Abstract
Key points
There are two electrophysiological dichotomous populations of parvalbumin (PV) interneurons located in the dorsal striatum.
Striatal PV interneurons in medial and lateral regions differ significantly in their intrinsic excitability.
Parvalbumin interneurons in the dorsomedial striatum, but not in the dorsolateral striatum, receive afferent glutamatergic input from cingulate cortex.
Abstract
Dorsomedial striatum circuitry is involved in goal‐directed actions or movements that become habits upon repetition, as encoded by the dorsolateral striatum. An inability to shift from habits can compromise action‐control and prevent behavioural adaptation. Although these regions appear to be clearly behaviourally distinct, little is known about their distinct physiology. Parvalbumin (PV) interneurons are a major source of striatal inhibition and are usually considered as a homogeneous population in the entire dorsal striatum. In the present study, we recorded PV interneurons in dorsal striatum slices from wild‐type male mice and suggest the existence of two electrophysiological dichotomous populations. We found that PV interneurons located at the dorsomedial striatum region have increased intrinsic excitability compared to PV interneurons in dorsolateral region. We also found that PV interneurons in the dorsomedial region, but not in the dorsolateral striatum region, receive short‐latency excitatory inputs from cingulate cortex. Therefore, the results of the present study demonstrate the importance of considering region specific parvalbumin interneuron populations when studying dorsal striatal function.
Keywords: parvalbumin, fast spiking interneurons, striatum
Key points
There are two electrophysiological dichotomous populations of parvalbumin (PV) interneurons located in the dorsal striatum.
Striatal PV interneurons in medial and lateral regions differ significantly in their intrinsic excitability.
Parvalbumin interneurons in the dorsomedial striatum, but not in the dorsolateral striatum, receive afferent glutamatergic input from cingulate cortex.
Introduction
Daily goal‐directed actions often become habitual automated responses after consecutive repetition (Yin and Knowlton, 2004; Yin et al. 2004, 2005, 2006; Hilário and Costa, 2008; Baldan Ramsey et al. 2011; Hilario et al. 2012). Striatum function is crucial for this habit formation and for proper psychomotor behaviour, such as motor control, procedural learning and behavioural switching (Yin and Knowlton, 2006; Hilário and Costa, 2008; Steiner and Tseng, 2010; Parent, 2012). Adult striatum dysfunction results in a loss of action‐control (Graybiel, 2008) and its dysfunction has recently been linked to obsessive compulsive disorder and acute stress disorder (Ahmari et al. 2013; Burguière et al. 2014; Monteiro and Feng, 2015, 2017; Ahmari, 2016), adding to the the list of previously known classic striatum‐related disorders, such as Parkinson's and Huntington's disease (Kreitzer and Malenka, 2008; Plotkin and Surmeier, 2015).
Parvalbumin (PV) interneurons are critical circuit modulators and are assumed to be malleable throughout life in the adult brain (Plotkin et al. 2005; Kepecs and Fishell, 2014; Dehorter et al. 2015). In the rodent striatum, PV interneurons represent only a small neuronal percentage (∼1%) but provide prominent feedforward inhibition to medium‐spiny projection neurons (MSNs) (Tepper et al. 2008; Gittis et al. 2010). Decreased numbers of striatal PV interneurons, but not MSNs, have been reported in post‐mortem caudate and putamen tissue from patients with Tourette syndrome, suggesting a link between action‐control and interneuron pathology in specific striatum subregions (Kataoka et al. 2010; Xu et al. 2015, 2016). In rodents, dorsomedial striatum (DMS) and dorsolateral striatum (DLS) regions are part of an homogeneous structure, lacking the anatomical segregation between caudate and putamen regions seen in primates (Reep et al. 2003; Voorn et al. 2004). However, PV expression is more abundant laterally than medially in rodents (Kita et al. 1990; Todtenkopf et al. 2004). Given this anatomical segregation of PV expression, we aimed to determine whether striatum PV interneurons could be electrophysiologically different in DLS versus DMS regions. Our data provide the first evidence of dichotomous physiological properties between PV interneurons located in the two striatum regions.
Methods
Ethical approval
All animal procedures were reviewed and approved by the MIT Committee on Animal Care. Only male mice were used for the experiments. Detailed methods are described below.
Experimental animals
PV‐Cre mice (Pvalb tm1(cre)Arbr) were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA) (JAX Stock No: 008069) and ROSA26‐stopflox‐tdTomato cKI mice were gently provided by Dr Fan Wang (Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, USA). Both mouse lines have been described previously (Hippenmeyer et al. 2005; Arenkiel et al. 2011). Specific primers were designed in the present study to distinguish PV‐Cre heterozygous from homozygous mice:
Primer 5'‐GCTCAGAGCCTCCATTCCCT‐3'
Primer 5'‐GCTCAGAGCCTCCATTCCCT‐3'
Primer 5'‐CAGCCTCTGTTCCACATACACTTC‐3'
ROSA26‐stopflox‐tdTomato +/+ mice were crossed with PV‐Cre mice to generate PV‐Cre +/−:ROSA26‐stopflox‐tdTomato +/+ mice for electrophysiological recordings. Animals were housed under 12:12 h light/dark cycles with temperature and humidity monitoring over 24 h, with two to five mice per cage and ad libitum access to food and water. All experimental procedures were reviewed and approved by the MIT Committee on Animal Care.
Slice preparation
Acute striatal slices were prepared from 6–8‐week‐old PV‐Cre +/−:ROSA26‐stopflox‐tdTomato +/+. Animals were anaesthetized by avertin i.p. injection (tribromoethanol, 20 mg mL–1, 0.5 mg g–1 body weight) and transcardially perfused with cutting 92 N‐methyl‐d‐glucamine (NMDG)‐based artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) (mm): 92 NMDG, 2.5 KCl, 1.20 NaH2PO4, 30 NaHCO3, 20 Hepes, 25 glucose, 2 thiourea, 5 Na‐ascorbate, 3 Na‐pyruvate, 0.5 CaCl2.2H2O and 10 MgSO4.7H2O (∼300 mOsm L–1, pH 7.2–7.4) (Ting et al., 2014). Following decapitation, the brain was removed and coronal brain slices (300 μm) were prepared using a Vibratome 1000 Plus (Leica Microsystems, Buffalo Grove, IL, USA). Slices were recovered in cutting solution at 32–34°C for 10–15 min and transferred to room temperature carbogenated regular aCSF (mm): 119 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 1.2 NaH2PO4, 24 NaHCO3, 12.5 glucose, 2 MgSO4.7H2O and 2 CaCl2.2H2O (∼300 mOsm L–1, pH 7.2–7.4 ). All slices were allowed to recover at least ≥1 h prior to whole‐cell recordings.
