Abstract
DNA methylation can serve to control diverse phenomena in eukaryotes and prokaryotes, including gene regulation leading to cell differentiation. In bacteria, DNA methylomes (i.e., methylation state of each base of the whole genome) have been described for several species, but methylome profile variation during the lifecycle has rarely been studied, and only in a few model organisms. Moreover, major phenotypic changes have been reported in several bacterial strains with a deregulated methyltransferase, but the corresponding methylome has rarely been described. Here we report the first methylome description of an entomopathogenic bacterium, Photorhabdus luminescens. Eight motifs displaying a high rate of methylation (>94%) were identified. The methylome was strikingly stable over course of growth, but also in a subpopulation responsible for a critical step in the bacterium’s lifecycle: successful survival and proliferation in insects. The rare unmethylated GATC motifs were preferentially located in putative promoter regions, and most of them were methylated after Dam methyltransferase overexpression, suggesting that DNA methylation is involved in gene regulation. Our findings bring key insight into bacterial methylomes and encourage further research to decipher the role of loci protected from DNA methylation in gene regulation.
Introduction
DNA methyltransferases (MTases) are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a methyl group from the universal methyl donor S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM) to a nucleotide1. MTases are widespread from eukaryotes to prokaryotes: 5-methylcytosine (m5C) and N6-methyladenine (m6A) methylation marks have been described in eukaryotes2,3 whereas additional N4-methylcytosine (m4C) marks can be detected in bacteria and archaea4,5. For years, DNA methylation studies mostly used whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS), which only detects m5C6, until the advent of Single Molecule Real Time (SMRT) sequencing made it possible to also detect m4C and m6A modifications7.
DNA methylation in bacteria is involved in many cellular processes. It provides a defense against foreign DNA in restriction-modification systems (RM), where a restriction endonuclease (REase) acts in coordination with a DNA MTase. The MTase methylates self-DNA whereas exogenous DNA is cleaved by the cognate REase due to different methylation patterns. RM-MTases are classified into 4 different groups based on biochemical properties (e.g. their subunit organization, their recognition of palindromic vs asymmetric target DNA sequences…)8. The REBASE database is designed to identify REases and MTases and currently lists thousands of putative RM-MTases9.
Many studies, particularly in Escherichia coli, have described the role of DNA methylation in discriminating between the parental and newly-synthesized strand using the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system10. During replication, errors may occur, and the MMR system excises the wrong base on the newly-synthesized unmethylated DNA strand10. The MMR system requires Dam (DNA adenine MTase), an MTase that is not coupled with a restriction enzyme and so called “orphan” or “solitary” MTase5. In Gammaproteobacteria, Dam methylates 5′-GATC-3′ motifs. Dam is also involved in epigenetic mechanisms by strongly contributing to the regulation of several genes expression5. In E. coli for example, the Lrp regulator can bind sites containing GATC sequences in the pap operon promoter region11. Lrp has greater affinity to unmethylated sites than fully-methylated (methylation on both strands) sites, and the competition between Dam and Lrp binding gives rise to two sub-populations, one expressing the Pap pilus and the other not12. Deregulation by mutation or overexpression of Dam in several bacterial species can lead to drastic phenotypic changes. For example, Dam overexpression leads to a decrease in virulence for Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, Vibrio cholerae, Salmonella enterica, Pasteurella multocida, Aeromonas hydrophila and Photorhabdus luminescens13–18. Dam mutants have also been described as showing impaired virulence in S. enterica, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, A. actinomycetemcomitans and Y. pestis19–23. Dam mutants are not viable in Y. pseudotuberculosis and V. cholera16 or suspected to be unviable in other bacterial species18. DNA cytosine MTase (Dcm) is another solitary MTase that is well conserved in Gammaproteobacteria24. The dcm gene is associated to vsr which encodes the very-short-patch repair system involved in T/G mismatches correction24. Dcm adds a methyl group to the second cytosine of CCWGG motifs. This solitary MTase has been shown to be involved in drug resistance, translation25 and stationary phase gene expression26. In addition to Dam, the best known example of solitary MTase involved in epigenetic mechanisms in bacteria27 is the CcrM (Cell cycle regulated MTase) found in many Alphaproteobacteria. Its main role in Caulobacter crescensus is regulation of the cell cycle and cell division28,29. It is essential for cell viability in fast-growing conditions30 but not in slow-growing conditions such as minimal media31. It has not been described as involved in MMR31. Many other solitary MTases are present in many bacterial genomes, but their role has not yet been described32.
SMRT sequencing can now detect all DNA methylation marks in genomes, opening opportunities to detect new methylated motifs7. This new-generation sequencing technology has been used to describe the methylome of several microorganisms. In bacteria, there has been a strong focus on animal pathogens, but the methylomes of some plant pathogens have also been reported32–41.
P. luminescens TT01 is an entomopathogenic bacterium member of the Enterobacteriaceae. It is found in symbiosis with a soil nematode from the genus Heterorhabditis. This nematobacterial complex is able to kill many crop-pest insects and can be used in biocontrol42. During its lifecycle, this bacterium has to switch between mutualism (within the nematode’s gut) and a pathogenic state (in the insect). This switch is controlled by a promoter inversion that results in Mad pilus expression43. However, phenotypic heterogeneity among a P. luminescens clonal population caused by an as-yet-unknown mechanism is also critical during another step of the bacterial lifecycle. It was recently demonstrated that only a minority (<1%) of the whole bacterial population is responsible for virulence in insects, as it is able to resist the antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) produced by the insect host44. The fact that this AMP-resistant subpopulation displays no genetic change compared to the wild-type population has raised the hypothesis that an epigenetic mechanism is involved in the occurrence of this subpopulation44. Moreover, we recently showed that overexpression of the P. luminescens Dam MTase decreases motility and virulence yet enhances biofilm formation18. However, the impact of this MTase overexpression on DNA methylation pattern remains to be investigated.
The aim of this study was to provide the first description of the full methylome of P. luminescens during different growth phases. We also investigated whether changes in DNA methylation pattern occur within the AMP-resistant subpopulation responsible for insect virulence, or after the Dam overexpression that leads to major phenotypic changes in P. luminescens. The various methylomes analyzed here led to the identification of eight methylation motifs, and open new fields of investigation into the role of DNA methylation in bacterial gene regulation.
Results
Predicted MTases in P. luminescens TT01
The P. luminescens TT01 genome harbors 47 genes which are annotated as methyltransferase or methylase, most of them encoding putative RNA MTases or protein MTases. Only 8 genes (plu0087, plu0338, plu0600, plu2710, plu2942, plu3417, plu3449 and plu3462) are annotated as DNA methyltransferase or DNA methylase45. Analysis of the P. luminescens TT01 genome using REBASE revealed 12 putative DNA MTase-encoding genes, i.e. the 8 genes cited above, plus plu0233, plu1935 and plu4197 which are annotated as encoding CHP (conserved hypothetical proteins) or unknown proteins, and plu4319 which is annotated as encoding a “Type I site-specific deoxyribonuclease HsdM”. Prediction of the protein domains revealed an S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent methyltransferase domain (Interpro domain IPR029063) in all of the 12 MTases.
The 12 putative DNA MTase-encoding-genes found in P. luminescens TT01 are listed in Table 1. While 4 MTases are associated with REases, 7 are solitary MTases, and one is a hybrid MTase. The 12 loci were located all over the chromosome (Fig. 1). One predicted MTase (plu4319) corresponded to a Type I9 while the remaining MTases were presumed to classify as Type II. For 8 of them, REBASE analysis proposed a recognition sequence (Table 1)9.
