Fig. 2.
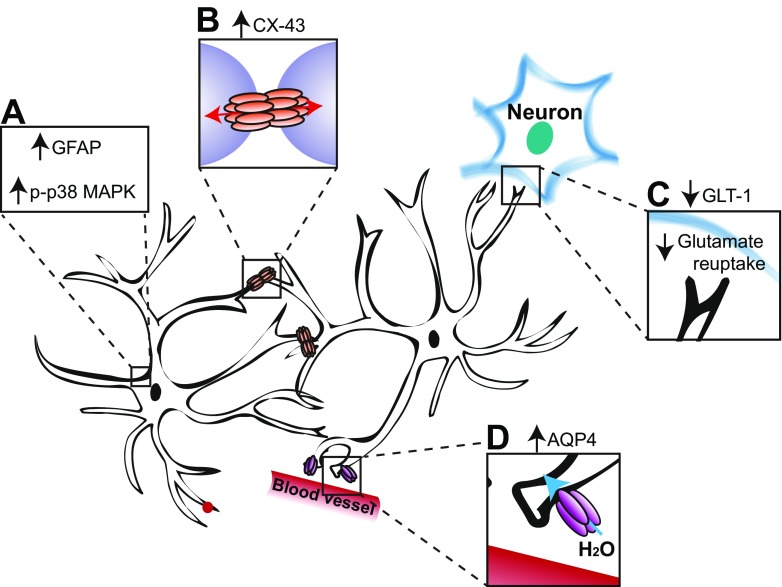
Reactive astrogliosis contributes to SCI pain. (A) Astrocytes at and below the lesion level upregulate expression of GFAP and p-p38 MAPK, indicators of reactive gliosis [ 37, 41, 62, 101, 103, 104]. (B) Concomitant increases in the astrocyte-specific gap junction protein, connexin-43 (CX-43), could increase connectivity between adjacent astrocytes [37]. (C) Reduced expression of glutamate transporter, GLT-1 [105], would be expected to lead to decreased reuptake of glutamate. (D) Increased upregulation of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is observed for up to 9 months, but only in rats that develop below-level hypersensitivity [101]. AQP4 is a water transport channel predominantly found in astrocytic foot processes that regulate the blood–brain barrier and may mediate pain behavior by causing astrocyte swelling that results in glutamate release [106]