ebnaof SO, Poma VV, Sanz JM, Passaro A, Pedriali M, Frassoldati A, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic microRNAs in the serum of breast cancer patients measured by droplet digital PCR. Biomark Res. 2015;3:12. doi: 10.1186/s40364-015-0037-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kleivi Sahlberg K, Bottai G, Naume B, Burwinkel B, Calin GA, Børresen-Dale AL, Santarpia L. A serum microRNA signature predicts tumor relapse and survival in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:1207–1214. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Margue C, Reinsbach S, Philippidou D, Beaume N, Walters C, Schneider JG, Nashan D, Behrmann I, Kreis S. Comparison of a healthy miRNome with melanoma patient miRNomes: are microRNAs suitable serum biomarkers for cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:12110–121127. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Fleming NH, Zhong J, da Silva IP, Vega-Saenz de Miera E, Brady B, Han SW, Hanniford D, Wang J, Shapiro RL, Hernando E, et al. Serum-based miRNAs in the prediction and detection of recurrence in melanoma patients. Cancer. 2015;121:51–59. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ono S, Oyama T, Lam S, Chong K, Foshag LJ, Hoon DS. A direct plasma assay of circulating microRNA-210 of hypoxia can identify early systemic metastasis recurrence in melanoma patients. Oncotarget. 2015;6:7053–7064. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Stark MS, Klein K, Weide B, Haydu LE, Pflugfelder A, Tang YH, Palmer JM, Whiteman DC, Scolyer RA, Mann GJ, et al. The prognostic and predictive value of melanoma-related microRNAs using tissue and serum: A microRNA expression analysis. EBioMedicine. 2015;2:671–680. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.05.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Friedman EB, Shang S, de Miera EV, Fog JU, Teilum MW, Ma MW, Berman RS, Shapiro RL, Pavlick AC, Hernando E, et al. Serum microRNAs as biomarkers for recurrence in melanoma. J Transl Med. 2012;10:155. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kanemaru H, Fukushima S, Yamashita J, Honda N, Oyama R, Kakimoto A, Masuguchi S, Ishihara T, Inoue Y, Jinnin M, et al. The circulating microRNA-221 level in patients with malignant melanoma as a new tumor marker. J Dermatol Sci. 2011;61:187–193. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2010.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Fogli S, Polini B, Carpi S, Pardini B, Naccarati A, Dubbini N, Lanza M, Breschi MC, Romanini A, Nieri P. Identification of plasma microRNAs as new potential biomarkers with high diagnostic power in human cutaneous melanoma. Tumour Biol. 2017;39:1010428317701646. doi: 10.1177/1010428317701646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Yokoi A, Yoshioka Y, Hirakawa A, Yamamoto Y, Ishikawa M, Ikeda S, Kato T, Niimi K, Kajiyama H, Kikkawa F, et al. A combination of circulating miRNAs for the early detection of ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:89811–89823. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Todeschini P, Salviato E, Paracchini L, Ferracin M, Petrillo M, Zanotti L, Tognon G, Gambino A, Calura E, Caratti G, et al. Circulating miRNA landscape identifies miR-1246 as promising diagnostic biomarker in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma: A validation across two independent cohorts. Cancer Lett. 2017;388:320–327. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zuberi M, Mir R, Das J, Ahmad I, Javid J, Yadav P, Masroor M, Ahmad S, Ray PC, Saxena A. Expression of serum miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-200c as candidate biomarkers in epithelial ovarian cancer and their association with clinicopathological features. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015;17:779–787. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1303-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Liang H, Jiang Z, Xie G, Lu Y. Serum microRNA-145 as a novel biomarker in human ovarian cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:5305–5313. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3191-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Gao YC, Wu J. MicroRNA-200c and microRNA-141 as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for ovarian cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:4843–4850. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Zhou J, Gong G, Tan H, Dai F, Zhu X, Chen Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Chen P, Wu X, et al. Urinary microRNA-30a-5p is a potential biomarker for ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2015;33:2915–2923. