Abstract
Acute respiratory virus infection (ARI) induces CD8+ T cells with diminished cytokine production and functional impairment. The role of cellular mediators of immune impairment, specifically CD4+ regulatory T cells (Tregs), is incompletely understood in ARI. Tregs are known suppressors of effector T cell function, but whether they are detrimental or beneficial in ARI remains controversial. We show here that Treg depletion leads to increased CD8+ T cell function and lower virus titer in mice infected with human metapneumovirus (HMPV). We further demonstrate that Tregs play a temporal role in the immune response to HMPV and influenza: Treg depletion before infection pathologically reduces virus-specific CD8+ T cell numbers and delays virus clearance, while depletion 2 days post-inoculation enhances CD8+ T cell functionality without reducing virus-specific CD8+ T cell numbers. Mechanistically, Treg depletion during immune priming led to impaired dendritic cell and CD8+ T cell migration. Further, early Treg depletion was associated with immune skewing towards a type 2 phenotype characterized by increased type 2 innate lymphoid cells and TH2 CD4+ T cells, which was not observed when Treg depletion was delayed until after inoculation. These results indicate that the presence of Tregs at inoculation is critical for efficient priming of the CD8+ T cell response to ARI, whereas later in infection Tregs are dispensable for virus clearance.
Introduction
Acute respiratory infection by human metapneumovirus (HMPV), influenza, and other viruses leads to CD8+ T cell functional impairment (1–4). Virus-specific CD8+ T cells are produced in response to infection, but over time these cells lose their ability to degranulate and make proinflammatory cytokines in response to cognate antigen (1–4). Our lab recently identified that the inhibitory receptor Programmed Cell Death-1 (PD-1) mediates this impairment early during infection with HMPV and influenza (1), and others have shown PD-1 mediated impairment in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection (5, 6). However, CD8+ T cell impairment occurs later in infection even in the absence of PD-1 (7), indicating that other immunoregulatory mechanisms act to restrain CD8+ T cell function. Optimal immune responses to viral infections require a careful balance of effector responses to clear infection and regulatory mechanisms to prevent immunopathology (8–11). This may be particularly important in the lung environment, where gas exchange must be maintained, even while the lung is flooded with inflammatory infiltrates, cell debris, and cytokines during infection.
CD4+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) are a principal mediator of immune regulation and have been implicated in a variety of diseases, including autoimmunity, cancer, and infectious disease (12, 13). In the setting of infection, the role of Tregs is complex and appears to be specific to a given pathogen. While some studies have shown that Tregs are detrimental to successful immune responses and in some cases can lead to establishment of chronic infection, others have shown that Tregs limit immunopathology (10, 14–17). Studies of respiratory virus infections have yielded conflicting data about the role of Tregs in these different models. Depletion of Tregs before and during RSV infection enhanced effector CD8+ T cell function, but either led to delayed virus clearance, enhanced virus clearance, or no change in clearance depending on the study (18–22). Treg depletion during influenza infection had no effect on viral titers or clearance in adult mice (23) and delayed viral clearance in neonates (24).
In this study, we sought to understand the role of Tregs in HMPV infection. HMPV is the second leading cause of viral respiratory infection in pediatric populations and causes significant morbidity and mortality in infants, elderly, and immunocompromised persons (25–28). We further sought to differentiate the roles of Tregs at different time points of respiratory virus infection. Other groups have found that Tregs are important for priming the adaptive immune response (18, 20, 29), but have not investigated whether these cells are beneficial or detrimental later in infection.
We found that Tregs became increased and activated in the murine lung in response to HMPV, and that Treg depletion led to significantly more functional anti-viral CD8+ T cell responses and reduced HMPV peak virus titer. Treg depletion immediately before inoculation with either HMPV or influenza reduced the frequency of virus-specific CD8+ T cells in the lung and delayed virus clearance. In contrast, depletion after inoculation enhanced CD8+ T cell function with no defect in CD8+ T cell frequency, and also accelerated clearance of influenza. In the absence of Tregs during the priming stage of infection, dendritic cells and CD8+ T cells failed to migrate efficiently. The absence of Tregs before inoculation led to type 2 immune skewing characterized by increased type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) and IL-4+ CD4+ cells, which was not seen when Treg depletion was delayed to 2 days post-inoculation. Furthermore, Treg depletion skewed the TH1:TH2 cell ratio as well as the ILC1:ILC2 ratio in favor of type 2, indicating that Tregs are strong suppressors of both innate and adaptive type 2 immunity.
Materials and Methods
Mice and viruses
C57BL/6 and FoxP3DTR (Alexander Rudensky (30)) mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. Animals were bred and maintained in specific pathogen free conditions in accordance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of Vanderbilt University and University of Pittsburgh. 6-14 week-old age- and sex-matched mice were used in all experiments. HMPV (clinical strain TN/94-49, subtype A2) and influenza virus (strain HK/x31, H3N2) were grown and titered in LLC-MK2 or MDCK cells as previously described(1, 31). For all animal experiments, mice were anesthetized with ketamine-xylazine and intranasally inoculated with 1×106-5×106 PFU HMPV or 50-100 PFU influenza x31, in a 100-μL volume. Mock-infected mice were inoculated with the same volume of UV-inactivated virus or mock cell lysate after we had determined that UV inactivated virus and cell lysate performed equally (data not shown). Viral titers were measured by plaque assay as previously described (31, 32). For bronchoalveolar lavage, mice were euthanized and lavaged twice with 1 ml cold PBS.
Flow cytometry
Pulmonary CD8+ T cells were tetramer-stained as described previously (1). MHC class I tetramers for HMPV (H2-Db/F528–536 and H2-Kb/N11–19) were generated as previously described (33). MHC class I tetramer for influenza (H2-Db/NP366-374) was obtained through the NIH Tetramer Core Facility. Lung Tregs were identified as viable (live/dead violet, Life Technologies), CD4+ (clone RM4-5, eBioscience), FoxP3+ (clone FJK-16s, eBioscience), +/− CD25+ (clone PC61 or 3C7, Biolegend). Tregs were stained for PD-1 (clone RMP1-30), LAG-3 (clone C9B7W), GITR (clone YGITR 765), TGFβ (clone TW7-16B4) Helios (clone 22F6), all BioLegend, and Neuropilin-1 (clone 3DS304M, eBioscience), or with appropriate isotype control Abs (all BioLegend). (Cell surface rather than intracellular TGFβ was measured, as reports have suggested that Treg suppression is mediated by cell surface-bound TFGβ rather than soluble TGFβ.(34, 35)) Cells were fixed and permeabilized with Foxp3/Transcription Factor Fixation/Permeabilization solution (eBioscience) before FoxP3 and Helios staining. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) were stained for viability (live/dead violet, Life Technologies), CD45 (clone 30-F11), CD127 (clone A7R34), lineage cocktail (TER-119 (clone TER-119), CD45R/B220 (clone RA3-6B2), Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1) (clone RB6-8C5), CD3e (clone 145-2C11), CD11b (clone M1/70), CD4 (clone RM4-5), and FcεR1a (clone MAR-1)), CD90.2 (clone 30-H12), and ICOS (clone 15F9), all from BioLegend. ILC2 identity was validated by exposing sorted cells ex vivo to IL-2 and IL-33 and measuring production of IL-5 and IL-13 (Supplemental Figure 1). ILC2s were also stained for ST2 (clone RMST2-2, eBioscience), CD25 (clone PC61, Biolegend), and KLRG-1 (clone 2F1/KLRG1, Biolegend). See supplemental figures 1 and 2 for ILC2 gating schematic. Flow cytometric data were collected using an LSRII or Fortessa cytometer (BD Biosciences) and analyzed with FlowJo software (FlowJo, LLC). MFI refers to median fluorescence intensity in Figure 1, and geometric mean fluorescence intensity in all other figures.
Figure 1. Tregs become increased and activated in the lungs of HMPV-infected mice.
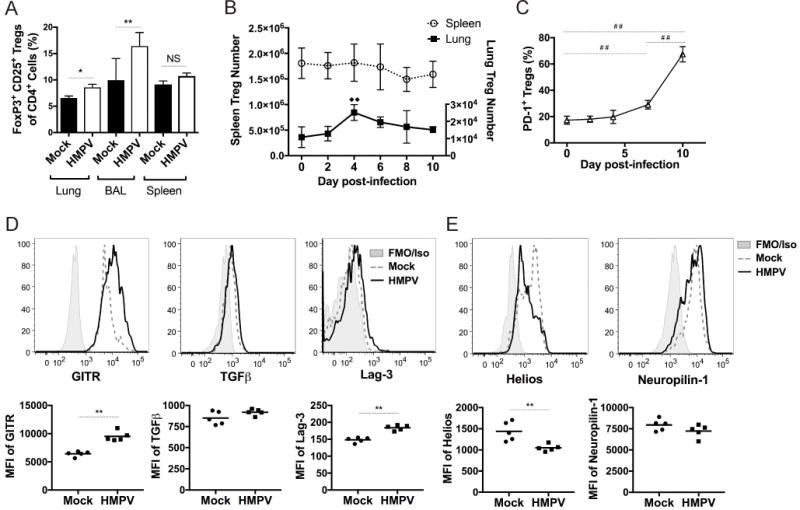
C57BL/6J mice were intranasally inoculated with HMPV and the percentage (A) of CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ Tregs was quantified in various organs at day 6 of infection compared to naïve mice. (B) The absolute number of pulmonary and splenic FoxP3+ cells was quantified for the duration of HMPV infection. (C) The expression of PD-1 on Tregs was measured throughout infection. The expression of Treg activation markers (D) and thymic Treg markers (E) was measured in mock and infected mice at day 6 and median fluorescence intensity (MFI) was calculated. Shaded gray represents isotype control (GITR, TGFβ, Helios, Neuropilin-1), or FMO (fluorescence minus one) control (Lag-3) when isotype staining was brighter than sample staining, dashed line represents mock infection, and solid line represents HMPV-inoculated. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Student’s t test; ##p<0.01, One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. □□ indicates significant compared to day 0, p<0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. N=3-6 mice/group, combined 2 repeat experiments (A-C) or representative of 2-3 experiments (D-E).
