Abstract
The increasing number of Killer Immunoglobulin-like Receptor (KIR) sequences available for non-human primate species and cattle has prompted development of a centralized database, guidelines for a standardized nomenclature, and minimum requirements for database submission. The guidelines and nomenclature are based on those used for human KIR and incorporate modifications made for inclusion of non-human species in the companion IPD-NHKIR database. Included in this first release are the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta), chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes), orangutan (Pongo abelii and Pongo pygmaeus), and cattle (Bos taurus).
Keywords: KIR, Nomenclature, Variant, Allele, Gene, Database, Sequence
Introduction
The KIR locus has been studied in a number of non-human species primates and is characterized by high levels of allelic polymorphism, haplotypic polymorphism in the number of genes, and extensive duplication and recombination (Hammond et al. 2016; Parham 2004). These factors have made it difficult to assign orthologues and have led to a number of different nomenclature systems being used to name genes and alleles. This report describes a common framework and guidelines for KIR nomenclature in non-human species. These have been developed by taking advantage of lessons learned in the development of a nomenclature system for the human KIR (Marsh et al. 2003).
General naming guidelines
To provide consistency with the IPD-MHC Database (Maccari et al. 2017), the non-human KIR nomenclature adopts the same four-character prefix used for species designation in the naming of MHC alleles (de Groot et al. 2012; Ellis et al. 2006; Klein et al. 1990). Also, genes and alleles will be named based on the conventions that have been adopted for the human KIR system (Marsh et al. 2003) that are based on the structures of the molecules they encode. The first digit following the KIR acronym corresponds to the number of Ig-like domains in the polypeptide and the “D” denotes “Domain.” The D is followed by either an “L” indicating a “Long” cytoplasmic tail, an “S” indicating a “Short” cytoplasmic tail or a “P” for pseudogenes. In addition, the inclusion of a “W” indicates “Workshop” following the “L,” “S,” or “P” to indicate any sequence that by phylogenetic analysis is sufficiently divergent to be considered a “new” gene, but lack either genomic sequencing or family studies to demonstrate that it does define a new gene and not a divergent lineage a known gene. Tables 1, 2, and 3 list the current gene designations and their previous names. Symbols for genes are italicized (e.g., Mamu-KIR3DL01), whereas symbols for proteins are not italicized (e.g., Mamu-KIR3DL01). Alleles follow the same conventions as gene names.
Table 1.
Gene designations and their previous names
| Species | KIR gene designation(s) | Previous KIR gene designation(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Rhesus macaque (Mamu) | Mamu-KIR1D | KIR1D, Mamu-KIR1D |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | 2DL501NK, 2DL503NK, KIR2DL4, KIR2DL4.1, MmKIR2DL4 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | 2DL426NK, 3DL34, KIR3DL, KIR3DL-like_1, KIR3DL1, KIR3DL1-like1, KIR3DL12, KIR3DL13, KIR3DL14, KIR3DL15, KIR3DL19, KIR3DL1_variant_2, KIR3DL2, KIR3DL2-old, KIR3DL3, KIR3DL4, KIR3DL5 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | KIR3DL-like_3, KIR3DL2, KIR3DL21, KIR3DL21-like1 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL04 | KIR3DL11 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | 3DL7b-3DL40, KIR3DL, KIR3DL-3, KIR3DL16, KIR3DL7, KIR3DL7-like2, KIR3DL07 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL06 | KIR3DL6 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | 2DL420, KIR3DL, KIR3DL18, KIR3DL7, KIR3DL7-like1, KIR3DL7-like3, KIR3DL03 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | KIR3DL, KIR3DL-like_2, KIR3DL17, KIR3DL8, KIRDL8, Mamu-KIR3DL04, Mamu-KIR3DL4 