Table 1.
List of putative P. luminescens TT01 MTase encoding genes.
| Gene name or Label | Protein label | Interpro Domains | MW (Da) | Type | Cognate partnera | Target Sequenceb | Genome Position | Genomic Locationc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dam (plu0087) | M.PluTDam | IPR012327, IPR012263, IPR029063, IPR023095, IPR002052 | 31567 | Solitary | Gm6ATC (motif I) | 81849–82661 | Core Genome | |
| plu0233 | PluTORF233 | IPR002052 | 121133 | Hybrid | ? | 242879–246085 | RGP5 | |
| dcm (plu0338) | M.PluTORF0338 | IPR001525, IPR029063, IPR018117, IPR031303 | 54918 | Solitary | plu0339,Vsr | Cm5CWGG (motif VI) | 361215–362651 | GI9 |
| plu0599 | M.PluTI | IPR001525, IPR029063 | 42313 | II/R-M | plu0600, PluTI | GGm5CGCC (motif VII) | 679941–682068 | Core Genome |
| plu1935 | M.PluTORF1935 | IPR002941, IPR029063, IPR001091, IPR002052 | 78939 | II/R-M | plu1934, PluTORF1935 | AGGCm4CT (motif IV) | 2301611–2303698 | RGP46 |
| plu2709 | M.PluTORF2709 | IPR029063, IPR025931, IPR025931 | 27200 | II/R-M | plu2710, PluTORF2710 | CTCGm6AG (motif V) | 3211074–3213464 | RGP66 |
| plu2942 | M.PluTORF2942 | IPR007757, IPR029063 | 24665 | Solitary | Gm6ATC | 3452873–3453517 | P71 | |
| plu3417 | M.PluTORF3417 | IPR002941, IPR029063, IPR001091 | 21450 | Solitary | ? | 4034728–4035285 | P80 | |
| plu3449 | M.PluTORF3449 | IPR012263, IPR029063, IPR023095 | 29802 | Solitary | ? | 4059699–4060469 | P80 | |
| plu3462 | M.PluTORF3462 | IPR002941, IPR001091, IPR029063, IPR002052 | 18578 | Solitary | ? | 4068792–4069265 | P80 | |
| plu4197 | M.PluTORF4197 | IPR009528, IPR029063 | 18824 | Solitary | CTGCm6AG | 4911020–4911514 | GI94 | |
| hsdM (plu4319) | M.PluTORF4319 | IPR003356, IPR022749, IPR004546, IPR029063, IPR002052 | 57671 | I/R-M | hsdS (plu4320), S.PluTORF4319, hsdR (plu4322), PluTORF4319 | GGm6AN6RTGA(motif IIIa)/TCm6AYN6TCC (motif IIIb) | 5043966–5044616 | GI95 |
aGene name and protein label of cognate partners (if any) is indicated.
bPredicted target sequence is indicated. Motifs identified in this study are underlined (with their number in brackets).
cAs described by Ogier et al.46. GI, genomic islands; RGP, regions of genomic plasticity; P, phagic regions.
Figure 1.
Circos plots displaying the distribution of methylated bases over the P. luminescens TT01 chromosome. Outermost track displays the genomic positions in megabases. The colored tracks display the location of the modification marks detected in at least one of the growth conditions tested, for each of the 8 identified motifs. Different colors represent different methylation types. From outer to inner: (red, m6A) GATC, GGANNNNNNRTGA/TCAYNNNNNNTCC, TGGCCA, CTCGAG; (green, m4C) AGGCCT; (blue, m5C) CCWGG, GGCGCC. Tick marks on the outermost track display the genomic positions of the 12 MTase-encoding genes (labelled with an asterisk) and their 5 cognate partners; see Table 1 for details. Note that the P. luminescens TT01 strain harbors no plasmid.
Distribution of predicted MTases in Gram-negative bacteria
The genomic context and taxonomic distribution of putative P. luminescens TT01 MTase-encoding genes are presented in Fig. S1. Most (n = 10) of the MTases encoding loci were located in the accessory genome and are associated with phagic regions (n = 4), genomic islands (n = 3), or regions of genomic plasticity (n = 3) (Table 1). The dam gene is located in the core genome and an ortholog was present in each of the Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus (a closely related genus, with similar lifestyle46) complete available genomes, with a conserved synteny (Fig. S1). dam was also broadly distributed among many (>100) organisms of the Enterobacteriaceae family (Fig. S1), suggesting that this gene was ancestral in the genome. In contrast, plu0599, encoding M.PluTI47, is also located in the core genome (Table 1) but only conserved in two other strains of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus (Fig. S1). Other P. luminescens TT01 MTase-encoding genes were variably distributed among Enterobacteriaceae. For example, plu4197 was only found in P. luminescens TT01 genome whereas putative orthologs of several MTases (dcm, plu2942, plu3417, plu3449, plu3462, plu4319) were found in more than 50 organisms of the Enterobacteriaceae family (Fig. S1). The variable taxonomic distributions of MTases encoding genes and their high prevalence in the accessory genome, including an association with phage or DNA recombination genes, suggest that most of these genes have been acquired by horizontal gene transfer.
Identification of Methylation Motifs in P. luminescens Genome
In order to have a complete overview of all the existing methylation sites over the P. luminescens genome, two complementary sequencing technologies were used: (i) SMRT sequencing by PacBio which can identify m6A and (to a lesser extent) m4C, and (ii) WGBS by Illumina (MiSeq) which can identify m5C.
The methylome analysis was first performed on DNA samples extracted from WT P. luminescens cells harvested during the mid-exponential-growth phase (OD = 0.3–0.4, hereafter referred to as EP for exponential phase). The SMRT sequencing yielded an average coverage of 182X allowing the identification of a high number (n = 41143) of statistically significant (QV score ≥30, see the Methods section for details) DNA modification marks and the identification of 6 conserved motifs: GATC; TGGCCA; GGANNNNNNRTGA; TCAYNNNNNNTCC; AGGCCT; CTCGAG (Table 2). Five of them display m6A modifications and one displays an m4C modification. The WGBS approach allowed the discovery of additional m5C modification marks (n = 10898), grouped in two motifs: CCWGG and GGCGCC (Table 3). Altogether, we found 52041 methylated nucleotides distributed all over the P. luminescens genome (Fig. 1). For convenience, the 8 identified motifs were numbered according to sequencing technology used and their occurrence in the P. luminescens TT01 genome, and are hereafter referred to as motifs I to V for SMRT, with partner motifs GGANNNNNNRTGA/TCAYNNNNNNTCC numbered IIIa and IIIb, respectively, and motifs VI and VII for WGBS (Tables 2 and 3). The number of methylated motifs found in the genome ranged from 28 (motif V) to 37465 (motif I). The proportion of a given motif found methylated in the P. luminescens TT01 genome ranged from 94.0% (motif VII) to 100% (motif V).
Table 2.
