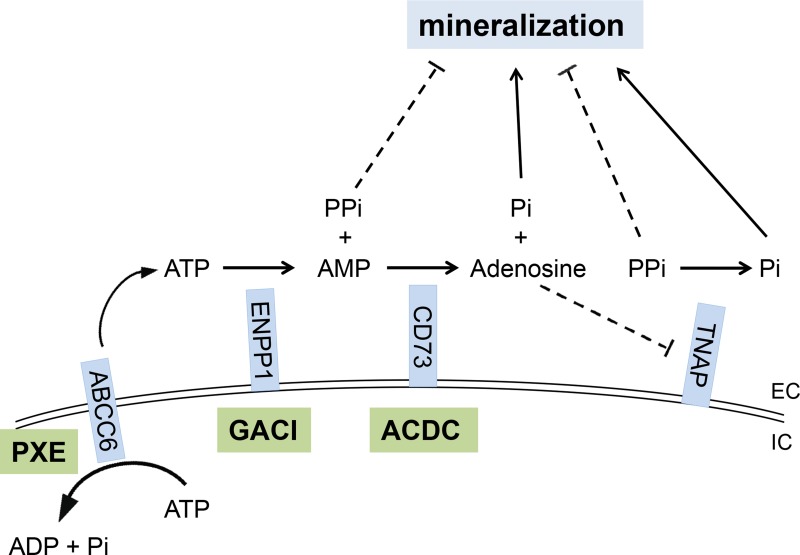
Figure 4. The PPi and Pi generating pathway points to the critical role of components of the pro-mineralization/anti-mineralization network.
Mutations in the ABCC6, ENPP1, and NT5E genes cause pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI), and arterial calcification due to CD73 deficiency (ACDC), respectively. ABCC6, a putative transmembrane transporter, mediates ATP release from hepatocytes to extracellular space where ATP is converted to PPi and AMP by ENPP1, a membrane-bound pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase. CD73 converts AMP to Pi and adenosine, the latter one being an inhibitor of tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP), an extracellular, yet membrane-bound protein, that hydrolyze PPi to Pi. PPi is an anti-mineralization factor, and Pi is a pro-mineralization factor. Deficiencies in ABCC6, ENPP1 and CD73 proteins lead to reduced plasma PPi levels and PPi/Pi ratio, thereby promoting mineralization in peripheral tissues. EC, extracellular; IC, intracellular.