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL10 | 3DL10-2DL501, 3DL3NK, KIR3DL, KIR3DL10, KIR3DL9, Mamu-KIR3DL05 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL11 | KIR3DL, KIR3DL-1, KIR3DL-6, KIR3DL-7, KIR3DL11 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | KIR3DL20, KIR3DL20_variant_2, KIR3DL06, KIR2DL5 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DLW03 | KIR3DL-4, KIR3DL-5, KIR3DL-like1-BNB, KIR3DL21 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DLX1 | KIR3DL0 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DS01 | KIR3DH-7, KIR3DH1, KIR3DH5, Mamu-KIR3DS01-JHB-HEFGH, | |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | 3DH2, 3DH42, KIR3DH-like_5, KIR3DH-like_6, KIR3DH10, KIR3DH12, KIR3DH13, KIR3DH14, KIR3DH15, KIR3DH16, KIR3DH2 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DS03 | KIR3DH3, KIR3DH8, KIR3DH9 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DS04 | KIR3DH-1, KIR3DH4, KIR3DH6 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DS05 | KIR3DH1, KIR3DM-1, KIR3DM1, KIR3DM6, KIR_Partial_Sequence_1 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DS06 | KIR3DH-4, KIR3DH-like8, KIR3DH-like_7, KIR3DH18, | |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW07 | KIR3DH-5, KIR3DH7, Mamu-KIR3DS07-JHB-HO | |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | KIR3DH-2, KIR3DH-3, KIR3DH-4, KIR3DH-5, KIR3DH-like_1, KIR3DH-like_2, KIR3DH-like_3, KIR3DH-like_4, KIR3DH21, KIR3DSW08 | |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW09 | KIR3DH-8, KIR3DH20, KIR3DH5, KIR3DH5-like1, mmKIR3DH-1 |
Table 2.
Gene designations and their previous names
| Species | KIR gene designation(s) | Previous KIR gene designation(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Chimpanzee (Patr) | Patr-KIR2DL4 | |
| Patr-KIR2DL5 | ||
| Patr-KIR2DL6 | Pt-NewII | |
| Patr-KIR2DL7 | ||
| Patr-KIR2DL8 | Pt-NewIII | |
| Patr-KIR2DL9 | ||
| Patr-KIR3DL1 | Pt-KIR3DL1/2, Pt-KIR3DL3, Pt-KIR3DL1, Pt-KIR3DL2 | |
| Patr-KIR3DL3 | Patr-KIRC1, Pt-NewI | |
| Patr-KIR3DL4 | ||
| Patr-KIR3DL5 | ||
| Patr-KIR3DS6 | Pt-KIR3DL6 |
Table 3.
Gene designations and their previous names
| Species | KIR gene designation(s) | Previous KIR gene designation(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Orangutan (Poab) | Poab-KIR2DL10 | Popy-KIR2DL10, 2DLA |
| Poab-KIR2DL11 | Popy-KIR2DL11, 2DLB | |
| Poab-KIR2DL12 | Popy-KIR2DL11, 2DLC | |
| Poab-KIR2DL5 | Popy-KIR2DL5. 2DL5 | |
| Poab-KIR2DS10 | 2DSD/2DSA | |
| Poab-KIR2DS13 | Popy-KIR2DS13, 2DSC1/2DSB | |
| Poab-KIR2DS14 | Popy-KIR2DS14, 2DSB/2DSD2, 2DSA/2DSD1 | |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Popy-KIR3DL1, 3DLH, 3DLC, 3DLD2, 3DLD1, 3DLA, 3DLI, 3DLB | |
| Poab-KIR3DL3 | Popy-KIR3DL3, 3DL3 | |
| Poab-KIR3DS1 | Popy-KIR3DS1, 3DS1 | |
| Poab-KIRDP | Popy-KIRDP, DP | |
| Orangutan (Popy) | Popy-KIR2DL11 | Popy-KIR2DLB |
| Popy-KIR2DL12 | Popy-KIR2DLC | |
| Popy-KIR2DL5 | ||
| Popy-KIR2DS10 | Popy-KIR2DSD/2DSA | |
| Popy-KIR2DS13 | Popy-KIR2DSC2/2DSB | |
| Popy-KIR2DS14 | Popy-KIR2DSB/2DSD2, 2DSA/2DSD1 | |
| Popy-KIR2DS15 | ||
| Popy-KIR3DL1 | Popy-KIR3DL1, 3DLF, 3DLE2, 3DLE1 | |
| Popy-KIR3DL3 | Popy-KIR3DL3, 3DL3 | |
| Popy-KIR3DS1 | Popy-KIR3DS1, 3DS1 | |
| Popy-KIRDP | Popy-KIRDP, DP |
Reflecting species-specific differences, there have been further additions/modifications to the general nomenclature for rhesus macaque and cattle. As with the human KIR nomenclature, alleles in each series have been named in order of their deposition into a generalist sequence databank, GenBank/EMBL-ENA/DDBJ (Benson et al. 2017; Chojnacki et al. 2017; Mashima et al. 2017). Where the identity is known of the animal providing the sequenced DNA, that information is included in the database, as well as information regarding the origin of the animal. Tables 4, 5, 6, and 7 provide a complete list of genes and alleles currently in the nomenclature, as well as the original name(s), accession number, and reference to the original report of the sequence.