Electrophysiology recordings
Slices were transferred to the recording chamber (RC‐27L; Warner Instruments, Hamden, CT, USA) and constantly perfused with carbogenated regular aCSF at 30 ± 2°C, ∼2 mL min–1. Borosilicate glass microelectrodes (King Precision Glass, Claremont, CA, USA) were pulled on a P‐97 horizontal puller (Sutter Instruments, Novato, CA, USA) and backfilled either with KGlu, CsCl or CsGlu internal (KGlu, in mm: 145 K‐gluconate, 10 Hepes, 1 EGTA, 2 MgATP, 0.3 NaGTP and 2 MgCl2, pH adjusted to 7.3 with KOH and osmolarity adjusted to ∼300 mOsm L–1 with sucrose; CsGlu, in mm: 110 CsOH, 110 d‐gluconic acid, 15 KCl, 4 NaCl, 5 TEA‐Cl, 20 Hepes, 0.2 EGTA, 5 lidocaine N‐ethyl chloride, 4 MgATP and 0.3 NaGTP, pH adjusted to 7.3 with KOH and osmolarity adjusted to ∼300 mOsm L–1 with K2SO4; CsCl, in mm: 103 CsCl, 12 CsOH, 12 methanesulphonic acid, 5 TEA‐Cl, 10 Hepes, 0.5 EGTA, 5 lidocaine N‐ethyl chloride, 4 MgATP, 0.3 NaGTP, 10 phosphocreatine and 4 NaCl, pH adjusted to 7.3 with KOH and osmolarity adjusted to ∼300 mOsm L–1 with K2SO4), presenting a typical resistance of ∼2–4 MΩ.
Slices were visualized under IR‐DIC (infrared‐>differential interference contrast) using a BX‐51WI microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and recordings were obtained after seal rupture and internal equilibrium from visually identified tdTomato‐positive cells. All recordings were always obtained in parallel for both cell populations (DLS‐PV and DMS‐PV) along the lateral–medial striatal axis within each brain slice. Only the DLS region close to the corpus callosum and DMS close to the lateral ventricles were targeted for recordings to avoid any potential ‘intermediate’ region. Input resistance was obtained through extrapolation from the I–V plot, as well as direct measurement via a –150 pA hyperpolarizing current step.
Picrotoxin 100 μm and TTX 1 μm were added for miniature EPSC (mEPSC) experiments and AP‐V 50 μm, NBQX 10 μm and TTX 10 μm were added for miniature IPSC (mIPSC) experiments (all drugs obtained from Tocris Bioscience, St Louis, MO, USA).
Striatal EPSCs and EPSPs were evoked by a 0.1 ms stimulation step (Isoflex; AMPI, Jerusalem, Israel) delivered at 0.05 Hz frequency by a platinum iridium concentric bipolar electrode (CBAPC75; FHC, Bowdoin, ME, USA) placed in cingulate cortex (Cg) layers 4/5 (stimulation electrode 1–1.5 mm away; stimulation intensity ranged from 0.1 to 3.0 mA). Latency was measured as the time between the stimulation (electrode artefact) and the onset of the resulting EPSC. EPSPs and action potential (AP) graphically displayed traces were obtained at −50 mV by gradual increasing stimulation intensity until AP firing. Stimulation artefacts were partly removed for clarity of the EPSP. Summary EPSP data (onset time, peak, rise and decay time) were extracted from the largest evoked EPSP at −70 mV from pairs of PV‐MSN adjacently located (same stimulation electrode location and intensity for each PV‐MSN pair). Analysis of EPSCs and EPSPs was performed on averaged responses from three to five sweeps. PV cells were identified based on tdTomato signal and all presented a hyperpolarized resting membrane potential (∼ −85 mV) and typical AP‐shape upon current‐injection. Putative MSNs were identified based on soma size (12–20 μm), absence of tdTomato signal, typical hyperpolarized resting membrane potential (∼ −85 mV) and typical AP‐shape upon current‐injection. EPSP rise time was measured from 10% to 90% of the peak amplitude of the synaptic response. Decay time was measured by a single exponential fit. Onset of Cg‐evoked DMS‐EPSPs was measured as the delay between the stimulus delivery and the EPSP foot. Data was acquired using a MultiClamp 700B amplifier and a Digidata 1440A (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Signals were filtered at 1–2 KHz and digitized at 10 KHz. For current clamp recordings, bridge balance was adjusted and pipette capacitance neutralized. Series resistance compensation (< 20 MΩ) was performed in voltage clamping mode. Theoretical liquid junction potential was estimated to be ∼ −11 mV and not corrected‐for.
Antibodies
Mouse and rabbit anti‐parvalbumin antibodies (PV235 and PV27; dilution 1:5000) from Swant (Marly, Switzerland); mouse anti‐DARPP32 (611520; dilution 1:1000) from BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA, USA); rabbit anti‐somatostatin (AB5494; dilution 1:200) from Milllipore (Billerica, MA, USA); rabbit anti‐neuropeptide Y (T‐4070; dilution 1:250) from Peninsula Laboratories International (Belmont, CA, USA); goat anti‐choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) antibody (AB144P; dilution 1:500) from Millipore; chicken anti‐GFP (ab13970; dilution 1:5000) from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA).
Morphological experiments and quantification of PV immunoreactivity
For morphological experiments, biocytin (0.3‐0.5% w/v) was included in KGlu internal solution during patch clamp recordings. Recorded slices were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), kept in 4% PFA overnight at 4°C, and then transferred to PBS. Next day slices were incubated for 2 h in AlexaFluor‐488 streptavidin conjugate (dilution 1:1000; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), washed three times in PBS and mounted for imaging. For tyramide signal amplification (TSA) immunohistochemistry, rabbit anti‐parvalbumin antibody (PV27; Swant) was used together with a TSA kit (T‐20922; Invitrogen) in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Quantification of PV‐immunoreactivity was performed using cellSens imaging software (Olympus).
