Abstract
Background
While odontogenic soft tissue infections of the head and neck are common, progression to necrotizing fasciitis is relatively rare. Necrotizing fasciitis is a potentially life-threatening and rapidly progressive soft tissue infection that can lead to significant skin and soft tissue loss, mediastinitis, vascular thrombosis or rupture, limb loss, organ failure, and death.
Methods
A PubMed literature search was conducted for case reports and case series on odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis. Individual patient data was analyzed and compiled and demographic, treatment, microbiology, and mortality data were extracted. Fisher’s exact test was used to examine the relationship between death from odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis and diabetes mellitus (DM) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positivity.
Results
A total of 58 studies totaling 164 patients were identified. Thirty-three patients had DM and 3 were HIV +. All patients underwent aggressive surgical debridement and treatment with IV antibiotics. Twenty patients were also treated with hyperbaric oxygen. There were 16 deaths reported, for a mortality rate of 9.8%. The mortality rate among patients with DM was 30.3 and 0% among HIV positive patients. There was a statistically significant increase in the mortality rate in DM patients with odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis (p = 0.0001, odds ratio for death 9.1).
Conclusions
Necrotizing fasciitis arising from odontogenic infection is a rapidly progressive and life-threatening illness. Prompt recognition of the infection, aggressive and often serial surgical debridement, and aggressive broad-spectrum antibiotics are necessary to prevent serious morbidity and mortality. Patients with diabetes mellitus are at a significantly increased risk of death from odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis.
Keywords: Odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis, Infection, Hyperbaric oxygen
Background
Necrotizing fasciitis is a potentially fatal soft tissue infection, characterized by extensive tissue necrosis and gas formation in the subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and deep tissues [1, 2]. It is most commonly bacterial in origin but sporadic cases caused by or associated with herpes zoster or herpes simplex have been reported [3–5]. In the head and neck region the etiology is most commonly odontogenic. Necrotizing fasciitis can spread rapidly, infiltrating tissue planes and leading to rapid progression with vascular compromise, organ failure, and mediastinitis or limb loss. The infection may be caused by myriad bacteria ranging from more common Streptococcal or Staphylococcal species to less common species such as Fusobacterium or Acinetobacter, and infections are often polymicrobial [1, 2]. The muscular, subdermal, and cutaneous vasculature often become compromised, leading to necrosis of muscle, skin, and loss of larger vessels. Underlying immune compromise such as diabetes mellitus (DM) or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection may predispose patients to necrotizing fasciitis or may increase the risks or morbidity or mortality of necrotizing fasciitis [1, 2]. Patients with odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis often appear acutely ill and may have a history of recent dental procedures or dental or maxillofacial trauma, or long-standing dental neglect. Patients may present with fever, tachycardia, dehydration, hypotension, and skin and soft tissue may appear cyanotic, mottled, cellulitic, tense, or overtly necrotic. Management depends upon prompt diagnosis with aggressive surgical debridement and serial debridement of any ongoing necrosis, aggressive intravenous (IV) antibiotic therapy, and hemodynamic and airway support when needed. While odontogenic infections are commonplace, the progression to life-threatening necrotizing fasciitis is relatively rare, and thus may not be recognized by emergency room, medical, or surgical practitioners until the disease has progressed significantly. To our knowledge, no recent study has examined the aggregate literature on odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis and systematically reviewed its etiologic factors, bacteriology, treatment, and comorbidities such as HIV or diabetes mellitus that may impact survival. For this reason, in this study we sought to review the available literature on necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin, and to examine patient demographics, the causative organisms, antimicrobials used, and to analyze the effect diabetes mellitus and HIV positivity have on mortality.