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Shah JS, Gard GB, Yang J, Maidens J, Valmadre S, Soon PS, Marsh DJ. Combining serum microRNA and CA-125 as prognostic indicators of preoperative surgical outcome in women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2018;148:181–188. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Gui J, Tian Y, Wen X, Zhang W, Zhang P, Gao J, Run W, Tian L, Jia X, Gao Y. Serum microRNA characterization identifies miR-885-5p as a potential marker for detecting liver pathologies. Clin Sci (Lond) 2011;120:183–193. doi: 10.1042/CS20100297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Yamamoto Y, Kosaka N, Tanaka M, Koizumi F, Kanai Y, Mizutani T, Murakami Y, Kuroda M, Miyajima A, Kato T, et al. MicroRNA-500 as a potential diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomarkers. 2009;14:529–538. doi: 10.3109/13547500903150771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Xu J, Wu C, Che X, Wang L, Yu D, Zhang T, Huang L, Li H, Tan W, Wang C, et al. Circulating microRNAs, miR-21, miR-122, and miR-223, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or chronic hepatitis. Mol Carcinog. 2011;50:136–142. doi: 10.1002/mc.20712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Zhou J, Yu L, Gao X, Hu J, Wang J, Dai Z, Wang JF, Zhang Z, Lu S, Huang X, et al. Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4781–4788. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Li LM, Hu ZB, Zhou ZX, Chen X, Liu FY, Zhang JF, Shen HB, Zhang CY, Zen K. Serum microRNA profiles serve as novel biomarkers for HBV infection and diagnosis of HBV-positive hepatocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010;70:9798–9807. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Moshiri F, Salvi A, Gramantieri L, Sangiovanni A, Guerriero P, De Petro G, Bassi C, Lupini L, Sattari A, Cheung D, et al. Circulating miR-106b-3p, miR-101-3p and miR-1246 as diagnostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2018;9:15350–15364. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kachakova D, Mitkova A, Popov E, Popov I, Vlahova A, Dikov T, Christova S, Mitev V, Slavov C, Kaneva R. Combinations of serum prostate-specific antigen and plasma expression levels of let-7c, miR-30c, miR-141, and miR-375 as potential better diagnostic biomarkers for prostate cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2015;34:189–200. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Bryant RJ, Pawlowski T, Catto JW, Marsden G, Vessella RL, Rhees B, Kuslich C, Visakorpi T, Hamdy FC. Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:768–774. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Lin HM, Castillo L, Mahon KL, Chiam K, Lee BY, Nguyen Q, Boyer MJ, Stockler MR, Pavlakis N, Marx G, et al. Circulating microRNAs are associated with docetaxel chemotherapy outcome in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014;110:2462–2471. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kotb S, Mosharafa A, Essawi M, Hassan H, Meshref A, Morsy A. Circulating miRNAs 21 and 221 as biomarkers for early diagnosis of prostate cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:12613–12617. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2584-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Srivastava A, Goldberger H, Dimtchev A, Ramalinga M, Chijioke J, Marian C, Oermann EK, Uhm S, Kim JS, Chen LN, et al. MicroRNA profiling in prostate cancer-the diagnostic potential of urinary miR-205 and miR-214. PLoS One. 2013;8:e76994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Singh PK, Preus L, Hu Q, Yan L, Long MD, Morrison CD, Nesline M, Johnson CS, Koochekpour S, Kohli M, et al. Serum microRNA expression patterns that predict early treatment failure in prostate cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2014;5:824–840. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Farran B, Dyson G, Craig D, Dombkowski A, Beebe-Dimmer JL, Powell IJ, Podgorski I, Heilbrun L, Bolton S, Bock CH. A study of circulating microRNAs identifies a new potential biomarker panel to distinguish aggressive prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2018;39:556–561. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Cochetti G, Poli G, Guelfi G, Boni A, Egidi MG, Mearini E. Different levels of serum microRNAs in prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia: Evaluation of potential diagnostic and prognostic role. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:7545–7553. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S119027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Brychta N, Krahn T, von Ahsen O. Detection of KRAS mutations in circulating tumor DNA by digital PCR in early stages of pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem. 2016;62:1482–1491. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.257469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Kinugasa H, Nouso K, Miyahara K, Morimoto Y, Dohi C, Tsutsumi K, Kato H, Matsubara T, Okada H, Yamamoto K. Detection of K-ras gene mutation by liquid biopsy in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 2015;121:2271–2280. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Couraud S, Zalcman G, Milleron B, Morin F, Souquet PJ. Lung cancer in never smokers-a review. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:1299–1311. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Perez-Carbonell L, Sinicrope FA, Alberts SR, Oberg AL, Balaguer F, Castells A, Boland CR, Goel A. miR-320e is a novel prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015;113:83–90. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Case M, Matheson E, Minto L, Hassan R, Harrison CJ, Bown N, Bailey S, Vormoor J, Hall AG, Irving JA. Mutation of genes affecting the RAS pathway is common in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6803–6809. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Lin CC, Huang WL, Wei F, Su WC, Wong DT. Emerging platforms using liquid biopsy to detect EGFR mutations in lung cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015;15:1427–1440. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1094379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Warton K, Mahon KL, Samimi G. Methylated circulating tumor DNA in blood: Power in cancer prognosis and response. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016;23:R157–171. doi: 10.1530/ERC-15-0369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Mitchell SM, Ho T, Brown GS, Baker RT, Thomas ML, McEvoy A, Xu ZZ, Ross JP, Lockett TJ, Young GP, et al. Evaluation of methylation biomarkers for detection of crculating tumor DNA and application to colorectal cancer. Genes (Basel) 2016;7:E125. doi: 10.3390/genes7120125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ghelani HS, Rachchh MA, Gokani RH. MicroRNAs as newer therapeutic targets: A big hope from a tiny player. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2012;3:217–227. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.99416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:597–610. doi: 10.1038/nrg2843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Sun K, Lai EC. Adult-specific functions of animal microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14:535–548. doi: 10.1038/nrg3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Chekulaeva M, Filipowicz W. Mechanisms of miRNAmediated post-transcriptional regulation in animal cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:452–460. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, Bartel DP. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature. 2010;466:835–840. doi: 10.1038/nature09267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Cammaerts S, Strazisar M, De Rijk P, Del Favero J. Genetic variants in microRNA genes: Impact on microRNA expression, function, and disease. Front Genet. 2015;6:186. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Friedländer MR, Lizano E, Houben AJS, Bezdan D, Báñez-Coronel M, Kudla G. Evidence for the biogenesis of more than 1,000 novel human microRNAs. Genome Biol. 2014;15:R57. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-4-r57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Cheng WC, Chung IF, Tsai CF, Huang TS, Chen CY, Wang SC. YM500v2: A small RNA sequencing (smRNA-seq) database for human cancer miRNome research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D862–D867. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Londin E, Loher P, Telonis AG, Quann K, Clark P, Jing Y. Analysis of 13 cell types reveals evidence for the expression of numerous novel primate-and tissue-specific microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:E1106–E1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420955112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ. miRBase: MicroRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:D140–D144. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Gambari R, Fabbri E, Borgatti M, Lampronti I, Finotti A, Brognara E, Bianchi N, Manicardi A, Marchelli R, Corradini R. Targeting microRNAs involved in human diseases: A novel approach for modification of gene expression and drug development. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;82:1416–1429. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Piva R, Spandidos DA, Gambari R. From microRNA functions to microRNA therapeutics: Novel targets and novel drugs in breast cancer research and treatment. Int J Oncol. 2013;43:985–994. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Gambari R, Brognara E, Spandidos DA, Fabbri E. Targeting oncomiRNAs and mimicking tumor suppressor miRNAs: Νew trends in the development of miRNA therapeutic strategies in oncology. Int J Oncol. 