IHC and microscope imaging
Mice were anaesthetized by isoflurane inhalation and transcardially perfused with PBS solution followed by 4% PFA fixative solution. Brains were kept in 4% PFA overnight at 4°C, then transferred to PBS and sectioned at 50 μm. Sections were washed three times in PBS and permeabilized for 5 min using a PBS solution containing 10% MeOH, 3% H2O2 and 0.5% NaBH2, except for ChAT immunostaining and virus experiments. Slices were again washed three times in PBS and incubated in 1.2% Triton‐X 100 for 15 min, followed by another three PBS washes. Blockade was then performed for 1 h in PBS containing 2% BSA and 0.2% Triton‐X. Primary antibodies were incubated overnight at 4°C for detection of the respective antigens. The next day, sections were washed three times in PBS, followed by 2–4 h of incubation with secondary antibody (species‐specific Alexa‐conjugated antibody; dilution 1:1500; Invitrogen) at room temperature. Lastly, sections were washed three times in PBS, stained for 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole, mounted in ProlongGold (Invitrogen) or Fluoro‐Gel (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA) and imaged using Fluoview FV1000 confocal and BX61 microscopes (Olympus). Serial sections were reconstructed as 3‐D models using BioVis3D software (http://www.biovis3d.com).
Surgeries and viruses
For this, 6–8 week‐old mice were anaesthetized with isoflurane, placed on a stereotactic frame and viral injections performed using a Nanoject device (Drummond Scientific, Broomall, PA, USA). For monosynaptic tracing experiments, we injected ∼0.2 μL of undiluted AAV2/8‐synP‐DIO‐sT‐P2A‐EGFP‐P2A‐B19G [2.29 × 1012 gc mL–1 (gc = genome copies)] at DLS or DMS (bregma co‐ordinates for guide cannula implantation: DLS medial–lateral +2.75, anterior–posterior +0.5, 2.0; DMS medial–lateral +2.0, anterior–posterior +0.5, 2.3; note that the injector/infusion cannula further extends 1 mm dorsoventrally). Then, 2–3 weeks later, we injected ∼0.2 μL of undiluted RV‐ΔG‐RFP(EnvA) [titre 2.75 × 109 i.u./ml (i.u. = infectious units)] at the same bregma location. All stereotaxic co‐ordinates are from the bregma/skull. Mice were killed 7 days later to observe expression pattern. AAV‐synP‐DIO‐sTpEpG and RVΔG‐RFP(EnvA) were generated by I.R.W. from the MIT Genetic Neuroengineering Group (Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA) (Kohara et al. 2014).
Experimental design and statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using Prism (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) and MATLAB Software (MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA, USA). Non‐normal distributions were assumed for all the datasets regardless of variance and sample size. Pairwise comparisons were performed using a Mann–Whitney test for unpaired data and a Wilcoxon signed rank test for paired data comparisons. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All datasets are presented as the mean ± SEM. Further details on particular analyses are provided as appropriate and as shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Experimental design and statistical analysis
| Figure | Measurement | n | Mean ± SEM | Statistical test and P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fig. 2B (top) | Input resistance (MΩ) | DMS‐PV = 25 cells | 42.76 ± 2.01 | Mann–Whitney test, *** P < 0.0001 |
| DLS‐PV = 25 cells | 28.21 ± 1.255 | |||
| Fig. 2B (bottom) | Membrane resistance (MΩ) | DMS‐PV = 25 cells | 118.1 0 ± 8.68 | Mann–Whitney test, ** P = 0.0013 |
| DLS‐PV = 25 cells | 84.70 ± 7.44 | |||
| Fig. 2D | Rheobase current (pA) | DMS‐PV = 25 cells | 424.4 ± 26.05 | Mann–Whitney test, ** P = 0.0019 |
| DLS‐PV = 25 cells | 583.6 ± 36.17 | |||
| Fig. 2E | Firing threshold (mV) | DMS‐PV = 15 cells | −39.40 ± 1.17 | Mann–Whitney test, P = 0.1624 |
| DLS‐PV = 15 cells | −41.20 ± 1.34 | |||
| Fig. 2G | mEPSC frequency (Hz) | DMS‐PV = 12 cells | 22.31 ± 1.78 | Mann–Whitney test, * P = 0.0229 |
| DLS‐PV = 10 cells | 15.49 ± 1.26 | |||
| mEPSC amplitude (pA) | 15.25 ± 0.83 | Mann–Whitney test, P = 0.1062 | ||
| 13.08 ± 0.80 | ||||
| Fig. 2H | mIPSC frequency (Hz) | DMS‐PV = 16 cells | 5.68 ± 0.49 | Mann–Whitney test, ** P = 0.0098 |
| DLS‐PV = 16 cells | 8.17 ± 0.79 | |||
| mIPSC amplitude (pA) | 29.66 ± 2.01 | Mann Whitney test, P = 0.1011 | ||
| 24.42 ± 1.43 | ||||
| Fig. 5D, 5E | EPSC Latency (ms) | DMS‐PV = 8 cells | 5.49 ± 0.44 | Wilcoxon signed rank test, * P = 0.0156 |
| DMS‐MSN = 8 cells | 7.04 ± 0.73 | |||
| Fig. 5F | EPSP onset time (ms) | DMS‐PV = 5 cells | 5.42 ± 0.71 | Wilcoxon signed rank test, P = 0.1250 |
| DMS‐MSN = 5 cells | 6.88 ± 1.32 | |||
| Fig. 5G | EPSP peak (mV) | DMS‐PV = 5 cells | 7.73 ± 1.96 | Wilcoxon signed rank test, P = 0.4375 |
| DMS‐MSN = 5 cells | 6.31 ± 1.43 | |||
| Fig. 5H | EPSP rise time (ms) | DMS‐PV = 5 cells | 3.58 ± 0.41 | Wilcoxon signed rank test, P = 1.0000 |
| DMS‐MSN = 5 cells | 3.67 ± 0.52 | |||
| Fig. 5I | EPSP decay time (ms) | DMS‐PV = 5 cells | 19.22 ± 1.64 | Wilcoxon signed rank test, P = 0.0625 |
| DMS‐MSN = 5 cells | 27.45 ± 1.43 |
Statistical analysis of intracellular recordings from DMS‐PV cells (parvalbumin cells located in dorsomedial striatum), DLS‐PV cells (parvalbumin cells located in dorsolateral striatum) and DMS‐MSN cells (medium spiny neurons located in dorsomedial striatum). Non‐normal distributions were assumed for all the datasets regardless of variance and sample size. Pairwise comparisons were performed using Mann Whitney test for unpaired data and Wilcoxon Signed Rank test for paired data comparisons, with a threshold of P<0.05 for significance. All datasets presented as means ± SEM.