Methods
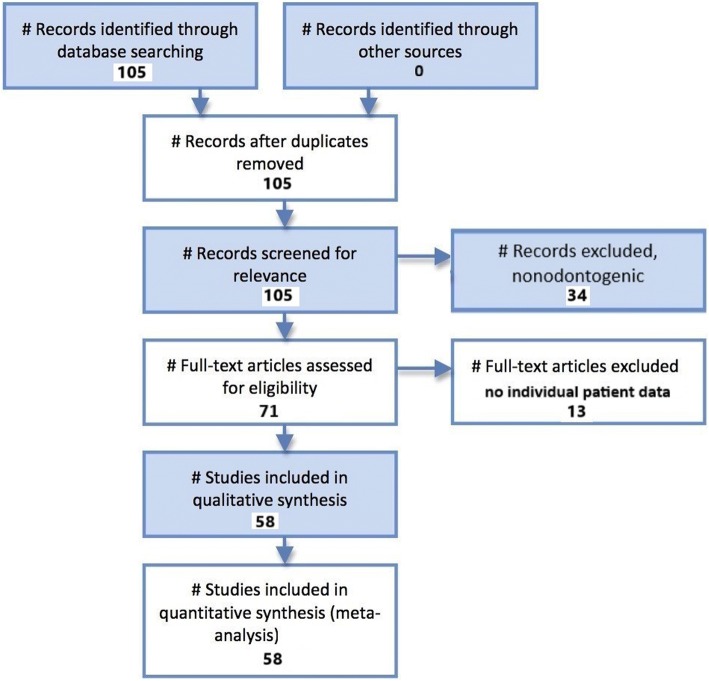
A Pubmed literature search was conducted using the search terms “odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis”. This literature review and meta-analysis was carried out and reported using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines for the reporting of observational studies [6]. Figure 1 illustrates the PRISMA flow diagram for study selection. For the period 1987–2018 105 total papers were identified. After excluding duplicate studies, nonodontogenic cases, review articles, and studies without analyzable individual patient data, a total of 58 studies reporting 164 total patients were identified [1, 7–63]. Case reports, case series, and cohort studies containing individual analyzable patient data on patients of any age with a pathologic diagnosis of odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis were included in the systematic review.
Fig. 1.
PRISMA flow diagram for odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis study selection
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with XLSTAT Biomed (Addinsoft, New York, NY, USA/Paris, France). Overall patient demographics, organisms isolated from culture, treatment type (surgical, antibiotic type, and use of hyperbaric oxygen) and mortality outcomes were compiled via standard summary statistical methods. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare non-DM and DM and HIV negative and HIV positive groups and to calculate the two-sided P values. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
A total of 164 patients with odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis were identified with analyzable individual patient data. Sixty-five patients had data on sex reported, with 45 males and 20 females reported (2.3:1 M:F ratio). A total of 33 patients were reported to have DM (20.1%), while 3 were HIV+ (1.8%). The median and average ages were 45.0 and 46.3 years, respectively (standard deviation 15.9 years).
The most common microbes isolated from culture were mixed anaerobes (9.8%), unspecified streptococcus species (9.8%), and mixed microbiological flora (9.1%). Table 1 summarizes the culture data from the cohort. All patients were treated with surgical debridement along with IV antibiotics. The most common IV antibiotics reported were metronidazole (21.3%), clindamycin (13.4%), penicillin (11.0%), and ceftriaxone (7.9%). Table 2 summarizes the antibiotic data from the cohort. Twenty patients (12.2%) were treated with hyperbaric oxygen, and there were no reported deaths in the hyperbaric oxygen + surgery + IV antibiotics group. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment in addition to surgery + IV antibiotics was not associated with a statistically significant decrease in mortality vs. surgery + IV antibiotics alone (p = 0.2).
Table 1.
Microbiological culture data from the odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis cohort
| Microbe isolated | Number of patients (n) | % of patients |
|---|---|---|
| Mixed microbiological flora | 15 | 9.10% |
| Prevotella buccae | 1 | 0.60% |
| Escherichia coli | 1 | 0.60% |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 6 | 3.70% |
| Staphylococcus capitis | 1 | 0.60% |
| alpha hemolytic streptococci | 3 | 1.80% |
| Prevotella species unspecified | 7 | 4.30% |
| Peptostreptococcus | 7 | 4.30% |
| coagulase-negative Staphylococcus | 7 | 4.30% |
| Corynebacterium | 1 | 0.60% |
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | 2 | 1.20% |
| mixed anaerobes | 16 | 9.80% |
| Gram-negative species | 6 | 3.70% |
| Streptococcus anginosus | 1 | 0.60% |
| Bacteroides species | 1 | 0.60% |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 3 | 1.80% |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | 4 | 2.40% |
| Acinetobacter | 1 | 0.60% |
| Fusobacterium | 1 | 0.60% |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 1 | 0.60% |
| no growth | 1 | 0.60% |
| Streptococcus group C | 1 | 0.60% |
| Streptococcus viridans | 1 | 0.60% |
| Streptococcus species unspecified | 16 | 9.80% |
| Diptheroids | 1 | 0.60% |
| Streptococcus milleri | 2 | 1.20% |
| Streptococcus sangius | 1 | 0.60% |
| Streptococcus porphyromonas | 1 | 0.60% |
Table 2.