Motifs detected by SMRT sequencing in P. luminescens TT01*.
| Motif | Fraction | N Detected | Mean Score | Mean IPD Ratio | Mean Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Motif I
GATC (37500) | |||||
| EP | 0.999 | 37465 | 213.9 | 5.28 | 148.3 |
| LE | 0.999 | 37445 | 146.2 | 5.34 | 93.4 |
| SP | 0.999 | 37466 | 109.0 | 6.18 | 63.8 |
| LS | 0.999 | 37476 | 177.0 | 5.19 | 120.0 |
| AMP-R | 0.999 | 37444 | 120.9 | 5.64 | 74.6 |
| Control | 0.998 | 37439 | 136.7 | 5.61 | 83.5 |
| DAM+ | >0.999 | 37496 | 211.2 | 5.23 | 141.0 |
|
Motif II
TGGCCA (1256) | |||||
| EP | 0.998 | 1254 | 205.0 | 5.37 | 149.7 |
| LE | 0.999 | 1255 | 136.0 | 5.30 | 94.6 |
| SP | 0.998 | 1254 | 100.9 | 6.09 | 63.9 |
| LS | 0.998 | 1253 | 161.6 | 5.04 | 120.0 |
| AMP-R | 0.998 | 1253 | 116.0 | 5.74 | 75.6 |
| Control | 0.998 | 1254 | 127.2 | 5.68 | 84.6 |
| DAM+ | 1.000 | 1256 | 194.2 | 5.13 | 143.8 |
|
Motif IIIa/IIIb
GGANNNNNNRTGA (1112)/TCAYNNNNNNTCC (1112) | |||||
| EP | 0.997 | 1109 | 207.3 | 5.27 | 147.2 |
| 0.996 | 1107 | 189.8 | 4.61 | 145.4 | |
| LE | 0.994 | 1105 | 125.9 | 4.48 | 92.3 |
| 0.996 | 1108 | 138.1 | 5.18 | 93.2 | |
| SP | 0.994 | 1105 | 96.2 | 5.23 | 63.1 |
| 0.998 | 1110 | 102.4 | 5.93 | 63.4 | |
| LS | 0.988 | 1099 | 147.9 | 4.19 | 120.2 |
| 0.996 | 1108 | 167.6 | 4.98 | 121.1 | |
| AMP-R | 0.993 | 1104 | 108.7 | 4.91 | 73.7 |
| 0.996 | 1108 | 116.0 | 5.57 | 74.3 | |
| Control | 0.994 | 1105 | 119.2 | 4.78 | 81.5 |
| 0.997 | 1109 | 128.8 | 5.48 | 83.4 | |
| DAM+ | 0.992 | 1103 | 174.0 | 4.28 | 139.2 |
| 0.997 | 1109 | 194.3 | 5.01 | 140.6 | |
|
Motif IV
AGGCCT (184) | |||||
| EP | 0.978 | 180 | 152.0 | 3.76 | 154.3 |
| LE | 0.978 | 180 | 98.6 | 3.78 | 93.8 |
| SP | 0.978 | 180 | 75.4 | 3.94 | 61.7 |
| LS | 0.973 | 179 | 117.4 | 3.82 | 110.7 |
| AMP-R | 0.962 | 177 | 89.6 | 3.82 | 78.7 |
| Control | 0.984 | 181 | 96.4 | 3.83 | 87.7 |
| DAM+ | 0.989 | 182 | 143.1 | 3.69 | 152.9 |
|
Motif V
CTCGAG (28) | |||||
| EP | 1.000 | 28 | 200 | 5.44 | 151 |
| LE | 1.000 | 28 | 137 | 5.26 | 93.4 |
| SP | 1.000 | 28 | 99.7 | 6.65 | 59.8 |
| LS | 1.000 | 28 | 160.9 | 5.21 | 122.4 |
| AMP-R | 1.000 | 28 | 77.6 | 6.25 | 47 |
| Control | 1.000 | 28 | 134 | 5.89 | 86.1 |
| DAM+ | 1.000 | 28 | 214 | 5.27 | 156 |
*Methylated base is underlined (m6A or m4C). The number of each motif found in the genome is indicated in brackets. EP, exponential phase; LE, late exponential phase; SP, stationary phase; LS, late stationary phase; AMP-R, polymyxinB-resistant subpopulation; Control, P. luminescens TT01 harboring the pBBR1MCS5 empty plasmid; Dam+, Dam overexpressing P. luminescens strain harboring the pBB-Dam plasmid. IPD, interpulse duration.
Table 3.
Motifs detected by bisulfite sequencing in P. luminescens TT01*.
| Motif | Fraction | N Detected | Mean Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Motif VI
CCWGG (10998) | |||
| EP | 0.948 | 10428 | 51.9 |
| SP | 0.953 | 10486 | 49.9 |
|
Motif VII
GGCGCC (500) | |||
| EP | 0.940 | 470 | 56.8 |
| SP | 0.942 | 471 | 50.5 |
*Methylated base is underlined (m5C). The number of each motif found in the genome is indicated in brackets. EP, exponential phase; SP, stationary phase.
Methylation motifs are conserved during various growth conditions
In order to determine whether the methylation pattern can evolve over the course of growth, methylome analysis after SMRT sequencing was also performed on bacterial cells harvested during other growth conditions: WT cells harvested during the late exponential-growth phase (OD = 0.9, hereafter referred as LE), stationary phase (overnight growth reaching OD = 1.5, hereafter referred as SP), and late-stationary phase (i.e., after 24 h of growth, with OD > 3, hereafter referred as LS). WGBS was also performed on WT cells harvested during SP (OD = 1.5). Moreover, the SMRT methylome of a previously-identified sub-population that is resistant to a cationic AMPs (i.e., polymyxin B44) was also investigated. The 8 identified motifs were found in all the methylomes analyzed. For a given motif, a high (>94%) and similar proportion (coefficient of variation <0.01) of methylated sites was observed (Tables 2 and 3). For a given motif identified by SMRT sequencing, the IPD (interpulse duration) ratio did not drastically change over the course of growth (Table 2). Taken together, these results indicate that in all the tested conditions, a high rate of methylation was reached for each of the MTases responsible for the methylation of the 8 identified motifs. This suggests that the corresponding MTase-encoding genes were expressed in all these growth conditions.
Expression of predicted MTases
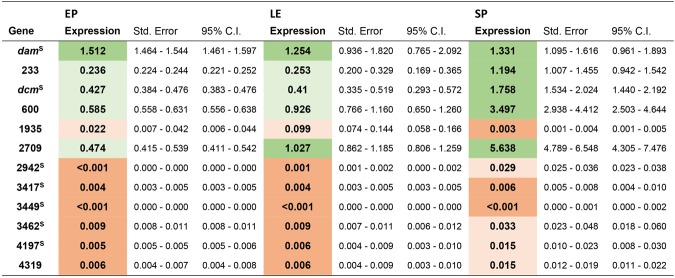
The expression level of the 12 MTase-encoding genes was analyzed by qRT-PCR on mRNA extracted from cells grown in LB and harvested during exponential phase (EP and LE) and stationary phase (SP) relative to gyrB, a housekeeping gene. Figure 2 shows that the 12 MTases could be split into two groups: MTases (n = 7) encoded by a gene with a low or very low level of expression compared to gyrB (less than 10-fold, or 100-fold, respectively) and MTase genes (n = 5) that were expressed at a higher level (>0.1-fold the gyrB level of expression). These two groups were identical for the 3 growth conditions tested, revealing that a given MTase gene was expressed at similar levels in the various tested conditions. This is in agreement with the finding that the methylome of TT01 was very similar for all the conditions tested.
Figure 2.
Relative expression levels of MTase genes in P. luminescens TT01. The fold difference in expression levels of each MTase gene relative to the gene coding for gyrB (plu0004) is indicated. Measurements were performed on RNA extracted from 3 independent experiments. EP, exponential phase; LE, late exponential phase; SP, stationary phase. Various colors represent various ranges of level of expression. Green, >1-fold the gyrB gene; light green, >0.1-fold the gyrB gene. Orange, <0.1-fold the gyrB gene; dark orange, <0.01-fold the gyrB gene. SSolitary MTase.