Results
To investigate dorsal striatum PV interneurons, we started by crossing PV‐Cre mice with ROSA26‐stopflox‐tdTomato reporter mice to fluorescence label PV interneurons for cell‐targeted patch clamp recordings. Immunostaining of PV‐Cre:tdTomato+ striatal brain sections showed faithful colocalization between tdTomato signal and PV immunostaining, indicating successful tdTomato expression under the control of endogenous PV promoter (Fig. 1). To further confirm correct PV interneuron labelling by this strategy, we also performed separate immunostaining protocols with other well‐known striatal markers. Colocalization was not observed between tdTomato native signal and immunostaining for other striatal markers, such as DARPP32, SOM, NPY or ChAT, indicating a correct reporting strategy (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Native tdTomato expression shows faithful colocalization with PV staining in striatal sections from PV‐cre:tdTomato mice.
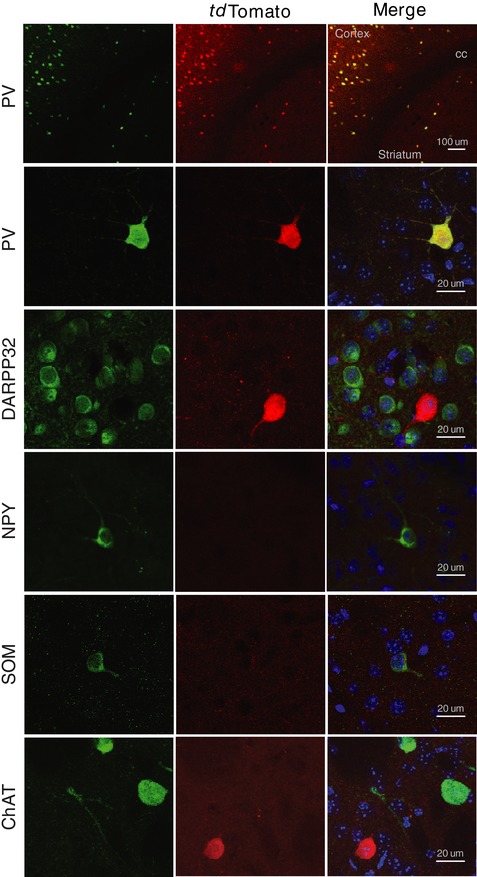
Pvalb tm1(cre)Arbr:ROSA26‐stopflox‐tdTomato mice express tdTomato fluorescence in striatal parvalbumin interneurons. Fluorescence images of histological sections show colocalization of native tdTomato expression (red) with endogenous PV immunoreactivity, but not DARPP32, SOM, NPY or ChAT.
We next examined passive and active membrane properties by performing whole‐cell intracellular electrophysiology. Recordings from PV interneurons located in DMS and DLS regions showed that these populations differed markedly in intrinsic excitability (Fig. 2 A–E and Table 1). PV located in DMS showed higher intrinsic excitability, as represented by their leftshifted I–V curve (Fig. 2 A). Input resistance obtained via extrapolation from the I–V plot, as well as direct measurement via a –150 pA hyperpolarizing current step, showed significantly higher values for DMS‐PV than DLS‐PV (DMS‐PV mean = 43 MΩ; DLS‐PV mean = 28 MΩ) (Fig. 2 B). In addition, significantly higher membrane resistance was observed for the DMS population (DMS‐PV mean = 118 MΩ; DLS‐PV mean = 85 MΩ) (Fig. 2 B). Active membrane properties also showed that DMS‐PV interneurons are more excitable, displaying a left‐shifted I–F curve (Fig. 2C). Action potential triggering (rheobase) also required less current injection compared to the DLS‐PV population (DMS‐PV mean = 424 pA; DLS‐PV mean = 584 pA) (Fig. 2 D). Resting membrane potential (DMS‐PV = –86 mV; DLS‐PV = –85 mV) and spike threshold (DMS‐PV mean = –39 mV; DLS‐PV mean = –41 mV) (Fig. 2 E) were not different between the two populations and thus do not appear to contribute for the observed excitability differences.
Figure 2. DMS‐PV interneurons have distinct intrinsic excitability and synaptic physiology from DLS‐PV interneurons.