Intracellular cytokine staining
Peptide restimulation and ICS for CD8+ T cells were performed as previously described (1). For CD4+ T cell and innate lymphoid cell ICS, lung cells were stimulated with PMA (50ng/ml) and ionomycin (1ug/ml) (Sigma) in the presence of 0.067% GolgiStop (BD) for 5 hours. After stimulation, cells were stained for viability (live/dead violet, Life Technologies) CD4 (clone RM4-5, eBioscience), IFNγ (clone XMG1.2, BD), and IL-4 (clone 11B11, Biolegend), or ILC markers (for Fig 6F, pan-ILC markers CD45, CD127, Lineage, CD90; for all ILC2 ICS figures, pan-ILC markers plus ICOS)(see above for clones) and IL-5 (clone TRFK5, BD), IL-13 (clone eBio13A, eBioscience) and IFNγ (clone XMG1.2, BD).
Figure 6. Treg deficiency leads to impaired DC and CD8+ T cell migration early in infection.
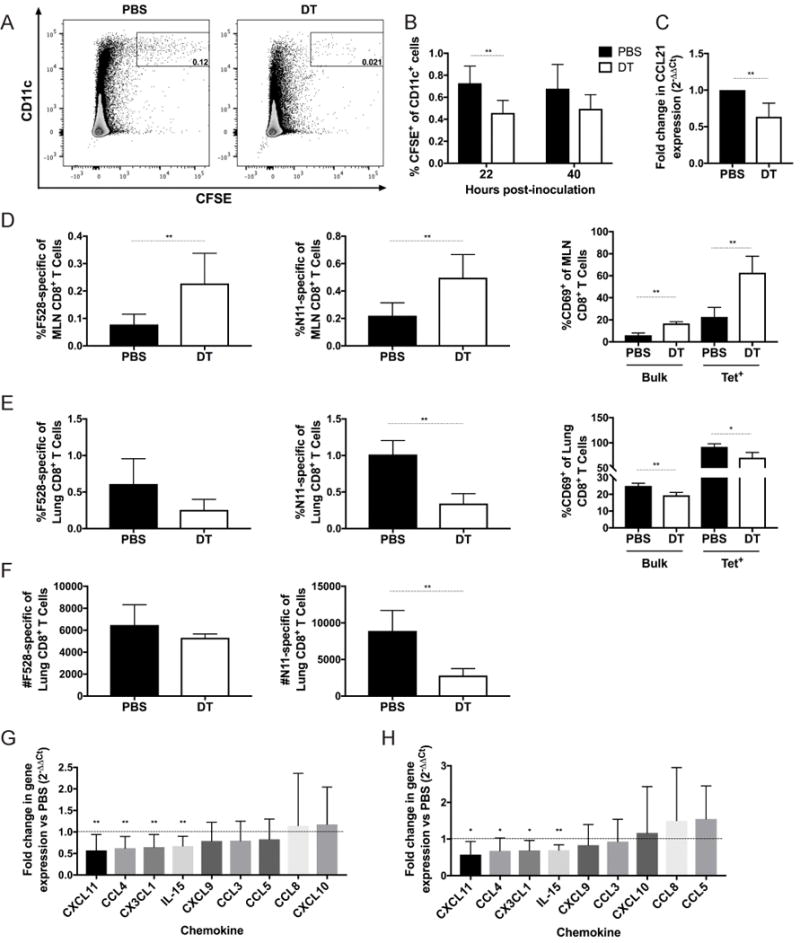
FoxP3 DTR mice were depleted of Tregs via i.p. injection of diphtheria toxin at days −2 and −1 (DT) or given PBS control (PBS). BMDCs were generated and matured overnight in the presence of 100 ng/ml LPS and 10 μM HMPV F528 peptide. Mature BMDCs were labeled with CFSE and intratracheally instilled into mice at day 0. (A,B) 22 and 40 hours post-instillation, mediastinal lymph nodes were collected from mice, and the percentage of CFSE+ CD11c+ cells was quantified via flow cytometry. (C) Mice were depleted of Tregs as above, and inoculated with HMPV. At day 2 post-inoculation, mediastinal lymph nodes were harvested, and expression of CCL21 was measured by qRT-PCR. At day 4 of infection, mediastinal lymph nodes (D) and lungs (E,F) were harvested, and the frequency, number, and activation status of CD8+ T cells recognizing the HMPV epitopes F528 and N11 were measured by flow cytometry. Chemokines were measured by qRT-PCR at day 5 of infection in the lung, and the fold change of DT (G) or Early (H) groups was compared to PBS controls. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Student’s t test. N=2-5 mice/group, combined from 2-3 independent experiments (A-C,G,H) or representative of 2 experiments (D-F).
In vivo Treg depletion
FoxP3DTR mice were injected i.p. with 50 ng/kg diphtheria toxin (Sigma) in 200 μL PBS or with PBS alone for two days before inoculation and every other day thereafter, as previously described (30), or for the indicated days as described in figure legends.
In vivo antibody blockade
For CD25 depletion, C57BL/6 mice were injected i.p. with 500 μg in 200 μL PBS anti-CD25 mAb (clone PC61.5.3) or isotype control (clone HRPN) (both Bio X Cell) at days −3 and 0 of infection.
ILC2 Stimulation
ILC2s were stained with Live/Dead, CD45, Lineage markers, CD127, CD90, and ICOS (see above) and sorted using a BD FACSAria II. 2,500 sorted cells were plated in a total volume of 200 ul RPMI with 10% FBS in a round-bottom 96-well plate. ILC2s were stimulated with 10 ng/ml IL-2 and/or 10 ng/ml IL-33 (both PeproTech). After 5 days cell supernatant was collected and IL-5 and IL-13 were measured by ELISA according to manufacturer instructions (DY405 and DY413, R&D Systems).
Mediastinal lymph node harvest
At indicated time points post-inoculation, mediastinal lymph nodes were collected and placed into RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS (R10) on ice. All 3 nodes were analyzed when possible, but when only 2 were found, these were analyzed. Absolute numbers were not calculated due to the difference in numbers of lymph nodes collected between mice. A single-cell suspension was made by pushing the lymph nodes through a 70 μm nylon cell strainer (Falcon). Cells were washed with R10 and red blood cells were lysed (ACK lysing buffer, Gibco). Cells were then stained for flow cytometry. CD8+ cells from mediastinal lymph nodes were stained for tetramers (see above) and CD69 (clone H1.2F3) (Biolegend).
Labeling and tracking of peptide-loaded BMDCs
Bone marrow derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) were generated as previously described (1). At day 7 of culture, BMDCs were matured overnight with 100 ng/ml LPS (Sigma-Aldrich) and 10 μM F528 HMPV peptide. The next day BMDCs were collected, counted, and resuspended in PBS. BMDCs were labeled as described (36) with some modifications. BMDCs were incubated in 8 μM CFSE (Molecular Probes) for 10 min at 37°C, then washed with RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS. BMDCs were allowed to rest for 1 hour at 37°C before 2×106 BMDCs were intratracheally instilled into mice in a total volume of 50 μL. At various time points post-instillation, mediastinal lymph nodes were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry as above. Migratory BMDCs were identified as CFSE+, CD11c+ (clone N418, Biolegend).
Quantitative RT-PCR
Lung homogenate from the whole lung or total mediastinal lymph node homogenate was frozen at −80°C until use for qRT-PCR. RNA was extracted from the lung homogenate with the Ambion MagMAX-96 Viral Isolation Kit (ThermoFisher) on an Applied Biosystems MagMAX Express-96 Deep Well Magnetic Particle Processor (ThermoFisher) and stored at −80°C until further use. 5 μl of extracted RNA was used for qRT-PCR in 25 μl reaction mixtures on an ABI StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (ThermoFisher) using the AgPath-ID One-Step RT-PCR kit (ThermoFisher). TaqMan primers and probes were used according to the manufacturer’s instructions (all ThermoFisher): IL-15 (Mm00434210_m1), CCL3/MIP-1a (Mm00441259_g1), CCL4/MIP-1b (Mm00443111_m1), CXCL9 (Mm00434946_m1), CXCL10 (Mm00445235_m1), CXCL11 (Mm00444662_m1), CCL8 (Mm01297183_m1), CCL5/RANTES (Mm01302427_m1), CX3CL1 (Mm00436454_m1), CCL21 (Mm03646971_gH). Cycling conditions were 50°C for 30 minutes, followed by an initial activation at 95°C for 10 minutes and 45 cycles of 15 seconds at 95°C, and 30 seconds at 60°C. All values were normalized to the housekeeping gene Hprt, and fold change in chemokine was measured in DT or Early groups compared to PBS groups using the ΔΔCt method.
Multiplex cytokine analysis
Lung homogenate from the whole lung (Day 5) or left lung (Day 7) was used for cytokine analysis by Bio-plex Mouse Cytokine 23-plex Assay (BioRad, Hercules, CA) according to manufacturer’s instructions. The following cytokines and chemokines were measured: IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, IL-12p40, IL-12p70, IL-13, IL-17A, Eotaxin, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IFNγ, CXCL1, MCP-1, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, RANTES, TNFα. Observed concentrations were normalized to lung weight.
Histology
Either the left lobe or accessory lobe of the lung was inflated and fixed in formalin, then subsequently sectioned and stained with H&E or PAS. All fields of each H&E stained slide were scanned at 200× magnification and each field was scored as follows: 0: normal lung tissue; 1: >0 to 25% of tissue area with inflammation; 2: 25-50% of tissue area with inflammation; 3: 50-75% of tissue area with inflammation; 4: 75-100% of tissue area with inflammation (37). Scores were added for each slide and divided by total number of fields scored to calculate average score. Scale bars represent 50 um.
Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was performed using Prism v 6.0 (GraphPad Software). Comparisons between two groups were performed using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test, and significance is noted by asterisks (*). Comparisons between multiple groups were performed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test, and significance is noted by hash signs (#). Error bars on each graph represent SD unless otherwise noted. ** or ## denotes p<0.01, even when p values were calculated to be <0.001 or <0.0001.
Results
Tregs are increased and activated in response to HMPV
To determine the Treg response to HMPV infection, we inoculated WT mice with HMPV and measured the frequency of Tregs in the lung, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid, and spleen at day 6 post-inoculation. Compared to mock-infected mice, Tregs were significantly increased in the lungs and BAL fluid (Figure 1A). We next measured the absolute number of FoxP3+ CD4+ T cells in the lung and spleen throughout the course of infection. Treg numbers peaked in the lung at day 4 of infection, while splenic Tregs did not change significantly in number during infection (Figure 1B). To assess the activation state of these cells, we measured expression of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 on the cell surface of pulmonary Tregs. PD-1 is involved in activation, maintenance, and function of Tregs (38). PD-1 was significantly upregulated on Tregs over the course of infection, suggesting that they were becoming activated (Figure 1C). In contrast, PD-1 expression on splenic Tregs did not change during infection (data not shown). To further characterize the Treg phenotype, Tregs were stained for surface expression of LAG-3, TGFβ, GITR, and Neuropilin-1, and intracellular expression of Helios, at day 6 of infection. The median fluorescence intensity of activation markers was higher on Tregs in infected mice compared to mock-infected mice, and Tregs from HMPV-infected animals expressed lower levels of Helios and Neuropilin-1, two suggested markers of thymic Tregs (39–41) (Figure 1D-E). These results indicate that Tregs respond to HMPV infection by becoming activated and increasing in number and frequency.
Treg depletion leads to enhanced anti-HMPV responses during infection
We next explored whether Tregs inhibit the HMPV-specific CD8+ T cell response during infection. To determine this, we used FoxP3DTR mice, which express the human diphtheria toxin (DT) receptor downstream of the FoxP3 promoter, so that Tregs can be specifically eliminated by injection of DT (30). In our study, DT injection reduced Treg numbers by >95% in the lung (data not shown). FoxP3DTR mice were depleted of Tregs before and throughout HMPV infection, and the virus-specific CD8+ T cell response was measured by flow cytometry. At day 7 and day 10 of infection, the percentage of pulmonary CD8+ T cells that recognized the immunodominant HMPV F528 epitope (1), as well as a secondary dominant epitope, N11 (1), was significantly reduced in Treg-depleted mice (Figure 2A,E and data not shown). However, this was primarily due to an increase in the total number of CD8+ T cells in DT-treated mice, as the absolute number of epitope-specific cells was not significantly different between DT-treated and control mice at day 7 (Figure 2B) or day 10 (Figure 2F). Similarly, at day 7 the percentage of HMPV-specific IFNγ-producing CD8+ T cells was lower in Treg-depleted mice (Figure 2A), with an IFNγ mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) similar to controls (Figure 2D). At day 10, however, Treg-depleted mice had significantly increased numbers of IFNγ+ cells (Figure 2F) with greater IFNγ production per cell (Figure 2H). To quantify the frequency of functional cells, the percentage of IFNγ+ cells was divided by the percentage of tetramer+ cells in each mouse. Treg-depleted mice had significantly more functional CD8+ T cells at both day 7 and day 10 of infection (Figure 2C,G). This increase in functionality per cell was also seen for a secondary dominant epitope, N11 (data not shown). To ensure that DT treatment had no off-target effects (42), WT mice were injected with DT on the same days and the CD8+ T cell response was quantified. No difference was seen in CD8+ T cell functionality in DT-treated WT mice compared to PBS-treated FoxP3DTR mice (data not shown). These data indicate that the absence of Tregs allows CD8+ T cells to become more functional in response to virus infection, even though the relative frequency of epitope-specific CD8+ T cells is reduced in proportion to bulk CD8+ T cells infiltrating the lung.
Figure 2. Treg depletion leads to an enhanced HMPV-specific CD8+ T cell response.
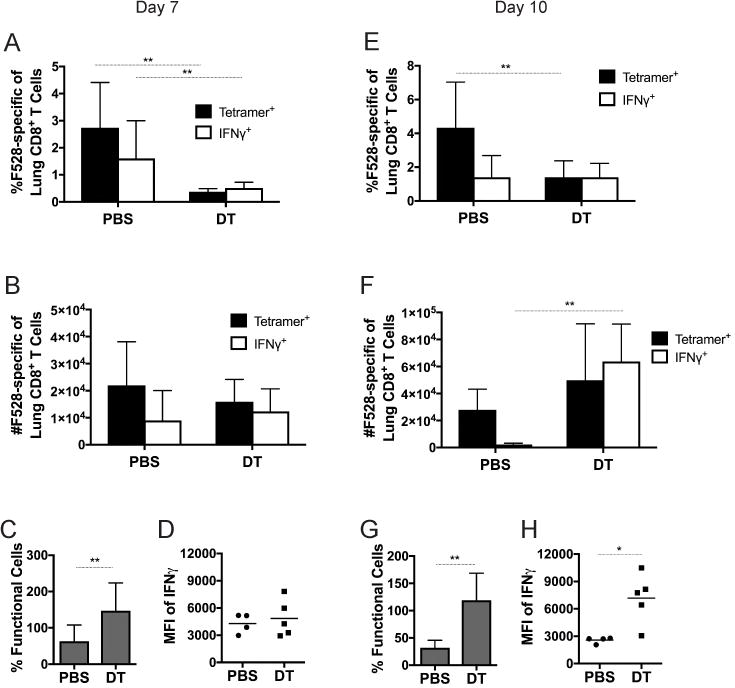
FoxP3DTR mice were depleted of Tregs by injection of DT or injected with PBS before and during infection with HMPV. The percentage (A,E), absolute number (B,F), and functionality (C,G) of the pulmonary CD8+ T cell response was analyzed by flow cytometry at day 7 and day 10. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the IFNγ signal was quantified at days 7 (D) and 10 (H). Functionality was calculated by dividing %IFNγ+/tet+. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Student’s t test. N=4-5 mice per group, combined 2 repeated experiments (A-C, E-G) or representative of 2 repeated experiments (D, H).
Tregs inhibit immune control of HMPV replication while decreasing inflammation
Since Treg depletion led to enhanced CD8+ T cell function, we next tested the biological effect on HMPV infection. We depleted Tregs in FoxP3DTR mice as above, inoculated them with HMPV, and at various times post-inoculation homogenized and quantified lung virus titer by plaque assay. At day 5 of infection, which is the peak of HMPV replication in B6 mice (1), HMPV titers were significantly lower in DT-treated mice compared to PBS-treated controls (Figure 3A). The kinetics of virus clearance on days 7 and 9 were not altered in the absence of Tregs. Lung sections were stained with H&E and scored histologically at days 7 and 10 (Figure 3B-D) to determine whether reduced viral titers came at the cost of increased immunopathology. While DT- and PBS-treated mice had similar lung histology at day 7, DT-treated mice exhibited greater perivascular lymphohistiocytic inflammation than PBS controls at day 10 post-inoculation. Additionally, Treg-depleted mice had a greater number of lung fields that scored 3 or higher (greater than 50% inflammation) compared to PBS controls. However, Treg-depleted, infected mice scored similarly to Treg-depleted, mock-infected mice, which suggests that increased inflammation was due primarily to the absence of Tregs rather than to damage mediated by the virus itself. Taken together, these data suggest that Tregs inhibit the immune system’s ability to curtail the peak of HMPV virus replication, but restrain immune-mediated pathology.
Figure 3. Treg depletion reduces virus titers but increases histopathology.
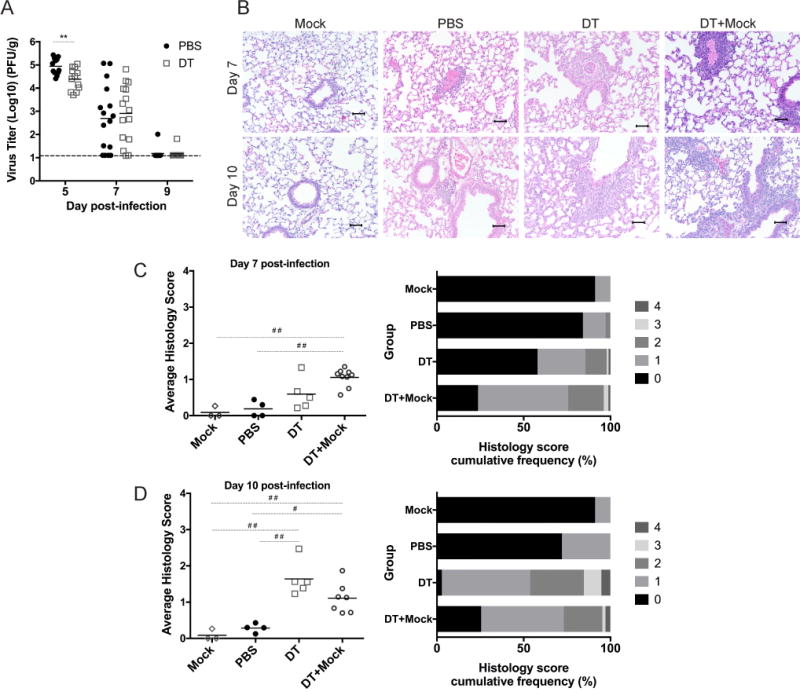
FoxP3 DTR mice were injected with PBS (Mock) or DT (DT+Mock) and mock-infected, or were injected with PBS (PBS) or DT (DT) and inoculated with HMPV. (A) Lungs were harvested at indicated times post-inoculation to quantify virus titer by plaque assay. Lung specimens were taken at days 7 and 10 and stained with H&E (B), and scored by a pathologist (C,D). Histological scoring was calculated by percent inflammation per field of view, with scores of 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 representing 0%, 1-25%, 26-50%, 51-75%, and 76-100%, respectively. **p<0.01, Student’s t test, #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc comparison. N=3-6 mice/group, combined 4 repeated experiments (A) or representative of 3 repeated experiments (B-D).