Most (5/7) solitary MTase-encoding genes were affiliated to the group with a low level of expression (compared to gyrB). Only dam and dcm, the two broadly conserved solitary MTase-encoding genes, could be assigned to the group with the higher expression (Fig. 2). In contrast, all MTases associated with a RM system except hsdM (plu4319), were affiliated to the group with a high level of expression (compared to gyrB).
Comparative analysis revealed that none of the 12 MTase-encoding genes was significantly differentially expressed between the LE and EP (Fig. S2A). In contrast, during SP compared to EP, the expression of two and five MTases was significantly downregulated or upregulated, respectively. Among the MTase genes affiliated to the group with a high level of expression, only plu0233 and plu0600 were significantly more expressed during SP compared to EP (Fig. S2B). However, methylome analysis of cells harvested during these two different growth conditions revealed no difference in motif detection, suggesting that a limited increase or decrease in the level of expression of these MTases did not significantly contribute to the genome methylation pattern in P. luminescens TT01.
Finally, given their very low expression levels (<0.001-fold the gyrB gene), five solitary MTases (Plu2942, Plu3417, Plu3449, Plu3462 and Plu4197) could be assumed to be inactive and therefore may not significantly contribute to the genome methylation pattern in P. luminescens TT01.
Motif-MTase assignment
Based on in silico analysis, 7 of the 8 identified motifs could be assigned to 6 of the MTases found in the genome (Table 1), as follows. The m6A modifications observed in motifs I, III and V could be targeted by the MTases Dam (plu0087, solitary MTase), HsdM (plu4319, RM system) and plu2709 (RM system), respectively; the m4C modifications observed in motif IV could be targeted by plu1935 (RM system); the m5C modifications observed in motifs VI and VII could be targeted by Dcm (plu0338, solitary MTase) and PluTI (plu0599, RM system), respectively (Table 1). Thus, only the m6A modifications observed in motif II could not be associated to an MTase based on in silico analysis. Considering the affiliation of plu0233 to the group with the high level of expression (Fig. 2), motif II could be targeted by plu0233 (a hybrid REase-MTase).
Genome-Wide Analysis of Modification Profiles
All of the 52041 methylated nucleotides found in these 8 methylated motifs were distributed across the genome (Fig. 1). A dedicated webpage with a genome browser displaying the precise position of the methylated nucleotides has been generated (access details can be found in the “Data Availability” section below).
The distribution over the TT01 chromosome of the most prevalent methylation motif (GATC) was analyzed using the DistAMO tool and revealed a heterogenic GATC motif distribution (Fig. S3). As regions with a high GATC density are also regions displaying a high DNA methylation rate, their genomic localization was identified, and their distribution in the core and accessory genome of P. luminescens was determined. The 38 high-GATC-density regions identified are listed in Table S1. Eighteen were distributed in the core genome, and 20 in the accessory genome as follows: genomic islands (GI, n = 14), regions of genomic plasticity (RGP, n = 4), or phagic regions (n = 2). The major functions associated with these regions were “metabolism” (n = 22), “virulence” (n = 5) and “antibiotic synthesis” (n = 5)46.
Methylation pattern of a clonal subpopulation
We previously identified a small fraction of the P. luminescens TT01 population that is resistant to cationic AMPs and revealed that this subpopulation is the one responsible for successful infection in insects. Using SMRT sequencing, we showed that this subpopulation was genetically identical to a bacterial population composed of >99% of cells with an AMP-sensitive phenotype44. Here, we analyzed the SMRT data on the methylation pattern of the AMP-resistant subpopulation in order to identify the differences in m4C or m6A modification marks compared to the control sample (EP) corresponding to cells with an AMP-sensitive phenotype. The number of modification marks identified was 41114 in the AMP-resistant subpopulation (Table 2) and 41143 in the control sample (EP). For each of the motifs analyzed, a similar proportion (ranging from 96.2% to 100% depending on motif) of methylated sites was observed (coefficient of variation <0.01) between the AMP-resistant subpopulation and the control sample (Table 2). Altogether, only 37 modification marks differed between the two samples, as follows: 26 in motif I, 3 in motif II, 4 in motif III, and 4 in motif IV (detailed data can be found in the genome browser). None of these differential modification marks was located in the vicinity of the genomic regions harboring the pbgP operon (encoding enzymes involved in LPS modification and required for the AMP resistance) or the phoP/phoQ genes (encoding a two-component system required for the activation of pbgP expression). Thus, the global methylome of the AMP-resistant subpopulation analyzed after SMRT sequencing was highly similar to that of the WT grown during the control condition.
Analysis of the location of unmethylated motifs
For each of the 8 motifs identified, and for the four growth conditions tested, the number of unmethylated motifs are rare in P. luminescens (Fig. 3), in agreement with the high fraction of modifications marks identified (Tables 2 and 3). The location of the motif-associated methylation marks was determined relative to the position of neighboring ORFs: either in a putative promoter region (i.e. <200 bp upstream from a start codon), intragenic (inside an ORF), or in other intergenic regions (i.e. >200 bp from a start codon, or downstream of an ORF). For each motif, the fraction of motifs with modification marks (detected in at least one growth condition) mapping to a putative promoter region, as well as the fraction of motif without modification marks (detected in the four growth conditions tested) was calculated. These fractions were compared to the fraction of the corresponding motif mapping to putative promoter regions found in the genome (Fig. 3). For motif II to motif VII, the fraction of unmethylated motifs located in putative promoter regions was not significantly different compared to that observed elsewhere in the genome (i.e. inside an ORF or >200 bp from a start codon, or downstream of an ORF). In contrast, the fraction of unmethylated motif I (in at least one of the four growth conditions tested) located in putative promoter regions was significantly higher than that observed elsewhere in the genome (p < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test) (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Location of identified motifs in putative gene-regulatory regions. Proportion of motifs identified by SMRT sequencing (a) or by WGBS (b) located in gene body (blue), in putative promoter regions (i.e. <200 bp upstream from a start codon) (orange), or in intergenic regions (grey). (all), all motifs found in the genome; (cons.), methylated motifs conserved in all of the 4 growth conditions tested (SMRT) or in the 2 growth conditions tested (WGBS); (diff.), methylated motifs in one, two or three of the 4 tested growth conditions (SMRT) or in one growth condition (WGBS); (unmet.), unmethylated motifs conserved in all of the 4 (SMRT) or 2 (WGBS) growth conditions tested. Asterisks indicate that the proportion of motifs located in the upstream region vs gene body is significantly different from the proportion observed in the ≪all≫ condition (p < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test). NS, not significant (p > 0.05).