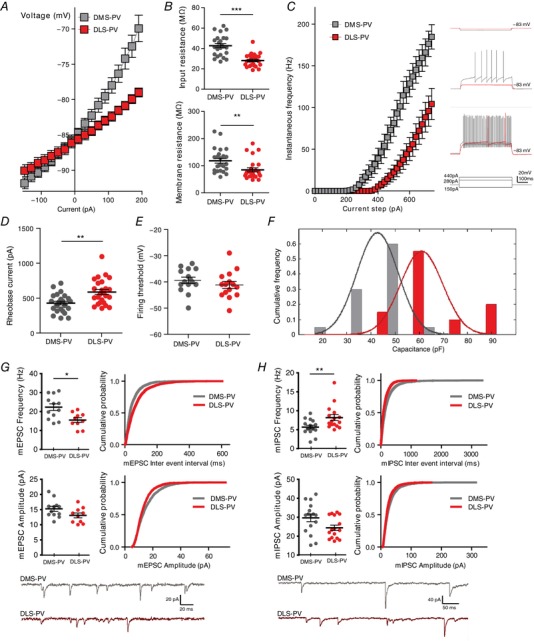
Higher intrinsic excitability for DMS‐PV is shown by their left‐shifted IV curve (A) and higher input and membrane resistance (B). C, I–F plot with representative current injection steps demonstrates increased excitability for DMS‐PV interneurons compared to DLS‐PV. Note that only current injections up to 740 pA ae shown, although many DLS‐PV required much higher current injections for firing. Given that, above 740 pA, many DMS‐PV entered in ‘depolarization blockade’ and become inexcitable, the graph is only shown up to that value. D, lower rheobase current values indicate higher excitability of DMS‐PV compared to DLS‐PV. E, no difference in firing threshold. F, DMS‐PV interneurons have smaller capacitance (P < 0.001, two‐sample Kolmogrov–Smirnov test). G, summary graphs and cumulative probability curves (200 events per interneuron) show a significantly increased mEPSC frequency in DMS‐PV, with no difference in amplitude. H, summary graphs and cumulative probability curves (140 events per interneuron) show that DMS‐PV interneurons have reduced mIPSC frequency; with no difference in amplitude. Example traces are shown at the bottom for (G) and (H). * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; All statistical analyses are shown in Table 1.
Because differences in excitability can also arise from differences in membrane surface area, we measured whole‐cell capacitance (more or less proportional to membrane surface area). Capacitance recordings confirmed smaller values for DMS‐PV than DLS‐PV (Fig. 2 F), suggesting that the differences in excitability could be attributable, at least in part, to different membrane areas.
To explore whether these differences in electrophysiology could accompany differences in morphology, we acquired morphological data from DMS‐PV and DLS‐PV using TSA‐enhanced parvalbumin immunostaining (Fig. 3) and biocytin‐filled patch pipettes during the electrophysiology recordings. We found that DLS‐PV consistently displayed more extensive arborization and complexity than DMS‐PV interneurons. This morphological observation supports the whole‐cell capacitance measurements, which indicated larger capacitance values for DLS‐PV than for DMS‐PV. Quantification of PV‐immunoreactivity also showed stronger detection in the more lateral regions of the striatum compared to DMS (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. DLS‐PV interneurons have more abundant parvalbumin expression and display more complex morphology than DMS‐PV.
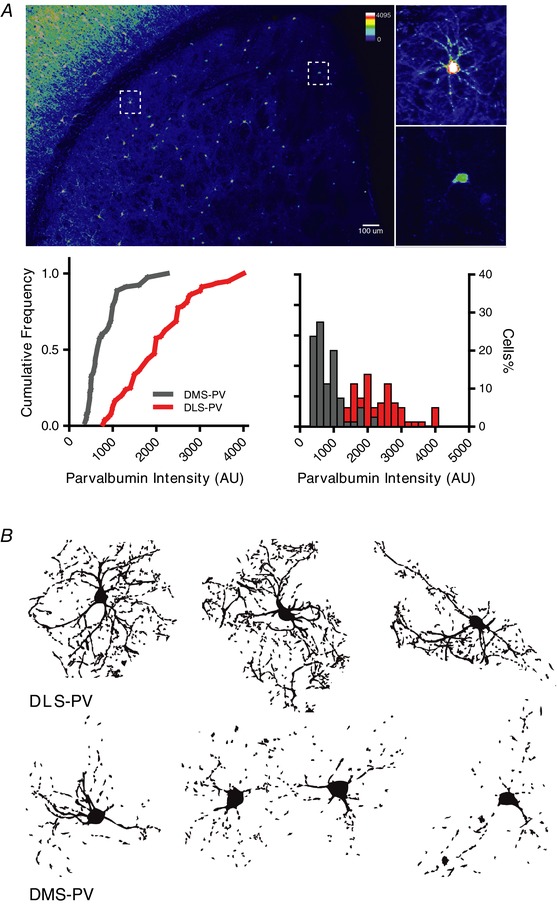
A, parvalbumin interneurons display significantly higher PV intensity per cell in DLS compared to dorsomedial striatum (*** P < 0.001; n = 80 DLS‐PV cells and n = 80 DMS‐PV cells; two‐way ANOVA for the left cumulative frequency curves and Kolmogorov–Smirnov test for right histogram distribution). B, reconstructed morphology of PV interneurons in DLS (top) and DMS (bottom) after TSA‐enhanced parvalbumin immunostaining.
We next investigated striatal synaptic connectivity for both PV populations. Significantly higher mEPSC frequency was observed in DMS‐PV interneurons compared to DLS‐PV interneurons, with no significant differences in amplitude (Fig. 2 G and Table 1). In addition, DMS‐PV received significantly fewer inhibitory synapses than DLS‐PV, with no differences in amplitude (Fig. 2 H and Table 1). These results could suggest the existence of two discrete PV populations with functional differences in synaptic connectivity. Given that local synapses within the striatum are inhibitory, the mEPSC frequency data suggested that either DMS‐PV received more excitatory inputs from a shared afferent source with DLS‐PV, or that DMS‐PV received inputs from an afferent source distinct from DLS‐PV.
To resolve this question at the cellular level, we aimed to generate modified pseudotyped rabies virus and performed, for the first time, in vivo Cre‐dependent monosynaptic retrograde tracing specifically from striatal PV interneurons.
First, a conditional helper virus (AAV‐synP‐DIO‐sTpEpG) was injected either into DMS or DLS region of PV‐Cre mice. After Cre‐mediated recombination, this AAV helper virus expressed EGFP and two proteins: TVA (receptor for the avian EnvA, necessary for subsequent rabies virus infection) and B19G (the rabies glycoprotein necessary for monosynaptic retrograde spreading) (Wall et al. 2010). Then, 2 weeks after injection, modified EnvA‐ΔG‐RFP‐rabies‐virus (EnvA‐pseudotyped, G‐deleted, RFP‐rabies) was injected into the same location, allowing monosynaptic retrograde tracing from striatum PV interneurons (Fig. 4A).
Figure 4. Cre‐dependent monosynaptic retrograde tracing from striatum parvalbumin interneurons.