Depletion and blockade of Tregs using αCD25 treatment improves anti-HMPV CD8+ T cell response
As a complementary approach, and because previous studies in RSV demonstrated different outcomes depending on the method of Treg depletion (18–22), we depleted and blocked Tregs in vivo using PC61, an antibody against CD25 that has been commonly used for Treg depletion in WT mice. Since a variety of dosages and schedules have been reported in the literature for respiratory virus infection (18–20), we performed a pilot study to determine the optimal dose for our model. We determined that i.p. injection of 500 μg at days -3 and 0 had the greatest effect on Treg frequency in the lung while sparing CD8+ T cells (data not shown). Mice that received αCD25 had increased HMPV-specific and functional CD8+ T cells, as measured by production of IFNγ and CD107a, an indicator of cytotoxic granule release (43), despite only a modest reduction in Treg percentages (Figure 4A-D). Furthermore, αCD25-treated mice exhibited increased IFNγ production by CD8+ T cells (Figure 4E). αCD25-treated mice had slightly lower virus titers than isotype-treated controls, which approached statistical significance (Figure 4F). This intermediate phenotype compared to Treg depletion in FoxP3DTR mice was likely due to the fact that αCD25 is not sufficient to completely eliminate all Tregs (Figure 4A). These findings indicate that αCD25 treatment directed at Tregs during HMPV infection has a similar, though less robust, effect on CD8+ T cell cytokine production and degranulation and virus clearance compared to complete elimination using FoxP3DTR mice.
Figure 4. Depletion and blockade of Tregs with αCD25 restores CD8+ T cell function.
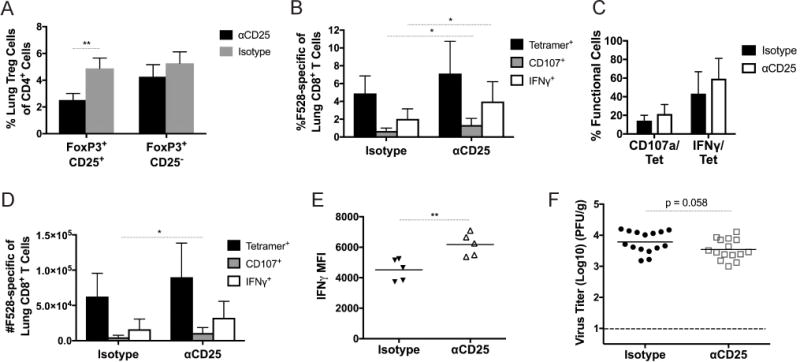
WT mice were injected with 500 ug anti-CD25 antibody or isotype at days −3 and 0 of HMPV infection. Treg percentages (A), percent CD8+ T cell response (B), function (C), and absolute number (D) were quantified at day 7 of infection. (E) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IFNγ signal was measured at day 7. (F) HMPV virus titer was calculated at day 5 of infection. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Student’s t test. N=2-6/group, combined 2-3 experiments (B-D,F) or representative of 2 experiments (A,E).
Treg depletion early or late in HMPV infection reveals differential functions of Tregs
Since Treg depletion throughout infection led to a decreased proportion of HMPV-specific CD8+ T cells (Figure 2A,D), we hypothesized that Tregs might be necessary to prime the adaptive immune response to HMPV. To test this, we depleted Tregs before and throughout infection (DT), only before inoculation with HMPV (early), or from 2 days post-inoculation onward (late) (Figure 5A). At day 7 of infection, Tregs in the “early” group were restored to nearly the same level (8.42% +/− 0.41) as the PBS group (9.93% +/− 0.60). Mice that were depleted of Treg later had a greater frequency and absolute number of HMPV-specific and IFNγ-producing CD8+ T cells at day 7 of infection (Figure 5B,C). In contrast, mice that underwent Treg depletion only before inoculation had decreased CD8+ T cell percentages and similarly functional cells as those that received DT throughout (Figure 5D). All mice had similar day 5 titer (Figure 5E); however, mice that received late depletion had significantly reduced virus titers at day 7 compared to those mice that had Tregs depleted early (Figure 5F). Both DT and early groups had delayed virus clearance compared to PBS-treated mice. Histologic analysis showed that both early and late Treg depletion led to increased lung immunopathology (Figure 5G), with the early group having more instances of inflammation scores of 2 or higher (Figure 5H). Lung sections were also stained with Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) to detect mucus. Early Treg-depleted groups had marked PAS positivity in large and small airways. DT and late groups had less PAS positivity than the early group, while the PBS-treated mice had rare PAS positivity in bronchioles (Figure 5I). These data indicate that Treg depletion after inoculation is sufficient to enhance function while also maintaining the number and frequency of HMPV-specific CD8+ T cells. Additionally, this suggests that Tregs play a role at the onset of infection for the recruitment of CD8+ T cells, but then impair CD8+ T cell function later on to prevent immune pathology.
Figure 5. CD8+ T cells fail to mount a robust response and clear virus efficiently when Tregs are depleted before inoculation.
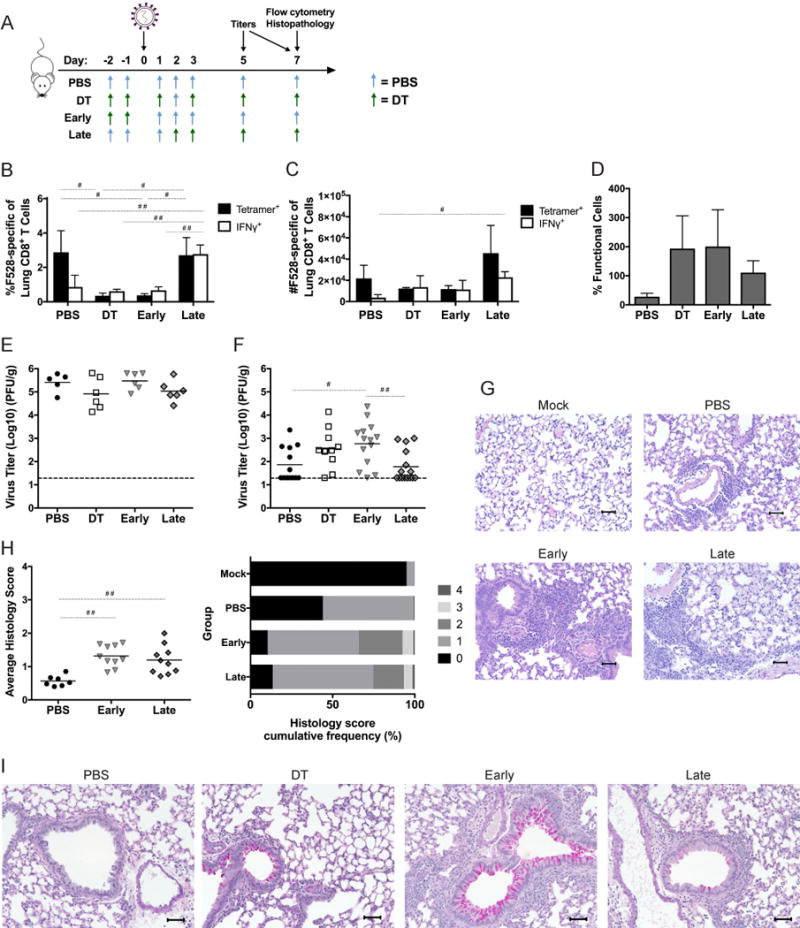
(A) FoxP3DTR mice were depleted of Tregs by injection of DT on days −2 and −1 (Early); on days 2, 3, and 5 (Late); or before and throughout the course of infection (DT); or injected with PBS before and throughout (PBS). Mice were inoculated with 1×106 PFU HMPV A2. The pulmonary CD8+ T cell response was analyzed by flow cytometry at day 7 for frequency (B), absolute number (C), and percent functionality (D). Virus titers were measured via plaque assay at days 5 (E) and 7 (F). Histological sections were stained with H&E (G) and scored (H) as in Figure 3, or stained with Periodic-acid Schiff (PAS) (I). #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc comparison. N=4-6 mice/group, pooled from 2-3 experiments (E-H) or representative of 3-4 experiments (B-D, I).
Absence of Tregs during priming phase of infection impairs migration of DCs and CD8+ T cells to lymph nodes and lung
We next sought to understand the mechanism of how a lack of Tregs at the priming stage of the immune response leads to a deficient proportion of HMPV-specific CD8+ T cells in the lung (Figures 2A, 5B). Others have found that in the absence of Tregs, dendritic cells (DCs) exhibit reduced migration to lymph nodes in response to HSV infection (29). To determine whether depletion of Tregs leads to impaired DC migration from the lung to the draining mediastinal lymph nodes (MLN), we instilled CFSE-labeled, HMPV peptide-loaded bone marrow derived DCs (BMDCs) intratracheally into mice that had either been depleted of Tregs or given PBS control. We found that at 22 hours post-instillation, significantly fewer CFSE+ BMDCs were found in the MLN of Treg-depleted mice compared to PBS controls (Figure 6A,B). There was a similar reduction of BMDCs in Treg-depleted mice at 40 hours post-instillation, though this was not statistically significant (Figure 6B). To better understand the mechanism of this reduction, we measured levels of the chemokine CCL21, a ligand for CCR7 on DCs and other cells, and found that CCL21 was reduced in MLNs of infected Treg-depleted mice compared to infected PBS controls (Figure 6C). We next asked whether a reduction of DCs led to decreased expansion of HMPV-specific CD8+ T cells in the MLN. We measured the percentage of CD8+ T cells specific for the HMPV epitopes F528 and N11 as well as the expression of CD69, an early marker of activation, on these cells at day 4 of infection in the MLN. We found that despite a phenotype that suggested impaired DC migration in Treg-depleted mice, there was a significantly greater frequency of HMPV-specific CD8+ T cells, as well as more activated CD8+ cells, in the MLN compared to PBS controls (Figure 6D). However, when we measured HMPV-specific CD8+ T cell recruitment to the lung at day 4 (the earliest time point that we could detect HMPV-specific CD8+ T cells in the lung (data not shown)), Treg-depleted mice had significantly fewer epitope-specific CD8+ T cells by frequency and number compared to PBS controls, suggesting a failure of migration in the absence of Tregs (Figure 6E,F). The frequency of HMPV-specific+ CD8+ T cells in MLN at day 3 of infection was less than 0.05% for either group (data not shown), which suggests that the difference in MLN and lung CD8+ T cell frequency was not due to earlier migration of HMPV-specific CD8+ T cells from the MLN to the lung in control mice.