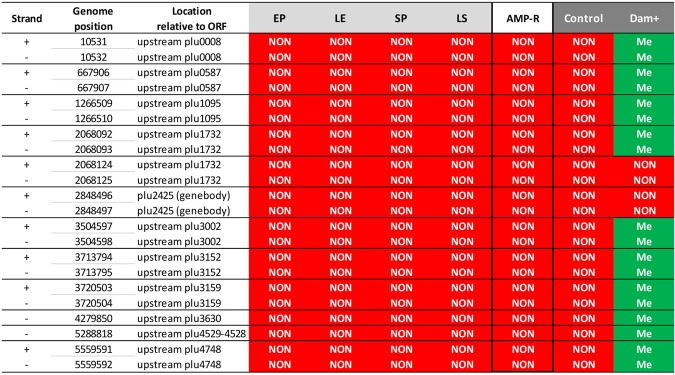
We therefore focused on the precise location of the conserved unmethylated motifs I (GATC). Unmethylated GATC motifs are rare in P. luminescens: only 56 sites out of 37500 were unmethylated in at least one of the 4 growth conditions tested (Fig. 3). Only a limited number (n = 16) of these unmethylated GATC motifs were located inside an ORF while the majority of them (n = 41) were located either in putative promoter regions, or in other intergenic regions (Fig. 3). As described above, the fraction of these unmethylated GATC motifs located in putative promoter regions was significantly higher than that observed elsewhere in the genome. Among the 56 GATC motifs unmethylated in at least one growth condition, 35 GATC motifs were unmethylated in three or four of the growth conditions tested (detailed data are available in the genome browser). Strikingly, 22 GATC motifs were unmethylated in all four growth conditions tested. Only two were located in a gene body, while the remaining 20 were located in putative promoter regions, with 4 of them mapping to the same promoter region (i.e. upstream plu1732) (Fig. 4). These 22 motifs were distributed all over the chromosome (Fig. 4). Interestingly, all these 22 motifs were still unmethylated in the AMP-resistant subpopulation described above (Fig. 4). Taken together, these results suggest the existence of factors (e.g., DNA binding proteins) hindering DNA methylation at these particular sites. Such factors are presumably always present in the various growth conditions tested, including in the AMP-R subpopulation. No conserved motif, recognizable by transcription factors was observed in these 22 loci based on MEME analysis (data not shown).
Figure 4.
P. luminescens unmethylated GATC motifs. List of the 22 adenines located in GATC sites which were always unmethylated during the 4 growth conditions tested (light grey). The methylation state of these loci is also indicated for the P. luminescens AMP-R (i.e. polymyxinB-resistant) subpopulation (white) and for the P. luminescens strains harboring a plasmid (dark grey). Twenty unmethylated adenines were located upstream from an ORF, and two in a gene body. Red (NON), no modification mark was detected on the adenine of the GATC motif; Green (Me), a modification mark was detected. Note that Dam overexpression (Dam+) restores the DNA methylation of most (18/22) of the adenines located in GATC.
Methylome modifications by Dam-MTase overexpression
We then investigated whether the high proportion (99.8%, Table 2) of the methylated GATC motifs identified in a reference condition could be increased by Dam MTase overexpression. The methylome of a strain overexpressing the Dam MTase was therefore analyzed and compared to its control strain (harboring an empty plasmid).
The number of modification marks identified in the strain overexpressing the Dam MTase and in the control sample (harboring an empty plasmid) was 41175 and 41119, respectively (Table 2). The 68 modification marks differing between the two samples were distributed as follows: 57 in motif I (GATC) which is recognized by Dam MTase, 2 in motif II, 2 in motif IIIa, 4 in motif IIIb and 3 in motif IV (detailed data can be found in the genome browser). As described above, 22 GATC motifs were unmethylated in all four growth-curve time-points tested and were also unmethylated in the control strain harboring an empty plasmid (Fig. 4). In contrast, most of these motifs (n = 18) were found methylated in the strain overexpressing the Dam MTase (Fig. 4). Thus, with only 4 out of 37500 GATC sites found unmethylated in the strain overexpressing the Dam MTase, the proportion of methylated motif I was therefore higher than in the control (99.99% vs 99.83%, respectively). For the other motifs analyzed, a similar proportion of methylated motifs was observed in the strain overexpressing the Dam MTase (coefficient of variation <0.01). Thus, besides an increase in GATC methylation, the global methylome of the strain overexpressing the Dam MTase displayed only a limited number of differences compared to the methylome of the control. These results reveal that Dam overexpression caused a modification of the DNA methylation pattern, which was focused on the unmethylated GATC sites found in the control condition as well as in other various growth conditions tested.
Discussion
There has been a recent surge in bacterial methylomic data released32,33,35,37–39,48. However, in these studies, SMRT sequencing only allowed the analysis of m6A and m4C modification marks, as the thorough identification of the third known DNA methylation mark (i.e. m5C) requires other investigations such as WGBS. Furthermore, most of these studies were performed in only one growth condition. While the genome of P. luminescens TT01 was sequenced in 200345, our study has only now revealed its complete epigenome (m6A, m4C and m5C) and found no major difference between the various growth conditions tested. Up to now, observation of a relatively stable methylome had only been described for E. coli49,50.
m4C methylation is restricted to archaea and prokaryotes, but in many bacterial species such as E. coli, no m4C-MTase was identified32,36,51,52. In contrast, P. luminescens displays a clear motif with m4C modification marks (motif IV), with 184 occurrences in the genome at a high rate of methylation (>96% of the motifs are detected as methylated). Based on our results, this motif is presumably methylated by an MTase for which orthologs are mostly found in the Photorhabdus genus (plu1935).
Several bacterial variants displaying genetic differences with their ancestor have been analyzed for their DNA methylation pattern (Haemophilus, Neisseria, Helicobacter, Campylobacter)53–56. In P. luminescens, we previously described the existence of an AMP-resistant (AMP-R) subpopulation which displays no difference in genome sequence compared to the control population (for which more than 99% of the cells are AMP-sensitive)44. The bacterial DNA methylation pattern in a bacterial population grown in presence of antibacterial agents has only been described in E. coli49. Here, we analyzed the methylome of the P. luminescens AMP-R subpopulation and found that it was highly similar to that of the control population. We thus provide evidence that the AMP used here (i.e. polymyxin B) does not drastically modify the DNA methylation pattern in P. luminescens. The precise mechanism allowing the AMP-R subpopulation to arise remains unknown, but it requires activation of the expression of the pbgPE locus in a PhoPQ-dependent manner44,57. In accordance with the high similarity observed between the methylomes of the AMP-R subpopulation and the wild-type control population, no particular modification mark (focused here on m6A and m4C modification marks) mapping to the loci responsible for the AMP resistance could be identified in the AMP-R subpopulation. In addition, Bisulfite sequencing of the promoter region of pbgPE genes revealed no m5C difference between both subpopulations (Mouammine & Brillard, unpublished data), suggesting that DNA methylation is not a mechanism triggering the occurrence of the AMP-R subpopulation.
The most prevalent methylation motifs throughout the P. luminescens genome are GATC (motif I) methylated by Dam, followed by CCwGG (motif VI), methylated by Dcm. Out of the 12 MTases found in P. luminescens TT01, these two MTases are the only ones for which orthologs are found in numerous bacterial genera other than Photorhabdus or the closely-related genus Xenorhabdus. As both MTases are widely distributed in Enterobacteria, they have been extensively studied24. The P. luminescens methylome analysis also confirmed the presence of a m5C modification mark in motif VII (GGCGCC), a motif previously described as recognized by an RM system (PluTI)47. Five additional motifs were also identified in this study, including two not found in REBASE (motifs IIIa and IIIb)9.