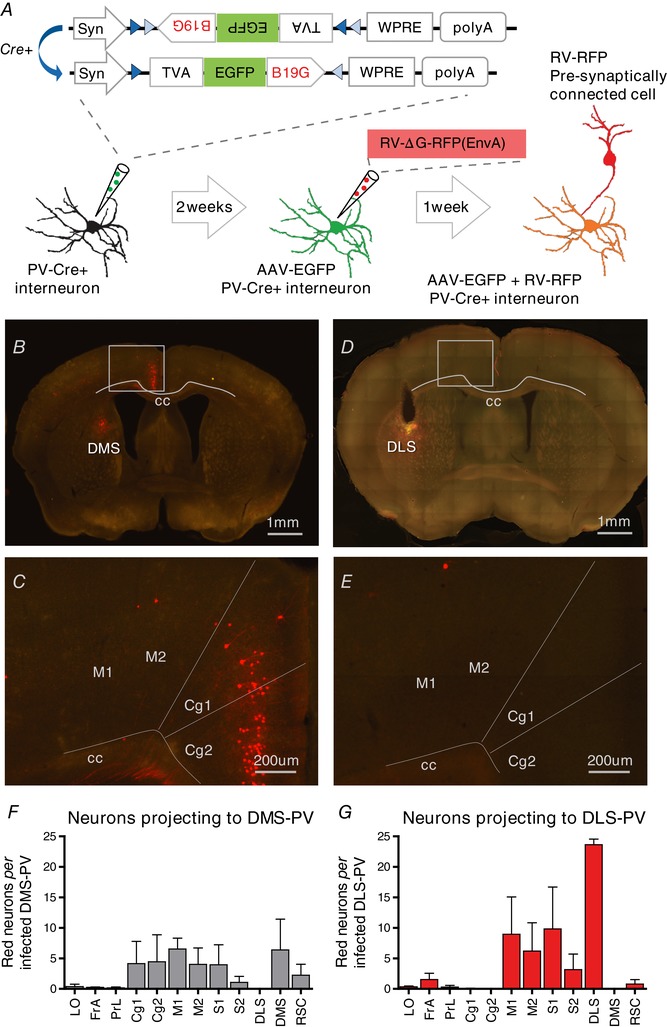
A, adult PV‐Cre mice are injected in the DLS or DMS with AAV expressing TVA, EGFP and rabies glycoprotein (AAV‐DIO‐sTpEpG) in a Cre‐dependent manner. Two weeks later, the same mice are injected with EnvA‐pseudotyped monosynaptic rabies that can only infect PV interneurons expressing TVA, and can only retrogradely spread from PV interneurons expressing rabies glycoprotein (G). One week after rabies injection, direct inputs onto striatal PV interneurons become labelled (RFP). B, C and F, DMS‐PV interneurons receive dense inputs from Cg. RFP labelled Cg‐axons can be observed in coronal section. D, E and G, DLS‐PV interneurons receive inputs from motor (M1, M2), somatosensory cortex and from other PV within DLS, but not Cg. LO, lateral orbital cortex; FrA, frontal association cortex; PrL, prelimbic cortex; Cg1, Cg area 1; Cg2, Cg area 2; M1, primary motor cortex; M2, secondary motor cortex; S1, primary somatosensory cortex; S2, secondary somatosensory cortex; RSC, retrosplenial cortex.
Histological analysis revealed that DMS‐PV interneurons receive dense afferent innervation from Cg (Figs 4 B, C and F and 5 A–C; see also Supporting information, Movie S1). This cortical projection was not observed for PV interneurons in DLS region (Fig. 4 D, E and G; see also Supporting information, Movie S2). Both populations of PV interneurons in DMS and DLS appeared to integrate histological inputs from thalamus and globus pallidus regions.
Figure 5. DMS‐PV interneurons receive afferent glutamatergic input from Cg.
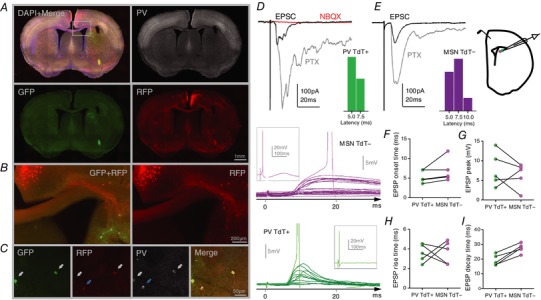
A, Cg projection neurons (RFP+) revealed by Cre‐dependent retrograde monosynaptic labelling from DMS‐PV infected interneurons (GFP+). B, zoomed image from square area depicted in (A); Cg axons (red) projecting to DMS‐PV interneurons (green) can be seen in detail. C, white arrows show DMS‐PV interneurons co‐infected by AAV‐sTpEpG (green) and RV‐ΔG‐RFP(EnvA) (red); blue arrow shows a DMS‐PV interneuron expressing only RFP as a result of rabies retrograde labelling from other synaptically connected PV interneurons. D and E, brain slice cartoon and representative traces showing that stimulation of Cg reliably evokes post‐synaptic excitatory responses (NBQX‐sensitive EPSC) in DMS‐PV interneurons and neighbouring MSNs; cumulative distribution of EPSC latency after Cg stimulation shows significantly shorter latencies for DMS‐PV interneurons compared to MSNs. F–I, summary data extracted from the largest evoked subthreshold EPSP in each pair of PV‐interneuron and its respective neighbouring‐MSN. Representative subthreshold EPSP traces are represented on the left for both cell types. Each trace results from a gradual increase in the stimulation intensity until action‐potential triggering (insets show the full action‐potential trace). Statistical analyses are shown in Table 1.
To functionally test this identified cortical‐DMS‐PV projection, we placed a stimulation electrode in deep‐layer Cg and recorded post‐synaptic evoked responses from the DMS region. Given that PV interneurons in DLS do not received inputs from Cg, we compared DMS PV interneurons with neighbouring MSN‐tdTomato negative neurons.