To better understand the mechanism of how Treg depletion leads to impaired CD8+ T cell migration to the lung, we measured a variety of chemokines that contribute to T cell migration in lung homogenate at day 5 of infection in PBS, Early, and DT treatment groups by qrtPCR (Table I). We found that CXCL11, CCL4, CX3CL1, and IL-15 were reduced up to 2-fold in the lungs of DT and Early groups compared to PBS controls (Figure 6G,H). These data indicate that in the absence of Tregs, cell migration in response to HMPV infection is impaired.
Table I.
Chemokines measured for T cell migration
| Chemokine | Role in T cell migration | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CXCL11 | Recruit CD4+ and CD8+ effector T cells (Teff) to sites of inflammation | (44–46) |
| CCL4 (MIP-1b) | Made by activated CD8+ T cells | (47) |
| CX3CL1 | Attract and induce endothelial adhesion of activated T cells | (48, 49) |
| IL-15 | Induce migration of CD8 Teff to lung | (50) |
| CXCL9 | Recruit CD4+ and CD8+ Teff to sites of inflammation | (45) |
| CCL5 (RANTES) | Recruit CD4+/CD8+ T cells | (51) |
| CCL3 (MIP-1a) | Attract CD8+ T cells to airways | (52) |
| CXCL10 | Recruit CD4+ and CD8+ Teff to sites of inflammation | (45) |
| CCL8 (MCP-2) | Attract human T cells (limited data in mice) | (53) |
Early Treg depletion leads to type 2 immune skewing, while late depletion maintains type 1 response
To further investigate the mechanism of how early Treg depletion alters the lung environment and delays virus clearance, we analyzed protein levels of cytokines and chemokines in lung homogenates in the groups defined in Figure 5A at days 5 and 7 post-HMPV inoculation. At day 5 of infection, IL-10 was lower in DT, early, and late treated groups compared to control mice. IL-5 levels were significantly higher in both DT and early treated mice, while type 1 cytokines IL-2 and IFNγ were higher in PBS controls and late depleted mice (Figure 7A). We found that type 2 cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and eotaxin, were increased at day 7 in mice that received early Treg depletion (Figure 7B). Furthermore, early Treg depletion led to even higher IL-5 and IL-13 levels than DT treatment throughout infection, indicating that the timing of Treg depletion was critical for this phenotype. To determine which cells were responsible for the type 2 cytokine skewing, we stimulated lung cells from infected mice in the 4 treatment groups ex vivo with PMA/ionomycin. We used flow cytometry to immunophenotype CD4+ T cells and measure type 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) numbers and cytokine production. We found that after early Treg depletion, there was a greater frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ T cells than after DT, late depletion, or PBS control (Figure 7C). Additionally, early Treg depletion led to greater numbers of ILC2s compared to late depletion (Figure 7D; for gating strategy see Supplemental Figure 1) as well as greater production of IL-5 and IL-13 from these cells (Figure 7E,F). Since previous studies have used a variety of markers to identify ILC2s (which may differ between tissue type and mouse strain) (54–58), we further stained the ILC2 population for ST2, CD25, and KLRG-1 (Supplemental Figure 2A). We found that although the overall absolute number of cells varied depending on the marker of interest, all revealed nearly identical patterns of increased ILC2s in Treg-depleted mice (Supplemental Figure 2B). When IFNγ (produced by ILC1s) and IL-13 (from ILC2s) were measured on bulk ILCs, the DT and early groups had a smaller proportion of IFNγ+ ILC1s compared to IL-13+ ILC2s (2.5:1), while this ratio was maintained near 5:1 in PBS-treated and late groups (Figure 7G). These data indicate that early Treg depletion is associated with skewing of both innate and adaptive cells towards a type 2 phenotype, and that Tregs control the ratio of both innate and adaptive type 1 and type 2 immune cells.
Figure 7. Early Treg depletion leads to imbalance of TH2 cytokines, TH2 cells, and ILC2s.

Cytokines and chemokines were measured by Luminex multiplex analysis of lung homogenate of groups from Figure 5A at day 5 (A) and 7 (B). FoxP3DTR mice were depleted of Tregs and inoculated as in Figure 5, and CD4+ cells (C) and ILC2s (D-F) were quantified and phenotyped by flow cytometry at day 7 post-inoculation. (G) The ratio of IFNγ+ to IL-13+ ILCs was calculated. CD4+ cells and ILC2s were stimulated prior to staining in C and E-G. For panel G, pan-ILCs were defined as CD45+, CD127+, Lin−, CD90+; for panels D-F, ILC2s were defined as pan-ILC markers plus ICOS+ (see supplemental figure 1). #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc comparison. N=4-6 mice/group, pooled from 2-3 independent experiments (A-D) or representative of 2 independent experiments (E-G).
Tregs have differential roles in early and late influenza virus infection
To determine whether the roles of Tregs early and late in infection was specific to HMPV or could be generalized to other respiratory viruses, we depleted Tregs either early or late during infection with influenza x31, a mouse adapted H3N2 strain. Since x31 is a mouse-adapted strain, mice had increased morbidity than with HMPV infection (19% vs. 5% body weight loss at day 7 post-inoculation, data not shown). As we observed with HMPV, at day 7 post-inoculation mice depleted of Tregs either early or throughout infection had significant reductions in epitope-specific CD8+ T cells, as well as significantly fewer IFNγ-producing cells compared to PBS-treated mice (Figure 8A,B). Though late Treg depletion led to significantly more IFNγ production by CD8+ T cells compared to DT- or early-treated groups, the frequency of epitope-specific cells in the late group was not equivalent to the PBS control group, in contrast to what we saw for HMPV infection (Figure 5B). This difference may be attributable to the increased severity of the mouse-adapted influenza virus infection. Mice depleted of Tregs at any time point had a trend towards more functional CD8+ T cells than PBS-treated mice (Figure 8C). At day 7 of infection, virus titers in the late group were reduced by 100-fold compared to early and DT groups, and 10-fold compared to PBS controls (Figure 8D). When we analyzed helper T cell skewing, we saw significantly more IL-4+ CD4 cells as well as more IL-4 produced per cell in the early and DT groups (Figure 8E,F). Absolute numbers of ILC2s were significantly increased in early-depleted mice (Figure 8G and Supplemental Figure 2C). The early group had a higher proportion of IL-5/IL-13+ ILC2s as well as more IL-5 per cell (Figure 8H,I). These data suggest that the temporal differences in the role of Tregs are conserved between infections by multiple respiratory viruses.
Figure 8. Tregs exert differential functions in the early and late immune response to influenza infection.
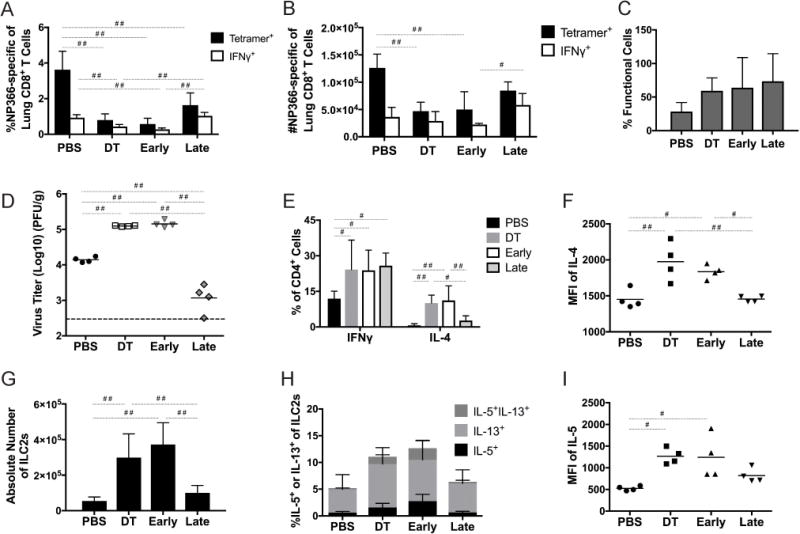
FoxP3DTR mice were depleted of Tregs early, late, or throughout infection as in Figure 5, then inoculated with 50-100 PFU influenza x31. (A-C) At day 7 of infection mice were sacrificed and the influenza-specific CD8+ T cell response was quantified. (D) Virus titers were measured at day 7 of infection. Cytokine production from CD4+ cells was measured at day 7 (E), and numbers (F) and cytokine production from ILC2s (H-I) was also measured. #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc comparison. N=4 mice/group, combined from 2-3 experiments (E,G) or representative of 2-3 independent experiments (A-D,F,H-I).
Discussion
The results from these studies demonstrate the importance of timing for determining whether Tregs are detrimental or beneficial during respiratory virus infection. We found that a complete absence of Tregs during the entire course of HMPV infection led to enhanced CD8+ T cell function and reduced peak virus titer; however, the magnitude of the HMPV-specific CD8+ T cell response was not increased. This led us to question whether the timing of Treg depletion could influence the CD8+ T cell response. We found that Tregs were important early in infection for enhancing the CD8+ T cell response through DC and CD8+ T cell migration, and that early depletion led to impaired virus clearance for both HMPV and influenza. In contrast, when Treg depletion was delayed until 2 days post-inoculation, the frequency of virus-specific CD8+ cells was maintained, while the functionality of these cells was enhanced. Furthermore, late Treg depletion enhanced the clearance of influenza. These results suggest that Tregs play an important role in priming the immune response to respiratory virus infections, but that they are dispensable and in some ways even detrimental after the immune response has already been initiated.