Here we also show that the Dam methyltransferase is very efficient in P. luminescens, causing the DNA methylation of more than 99% of the GATC sites in the genome, similarly as what was described in E. coli or Salmonella5. Despite this high level of methylation, we identified several loci that were always unmethylated in the tested conditions, suggesting the existence of factors, such as DNA-binding proteins, that hinder these particular GATC sites, as described elsewhere58. Strikingly, a significant enrichment of putative promoter regions was observed for these unmethylated motifs but not for the other 6 motifs identified. Dam has been described to act as a regulator of gene expression in E. coli and Salmonella strains, and is therefore considered as involved in epigenetic mechanisms, but such a role in other bacteria remains to be investigated5. Our results suggest that in P. luminescens, Dam may be responsible for a similar mechanism. Furthermore, we provide evidence that Dam overexpression can allow the methylation of these usually-unmethylated sites, suggesting a competition between as-yet-unidentified DNA-binding proteins and the Dam MTase.
MTase overexpression is reported to be related to strong phenotype modifications in several bacterial species, but their methylome has never been investigated13,15,17,18,59. In E. coli, SMRT sequencing of strains overexpressing 3 MTases, for which no particular phenotype was described, revealed signatures in the kinetic variations of the DNA polymerase that were not detected in the parental strain (i.e. methylation of adenines which were not located in a particular motif), suggesting nonspecific activity of these overexpressed MTases36. In P. luminescens, the Dam overexpression was not associated with particular signatures in the kinetic variations of the DNA polymerase compared to the control strain. In contrast, it was associated with an increase in GATC methylation frequency. Further research is required to find out whether this change in the DNA-methylation pattern may be related to the modification of several phenotypes observed in the Dam-overexpressing strain, including impaired motility, impaired virulence in insects, and increased biofilm-forming ability18.
Conclusion
This study brings the first description of the methylome of an entomopathogenic bacterium, with the identification of eight motifs displaying a high rate of methylation (Fig. 5). The methylome was stable over growth curve, as well as in an antimicrobial peptide-resistant subpopulation responsible for virulence in insects. The rare unmethylated GATC motifs were located preferentially in putative promoter regions, suggesting that DNA methylation is involved in gene regulation. Overexpression of the Dam MTase can lead to a slight modification of the DNA-methylation pattern, including the methylation of 18/22 sites which are usually protected from methylation by a presumed DNA-binding protein. Given the major modification of phenotypes associated with MTase-overexpression in several bacterial species, the strategy employed here can prove a powerful tool to open a new field of investigation to determine the role of loci protected from DNA methylation in gene regulation.
Figure 5.

Methylation status of the 8 identified motifs in P. luminescens TT01. (a) For each of the 8 identified motifs, the percentage found methylated in all growth conditions tested (green), in some of the growth conditions tested (purple), or the percentage of motifs found always unmethylated (red) is indicated. (b) Location of the 56 GATC motifs which were found unmethylated in at least one of the growth conditions tested in the WT strain (gene body, full color area; intergenic region, hatched area). The methylation status in the dam-overexpressing strain is indicated (purple, methylated; red, unmethylated).
Methods
Strains and growth conditions
The P. luminescens TT01 bacterial strains were routinely grown in Luria broth (LB) medium with a 180 rpm agitation at 28 °C. As required, antibiotic concentrations used for bacterial selection were gentamycin at 15 μg mL−1; polymyxin B (polyB), 100 μg mL−1. The AMP-R subpopulation was isolated as previously described44. Briefly, addition of polymyxin B to WT cells grown in LB at an OD540 of 0.3–0.4 (EP) led to a decrease in OD due to the death of the AMP-sensitive population (about 0.5% of the WT population was found to be AMP-R). The AMP-R cells were then collected when the OD540 had returned to 0.3 in the presence of polymyxin B. Genomic DNA was extracted on these cells for methylome analysis.
Genomic analysis of MTases encoding genes
The REBASE database9 was used to identify the putative DNA MTases in the P. luminescens TT01 genome45. The MaGe tool (available at https://www.genoscope.cns.fr/agc/microscope/mage/) was used to analyse the genomic context of their encoding genes. The genomic locations were defined in the core or accessory genome (Regions of genomic plasticity (RGP), Genomic Island (GI) and Prophage regions (P)) as previously described (Ogier et al.46). The MaGe tool was also used to analyse gene distribution and their synteny among a panel of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus genomes (27 and 16 strains, respectively, for which a complete genome was available). Distribution of the MTases in other Enterobacterial organisms was performed using a BlastP search on the NCBI non-redundant protein database with default parameters and a maximal target sequences set at 1000.
Single-molecule real-time (SMRT) DNA sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted from bacteria grown in LB and harvested at an OD540 of 0.3–0.4 (EP), OD = 0.9 (LE), OD = 1.5 (SP), and after 24 h of growth (OD > 3, LS) as follows. Bacterial cells corresponding to 2 ml of culture were washed in PBS and pellets were stored at −80 °C. To perform lysis, cells were resuspended in 200 µl of TSE-lysozyme for 15 minutes at 37 °C, followed by addition of 640 µl EDTA pH8 0.5 M and 160 µl SDS 10% and incubated 15 minutes at 60 °C. Lysates were incubated for 1 hour at 56 °C after addition of 20 µl proteinase K (20 mg·ml−1), cooled on ice and incubated 5 minutes at room temperature with 30 µl of RNAse A (20 mg·ml−1). Precipitation of contaminants was performed by addition of chilled 350 µl potassium acetate 5 M and a centrifugation step (10,000 × g for 10 min at 4 °C). The genomic DNA was purified with magnetic beads (Sera-Mag Speed beads, Thermo-Scientific) as previously described60. The DNA libraries were prepared according to PacBio guidelines: 20-kb Template Preparation Using BluePippin Size-Selection System (15-kb size cutoff); shearing at 40 kb was performed using Megaruptor system (Diagenode); sizing at 17 kb was performed using BluePippin system (Sage). Libraries were sequenced on one or two PacBio SMRT cells at 0.25 nM with the Protocol OneCellPerWell (OCPW), P6C4 chemistry and 360 minutes movies on a Pacific Biosciences RSII instrument (GeT-PlaGe, Toulouse, France). The raw data were processed with the PacBio SMRT Analysis Suite (version v2.3.0 p4). For samples EP, SP and AMP-R, the reads were assembled de novo, with the high-quality Hierarchical Genome Assembly Process HGAP.3 algorithm and no rearrangement was observed with progressiveMauve 2.1.0.a161. Conserved Synteny LinePlot revealed 100% conservation of synteny groups between the TT01 genomes studied, with a synton size ≥3 and the P. luminescens TT01 NC_005126 genome as the reference (data not shown).
DNA methylation detection and motifs identification after SMRT sequencing
DNA methylation was determined using the RS_Modification_and_Motif_Analysis protocol within SMRT Portal 2.3.0p4 which uses an in silico kinetic reference and a Welch’s t-test based kinetic score detection of modified base positions62 with parameters set as follow: subread/polymerase read length > = 500, polymerase read quality > = 80 and modification QV > = 30. A score of 30 for the “Modification QV” is the default threshold for calling a position as modified, and corresponds to a p-value of 0.001. Homemade script was used to keep methylated bases for adenine or cytosine with score > = 30 and known motifs.
Whole Genome Bisulfite DNA sequencing (WBGS) and DNA methylation detection
Genomic DNA from bacteria grown in EP and SP was extracted as described above and was sequenced using Illumina MiSeq technology as previously described63.