Stimulation of Cg evoked a reliable glutamatergic excitatory response in both DMS‐MSN neurons and DMS‐PV interneurons (Fig. 5 D–E and Table 1). The average latency of cortical‐evoked DMS‐EPSCs was significantly shorter in PV interneurons than DMS‐MSNs, indicating a rapid cortical recruitment of striatal inhibition (Fig. 5 D–E and Table 1). Cortical‐evoked subthreshold DMS‐EPSPs had a trend for faster onset time and trend for larger amplitude in DMS‐PV interneurons compared to neighbouring DMS‐MSNs (Fig. 5 F–G and Table 1). Rise time was not significantly different between MSN and PV interneurons, although DMS‐EPSPs decay time had a trend for slower in MSNs (Fig. 5 H–I and Table 1). These observations indicated that DMS‐PV interneurons are strongly enervated by Cg and cortical inputs may affect PV interneurons more strongly than MSN neurons, potentially allowing PV interneurons to control the recruitment and spread of second messengers more efficiently in the striatum. Moreover, for the first time, these findings demonstrate that, similar to medium‐spiny neurons, PV interneurons also receive glutamatergic inputs from distinct cortical regions along the medial–lateral axis of the striatum.
Discussion
The findings of the present study demonstrate the existence of two dichotomous PV interneuron populations along the medial‐lateral axis of the dorsal striatum. Whole‐cell recordings revealed that DMS‐PV interneurons have more excitable intrinsic membrane properties compared to PV interneurons in dorsolateral region. Given the important role of the DMS region during initial behavioural learning (Yin et al. 2005; Ragozzino, 2007), having a more excitable PV population in this region could provide means for efficient behavioural inhibition during an initial ‘trial‐and‐error’ learning phase. In a scenario where an unexpected outcome occurs and behavioural flexibility is required (e.g. early learning phase), a more excitable PV population, such as the DMS‐PV population, could therefore be more easily triggered and inhibit/shape local MSNs firing to promote behavioural adaptation. On the other hand, once a task has been extensively repeated and a specific behavioural strategy is confirmed to be effective, it should be preserved and not easily changed (habitual behaviour; DLS‐mediated). In this second habitual scenario, stronger inputs would thus be needed to activate the less excitable DLS‐PV interneurons and stop an ongoing habitual response.
Moreover, the fact that associative Cg inputs specifically target DMS‐PV interneurons, but not PV interneurons in DLS, further suggests that these discrete PV populations in lateral and medial territories are part of distinct corticostriatal networks and may contribute to the hypothesized parallel/competing roles of DLS and DMS in controlling behaviour (Hilario et al. 2012). Our data provide the first evidence of dichotomous physiological properties between PV interneurons along the medial–lateral axis of the dorsal striatum, and highlight the importance of considering region specific parvalbumin interneuron populations when studying the dorsal striatum.
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author contributions
PM and GF were responsible for the conception or design of the work. PM, BB, YZ, RMR, DR, IRW and GF were responsible for the acquisition or analysis or interpretation of data. PM and GF were responsible for drafting the manuscript or revising it critically for important intellectual content. PM, BB, YZ, RMR, DR, IRW and GF were responsible for final approval of the version submitted for publication. PM, BB, YZ, RMR, DR, IRW and GF agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work
Funding
This work was funded by the Stanley Center for Psychiatric Research at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and a doctoral fellowship from the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology to PM (SFRH/BD/33894/2009). Research in the Laboratory of Guoping Feng related to this project was supported by the Poitras Center for Affective Disorders Research at MIT, Stanley Center for Psychiatric Research at Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, National Institute of Health (NIMH R01MH097104), Nancy Lurie Marks Family Foundation, and the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative (SFARI). DR is supported by a doctoral fellowship from the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (PD/BD/127823/2016). BB was supported by postdoctoral fellowships from the Simons Center for the Social Brain at MIT and the Autism Science Foundation and is currently a faculty member at The School of Psychological Sciences and Sagol School of Neuroscience, Tel Aviv University, Israel. PM is currently supported by Society in Science, The Branco Weiss Fellowship, as administered by Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule (ETH) Zürich, and a European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) Long‐Term Fellowship (ALTF 89‐2016).
Supporting information
Disclaimer: Supporting information has been peer‐reviewed but not copyedited.
Movie S1: 3‐D model reconstructed from serial sections showing afferent cells that project onto dorsomedial striatal PV interneurons.
Movie S2: 3‐D model reconstructed from serial sections showing afferent cells that project onto dorsolateral striatal PV interneurons.
Acknowledgements
We thank Triana Dalia, Sarah Schneck and Heather Sullivan for technical support and all members of the Laboratory of Guoping Feng for helpful discussions, especially Holly Robertson, Qiangge Zhang and Dongqing Wang. PM would like to thank Professor Nuno Sousa and Fernanda Marques (ICVS, UMinho, Portugal), as well as Professor Carlos Duarte (UCoimbra, Portugal), and also acknowledges support from ‘Programa Doutoral em Biologia Experimental e Biomedicina’ (CNC, Coimbra, Portugal).
Biography
Patricia Monteiro is an EMBO long‐term fellow with Professor Nuno Sousa at the Life and Health Sciences Research Institute (ICVS), School of Medicine, University of Minho, Portugal. She carried out her PhD work with Professor Guoping Feng at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT, USA), where she focused on synaptic and circuitry mechanisms of basal ganglia dysfunction in compulsive and repetitive behaviours. Her current research interests are stress‐related disorders, acute stress disorder and the role of inhibition in the brain. Patricia is supported by The Branco Weiss Fellowship – Society in Science, administered by Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule (ETH) Zürich, Switzerland.