The findings from our studies contrast with results from other respiratory viruses. The closest human pathogen to HMPV is RSV. Previous studies that explored the role of Tregs in the immune response to RSV found that while Treg depletion led to a greater percentage of functional epitope-specific CD8+ cells, virus clearance was delayed (18–20) or unchanged (21). In contrast, for HMPV, we saw that Treg depletion led to lower peak virus titer but unchanged virus clearance. These discordant findings could simply be due to the fact that even though these are both pneumoviruses, they are distinct viruses. In addition, RSV is often studied in a BALB/c mouse model, while the experiments for this study were done in C57BL/6 mice. Most previous studies of Tregs in RSV relied on αCD25 antibodies to deplete and block Tregs (18–20). However, we still saw increased cytokine production and cytotoxic degranulation, with a trend towards reduced peak virus, using αCD25 treatment, though it is possible that these differences can be explained by different dosing schedules. αCD25 may have targeted effector cells in those earlier studies, since effector CD8+ and CD4+ T cells can upregulate CD25 upon activation. If this was the case, then the reduced CD4/CD8 response could have delayed virus clearance in those previous reports. DT-mediated depletion of FoxP3+ cells has become standard for Treg depletion studies. One RSV study using DEREG (59) mice, which also allow for DT-mediated Treg depletion, demonstrated lower viral titers with DT treatment, similar to our findings for HMPV infection (22).
Several reports have suggested that Tregs of thymic origin (tTregs) are primarily involved in preventing autoimmunity, while Tregs derived from a naïve CD4+ cell (pTregs) are often specific to exogenous antigen and therefore dampen the immune response to pathogens and other foreign insults (60–62). Some controversy exists over markers to discriminate thymically or peripherally derived Tregs; therefore, we used both Helios and Neuropilin-1 to phenotype the Tregs responding to HMPV infection. Both of these markers have been suggested to have higher expression on tTregs, even if some tTregs or pTregs have been shown to either not express or express both of these molecules (63). In our experiments, we found that Tregs in the lungs of mice inoculated with HMPV had fewer Helios+ cells compared to those from mock-infected mice, which suggests that more of the Tregs responding to HMPV might be peripherally derived. However, our results cannot definitively conclude whether the increased number of Tregs seen at days 4 and 6 in the lung are specifically due to maturation of naïve CD4+ cells into pTregs.
When we measured the effect of early and late Treg depletion, we found that the absence of Tregs before inoculation reduced epitope-specific CD8+ T cells in the lung tissue (Figures 5,8). This is consistent with earlier studies (18, 20, 29) that suggested that Tregs are important for priming CD8+ T cells at the beginning of infection.
Our finding of delayed BMDC trafficking and reduced CCL21 levels in Treg-depleted mice is consistent with data from herpes simplex virus that showed that Tregs are necessary early in HSV infection for DC trafficking to lymph nodes (29). We show that this is also true for respiratory virus infection, and by pre-loading the BMDCs with antigen, we further find that DC trafficking is impaired regardless of antigen uptake efficiency.
Additionally, we found that CD8+ T cell trafficking to the lung was impaired in mice that had been depleted of Tregs before infection. Even though Treg depletion led to reduced DC trafficking to the mediastinal lymph node, there was still a greater frequency of HMPV-specific CD8+ T cells in the lymph node in Treg-depleted mice. This could have been due to an overall increased proliferative capacity of these cells in the absence of Tregs. However, these HMPV-specific cells were reduced both by frequency and number in the lung of Treg-depleted mice compared to PBS controls. Because the absolute number of these cells was lower in the lungs of Treg-depleted mice at day 4, it is unlikely that the difference in frequencies between the groups at this time point was simply due to overabundant proliferation of bulk CD8+ T cells triggered by an absence of Tregs immediately before infection.
It is possible that the reduced HMPV-specific CD8+ T cell numbers and frequencies could be due to decreased proliferation of these cells once they had migrated from the MLN to the lung, rather than due to strict deficiencies in migration. However, when we measured lung expression of a variety of chemokines that promote T cell migration, we found that Treg-depleted mice had significantly reduced levels of CXCL11, CCL4, CX3CL1, and IL-15, which supports a mechanism of a failure of virus-specific CD8+ cells to traffic efficiently to the lung.
Of the chemokines measured, CXCL11 (also known as I-TAC (Interferon-inducible T-cell alpha chemoattractant)) had the greatest fold reduction in expression in Treg-depleted mice compared to PBS controls (Figure 6G,H). CXCL11 is related to CXCL9 and CXCL10, but has the highest affinity of the three for the CXCR3 receptor on activated T cells (64). CXCL11 is strongly induced by IFNγ (65), which we saw was reduced in the lungs at day 5 of infection in the absence of Tregs (Fig 7A). Therefore, a potential mechanism for the observed reduction in virus-specific CD8+ T cells at day 7 in the lung is that the absence of Tregs leads to reduced IFNγ in the lung early in infection, which causes reduced CXCL11 levels, and finally, deficient effector CD8+ T cell migration to the infected lung.
Interestingly, we saw that when Tregs were depleted 2 days after influenza inoculation, there was a significant reduction in viral titer at day 7 post-inoculation compared to all other groups (Figure 8D). This accelerated virus clearance was unique to influenza, as at day 7 of HMPV infection, titers were equally low in the late and PBS groups (Figure 5F). This discrepancy may be attributable to differences in the kinetics of HMPV and influenza clearance, or due to differential roles of Tregs between the two infections, and is worth further investigation.
We saw that early Treg depletion in both infections was associated with immunological skewing towards a type 2 biased response. It is unclear whether this type 2 skewing contributed to the reduction in virus-specific effector T cells during early Treg depletion or whether type 2 skewing also occurs in the population of virus-specific effector cells in the absence of Tregs. A future study could assess this by quantifying the ratio of IFNγ+/IL-4+ CD4+ cells after stimulation with a pool of HMPV peptides representing CD4+ epitopes; however, MHC-II epitopes have not yet been identified for HMPV.
A study by Josefowicz et al. found that pTregs specifically were responsible for controlling TH2 responses in the mucosa (66). Our study depleted both tTregs and pTregs indiscriminately, but it would be intriguing to see if our findings would be recapitulated in a model of respiratory virus infection with deficient pTreg induction.
Other groups have shown that Tregs constrain TH2 cells more strongly than they do TH1 or TH17 cells in respiratory virus infection (21, 24, 67). We not only saw skewing towards TH2 CD4+ cells following early Treg depletion, but we also saw increased numbers and function of type 2 ILCs and an increased ratio of ILC2s to ILC1s in Treg-depleted mice (Figure 7,8). This finding is consistent with other groups that demonstrated that Tregs suppress ILC2s (68, 69), but here we further demonstrate that Tregs also control the innate type 1 to type 2 ratio.
Though other groups have found that ST2/IL-33R is highly expressed on ILC2s (70), we found low expression of ST2 on our ILC2s (Supplemental figure 2). Furthermore, when we analyzed ST2+ cells for ICS production of IL-5 or IL-13, we found that the ST2+ gate failed to capture 90% of the IL-5+ or IL-13+ cells that were detected in our ICOS+ ILC2 gate (data not shown). Our findings here for ST2 staining are consistent with others who reported that ILC2 surface markers can be heterogenous in mice (71). It is likely that mouse strains, tissue types, disease models, and microbiome may all contribute to variation in surface marker expression. To better understand the ILC2 phenotype in our model, we also stained for KLRG-1 and CD25, two other markers that have been used to distinguish ILC2s (54–58). Though absolute numbers of cells differed depending on the specific marker used, we found that the trend of increased ILC2s after early Treg depletion held true regardless of ILC2 marker, in both HMPV and influenza infections (Supplemental figure 2), emphasizing the role of Tregs in regulating innate lymphoid cells during infection.
Overall, our findings and those from other groups indicate that Tregs exert tight control over both innate and adaptive type 2 responses in the lung, which is important when considering the pathogenic role of TH2 and ILC2s in immune-mediated diseases such as asthma (72). This is especially significant given the known association between infection by respiratory viruses such as HMPV or RSV and subsequent asthma (73). It is intriguing to imagine that Treg numbers or function during respiratory infection in early life could have predictive value on the predisposition to future allergic asthma, and perhaps could be manipulated during infection in order to reduce this risk.
We have demonstrated that Tregs constrain the antiviral CD8+ T cell response in HMPV infection, allowing higher virus titers while reducing immunopathology. Tregs are essential during the priming phase of respiratory virus infection, and depletion of these cells immediately before infection impedes immune cell migration and virus clearance. Interestingly, early Treg depletion skews both the innate and adaptive immune response towards a type 2 bias in viral respiratory infection.
Our findings and those of other groups emphasize the fine-tuning required to balance the antiviral immune response against harmful immunopathology. Moving the dial too far in either direction could lead to establishment of chronic infection or to potentially severe reductions in lung function. This is already a potential consequence of the increasing use of immunomodulatory drugs in diseases such as cancer. As immunomodulatory therapies such as PD-1 blockade are used more widely, off-target effects such as immune-related lung injury associated with common respiratory viruses could become more frequent. An understanding of the mechanisms regulating the lung immune response to viruses is essential to managing these therapeutic complications.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank D. Flaherty, B. Matlock, and K. Weller at the VMC Flow Cytometry Shared Resource and J. Michel at the Rangos Research Flow Core at the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh for their assistance with flow cytometry. Thank you to P. Gilchuk and A. Kumar for synthesis of HMPV F528 and N11 tetramers and the NIH Tetramer Core Facility for synthesis of influenza NP366 tetramer. We thank the Research Histology Core at the Department of Pathology, Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC, for their histology services.