Fastq files were trimmed for adapters and low quality bases with Trim Galore! (v0.4.4)64 then mapped to the public reference genome (NC005126) with Bismark (v0.17.0)65. Picard tools were used to remove duplicated reads. Then methylation calling was performed with Bismark_methylation_extractor (v0.17.0) for every single cytosine65. Positions at which a sequencing coverage reached 25X or more, and where the proportion of instances that was detected as modified (i.e. number of reads detecting a modification/total number of reads at a given position) reached at least 90% were considered as a methylated base. The surrounding sequences (+/−20 nt) of each methylated cytosine were extracted and analyzed for a motif search using MEME-ChIP (v4.12)66. For the 2 motifs identified by WGBS, the mean proportion of reads that was detected as modified at a given position was high (97.3 for motif VI and 96.5 for motif VII). The fraction of motifs methylated was calculated as the number of motifs with a methylated based out of the total number of motifs found in the genome.
Determination of GATC-rich and GATC-poor regions
DistAMO analysis, which calculate a z-score (with value of 2/-2 considered as a significant value)67 revealed heterogenic GATC motif distribution over the TT01 chromosome (Supp. Data Fig. S3). However, the large window sizes used for the calculation of the z-scores of the GATC motif distribution range from 500 kb (at the inner ring) to 50 kb (on the outer ring increasing in 50 kb steps, Fig. S3). In order to have a clearer view of the GATC motif distribution over the TT01 chromosome, we used overlapping windows of a size of 1 kb, sliding every 100 bp. The mean proportion of GATC occurrence found per kb of the whole genome was calculated, and regions of 1 kb displaying at least +/−2 SEM were considered as GATC-enriched or GATC-depleted regions. Such regions were then compared to the position of regions of genomic plasticity previously described46.
RT-qPCR analysis
Total RNA extraction was performed on cells harvested during exponential phase (EP and LE) and stationary phase (SP), from three independent cultures for each strain, using RNeasy miniprep Kit (Qiagen), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. An additional incubation step with DNase I (Qiagen) was performed. The quantity and quality of RNA were assessed with an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer with the RNA 6000 Nano LabChip kit. Lack of DNA contamination was controlled by carrying out a PCR on each RNA preparation.
Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR) were carried out as previously described18. Briefly, RNA samples from 3 biological replicates for each strain were used for cDNA synthesis. The SuperScript II reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) was used on 1 µg of total RNA with random hexamers (100 ng·µl−1; Roche Diagnostics). qPCR analyses were performed using SYBR green Master kit (Roche Diagnostics) with 1 µl of cDNA and specific gene primers at 1 µM (Table S2). The reactions were performed in duplicate at 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 45 cycles at 95 °C for 5 s, 61 °C for 10 s, and 72 °C for 15 s and monitored in the LightCycler 480 system (Roche). Melting curves were analyzed and always contained a single peak. The data analyzed with the REST software 200968 using the pairwise fixed randomization test with 2,000 permutations are presented as a ratio with respect to the reference housekeeping gene gyrB, as previously described18.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
The authors thank INRA Plant Health and Environment (SPE) division for financial support (SPE2015-65359 & SPE-IB17-DiscriMet), GAIA doctoral school #584 for supporting AP’s PhD, and Alice Guidot for critical review of the manuscript.
Author Contributions
A.P., A.G. and J.B. designed the experiments; A.P. performed the experiments; L.L. and J.C.O. performed bioinformatics analysis; C.R., A.R., O.B. performed the SMRT and WGBS sequencing; A.P., L.L., J.C.O., A.M., A.G. and J.B. analyzed the data; A.P. and J.B. wrote the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript and have approved its final version.
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available at https://lipm-browsers.toulouse.inra.fr/jbrowse/current/?data=data/private/COLLABORATIONS/photorhabdus-APayelleville-2018/data. SMRT data have also been deposited in REBASE.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Amaury Payelleville and Ludovic Legrand contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41598-018-30620-5.
References
- 1.Lu SC. S-Adenosylmethionine. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology. 2000;32:391–395. doi: 10.1016/S1357-2725(99)00139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vanyushin BF. Adenine Methylation in Eukaryotic DNA. Molecular Biology. 2005;39:473–481. doi: 10.1007/s11008-005-0064-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vanyushin BF, Mazin AL, Vasilyev VK, Belozersky AN. The content of 5-methylcytosine in animal DNA: The species and tissue specificity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis. 1973;299:397–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ehrlich M, et al. DNA methylation in thermophilic bacteria: N4-methylcytosine, 5-methylcytosine, and N6-methyladenine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13:1399–1412. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Casadesus J. Bacterial DNA Methylation and Methylomes. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. 2016;945:35–61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43624-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Clark SJ, Statham A, Stirzaker C, Molloy PL, Frommer M. DNA methylation: bisulphite modification and analysis. Nature protocols. 2006;1:2353–2364. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Flusberg BA, et al. Direct detection of DNA methylation during single-molecule, real-time sequencing. Nature methods. 2010;7:461–465. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Loenen WA, Dryden DT, Raleigh EA, Wilson GG, Murray NE. Highlights of the DNA cutters: a short history of the restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:3–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Roberts RJ, Vincze T, Posfai J, Macelis D. REBASE–a database for DNA restriction and modification: enzymes, genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D298–299. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marinus, M. DNA Mismatch Repair. EcoSal Plus, 10.1128/ecosalplus.7.2.5 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Braaten BA, et al. Leucine-responsive regulatory protein controls the expression of both the pap andfan pili operons in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1992;89:4250–4254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Braaten BA, Nou X, Kaltenbach LS, Low DA. Methylation patterns in pap regulatory DNA control pyelonephritis-associated pili phase variation in E. coli. Cell. 1994;76:577–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen L, et al. Alteration of DNA adenine methylase (Dam) activity in Pasteurella multocida causes increased spontaneous mutation frequency and attenuation in mice. Microbiology. 2003;149:2283–2290. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Erova TE, et al. Mutations within the catalytic motif of DNA adenine methyltransferase (Dam) of Aeromonas hydrophila cause the virulence of the Dam-overproducing strain to revert to that of the wild-type phenotype. Infection and Immunity. 2006;74:5763–5772. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00994-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Heithoff DM, et al. Salmonella DNA adenine methylase mutants confer cross-protective immunity. Infect Immun. 2001;69:6725–6730. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.6725-6730.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Julio SM, et al. DNA adenine methylase is essential for viability and plays a role in the pathogenesis of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 2001;69:7610–7615. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7610-7615.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Julio SM, Heithoff DM, Sinsheimer RL, Low DA, Mahan MJ. DNA adenine methylase overproduction in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis alters YopE expression and secretion and host immune responses to infection. Infect Immun. 2002;70:1006–1009. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.1006-1009.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Payelleville A, et al. DNA Adenine Methyltransferase (Dam) Overexpression Impairs Photorhabdus luminescens Motility andVirulence . Frontiers in microbiology. 2017;8:1671. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Heithoff DM, Sinsheimer RL, Low DA, Mahan MJ. An essential role for DNA adenine methylation in bacterial virulence. Science. 1999;284:967–970. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5416.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mehling JS, Lavender H, Clegg S. A Dam methylation mutant of Klebsiella pneumoniae is partially attenuated. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2007;268:187–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00581.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Robinson VL, Oyston PC, Titball RW. A dam mutant of Yersinia pestis is attenuated and induces protection against plague. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2005;252:251–256. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Watson ME, Jr., Jarisch J, Smith AL. Inactivation of deoxyadenosine methyltransferase (dam) attenuates Haemophilus influenzae virulence. Molecular Microbiology. 2004;53:651–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wu H, et al. Inactivation of DNA adenine methyltransferase alters virulence factors in Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Oral Microbiology and Immunology. 2006;21:238–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2006.00284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Marinus, M. G. & Lobner-Olesen, A. DNA Methylation. Eco Sal Plus6, 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0003-2013 (2014).