Intravenous antibiotic usage data from the odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis cohort
| Antibiotic used | Number of patients (n) | % of patients |
|---|---|---|
| ceftriaxone | 13 | 7.90% |
| metronidazole | 35 | 21.30% |
| ciprofloxacin | 3 | 1.80% |
| clindamycin | 22 | 13.40% |
| imipenem | 1 | 0.60% |
| vancomycin | 1 | 0.60% |
| penicillin | 18 | 11.00% |
| Ampicillin + sulbactam | 2 | 1.20% |
| cefotaxime | 2 | 1.20% |
| gentamicin | 5 | 3.00% |
| amoxicillin-clavulanate | 2 | 1.20% |
| amikacin | 1 | 0.60% |
| amoxicillin | 1 | 0.60% |
| ceftazidime | 5 | 3.00% |
| cefuroxime | 1 | 0.60% |
There were 16 total deaths reported for a mortality rate of 9.8%. Of the 33 patients with diabetes mellitus there were 10 deaths (30.3%). Of the 131 non-DM patients there were 6 deaths (4.6%). Of the 3 patients who were HIV+ there were no deaths. The odds ratio for death for odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis patients with DM vs. those without DM was 9.1 (95% confidence interval (CI) =3.0 to 27.4, p = 0.0001). The number needed to treat/number needed to harm (NNT/NNH) was 4.0. The odds ratio for death for odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis patients with HIV vs. HIV- patients was 1.0 (95% CI = 0.05 to 19.7, p = 1.0, NNT/NNH = 8.0). Table 3 summarizes the odds ratio analysis for DM and HIV in patients with odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis.
Table 3.
Odds ratio analysis for mortality risk with DM and HIV in patients with odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis
| Diabetes mellitus | |
| Odds ratio for death | 9.1 |
| 95% CI of odds ratio: | 3.0 to 27.4 |
| Significance level | P = 0.0001 |
| NNT/NNH | 3.9 |
| HIV | |
| Odds ratio for death | 0.98 |
| 95% CI of odds ratio: | 0.05 to 19.7 |
| Significance level | P = 0.99 |
| NNT/NNH | 8 |
Discussion
Necrotizing fasciitis is an aggressive soft tissue infection that can be polymicrobial or due to a single organism [1, 2, 11, 64]. Multiple organisms as well as mixed infections have been reported to cause necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin. In the present study there were 30 different distinct microbiological results isolated from cultures taken from patients with odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis. The microbes isolated ranged from multiple species of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus to mixed anaerobic species and less common bacteria such as Prevotella and Fusobacterium.
Odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis is often characterized by rapidly progressive bacterial infection along multiple fascial tissue planes, leading to vascular compromise, thrombosis, or rupture, along with necrosis of adipose, integumentary, muscular, and subcutaneous and cutaneous tissues. Preexisting immunosuppressive conditions such as diabetes mellitus may predispose patients to odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis, and may increase the mortality risk [1, 2, 11, 64]. In the present study approximately 20% of patients were reported to have DM, and these patients were 9 times more likely to die from their odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis than non-diabetic patients (p = 0.0001). This highlights the need to identify co-morbidities such as DM and treat them appropriately while the patient is concomitantly being treated for odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis. In contrast to DM, only 1.8% of patients in the present study had HIV. These patients did not have an increased risk of death from odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis vs. HIV negative patients (OR = 1.0, p = 1.0). While most cases of head and neck necrotizing fasciitis are odontogenic in origin, idiopathic or pharyngeal etiologies are possible.