Footnotes
This work was supported by NIH grants AI085062 (JVW) and T32GM007347 for the Vanderbilt Medical Scientist Training Program (MCR). SJ is supported by a VA Merit Award. This project used the UPMC Hillman Cancer Center and Tissue and Research Pathology/Health Sciences Tissue Bank shared resource, which is supported in part by award P30CA047904. The VMC Flow Cytometry Shared Resource is supported by the Vanderbilt Ingram Cancer Center (P30 CA68485) and the Vanderbilt Digestive Disease Research Center(DK058404). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author contributions
MCR and JVW designed the experiments. MCR, KDL, NS, and MJ performed the experiments. MCR, TDO, and JVW analyzed the data. SJ provided essential reagents. JVW supervised the work. MCR interpreted the results, designed the figures, and wrote the manuscript with input from JVW. All authors provided feedback to the manuscript.
References
- 1.Erickson JJ, Gilchuk P, Hastings AK, Tollefson SJ, Johnson M, Downing MB, Boyd KL, Johnson JE, Kim AS, Joyce S, Williams JV. Viral acute lower respiratory infections impair CD8+ T cells through PD-1. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:2967–2982. doi: 10.1172/JCI62860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chang J, Braciale TJ. Respiratory syncytial virus infection suppresses lung CD8+ T-cell effector activity and peripheral CD8+ T-cell memory in the respiratory tract. Nat Med. 2002;8:54–60. doi: 10.1038/nm0102-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vallbracht S, Unsold H, Ehl S. Functional impairment of cytotoxic T cells in the lung airways following respiratory virus infections. European journal of immunology. 2006;36:1434–1442. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.DiNapoli JM, Murphy BR, Collins PL, Bukreyev A. Impairment of the CD8+ T cell response in lungs following infection with human respiratory syncytial virus is specific to the anatomical site rather than the virus, antigen, or route of infection. Virology journal. 2008;5:105. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-5-105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Telcian AG, Laza-Stanca V, Edwards MR, Harker JA, Wang H, Bartlett NW, Mallia P, Zdrenghea MT, Kebadze T, Coyle AJ, Openshaw PJ, Stanciu LA, Johnston SL. RSV-induced bronchial epithelial cell PD-L1 expression inhibits CD8+ T cell nonspecific antiviral activity. The Journal of infectious diseases. 2011;203:85–94. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yao S, Jiang L, Moser EK, Jewett LB, Wright J, Du J, Zhou B, Davis SD, Krupp NL, Braciale TJ, Sun J. Control of pathogenic effector T-cell activities in situ by PD-L1 expression on respiratory inflammatory dendritic cells during respiratory syncytial virus infection. Mucosal immunology. 2014 doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Erickson JJ, Rogers MC, Tollefson SJ, Boyd KL, Williams JV. Multiple Inhibitory Pathways Contribute to Lung CD8+ T Cell Impairment and Protect against Immunopathology during Acute Viral Respiratory Infection. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2016;197:233–243. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Duan S, Thomas PG. Balancing Immune Protection and Immune Pathology by CD8(+) T-Cell Responses to Influenza Infection. Frontiers in immunology. 2016;7:25. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Olson MR, Varga SM. Pulmonary immunity and immunopathology: lessons from respiratory syncytial virus. Expert review of vaccines. 2008;7:1239–1255. doi: 10.1586/14760584.7.8.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stephen-Victor E, Bosschem I, Haesebrouck F, Bayry J. The Yin and Yang of regulatory T cells in infectious diseases and avenues to target them. Cellular microbiology. 2017;19 doi: 10.1111/cmi.12746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Newton AH, Cardani A, Braciale TJ. The host immune response in respiratory virus infection: balancing virus clearance and immunopathology. Seminars in immunopathology. 2016;38:471–482. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0558-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Plitas G, Rudensky AY. Regulatory T Cells: Differentiation and Function. Cancer immunology research. 2016;4:721–725. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 2008;133:775–787. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Richert-Spuhler LE, Lund JM. The Immune Fulcrum: Regulatory T Cells Tip the Balance Between Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Outcomes upon Infection. Progress in molecular biology and translational science. 2015;136:217–243. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Berod L, Puttur F, Huehn J, Sparwasser T. Tregs in infection and vaccinology: heroes or traitors? Microbial biotechnology. 2012;5:260–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2011.00299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Boer MC, Joosten SA, Ottenhoff TH. Regulatory T-Cells at the Interface between Human Host and Pathogens in Infectious Diseases and Vaccination. Frontiers in immunology. 2015;6:217. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Veiga-Parga T, Sehrawat S, Rouse BT. Role of regulatory T cells during virus infection. Immunol Rev. 2013;255:182–196. doi: 10.1111/imr.12085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fulton RB, Meyerholz DK, Varga SM. Foxp3+ CD4 regulatory T cells limit pulmonary immunopathology by modulating the CD8 T cell response during respiratory syncytial virus infection. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2010;185:2382–2392. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lee DCP, Harker JAE, Tregoning JS, Atabani SF, Johansson C, Schwarze J, Openshaw PJM. CD25+ Natural Regulatory T Cells Are Critical in Limiting Innate and Adaptive Immunity and Resolving Disease following Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Journal of Virology. 2010;84:8790–8798. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00796-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ruckwardt TJ, Bonaparte KL, Nason MC, Graham BS. Regulatory T Cells Promote Early Influx of CD8+ T Cells in the Lungs of Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Infected Mice and Diminish Immunodominance Disparities. Journal of Virology. 2009;83:3019–3028. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00036-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Durant LR, Makris S, Voorburg CM, Loebbermann J, Johansson C, Openshaw PJ. Regulatory T cells prevent Th2 immune responses and pulmonary eosinophilia during respiratory syncytial virus infection in mice. J Virol. 2013;87:10946–10954. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01295-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Loebbermann J, Thornton H, Durant L, Sparwasser T, Webster KE, Sprent J, Culley FJ, Johansson C, Openshaw PJ. Regulatory T cells expressing granzyme B play a critical role in controlling lung inflammation during acute viral infection. Mucosal immunology. 2012;5:161–172. doi: 10.1038/mi.2011.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Betts RJ, Ho AW, Kemeny DM. Partial depletion of natural CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells with anti-CD25 antibody does not alter the course of acute influenza A virus infection. PloS one. 2011;6:e27849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Oliphant S, Lines JL, Hollifield ML, Garvy BA. Regulatory T Cells Are Critical for Clearing Influenza A Virus in Neonatal Mice. Viral immunology. 2015;28:580–589. doi: 10.1089/vim.2015.0039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schuster JE, Williams JV. Human metapneumovirus. Pediatrics in review/American Academy of Pediatrics. 2013;34:558–565. doi: 10.1542/pir.34-12-558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Boivin G, Abed Y, Pelletier G, Ruel L, Moisan D, Côté S, Peret TCT, Erdman DD, Anderson LJ. Virological Features and Clinical Manifestations Associated with Human Metapneumovirus: A New Paramyxovirus Responsible for Acute Respiratory-Tract Infections in All Age Groups. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2002;186:1330–1334. doi: 10.1086/344319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.van den Hoogen BG, de Jong JC, Groen J, Kuiken T, de Groot R, Fouchier RA, Osterhaus AD. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from young children with respiratory tract disease. Nat Med. 2001;7:719–724. doi: 10.1038/89098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Widmer K, Zhu Y, Williams JV, Griffin MR, Edwards KM, Talbot HK. Rates of Hospitalizations for Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Human Metapneumovirus, and Influenza Virus in Older Adults. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2012;206:56–62. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Soerens AG, Da Costa A, Lund JM. Regulatory T cells are essential to promote proper CD4 T-cell priming upon mucosal infection. Mucosal immunology. 2016;9:1395–1406. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kim JM, Rasmussen JP, Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cells prevent catastrophic autoimmunity throughout the lifespan of mice. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:191–197. doi: 10.1038/ni1428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Williams JV, Tollefson SJ, Johnson JE, Crowe JE., Jr The cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus) is a permissive small animal model of human metapneumovirus infection, pathogenesis, and protective immunity. J Virol. 2005;79:10944–10951. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.10944-10951.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shafagati N, Fite K, Patanarut A, Baer A, Pinkham C, An S, Foote B, Lepene B, Kehn-Hall K. Enhanced detection of respiratory pathogens with nanotrap particles. Virulence. 2016;7:756–769. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1185585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gilchuk P, Spencer CT, Conant SB, Hill T, Gray JJ, Niu X, Zheng M, Erickson JJ, Boyd KL, McAfee KJ, Oseroff C, Hadrup SR, Bennink JR, Hildebrand W, Edwards KM, Crowe JE, Jr, Williams JV, Buus S, Sette A, Schumacher TN, Link AJ, Joyce S. Discovering naturally processed antigenic determinants that confer protective T cell immunity. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:1976–1987. doi: 10.1172/JCI67388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nakamura K, Kitani A, Strober W. Cell contact-dependent immunosuppression by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells is mediated by cell surface-bound transforming growth factor beta. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2001;194:629–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.5.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Oida T, Zhang X, Goto M, Hachimura S, Totsuka M, Kaminogawa S, Weiner HL. CD4+CD25- T cells that express latency-associated peptide on the surface suppress CD4+CD45RBhigh-induced colitis by a TGF-beta-dependent mechanism. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2003;170:2516–2522. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.5.2516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Williams NL, Morris JL, Rush CM, Ketheesan N. Migration of dendritic cells facilitates systemic dissemination of Burkholderia pseudomallei. Infection and immunity. 2014;82:4233–4240. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01880-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Slight SR, Monin L, Gopal R, Avery L, Davis M, Cleveland H, Oury TD, Rangel-Moreno J, Khader SA. IL-10 restrains IL-17 to limit lung pathology characteristics following pulmonary infection with Francisella tularensis live vaccine strain. The American journal of pathology. 2013;183:1397–1404. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Francisco LM, Sage PT, Sharpe AH. The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunological Reviews. 