Edited by: Jaideep Bains & Jesper Sjöström
References
- Ahmari SE (2016). Using mice to model obsessive compulsive disorder: from genes to circuits. Neuroscience 321, 121–137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmari SE, Spellman T, Douglass NL, Kheirbek MA, Simpson HB, Deisseroth K, Gordon JA & Hen R (2013). Repeated cortico‐striatal stimulation generates persistent OCD‐like behavior. Science 340, 1234–1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenkiel BR, Hasegawa H, Yi JJ, Larsen RS, Wallace ML, Philpot BD, Wang F & Ehlers MD (2011). Activity‐induced remodeling of olfactory bulb microcircuits revealed by monosynaptic tracing. PLoS ONE 6, e29423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldan Ramsey LC, Xu M, Wood N & Pittenger C (2011). Lesions of the dorsomedial striatum disrupt prepulse inhibition. Neuroscience 180, 222–228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burguière E, Monteiro P, Mallet L, Feng G & Graybiel AM (2014). Striatal circuits, habits, and implications for obsessive‐compulsive disorder. Curr Opin Neurobiol 30C, 59–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehorter N, Ciceri G, Bartolini G, Lim L, del Pino I & Marin O (2015). Tuning of fast‐spiking interneuron properties by an activity‐dependent transcriptional switch. Science 349, 1216–1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittis AH, Nelson AB, Thwin MT, Palop JJ & Kreitzer AC (2010). Distinct roles of GABAergic interneurons in the regulation of striatal output pathways. J Neurosci 30, 2223–2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel AM (2008). Habits, rituals, and the evaluative brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 31, 359–387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilario M, Holloway T, Jin X & Costa RM (2012). Different dorsal striatum circuits mediate action discrimination and action generalization. Eur J Neurosci 35, 1105–1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilário MRF & Costa RM (2008). High on habits. Front Neurosci 2, 208–217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippenmeyer S, Vrieseling E, Sigrist M, Portmann T, Laengle C, Ladle DR & Arber S (2005). A developmental switch in the response of DRG neurons to ETS transcription factor signaling. PLoS Biol 3, e159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka Y, Kalanithi PSA, Grantz H, Schwartz ML, Saper C, Leckman JF & Vaccarino FM (2010). Decreased number of parvalbumin and cholinergic interneurons in the striatum of individuals with Tourette syndrome. J Comp Neurol 518, 277–291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepecs A & Fishell G (2014). Interneuron cell types are fit to function. Nature 505, 318–326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita H, Kosaka T & Heizmann CW (1990). Parvalbumin‐immunoreactive neurons in the rat neostriatum: a light and electron microscopic study. Brain Res 536, 1–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara K, Pignatelli M, Rivest AJ, Jung H‐Y, Kitamura T, Suh J, Frank D, Kajikawa K, Mise N, Obata Y, Wickersham IR & Tonegawa S (2014). Cell type‐specific genetic and optogenetic tools reveal hippocampal CA2 circuits. Nat Neurosci 17, 269–279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitzer AC & Malenka RC (2008). Striatal plasticity and basal ganglia circuit function. Neuron 60, 543–554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro P & Feng G (2015). Learning from animal models of obsessive‐compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 79, 7–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro P & Feng G (2017). SHANK proteins: roles at the synapse and in autism spectrum disorder. Nat Rev Neurosci 18, 147–157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A (2012). The history of the basal ganglia: the contribution of Karl Friedrich Burdach. Neurosci Med 3, 374–379. [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin JL & Surmeier DJ (2015). Corticostriatal synaptic adaptations in Huntington's disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 33, 53–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin JL, Wu N, Chesselet MF & Levine MS (2005). Functional and molecular development of striatal fast‐spiking GABAergic interneurons and their cortical inputs. Eur J Neurosci 22, 1097–1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragozzino ME (2007). The contribution of the medial prefrontal cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, and dorsomedial striatum to behavioral flexibility. Ann NY Acad Sci 1121, 355–375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reep RL, Cheatwood JL & Corwin JV (2003). The associative striatum: organization of cortical projections to the dorsocentral striatum in rats. J Comp Neurol 467, 271–292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H. & Tseng KY. eds. (2010). Handbook of Basal Ganglia Structure and Function. Academic Press; San Diego, CA. [Google Scholar]
- Tepper JM, Wilson CJ & Koós T (2008). Feedforward and feedback inhibition in neostriatal GABAergic spiny neurons. Brain Res Rev 58, 272–281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting JT, Daigle TL, Chen Q & Feng G (2014). Acute brain slice methods for adult and aging animals: application of targeted patch clamp analysis and optogenetics. Methods Mol Biol 1183, 221–242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todtenkopf MS, Stellar JR, Williams EA & Zahm DS (2004). Differential distribution of parvalbumin immunoreactive neurons in the striatum of cocaine sensitized rats. Neuroscience 127, 35–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorn P, Vanderschuren LJMJ, Groenewegen HJ, Robbins TW & Pennartz CM (2004). Putting a spin on the dorsal‐ventral divide of the striatum. Trends Neurosci 27, 468–474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall NR, Wickersham IR, Cetin A, De La Parra M & Callaway EM (2010). Monosynaptic circuit tracing in vivo through Cre‐dependent targeting and complementation of modified rabies virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107, 21848–21853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M, Kobets A, Du J‐C, Lennington J, Li L, Banasr M, Duman RS, Vaccarino FM, DiLeone RJ & Pittenger C (2015). Targeted ablation of cholinergic interneurons in the dorsolateral striatum produces behavioral manifestations of Tourette syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112, 893–898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M, Li L & Pittenger C (2016). Ablation of fast‐spiking interneurons in the dorsal striatum, recapitulating abnormalities seen post‐mortem in Tourette syndrome, produces anxiety and elevated grooming. Neuroscience 324, 321–329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin HH & Knowlton BJ (2004). Contributions of striatal subregions to place and response learning. Learn Mem 11, 459–463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin HH & Knowlton BJ (2006). The role of the basal ganglia in habit formation. Nat Rev Neurosci 7, 464–476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin HH, Knowlton BJ & Balleine BW (2004). Lesions of dorsolateral striatum preserve outcome expectancy but disrupt habit formation in instrumental learning. Eur J Neurosci 19, 181–189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin HH, Knowlton BJ & Balleine BW (2006). Inactivation of dorsolateral striatum enhances sensitivity to changes in the action‐outcome contingency in instrumental conditioning. Behav Brain Res 166, 189–196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin HH, Ostlund SB, Knowlton BJ & Balleine BW (2005). The role of the dorsomedial striatum in instrumental conditioning. Eur J Neurosci 22, 513–523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Disclaimer: Supporting information has been peer‐reviewed but not copyedited.
Movie S1: 3‐D model reconstructed from serial sections showing afferent cells that project onto dorsomedial striatal PV interneurons.
Movie S2: 3‐D model reconstructed from serial sections showing afferent cells that project onto dorsolateral striatal PV interneurons.