Patients with odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis should be treated aggressively with surgical debridement of necrotic tissue and close monitoring with serial debridement and/or frequent dressing changes as indicated. Broad-spectrum IV antibiotics targeting the most common organisms are also vital. In the present study all patients were treated with surgical debridement and IV antibiotics. The most common antibiotics were metronidazole, clindamycin, penicillin, and ceftriaxone but antimicrobial treatment may need to be adjusted once culture results are available in a given case. Debridement of necrotic tissue until viable tissue that bleeds is reached is typically recommended, although care must be taken in necrotizing fasciitis in close proximity to the great vessels, mediastinum, or lungs. The 9.8% overall mortality rate in this study highlights the importance of aggressive treatment with surgery and IV antibiotics. In this study 12.2% of patients were also treated with hyperbaric oxygen, which may be a useful adjunct in refractory cases and when hyperbaric oxygen is readily available. Critical care team involvement is often necessary, and airway management and management of hypotension, hypovolemia, and malnutrition may be necessary in patients with odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis.
Prompt recognition of odontogenic infections that have progressed to necrotizing fasciitis is key. While typical odontogenic infections such as cellulitis and periapical or cervical abscess may present with common or nonspecific symptoms such as swelling, pain, and trismus patients with dusky, tense, insensate, crepitant, or mottled skin, or evidence of involvement of multiple fascial planes and tissue compartments or evidence of gas formation on CT or MRI imaging may have concomitant necrotizing fasciitis needing more aggressive treatment. Survivors of odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis may also have extensive skin and soft tissue loss that may necessitate weeks to months of dressing changes or secondary reconstructive procedures such as skin grafts. Additionally, chronically poor dentition or carious teeth may need to be addressed by dental or oral surgery consultants to prevent recurrence.
The clinical implications of this study are several. The study demonstrates that patients with DM are at greater risk for morbidity and mortality in the setting of odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis. This highlights the need for recognition of DM as a comorbidity using serum glucose testing and hemoglobin A1C testing to assess known and newly diagnosed diabetics. Additionally, diabetics should have tight glucose control during their treatment for odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis, as this may impact the efficacy of their treatment and may affect the length of treatment. The study also demonstrates that a myriad of microorganisms can be causative agents in odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis, making cultures and sensitivities along with broad spectrum antibiotics transitioning to culture-directed antibiotics vital. The study also reiterates the need for aggressive surgical treatment and debridement to remove diseased, necrotic tissue. Extensive reconstructive procedures may be necessary once the necrotizing fasciitis is resolved, but surgical debridement to prevent mortality is of paramount importance. Additionally, the study suggests that adjunctive measures such as hyperbaric oxygen may be beneficial in cases where the patient is stable enough to undergo these procedures, and they are readily available to the treatment team.
The retrospective data in the study makes recall and selection bias a possibility. Nevertheless, the relatively large cohort (164 patients) for this relatively rare disease, combined with the highly significant mortality increase for patients with DM and the consistent therapy applied across the cohort (all patients were treated with surgical debridement and IV antibiotics) supports the validity of the study and its conclusions. The rarity of odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis makes prospective randomized trials difficult to assemble and the often rapid mortality and morbidity might make such trials ethically unfeasible, so relatively large patient cohort, rigorous statistical analysis, and diverse patient base represented in the literature makes this retrospective study a useful addition to the body of scientific knowledge on odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis.
Conclusions
Odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis is a relatively uncommon but life-threatening and rapidly progressive illness. The present study showed an overall mortality rate of 9.8%, with a significantly increased mortality rate of 30.3% in patients with diabetes mellitus. HIV infection did not appear to increase the risk of death from odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis in the present study. Management of odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis should involve aggressive and often serial surgical debridement, broad-spectrum IV antibiotics, resuscitation as indicated and management of concomitant systemic conditions such as diabetes. In patients with resultant skin or soft tissue loss physical rehabilitation and reconstructive procedures may also be needed. Hyperbaric oxygen may be a useful adjunctive treatment to surgery and IV antibiotics.
Availability of data and materials
All data is contained within the manuscript or available from Pubmed/the author.