2010;236:219–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.00923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Thornton AM, Korty PE, Tran DQ, Wohlfert EA, Murray PE, Belkaid Y, Shevach EM. Expression of Helios, an Ikaros transcription factor family member, differentiates thymic-derived from peripherally induced Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2010;184:3433–3441. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0904028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Weiss JM, Bilate AM, Gobert M, Ding Y, Curotto de Lafaille MA, Parkhurst CN, Xiong H, Dolpady J, Frey AB, Ruocco MG, Yang Y, Floess S, Huehn J, Oh S, Li MO, Niec RE, Rudensky AY, Dustin ML, Littman DR, Lafaille JJ. Neuropilin 1 is expressed on thymus-derived natural regulatory T cells, but not mucosa-generated induced Foxp3+ T reg cells. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2012;209:1723–1742, s1721. doi: 10.1084/jem.20120914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yadav M, Louvet C, Davini D, Gardner JM, Martinez-Llordella M, Bailey-Bucktrout S, Anthony BA, Sverdrup FM, Head R, Kuster DJ, Ruminski P, Weiss D, Von Schack D, Bluestone JA. Neuropilin-1 distinguishes natural and inducible regulatory T cells among regulatory T cell subsets in vivo. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2012;209(1713–1722):s1711–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.20120822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Christiaansen AF, Boggiatto PM, Varga SM. Limitations of Foxp3(+) Treg depletion following viral infection in DEREG mice. Journal of immunological methods. 2014;406:58–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2014.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Betts MR, Brenchley JM, Price DA, De Rosa SC, Douek DC, Roederer M, Koup RA. Sensitive and viable identification of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by a flow cytometric assay for degranulation. Journal of immunological methods. 2003;281:65–78. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(03)00265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Widney DP, Xia YR, Lusis AJ, Smith JB. The murine chemokine CXCL11 (IFN-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant) is an IFN-gamma- and lipopolysaccharide-inducible glucocorticoid-attenuated response gene expressed in lung and other tissues during endotoxemia. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2000;164:6322–6331. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.12.6322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ariotti S, Beltman JB, Borsje R, Hoekstra ME, Halford WP, Haanen JB, de Boer RJ, Schumacher TN. Subtle CXCR3-Dependent Chemotaxis of CTLs within Infected Tissue Allows Efficient Target Localization. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2015;195:5285–5295. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cole KE, Strick CA, Paradis TJ, Ogborne KT, Loetscher M, Gladue RP, Lin W, Boyd JG, Moser B, Wood DE, Sahagan BG, Neote K. Interferon-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant (I-TAC): a novel non-ELR CXC chemokine with potent activity on activated T cells through selective high affinity binding to CXCR3. The Journal of experimental medicine. 1998;187:2009–2021. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.12.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kamin-Lewis R, Abdelwahab SF, Trang C, Baker A, DeVico AL, Gallo RC, Lewis GK. Perforin-low memory CD8+ cells are the predominant T cells in normal humans that synthesize the beta -chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein-1beta. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001;98:9283–9288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.161298998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Fong AM, Robinson LA, Steeber DA, Tedder TF, Yoshie O, Imai T, Patel DD. Fractalkine and CX3CR1 mediate a novel mechanism of leukocyte capture, firm adhesion, and activation under physiologic flow. The Journal of experimental medicine. 1998;188:1413–1419. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.8.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bazan JF, Bacon KB, Hardiman G, Wang W, Soo K, Rossi D, Greaves DR, Zlotnik A, Schall TJ. A new class of membrane-bound chemokine with a CX3C motif. Nature. 1997;385:640–644. doi: 10.1038/385640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Verbist KC, Cole CJ, Field MB, Klonowski KD. A role for IL-15 in the migration of effector CD8 T cells to the lung airways following influenza infection. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2011;186:174–182. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Culley FJ, Pennycook AM, Tregoning JS, Dodd JS, Walzl G, Wells TN, Hussell T, Openshaw PJ. Role of CCL5 (RANTES) in viral lung disease. J Virol. 2006;80:8151–8157. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00496-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Denis M. Proinflammatory cytokines in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 1995;151:164–169. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.151.1.7812548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Taub DD, Proost P, Murphy WJ, Anver M, Longo DL, van Damme J, Oppenheim JJ. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), -2, and -3 are chemotactic for human T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1995;95:1370–1376. doi: 10.1172/JCI117788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Halim TY, Takei F. Isolation and characterization of mouse innate lymphoid cells. In: Coligan John E, et al., editors. Current protocols in immunology. Vol. 106. 2014. pp. 3.25.21–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Monticelli LA, Buck MD, Flamar AL, Saenz SA, Tait Wojno ED, Yudanin NA, Osborne LC, Hepworth MR, Tran SV, Rodewald HR, Shah H, Cross JR, Diamond JM, Cantu E, Christie JD, Pearce EL, Artis D. Arginase 1 is an innate lymphoid-cell-intrinsic metabolic checkpoint controlling type 2 inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:656–665. doi: 10.1038/ni.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Walker JA, Oliphant CJ, Englezakis A, Yu Y, Clare S, Rodewald HR, Belz G, Liu P, Fallon PG, McKenzie ANJ. Bcl11b is essential for group 2 innate lymphoid cell development. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2015;212:875. doi: 10.1084/jem.20142224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ebihara T, Song C, Ryu SH, Plougastel-Douglas B, Yang L, Levanon D, Groner Y, Bern MD, Stappenbeck TS, Colonna M, Egawa T, Yokoyama WM. Runx3 specifies lineage commitment of innate lymphoid cells. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:1124–1133. doi: 10.1038/ni.3272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.de Kleer IM, Kool M, de Bruijn MJW, Willart M, van Moorleghem J, Schuijs MJ, Plantinga M, Beyaert R, Hams E, Fallon PG, Hammad H, Hendriks RW, Lambrecht BN. Perinatal Activation of the Interleukin-33 Pathway Promotes Type 2 Immunity in the Developing Lung. Immunity. 2016;45:1285–1298. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.10.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lahl K, Loddenkemper C, Drouin C, Freyer J, Arnason J, Eberl G, Hamann A, Wagner H, Huehn J, Sparwasser T. Selective depletion of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induces a scurfy-like disease. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2007;204:57–63. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Schmitt EG, Williams CB. Generation and function of induced regulatory T cells. Frontiers in immunology. 2013;4:152. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kretschmer K, Apostolou I, Hawiger D, Khazaie K, Nussenzweig MC, von Boehmer H. Inducing and expanding regulatory T cell populations by foreign antigen. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1219–1227. doi: 10.1038/ni1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yadav M, Stephan S, Bluestone JA. Peripherally induced tregs - role in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Frontiers in immunology. 2013;4:232. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Szurek E, Cebula A, Wojciech L, Pietrzak M, Rempala G, Kisielow P, Ignatowicz L. Differences in Expression Level of Helios and Neuropilin-1 Do Not Distinguish Thymus-Derived from Extrathymically-Induced CD4+Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells. PloS one. 2015;10:e0141161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Cole KE, Strick CA, Paradis TJ, Ogborne KT, Loetscher M, Gladue RP, Lin W, Boyd JG, Moser B, Wood DE, Sahagan BG, Neote K. Interferon-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant (I-TAC): a novel non-ELR CXC chemokine with potent activity on activated T cells through selective high affinity binding to CXCR3. The Journal of experimental medicine. 1998;187:2009–2021. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.12.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Widney DP, Xia YR, Lusis AJ, Smith JB. The murine chemokine CXCL11 (IFN-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant) is an IFN-gamma- and lipopolysaccharide-inducible glucocorticoid-attenuated response gene expressed in lung and other tissues during endotoxemia. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2000;164:6322–6331. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.12.6322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Josefowicz SZ, Niec RE, Kim HY, Treuting P, Chinen T, Zheng Y, Umetsu DT, Rudensky AY. Extrathymically generated regulatory T cells control mucosal TH2 inflammation. Nature. 2012;482:395–399. doi: 10.1038/nature10772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Krishnamoorthy N, Khare A, Oriss TB, Raundhal M, Morse C, Yarlagadda M, Wenzel SE, Moore ML, Peebles RS, Ray A, Ray P. Early infection with respiratory syncytial virus impairs regulatory T cell function and increases susceptibility to allergic asthma. Nat Med. 2012;18:1525–1530. doi: 10.1038/nm.2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rigas D, Lewis G, Aron JL, Wang B, Banie H, Sankaranarayanan I, Galle-Treger L, Maazi H, Lo R, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH, Soroosh P, Akbari O. Type 2 innate lymphoid cell suppression by regulatory T cells attenuates airway hyperreactivity and requires inducible T-cell costimulator-inducible T-cell costimulator ligand interaction. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. 2017;139:1468–1477.e1462. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.08.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Krishnamoorthy N, Burkett PR, Dalli J, Abdulnour RE, Colas R, Ramon S, Phipps RP, Petasis NA, Kuchroo VK, Serhan CN, Levy BD. Cutting edge: maresin-1 engages regulatory T cells to limit type 2 innate lymphoid cell activation and promote resolution of lung inflammation. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2015;194:863–867. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Moro K, Yamada T, Tanabe M, Takeuchi T, Ikawa T, Kawamoto H, Furusawa J, Ohtani M, Fujii H, Koyasu S. Innate production of T(H)2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit(+)Sca-1(+) lymphoid cells. Nature. 2010;463:540–544. doi: 10.1038/nature08636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Li BWS, Stadhouders R, de Bruijn MJW, Lukkes M, Beerens D, Brem MD, Klein Jan A, Bergen I, Vroman H, Kool M, van IWFJ, Rao TN, Fehling HJ, Hendriks RW. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Exhibit a Dynamic Phenotype in Allergic Airway Inflammation. Frontiers in immunology. 2017;8:1684. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Fahy JV. Type 2 inflammation in asthma–present in most, absent in many. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:57–65. doi: 10.1038/nri3786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Edwards MR, Strong K, Cameron A, Walton RP, Jackson DJ, Johnston SL. Viral infections in allergy and immunology: How allergic inflammation influences viral infections and illness. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. 2017;140:909–920. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