2016;49:5–32. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Bertucci A, Prasetyanto EA, Septiadi D, Manicardi A, Brognara E, Gambari R, Corradini R, De Cola L. Combined Delivery of temozolomide and anti-miR221 PNA using mesoporous silica nanoparticles induces apoptosis in resistant glioma cells. Small. 2015;11:5687–5695. doi: 10.1002/smll.201500540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Gheinani AH, Vögeli M, Baumgartner U, Vassella E, Draege RA, Burkhard FC, Monastyrskaya K. Improved isolation strategies to increase the yield and purity of human urinary exosomes for biomarker discovery. Sci Rep. 2018;8:3945. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22142-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.da Silveira JC, Andrade GM, Del Collado M, Sampaio RV, Sangalli JR, Silva LA, Pinaffi FVL, Jardim IB, Cesar MC, Nogueira MFG, et al. Supplementation with small-extracellular vesicles from ovarian follicular fluid during in vitro production modulates bovine embryo development. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0179451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Halvorsen AR, Helland Å, Gromov P, Wielenga VT, Talman MM, Brunner N, Sandhu V, Børresen-Dale AL, Gromova I, Haakensen VD. Profiling of microRNAs in tumor interstitial fluid of breast tumors - a novel resource to identify biomarkers for prognostic classification and detection of cancer. Mol Oncol. 2017;11:220–234. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Valentino A, Reclusa P, Sirera R, Giallombardo M, Camps C, Pauwels P, Crispi S, Rolfo C. Exosomal microRNAs in liquid biopsies: Future biomarkers for prostate cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2017;19:651–657. doi: 10.1007/s12094-016-1599-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Wecker T, Hoffmeier K, Plötner A, Grüning BA, Horres R, Backofen R, Reinhard T, Schlunck G. MicroRNA profiling in aqueous humor of individual human eyes by next-generation sequencing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57:1706–1713. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-17828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Nishida-Aoki N, Ochiya T. Interactions between cancer cells and normal cells via miRNAs in extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72:1849–1861. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1811-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Schetter AJ, Okayama H, Harris CC. The role of microRNAs in colorectal cancer. Cancer J. 2012;18:244–252. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e318258b78f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Markowitz SD, Bertagnolli MM. Molecular origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2449–2460. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0804588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Bellassai N, Spoto G. Biosensors for liquid biopsy: Circulating nucleic acids to diagnose and treat cancer. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:7255–7264. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9806-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Das J, Ivanov I, Montermini L, Rak J, Sargent EH, Kelley SO. An electrochemical clamp assay for direct, rapid analysis of circulating nucleic acids in serum. Nat Chem. 2015;7:569–575. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Pinheiro LB, Coleman VA, Hindson CM, Herrmann J, Hindson BJ, Bhat S, Emslie KR. Evaluation of a Droplet Digital polymerase chain reaction format for DNA copy number quantification. Anal Chem. 2012;84:1003–1011. doi: 10.1021/ac202578x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Podlesniy P, Trullas R. Biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid: Analysis of cell-free circulating mitochondrial DNA by digital PCR. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1768:111–126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7778-9_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Macagno N, Fina F, Penel N, Bouvier C, Nanni I, Duffaud F, Rouah R, Lacarelle B, Ouafik L, Bonvalot S, et al. Proof of concept: Prognostic value of the plasmatic concentration of circulating cell free DNA in desmoid tumors using ddPCR. Oncotarget. 2018;9:18296–18308. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.DiNardo CD, Routbort MJ, Bannon SA, Benton CB, Takahashi K, Kornblau SM, Luthra R, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Medeiros LJ, Garcia-Manero G, et al. Improving the detection of patients with inherited predispositions to hematologic malignancies using next-generation sequencing-based leukemia prognostication panels. Cancer. 2018;124:2704–2713. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Müllauer L. Next generation sequencing: Clinical applications in solid tumours. Memo. 2017;10:244–247. doi: 10.1007/s12254-017-0361-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Giuffrida MC, Spoto G. Integration of isothermal amplification methods in microfluidic devices: Recent advances. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;90:174–186. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.11.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Giuffrida MC, Zanoli LM, D'Agata R, Finotti A, Gambari R, Spoto G. Isothermal circular-strand-displacement polymerization of DNA and microRNA in digital microfluidic devices. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407:1533–1543. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-8405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Garcia-Olmo DC, Gutierrez-Gonzalez L, Ruiz-Piqueras R, Picazo MG, Garcia-Olmo D. Detection of circulating tumor cells and of tumor DNA in plasma during tumor progression in rats. Cancer Lett. 2005;217:115–123. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.06.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Rago C, Huso DL, Diehl F, Karim B, Liu G, Papadopoulos N, Samuels Y, Velculescu VE, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW, et al. Serial assessment of human tumor burdens in mice by the analysis of circulating DNA. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9364–9370. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Thierry AR, Mouliere F, Gongora C, Ollier J, Robert B, Ychou M, Del Rio M, Molina F. Origin and quantification of circulating DNA in mice with human colorectal cancer xenografts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:6159–6175. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant KC, Allen A, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A. 2008;105:10513–10518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804549105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Selth LA, Townley S, Gillis JL, Ochnik AM, Murti K, Macfarlane RJ, Chi KN, Marshall VR, Tilley WD, Butler LM. Discovery of circulating microRNAs associated with human prostate cancer using a mouse model of disease. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:652–661. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Waters PS, McDermott AM, Wall D, Heneghan HM, Miller N, Newell J, Kerin MJ, Dwyer RM. Relationship between circulating and tissue microRNAs in a murine model of breast cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7:e50459. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Greystoke A, Ayub M, Rothwell DG, Morris D, Burt D, Hodgkinson CL, Morrow CJ, Smith N, Aung K, Valle J, et al. Development of a circulating miRNA assay to monitor tumor burden: From mouse to man. Mol Oncol. 2016;10:282–291. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Gasparello J, Allegretti M, Tremante E, Fabbri E, Amoreo CA, Romania P, Melucci E, Messana K, Borgatti M, Giacomini P, et al. Liquid biopsy in mice bearing colorectal carcinoma xenografts: Gateways regulating the levels of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and miRNA (ctmiRNA) J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37:124. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0788-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Hofman P. Liquid biopsy for early detection of lung cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2017;29:73–78. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Pérez-Ramírez C, Cañadas-Garre M, Robles AI, Molina MÁ, Faus-Dáder MJ, Calleja-Hernández MÁ. Liquid biopsy in early stage lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016;5:517–524. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2016.10.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Bedin C, Enzo MV, Del Bianco P, Pucciarelli S, Nitti D, Agostini M. Diagnostic and prognostic role of cell-free DNA testing for colorectal cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2017;140:1888–1898. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Allenson K, Castillo J, San Lucas FA, Scelo G, Kim DU, Bernard V, Davis G, Kumar T, Katz M, Overman MJ, et al. High prevalence of mutant KRAS in circulating exosome-derived DNA from early-stage pancreatic cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:741–747. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Shimomura A, Shiino S, Kawauchi J, Takizawa S, Sakamoto H, Matsuzaki J, Ono M, Takeshita F, Niida S, Shimizu C, et al. Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting breast cancer in the early stage. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:326–334. doi: 10.1111/cas.12880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Schröck A, Leisse A, de Vos L, Gevensleben H, Dröge F, Franzen A, Wachendörfer M, Schröck F, Ellinger J, Teschke M, et al. Free-circulating methylated DNA in blood for diagnosis, staging, prognosis, and monitoring of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients: An observational prospective cohort study. Clin Chem. 2017;63:1288–1296. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.270207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Quandt D, Dieter Zucht H, Amann A, Wulf-Goldenberg A, Borrebaeck C, Cannarile M, Lambrechts D, Oberacher H, Garrett J, Nayak T, et al. Implementing liquid biopsies into clinical decision making for cancer immunotherapy. Oncotarget. 2018;8:48507–48520. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Goodall J, Mateo J, Yuan W, Mossop H, Porta N, Miranda S, Perez-Lopez R, Dolling D, Robinson DR, Sandhu S, et al. Circulating cell-free DNA to quide prostate cancer treatment with PARP inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:1006–1017. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.He J, Tan W, Ma J. Circulating tumor cells and DNA for real-time EGFR detection and monitoring of non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2017;13:787–797. doi: 10.2217/fon-2016-0427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Craw P, Balachandran W. Isothermal nucleic acid amplification technologies for point-of-care diagnostics: A critical review. Lab Chip. 2012;12:2469–2486. doi: 10.1039/c2lc40100b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Kim J, Easley CJ. Isothermal DNA amplification in bioanalysis: strategies and applications. Bioanalysis. 2011;3:227–239. doi: 10.4155/bio.10.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Guo Q, Yang X, Wang K, Tan W, Li W, Tang H, Li H. Sensitive fluorescence detection of nucleic acids based on isothermal circular strand-displacement polymerization reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:e20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.D'Agata R, Breveglieri G, Zanoli LM, Borgatti M, Spoto G, Gambari R. Direct detection of point mutations in nonamplified human genomic DNA. Anal Chem. 2011;83:8711–8717. doi: 10.1021/ac2021932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Albitar M. Hematopoietic cell phenotyping using circulating cell-free markers. 9,255,926 B2. US Patent. Filed August 17, 2006, issued February 9, 2016.
- 166.Thierry A, Molina F. Analytical methods for cell free nucleic acids and applications. 2,426,217A1. European Patent. Filed September 9, 2010; issued March 7, 2012.
- 167.Platica O. Method of mutation detection in blood cell-free DNA using primer extension (PE) and PCR. 9,062,350 B2. US Patent. Filed March 11, 2012; issued June 23, 2015.
- 168.Hoon DSB, Taback B. DNA markers for management of cancer. 7,718,364 B2. US Patent. Filed March 25, 2004; issued May 18, 2010.
- 169.Cortese Rand Petronis A: Method for analysis of DNA methylation profiles of cell-free circulating DNA in bodily fluids. 2,483,426 A4. European Patent. Filed October 1, 2010; issued April 4, 2013.
- 170.Schutz E, Beck J, Urnovitz H. Colorectal cancer associated circulating nucleic acid biomarkers. 2014/0303008A1. US Patent. Filed October 19, 2012; issued October 9, 2014.
- 171.Murtaza M, Contente-Cuomo T. Quality assessment of circulating cell-free DNA using multiplexed droplet digital PCR. 2016/168844A1. WO Patent. Filed April 17, 2015; issued October 10, 2016.
- 172.Hoon DSB, Umetani N, Sunami E. Use of free circulating DNA for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of cancer. 2006/128192 A2. WO Patent. Filed May 27, 2005; issued November 30, 2006.
- 173.Raymond CK, Lim LP, Armour CD. Methods for quantitative genetic analysis of cell free DNA. 2016/0053301 A1. US Patent. Filed August 22, 2014; issued February 25, 2016.
- 174.Ambros V, Lee R, Fusco AP. Isolating Circulating microRNA (miRNA) 9,896,683 B2. US Patent. Filed July 29, 2015; issued February 20, 2018.
- 175.Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. Cancer-derived microvesicle-associated microrna as a diagnostic marker. 8,216,784 B2. US Patent. Filed July 25, 2008; issued July 10, 2012.
- 176.Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. Exosome-associated microRNA as a diagnostic marker. 2,806,273 B1. European Patent. Filed August 12, 2013; issued December 5, 2013.
- 177.Croce CM, Calin GA, Volinia S. Methods for Diagnosing Pancreatic Cancer Using MicroRNAs. 2013/0324589 A1. US Patent. Filed August 12, 2013; issued December 5, 2013.
- 178.Ditzel H, Kodahl AR. Circulating microRNA based cancer biomarkers. 3,011,058 A1. European Patent. Filed December 24, 2014; issued April 27, 2016.
- 179.Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. 3,138,926 A3. European Patent. Filed September 8, 2008; issued April 5, 2017.