Abbreviations
- CI
Confidence interval
- DM
Diabetes mellitus
- HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus
- IV
Intravenous
- NNT/NNH
Number needed to treat/number needed to harm
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Authors’ contributions
MRG designed the study, performed the literature search, reviewed articles for inclusion and exclusion, performed literature review and statistical analysis, and wrote the manuscript. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Camino Junior R, Naclerio-Homem MG, Cabral LM, Luz JG. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin in a diabetic patient complicated by substance abuse. Braz Dent J. 2014;25(1):69–72. doi: 10.1590/0103-6440201302336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Irani S. Orofacial bacterial infectious diseases: an update. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2017;7(Suppl 2):61–67. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_290_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ha KY, Tyring SK. Vibrio vulnificus necrotizing fasciitis preceding herpes zoster. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2013;26(1):55–57. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2013.11928921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vinikoor MJ, Wong YT, Margolis DM. Herpes simplex virus type 2 mimicking necrotizing fasciitis. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):567–568. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fung V, Rajapakse Y, Longhi P. Periorbital necrotising fasciitis following cutaneous herpes zoster. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65(1):106–109. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2011.06.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(10):1006–1012. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Al-Ali MA, Hefny AF, Idris KM, Abu-Zidan FM. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis: an overlooked diagnosis of a fatal disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018;138(4):411–414. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2017.1393841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Inan CH, Yener HM, Yilmaz M, Gözen ED, Erdur ZB, Oroğlu B, Olcay E, Memmedova N. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin and hyperbaric oxygen therapy. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(7):691–692. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000003842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cavalcante MB, Lima ALO, Moreira RT, de Oliveira E, Silva ED, Branco BLC. Cervical-thoracic necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin in a diabetic patient: a case report. Gen Dent. 2017;65(4):25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lareyre F, Cohen C, Declemy S, Raffort J, Quintard H. A fatal aortic arch rupture due to descending necrotizing Mediastinitis in a 24-year-old woman. Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2017;51(6):408–412. doi: 10.1177/1538574417715193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Abdurrazaq TO. Ibikunle AA, Braimah RO. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis: a potentially fatal disease with varied etiology. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2016;6(4):251–256. doi: 10.4103/amhsr.amhsr_33_16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bayetto K, Cheng A, Sambrook P. Necrotizing fasciitis as a complication of odontogenic infection: a review of management and case series. Aust Dent J. 2017;62(3):317–322. doi: 10.1111/adj.12508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kloth C, Hoefert S, Fischborn T, Schraml C. Dentogene focus as a rare cause of necrotizing fasciitis. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2017;142(3):212–215. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-121849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cariati P, Monsalve-Iglesias F, Cabello-Serrano A, Valencia-Laseca A, Garcia-Medina B. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis and acute mediastinitis of odontogenic origin: a case series. J Clin Exp Dent. 2017;9(1):150–152. doi: 10.4317/jced.53009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cortese A, Pantaleo G, Borri A, Amato M, Claudio PP. Necrotizing odontogenic fasciitis of head and neck extending to anterior mediastinum in elderly patients: innovative treatment with a review of the literature. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017;29(Suppl 1):159–165. doi: 10.1007/s40520-016-0650-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zemplenyi K, Lopez B, Sardesai M, Dillon JK. Can progression of odontogenic infections to cervical necrotizing soft tissue infections be predicted? Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;46(2):181–88. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 17.Juncar M, Bran S, Juncar RI, Baciut MF, Baciut G, Onisor-Gligor F. Odontogenic cervical necrotizing fasciitis, etiological aspects. Niger J Clin Pract. 2016;19(3):391–396. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.179278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Noy D, Rachmiel A, Levy-Faber D, Emodi O. Lemierre’s syndrome from odontogenic infection: review of the literature and case description. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2015;5(2):219–225. doi: 10.4103/2231-0746.175746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Botha A, Jacobs F, Postma C. Retrospective analysis of etiology and comorbid diseases associated with Ludwig's angina. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2015;5(2):168–173. doi: 10.4103/2231-0746.175758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Muhammad JK, Almadani H, Al Hashemi BA, Liaqat M. The value of early intervention and a multidisciplinary approach in the management of necrotizing fasciitis of the neck and anterior mediastinum of odontogenic origin. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;73(5):918–927. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2014.12.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cruz Toro P, Callejo Castillo À, Tornero Saltó J, González Compta X, Farré A, Maños M. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis: report of 6 cases and review of literature. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2014;131(6):357–359. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2013.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sumi Y. Descending necrotizing mediastinitis: 5 years of published data in Japan. Acute Med Surg. 2014;2(1):1–12. doi: 10.1002/ams2.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Novelli G, Catanzaro S, Canzi G, Sozzi D, Bozzetti A. Vacuum assisted closure therapy in the management of cervico-facial necrotizing fasciitis: a case report and review of the literature. Minerva Stomatol. 2014;63(4):135–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.van Niekerk C, Khammissa RA, Altini M, Lemmer J, Feller L. Noma and cervicofacial necrotizing fasciitis: clinicopathological differentiation and an illustrative case report of Noma. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 2014;30(3):213–216. doi: 10.1089/aid.2013.0259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Antunes AA, Avelar RL, de Melo WM, Pereira-Santos D, Frota R. Extensive cervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin. J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24(6):e594–e597. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31829ad57b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bucak A, Ulu S, Kokulu S, Oz G, Solak O, Kahveci OK, Ayçiçek A. Facial paralysis and mediastinitis due to odontogenic infection and poor prognosis. J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24(6):1953–1956. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31829ac617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bali A, Chadha I, Sharma A. Necrotizing fasciitis of the chest wall caused by infected dentigerous cyst: a case report. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012;11(3):347–350. doi: 10.1007/s12663-011-0214-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chunduri NS, Madasu K, Tammannavar PS, Pushpalatha C. Necrotising fasciitis of odontogenic origin. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:1–2. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-008506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ulu S, Ulu SM, Oz G, Kaçar E, Yücedağ F, Ayçiçek A. Paralysis of cranial nerve and striking prognosis of cervical necrotizing fasciitis. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23(6):1812–1814. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e318271024e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nanda S, Chakraborty S, Ray A, Inamuddin Healing of cervical necrotizing fasciitis using amniotic membrane as a dressing material. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2011;2(2):147–151. doi: 10.4103/0975-5950.94469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Park E, Hirsch EM, Steinberg JP, Olsson AB. Ascending necrotizing fasciitis of the face following odontogenic infection. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23(3):211–214. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31824de3e7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bilodeau E, Parashar VP, Yeung A, Potluri A. Acute cervicofacial necrotizing fasciitis: three clinical cases and a review of the current literature. Gen Dent. 2012;60(1):70–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kim YJ, Kim JD, Ryu HI, Cho YH, Kong JH, Ohe JY, Kwon YD, Choi BJ, Kim GT. Application of radiographic images in diagnosis and treatment of deep neck infections with necrotizing fasciitis: a case report. Imaging Sci Dent. 2011;41(4):189–193. doi: 10.5624/isd.2011.41.4.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Medeiros Júnior R, Melo Ada R, Oliveira HF, Cardoso SM, Lago CA. Cervical-thoracic facial necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;77(6):805. doi: 10.1590/S1808-86942011000600019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lorenzini G, Picciotti M, Di Vece L, Pepponi E, Brindisi L, Vessio V, Maffei M, Viviano M. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin involving the temporal region--a case report. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2011;39(8):570–573. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2010.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Juncar M, Popa AR, Lung T, Onişor F. Septic metastases of suppuration of odontogenic origin. Chirurgia (Bucur) 2011;106(3):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Huang D, Deng W, Li C, Chen S. Craniocervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin with thoracic extension. J Craniofac Surg. 2011;22(3):1109–1111. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3182108edb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lopez-Fernandez R, Ramirez-Melgoza J, Martinez-Aguilar NE, Leon-Chavez A, Martinez-Fong D, Gonzalez-Barrios JA. Growth factor-enriched autologous plasma improves wound healing after surgical debridement in odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2011;5:98. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Maria A, Rajnikanth K. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis caused by dental infection: a review and case report. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2010;1(2):135–138. doi: 10.4103/0975-5950.79215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhang WJ, Cai XY, Yang C, Zhou LN, Cai M, Lu XF, Zheng LY, Jiang B. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;39(8):830–834. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2010.03.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lingaraj JB, Rao S, Kotrashetti SM, Narad C. Necrotizing cervical fasciitis: a case report and review of literature. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2010;9(1):54–56. doi: 10.1007/s12663-010-0015-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ouazzani A, Dequanter D, Buttafuoco F, Raynal P, Lothaire P. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis arising from dental abscess: a rare clinical observation. Rev Med Brux. 2009;30(2):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Flanagan CE, Daramola OO, Maisel RH, Adkinson C, Odland RM. Surgical debridement and adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen in cervical necrotizing fasciitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140(5):730–734. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2009.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Subhashraj K, Jayakumar N, Ravindran C. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis: an unusual sequel of odontogenic infection. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2008;13(12):788–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Heath N, Macleod I, Chippindale A, Greenwood M, Ripley C. Severe necrotizing fasciitis complicating odontogenic infection: a case report. Dent Update. 2008;35(5):353–355. doi: 10.12968/denu.2008.35.5.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Suehara AB, Gonçalves AJ, Alcadipani FA, Kavabata NK, Menezes MB. Deep neck infection: analysis of 80 cases. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;74(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/S1808-8694(15)31097-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Farrier JN, Kittur MA, Sugar AW. Necrotising fasciitis of the submandibular region; a complication of odontogenic origin. Br Dent J. 2007;202(10):607–609. doi: 10.1038/bdj.2007.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Edwards JD, Sadeghi N, Najam F, Margolis M. Craniocervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin with mediastinal extension. Ear Nose Throat J. 2004;83(8):579–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ashar A. Odontogenic cervical necrotizing fasciitis. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2004;14(2):119–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Daniel E, Whang CS, Cohen JT. Radiology quiz case 2. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis (CNF), odontogenic origin. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;130(4):480. doi: 10.1001/archotol.130.4.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Shand JM, Breidahl A, Hing NR, Johnstone BR, Wiesenfeld D. Ascending necrotising fasciitis as a result of odontogenic infection: a report of two cases. Aust Dent J. 2001;46(2):134–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2001.tb00568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tung-Yiu W, Jehn-Shyun H, Ching-Hung C, Hung-An C. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin: a report of 11 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(12):1347–1352. doi: 10.1053/joms.2000.18259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Peter B. Cervicofacial necrotizing fasciitis. Schweiz Med Wochenschr Suppl. 2000;116:58S–61S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Whitesides L, Cotto-Cumba C, Myers RA. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin: a case report and review of 12 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(2):144–151. doi: 10.1016/S0278-2391(00)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Helmy AS, Salah MA, Nawara HA, Khatab H, Khalaf HA, Abd el-Maguid N. Life-threatening cervical necrotizing fasciitis. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1997;42(6):410–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ficheva M, Marina M, Ivanova K, Tomova M. Odontogenic craniofaciocervical necrotizing fasciitis. Khirurgiia (Sofiia) 1997;50(3):21–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mohammedi I, Ceruse P, Fontaine P, Védrinne JM, Moreon AH, Motin J. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis disclosing HIV infection. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 1997;114(6):228–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chin RS, Kaltman SI, Colella J. Fatal necrotizing fasciitis following a mandibular fracture. J Craniomaxillofac Trauma. 1995;1(3):22–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zbären P, Rothen HU, Läng H, Becker M. Necrotizing fasciitis of soft tissues of the face and neck. HNO. 1995;43(10):619–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Langford FP, Moon RE, Stolp BW, Scher RL. Treatment of cervical necrotizing fasciitis with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995;112(2):274–278. doi: 10.1016/S0194-5998(95)70250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Maisel RH, Karlen R. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis. Laryngoscope. 1994;104(7):795–798. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199407000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Reed JM, Anand VK. Odontogenic cervical necrotizing fasciitis with intrathoracic extension. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992;107(4):596–600. doi: 10.1177/019459989210700414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rapoport Y, Himelfarb MZ, Zikk D, Bloom J. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1991;72(1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(91)90181-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lambade PN, Dolas RS, Virani N, Lambade DP. Cervicofacial necrotising fasciitis of odontogenic origin: a review. Sci Rep. 2012;1:414. [Google Scholar]