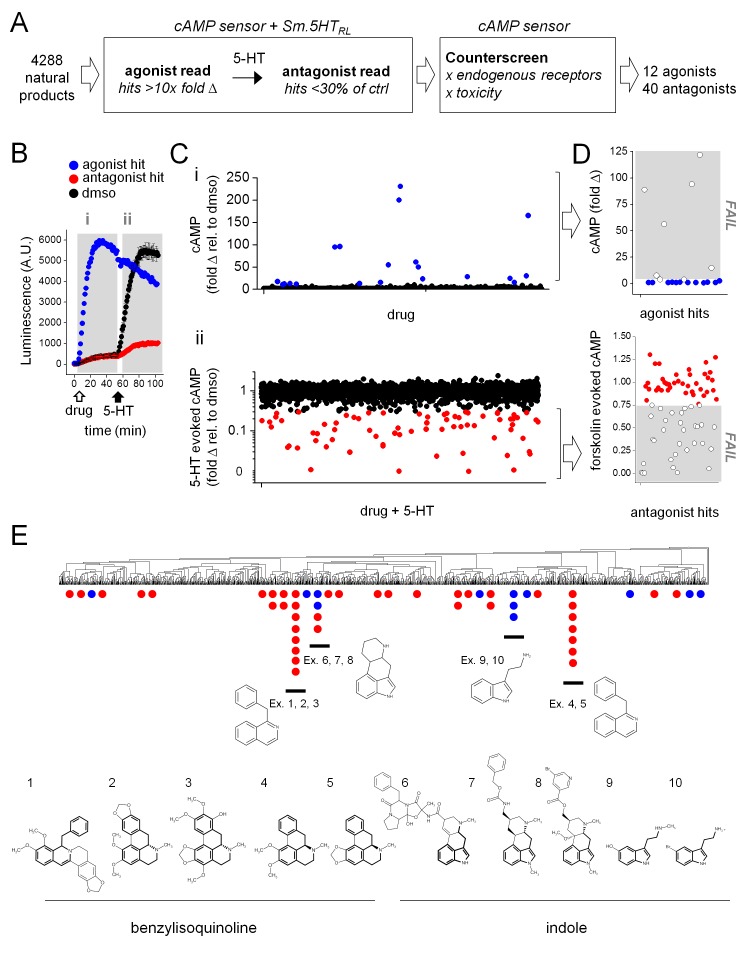
Figure 2. High-throughput screen of natural product libraries against Sm.5HTRL.
(A) Assay workflow for drug screen. Compounds were screened against HEK293 cells stably expressing a cAMP sensor and Sm.5HTRL, followed by counter-screening hits against a cell line lacking Sm.5HTRL. (B) Kinetic readout of luminescence from cAMP biosensor following addition of (i) test compound (10 µM, open arrow; agonist hits increase luminescence), followed by (ii) the addition of 5-HT (1 µM, solid arrow; antagonist hits decrease luminescence relative to controls). (C) Scatter plot of compounds assaying for (i) agonists and (ii) antagonists. Putative hits surpassing threshold are shown in color (blue, agonists; red, antagonists). (D) Counter-screen of putative hit compounds from (C) against cell lines lacking 5-HT receptor to exclude compounds with off-target increases in cAMP (top) or compounds that reduce forskolin (25 µM) evoked cAMP signals (bottom). (E) Hits clustered into compound classes by structure. Groups contain common ring systems such as benzylisoquinoline (ex. 1. ST059293, 2. Nantenine, 3. 785163, 4. Nuciferine, 5. Remerine) or indole (6. Ergotamine, 7. Metergoline, 8. Nicergoline, 9. N-methylserotonin, 10. 5-bromotryptamine) structures. Blue = agonists, red = antagonists.