- 180.Plasma microRNAs for the detection of early colorectal cancer. 2,944,700 B1. European Patent. Filed October 10, 2012; issued October 18, 2017.
- 181.Zhang C, Zeng K, Zhang J, Ba Y, Chen X, Li H. Serum or plasma microRNA as biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer. 9,388,470 B2. US Patent. Filed December 14, 2009; issued July 12, 2016.
- 182.Croce CM, Calin GA, Volinia S. Methods for diagnosing breast cancer using MicroRNAs. 8,603,744 B2. US Patent. Filed February 28, 2012; issued December 10, 2013.
- 183.NCT02639832, A Pilot Surveillance Study to Monitor Natural Killer Cells and Circulating Tumor Cells in Women With Previously Treated Non-metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer and Women With Previously Treated Non-metastatic Breast Cancer With a Confirmed BRCA Mutation, 2015
- 184.NCT02626039, Characterization & Comparison of Drugable Mutations in Primary and Metastatic Tumors, CTCs and cfDNA in MBCpatients, 2015
- 185.NCT02186236, Detection of Oncogenic Tumor Mutations in the Urine and Blood of Lung and Colorectal Cancer Patients, 2014
- 186.NCT02788084, Development of a Tissue-Based & Cell Free DNA Next-Generation Sequencing Workflow, 2016
- 187.NCT02883517, Cell-free Circulating DNA in Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas, 2016
- 188.NCT02887612, ctDNA for Prediction of Relapse in Gastric Cancer, 2016
- 189.NCT02738593, Detection Cell Free DNA in Lung Cancer Patients, 2016
- 190.NCT02610218, Liquid Biopsy in Monitoring the Therapeutic Efficacy of Targeted Therapy in Advanced/Metastatic Gastric Cancer, 2015
- 191.NCT02872779, Correlation Between Circulating Tumour Markers Early Variations and Clinical Response in First Line Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (COCA-MACS), 2016
- 192.NCT02443948, Circulating Cell-free Tumor DNA in the Plasma of Patients With Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST), 2015
- 193.NCT02133222, Mutational Analyses in Consecutive Measurement Before and After Chemotherapy (AMMAM), 2014
- 194.NCT02934984, Circulating Cell-free Tumor DNA (ctDNA) in Pancreatic Cancer, 2016
- 195.NCT02784639, Comparison of KRAS/BRAF Mutational Status With Conventional Techniques and Plasma Samples Analysis, 2016
- 196.NCT02036216, Circulating Cell-free DNA as a Predictive Biomarker for Hepatocelluar Carcinoma, 2014
- 197.NCT02791217, Identification of Hematological Malignancies and Therapy Predication Using microRNAs as a Diagnostic Tool, 2016
- 198.NCT02928627, Clinical Significance of Hepatic and Circulating microRNAs miR-221 and miR-222 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, 2016
- 199.NCT02964351, microRNA Profiles Identification in Adeno Carcinoma Prostate Cancer, 2016
- 200.NCT01541800, Circulating microRNAs as Disease Markers in Pediatric Cancers, 2012
- 201.NCT02065908, Circulating MicroRNA as Biomarker of Cardiotoxicity in Breast Cancer, 2014
- 202.NCT02812680, The Utility of Circulating Tumour Cells and Plasma microRNA in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma, 2016
- 203.NCT01612871, Circulating miRNAs as Biomarkers of Hormone Sensitivity in Breast Cancer (MIRHO), 2012
- 204.Circulating miRNAs ICORG. 2012;10(11):V2. NCT01722851. [Google Scholar]
- 205.D'Agata R, Corradini R, Ferretti C, Zanoli L, Gatti M, Marchelli R, Spoto G. Ultrasensitive detection of non-amplified genomic DNA by nanoparticle-enhanced surface-plasmon resonance imaging. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;25:2095–2100. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.D'Agata R, Spoto G. Surface plasmon resonance imaging for nucleic acid detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013;405:573–584. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-6563-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.