- 25.Militello KT, Mandarano AH, Varechtchouk O, Simon RD. Cytosine DNA methylation influences drug resistance in Escherichia coli through increased sugE expression. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2014;350:100–106. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kahramanoglou C, et al. Genomics of DNA cytosine methylation in Escherichia coli reveals its role in stationary phase transcription. Nature communications. 2012;3:886. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Casadesus J, Low D. Epigenetic gene regulation in the bacterial world. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006;70:830–856. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00016-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Collier J, McAdams HH, Shapiro L. A DNA methylation ratchet governs progression through a bacterial cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:17111–17116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708112104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zweiger G, Marczynski G, Shapiro L. A Caulobacter DNA methyltransferase that functions only in the predivisional cell. J Mol Biol. 1994;235:472–485. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stephens C, Reisenauer A, Wright R, Shapiro L. A cell cycle-regulated bacterial DNA methyltransferase is essential for viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:1210–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.3.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gonzalez D, Kozdon JB, McAdams HH, Shapiro L, Collier J. The functions of DNA methylation by CcrM in Caulobacter crescentus: a global approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:3720–3735. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Blow MJ, et al. The Epigenomic Landscape of Prokaryotes. Plos Genet. 2016;12:e1005854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chen, P. et al. Comparative Genomics Reveals the Diversity of Restriction-Modification Systems and DNA Methylation Sites in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol83, 10.1128/AEM.02091-16 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Davis-Richardson AG, et al. Integrating DNA Methylation and Gene Expression Data in the Development of the Soybean-Bradyrhizobium N2-Fixing Symbiosis. Frontiers in microbiology. 2016;7:518. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Erill I, et al. Comparative Analysis of Ralstonia solanacearum Methylomes. Frontiers in plant science. 2017;8:504. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fang G, et al. Genome-wide mapping of methylated adenine residues in pathogenic Escherichia coli using single-molecule real-time sequencing. Nature biotechnology. 2012;30:1232–1239. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lee WC, et al. The complete methylome of Helicobacter pylori UM032. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:424. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1585-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mou KT, et al. A comparative analysis of methylome profiles of Campylobacter jejuni sheep abortion isolate and gastroenteric strains using PacBio data. Frontiers in microbiology. 2014;5:782. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhu L, et al. Precision methylome characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) using PacBio single-molecule real-time (SMRT) technology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:730–743. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Seong HJ, et al. Methylome Analysis of Two Xanthomonas spp. Using Single-Molecule Real-Time Sequencing. The plant pathology journal. 2016;32:500–507. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.FT.10.2016.0216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zautner AE, et al. SMRT sequencing of the Campylobacter coli BfR-CA-9557 genome sequence reveals unique methylation motifs. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:1088. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2317-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nielsen-LeRoux C, Gaudriault S, Ramarao N, Lereclus D, Givaudan A. How the insect pathogen bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis and Xenorhabdus/Photorhabdus occupy their hosts. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012;15:220–231. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2012.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Somvanshi VS, et al. A single promoter inversion switches Photorhabdus between pathogenic and mutualistic states. Science. 2012;337:88–93. doi: 10.1126/science.1216641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mouammine A, et al. An antimicrobial peptide-resistant minor subpopulation of Photorhabdus luminescens is responsible for virulence. Scientific reports. 2017;7:43670. doi: 10.1038/srep43670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Duchaud E, et al. The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Nature biotechnology. 2003;21:1307–1313. doi: 10.1038/nbt886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ogier JC, et al. Units of plasticity in bacterial genomes: new insight from the comparative genomics of two bacteria interacting with invertebrates, Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:568. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Khan F, et al. A putative mobile genetic element carrying a novel type IIF restriction-modification system (PluTI) Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:3019–3030. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Doberenz, S. et al. Identification of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 DNA Methyltransferase, Its Targets, and Physiological Roles. mBio8, 10.1128/mBio.02312-16 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 49.Cohen NR, et al. A role for the bacterial GATC methylome in antibiotic stress survival. Nature genetics. 2016;48:581–586. doi: 10.1038/ng.3530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Westphal, L. L., Sauvey, P., Champion, M. M., Ehrenreich, I. M. & Finkel, S. E. Genomewide Dam Methylation in Escherichia coli during Long-Term Stationary Phase. mSystems1, 10.1128/mSystems.00130-16 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 51.Forde BM, et al. Lineage-Specific Methyltransferases Define the Methylome of the Globally Disseminated Escherichia coli ST131 Clone. mBio. 2015;6:e01602–01615. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01602-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Powers JG, et al. Efficient and accurate whole genome assembly and methylome profiling of E. coli. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:675. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Anjum A, et al. Phase variation of a Type IIG restriction-modification enzyme alters site-specific methylation patterns and gene expression in Campylobacter jejuni strain NCTC11168. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016;44:4581–4594. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Atack JM, et al. A biphasic epigenetic switch controls immunoevasion, virulence and niche adaptation in non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae. Nature communications. 2015;6:7828. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Gorrell, R. & Kwok, T. In Molecular Pathogenesis and Signal Transduction by Helicobacter pylori (eds Nicole Tegtmeyer & Steffen Backert) 105–127 (Springer International Publishing, 2017).
- 56.Seib, K. L., Jen, F. E., Scott, A. L., Tan, A. & Jennings, M. P. Phase variation of DNA methyltransferases and the regulation of virulence and immune evasion in the pathogenic Neisseria. Pathogens and disease75, 10.1093/femspd/ftx080 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 57.Derzelle S, et al. The PhoP-PhoQ two-component regulatory system of Photorhabdus luminescens is essential for virulence in insects. Journal of bacteriology. 2004;186:1270–1279. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.5.1270-1279.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ardissone S, et al. Cell Cycle Constraints and Environmental Control of Local DNA Hypomethylation in α-Proteobacteria. Plos Genetics. 2016;12:e1006499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Erova TE, et al. DNA adenine methyltransferase influences the virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infection and Immunity. 2006;74:410–424. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.410-424.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mayjonade B, et al. Extraction of high-molecular-weight genomic DNA for long-read sequencing of single molecules. BioTechniques. 2016;61:203–205. doi: 10.2144/000114460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Darling AC, Mau B, Blattner FR, Perna NT. Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome research. 2004;14:1394–1403. doi: 10.1101/gr.2289704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Murray IA, et al. The methylomes of six bacteria. Nucleic Acids Research. 2012;40:11450–11462. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lluch J, et al. The Characterization of Novel Tissue Microbiota Using an Optimized 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Pipeline. Plos One. 2015;10:e0142334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Clark SJ, et al. Genome-wide base-resolution mapping of DNA methylation in single cells using single-cell bisulfite sequencing (scBS-seq) Nature protocols. 2017;12:534–547. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Krueger F, Andrews SR. Bismark: a flexible aligner and methylation caller for Bisulfite-Seq applications. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:1571–1572. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Machanick P, Bailey TL. MEME-ChIP: motif analysis of large DNA datasets. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:1696–1697. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sobetzko P, et al. DistAMo: A Web-Based Tool to Characterize DNA-Motif Distribution on Bacterial Chromosomes. Frontiers in microbiology. 2016;7:283. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L. Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:e36. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.9.e36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available at https://lipm-browsers.toulouse.inra.fr/jbrowse/current/?data=data/private/COLLABORATIONS/photorhabdus-APayelleville-2018/data. SMRT data have also been deposited in REBASE.