Table 4.
Allele designations and their previous names
| Gene | Allele designation | Previous designations | Accession number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mamu-KIR1D | Mamu-KIR1D*001 | KIR1D | AF334634 | (Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR1D | Mamu-KIR1D*002 | KIR1D,Mamu-KIR1D*00202-JHB-HA | AY728181, GU112257, GU112266, GU112332 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*001:01 | KIR2DL4, KIR2DL4.1, MmKIR2DL4*0010101-JHB | EU702486, AF361088, AF334644, FJ824091, GU112331, GU112318, GU112263, GU112303, GU112287 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a; Blokhuis et al. 2009b; Blokhuis et al. 2010; Grendell et al. 2001; Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*001:02 | 2DL501NK | GU299490 | (Colantonio et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*002 | MmKIR2DL4*0020101-JHB | FJ824092, GU112279 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*003 | KIR2DL4, MmKIR2DL4*0040101-JHB | AY505486, FJ824093, GU112322, GU112284 | (Andersen et al. 2004; Blokhuis et al. 2009b; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*004 | KIR2DL4 | AY728182 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*005 | MmKIR2DL4*0050101-JHB | FJ824094 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*006:01 | MmKIR2DL4*0060101-JHB | FJ824095 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*006:02 | 2DL503NK | GU014298 | (Colantonio et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*007 | MmKIR2DL4*0070101-JHB | FJ824096 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*008:01 | MmKIR2DL4*0080101-JHB | FJ824097 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*008:02 | MmKIR2DL4*0080201-JHB | FJ824098, GU112326 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*010 | MmKIR2DL4*0100101-JHB | FJ824100 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*011 | MmKIR2DL4*0110101-JHB | FJ824101 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*012 | MmKIR2DL4*0120101-JHB | FJ824102 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*013 | MmKIR2DL4*0130101-JHB | FJ824103 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*014:01 | MmKIR2DL4*0140101-JHB | FJ824104, GU112316 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*014:02 | MmKIR2DL4*0140201-JHB | FJ824105 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*015:01 | MmKIR2DL4*0150101-JHB | FJ824106, GU112313 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*015:02 | MmKIR2DL4*0150201-JHB | FJ824107, GU112280 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*016 | MmKIR2DL4*0160101-JHB | FJ824108 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*017 | MmKIR2DL4*0170101-JHB | FJ824109 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*018 | MmKIR2DL4*0180101-JHB | FJ824110 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*019 | MmKIR2DL4*0190101-JHB | FJ824111 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b) |
| Mamu-KIR2DL04 | Mamu-KIR2DL04*020 | MmKIR2DL4*0200101-JHB | FJ824112, GU112274 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009b; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*001 | KIR3DL1, 3DL34 | AF334616, GU299488 | (Colantonio et al. 2011; Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*002 | KIR3DL2-old, 2DL426NK | AF334617, GU299488 | (Hershberger et al. 2001), (Colantonio et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*003 | KIR3DL3 | AF361083, GU112305 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010; Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*004 | KIR3DL4 | AF334619 | (Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*005 | KIR3DL5 | AF334620 | (Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*006 | KIR3DL12 | AF361082 | (Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*007N | KIR3DL13 | AF408151 | (Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*008N | KIR3DL14 | AF408152 | (Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*009N | KIR3DL15 | AF408153 | (Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*010 | KIR3DL19 | AF408150 | (Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*011 | KIR3DL1_variant_2 | AY728187 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*012 | KIR3DL1*002-BNB, KIR3DL-like_1 | EU419033, AY505476, GU112286 | (Andersen et al. 2004; Blokhuis et al. 2010; Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*013 | KIR3DL1*003-BNB | EU419034 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*014 | KIR3DL1*005-BNB | EU419035 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*015 | KIR3DL1*006-BNB | EU419036 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*016 | KIR3DL1*007-BNB | EU419037, GU112258 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010; Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*017 | KIR3DL12*001-BNB | EU419044 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*018 | KIR3DL2*001-BNB | EU419046 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*019:01 | KIR3DL1*001-BNB | EU419032, GU112300 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010; Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*019:02 | None | GU112283 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*020 | KIR3DL1-like1 | EU688987 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*021 | KIR3DL | FJ562108 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*022 | None | GU112267 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*023 | None | GU112292 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*024 | None | GU112321 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*025 | None | GU112324 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*026 | KIR3DL allele 2 | FJ562109 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL01 | Mamu-KIR3DL01*027 | KIR3DL allele 3 | FJ562110 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | Mamu-KIR3DL02*001 | KIR3DL2 | AY728188 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | Mamu-KIR3DL02*002 | KIR3DL-like_3 | AY505478 | (Andersen et al. 2004) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | Mamu-KIR3DL02*003 | KIR3DL21*001-BNB | EU419050 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | Mamu-KIR3DL02*004:01 | KIR3DL21*003-BNB | EU419052 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | Mamu-KIR3DL02*004:02 | KIR3DL21*005-BNB | EU419053 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | Mamu-KIR3DL02*005 | KIR3DL21*006-BNB | EU419054 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | Mamu-KIR3DL02*006 | KIR3DL21-like1 | EU688989 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | Mamu-KIR3DL02*007 | None | GU112277 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL02 | Mamu-KIR3DL02*008 | None | GU112281 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DLW03 | Mamu-KIR3DLW03*001 | KIR3DL21*002-BNB | EU419051 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DLW03 | Mamu-KIR3DLW03*002 | KIR3DL21*007-BNB | EU419055 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DLW03 | Mamu-KIR3DLW03*003 | KIR3DL-like1-BNB | EU419031 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DLW03 | Mamu-KIR3DLW03*004 | KIR3DL-4 | FN424253 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DLW03 | Mamu-KIR3DLW03*005 | KIR3DL-5 | FN424256 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL04 | Mamu-KIR3DL04*001:01 | KIR3DL11*002-BNB | EU419040 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL04 | Mamu-KIR3DL04*001:02 | None | GU112311 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL04 | Mamu-KIR3DL04*001:03 | None | GU112319 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL04 | Mamu-KIR3DL04*002 | KIR3DL11*003-BNB | EU419042 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*001 | KIR3DL16*001-BNB | EU419045 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*002 | KIR3DL7*004-BNB | EU419061 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*003 | KIR3DL7*005-BNB | EU419062 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*004 | KIR3DL7*009-BNB | EU419066 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*005 | KIR3DL7*013-BNB | EU419069 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*006:01 | KIR3DL7-like2 | EU688991 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*006:02 | None | GU112293 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*007 | KIR3DL-3 | FN424252 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*008 | 3DL7b-3DL40 | GU112291, GU014295 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) (Colantonio et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*009 | None | GU112310 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*010 | KIR3DL allele 13 | FJ562120 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL05 | Mamu-KIR3DL05*011 | KIR3DL allele 14 | FJ562121 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL06 | Mamu-KIR3DL06*001 | KIR3DL6 | AF334621 | (Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL06 | Mamu-KIR3DL06*002 | KIR3DL6*001-BNB | EU419056 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*001 | KIR3DL7 | AF334622 | (Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*002 | KIR3DL18 | AF361086 | (Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*003 | KIR3DL7*001-BNB | EU419057 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*004 | KIR3DL7*003-BNB | EU419060 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*005 | KIR3DL7*006-BNB | EU419063 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*006 | KIR3DL7*007-BNB | EU419064 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*007 | KIR3DL7*008-BNB | EU419065 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*008 | KIR3DL7*012-BNB | EU419068 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*009:01 | KIR3DL7-like1, 2DL420 | EU688990, GU299489 | (Colantonio et al. 2011; Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*009:02 | None | GU112282 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*010 | KIR3DL7-like3 | EU688992 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*011 | KIR3DL allele 10 | FJ562117 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL07 | Mamu-KIR3DL07*012 | KIR3DL allele 11 | FJ562118 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*001:01 | KIR3DL8 | AY728189 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*001:02 | KIR3DL8*002-BNB | EU419071 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*002 | KIR3DL17 | AF361084, GU112306 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010; Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*003 | KIR3DL17 | AF361085 | (Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*004 | KIR3DL-like_2 | AY505477 | (Andersen et al. 2004) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*005 | KIRDL8 | AY728189 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*006 | KIR3DL8*001-BNB | EU419070 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*007 | None | GU112268 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*008 | None | GU112285 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*009 | None | GU112290 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*010 | None | GU112330 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL08 | Mamu-KIR3DL08*011 | KIR3DL allele 8 | FJ562115 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL10 | Mamu-KIR3DL10*001 | KIR3DL10 | AY728183 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL10 | Mamu-KIR3DL10*002:01 | KIR3DL9, KIR3DL allele 5 | AF334624, GU112259, FJ562112 | (Hershberger et al. 2001)(Blokhuis et al. 2010; Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL10 | Mamu-KIR3DL10*002:02 | 3DL3NK | GU299486 | (Colantonio et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL10 | Mamu-KIR3DL10*003 | KIR3DL10*001-BNB | EU419038 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL10 | Mamu-KIR3DL10*004 | KIR3DL10*002-BNB | EU419039 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL10 | Mamu-KIR3DL10*005:01 | 3DL10-2DL501 | GU014294 | (Colantonio et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL10 | Mamu-KIR3DL10*005:02 | None | GU112295 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL10 | Mamu-KIR3DL10*006 | KIR3DL allele 6 | FJ562113 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL11 | Mamu-KIR3DL11*001 | KIR3DL11 | AF334626, GU112271 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010; Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL11 | Mamu-KIR3DL11*002 | KIR3DL-1 | FN424250 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL11 | Mamu-KIR3DL11*003 | KIR3DL-6 | FN424259 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL11 | Mamu-KIR3DL11*004 | KIR3DL-7 | FN424261 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL11 | Mamu-KIR3DL11*005 | None | GU112276 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL11 | Mamu-KIR3DL11*006 | None | GU112296 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL11 | Mamu-KIR3DL11*007 | KIR3DL allele 9 | FJ562116 | (Bostik et al. 2009) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*001 | KIR3DL20*001-BNB | EU419047 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*002 | KIR3DL20 | AY728184, GU112327 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010; Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*003 | KIR3DL20_variant_2 | AY728186 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*004 | KIR3DL20*003-BNB | EU419048 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*005 | KIR3DL20*004-BNB | EU419049 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*006 | None | GU112255 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*007 | None | GU112256 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*008 | None | GU112264 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*009 | None | GU112270 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*010 | None | GU112275 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*011 | None | GU112289 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*012 | None | GU112299 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*013 | None | GU112304, GU112317 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*014 | None | GU112308 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DL20 | Mamu-KIR3DL20*015 | None | GU134802 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS01 | Mamu-KIR3DS01*001:01 | KIR3DH5 | AF361087 | (Grendell et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS01 | Mamu-KIR3DS01*001:02 | None | GU112307 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS01 | Mamu-KIR3DS01*002 | KIR3DH1 | AY728190 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS01 | Mamu-KIR3DS01*003 | KIR3DH-7 | GU564161 | (Chaichompoo et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*001 | KIR3DH2 | AF334649 | (Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*002 | KIR3DH-like_5 | AY505483 | (Andersen et al. 2004) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*003 | KIR3DH-like_6 | AY505484 | (Andersen et al. 2004) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*004:01 | KIR3DH2*001-BNB, KIR3DH14 | EU419026, EU702460 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a; Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*004:02 | KIR3DH13, 3DH42 | EU702459, GU014296 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a) (Colantonio et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*004:03 | KIR3DH12 | EU702458 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*005 | KIR3DH2*002-BNB | EU419027 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*006 | KIR3DH16 | EU702462 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*007 | KIR3DH15 | EU702461 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*008 | KIR3DH10 | EU702456, GU112278 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*009 | None | GU112261, GU112315 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*010 | None | GU112297 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*011 | None | GU112323 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*012 | 3DH2*NEW1 | JN613291 | (Hellmann et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS02 | Mamu-KIR3DS02*013 | 3DH2*NEW1 | JN613299 | (Hellmann et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS03 | Mamu-KIR3DS03*001:01 | KIR3DH3 | AF334650, GU112312 | (Hershberger et al. 2001) (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS03 | Mamu-KIR3DS03*001:02 | None | GU112294 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS03 | Mamu-KIR3DS03*002 | KIR3DH9 | EU702455, GU112269 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS03 | Mamu-KIR3DS03*003 | KIR3DH8 | EU702454 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS04 | Mamu-KIR3DS04*001 | KIR3DH4 | AF334651 | (Hershberger et al. 2001) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS04 | Mamu-KIR3DS04*002 | KIR3DH4*001-BNB | EU419028 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS04 | Mamu-KIR3DS04*003 | KIR3DH4*002-BNB, KIR3DH4 | EU419029, JN613296 | (Hellmann et al. 2011; Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS04 | Mamu-KIR3DS04*004 | KIR3DH6 | EU702452 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS04 | Mamu-KIR3DS04*005 | KIR3DH4 | JN613300 | (Hellmann et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS04 | Mamu-KIR3DS04*006 | KIR3DH-1 | GU564157 | (Chaichompoo et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS05 | Mamu-KIR3DS05*001 | KIR3DH1*001-BNB | EU419024, EU419025, EU702468, AY505487, GU112262 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS05 | Mamu-KIR3DS05*002:01 | KIR3DH1*002-BNB, KIR3DM1, KIR_Partial_Sequence_1 | EU419025, EU702468, AY505487, GU112262 | (Andersen et al. 2004; Blokhuis et al. 2009a; Blokhuis et al. 2010; Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS05 | Mamu-KIR3DS05*002:02 | KIR3DM6 | EU702473 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS05 | Mamu-KIR3DS05*003 | KIR3DM-1 | FN424260 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS06 | Mamu-KIR3DS06*001 | KIR3DH-like_7 | AY505485 | (Andersen et al. 2004) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS06 | Mamu-KIR3DS06*002:01 | KIR3DH-like8 | EU688985 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS06 | Mamu-KIR3DS06*002:02 | None | GU112298 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS06 | Mamu-KIR3DS06*003 | KIR3DH18 | EU702464 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS06 | Mamu-KIR3DS06*004 | KIR3DH-4 | FN424257 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS06 | Mamu-KIR3DS06*005 | None | GU112260 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DS06 | Mamu-KIR3DS06*006 | None | GU112314 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW07 | Mamu-KIR3DSW07*001 | KIR3DH7 | EU702453, GU112272 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a; Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW07 | Mamu-KIR3DSW07*002 | KIR3DH-5 | FN424258 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*001 | KIR3DH-like_1 | AY505479 | (Andersen et al. 2004) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*002 | KIR3DH-like_2 | AY505480 | (Andersen et al. 2004) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*003 | KIR3DH-like_3 | AY505481 | (Andersen et al. 2004) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*004 | KIR3DH-like_4 | AY505482 | (Andersen et al. 2004) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*005 | KIR3DH21 | EU702467 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*006 | KIR3DH-2 | FN424254 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*007 | KIR3DH-3 | FN424255 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*008 | None | GU112325 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*009 | None | GU112328 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*010 | KIR3DSW08 | JN613297 | (Hellmann et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*011 | KIR3DH-4 | GU564158 | (Chaichompoo et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW08 | Mamu-KIR3DSW08*012 | KIR3DH-5 | GU564159 | (Chaichompoo et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW09 | Mamu-KIR3DSW09*001 | KIR3DH5*001-BNB | EU419030 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW09 | Mamu-KIR3DSW09*002 | KIR3DH5-like1 | EU688986 | (Moreland et al. 2011) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW09 | Mamu-KIR3DSW09*003 | None | GU112301 | (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW09 | Mamu-KIR3DSW09*004 | KIR3DH20 | EU702466, GU112273 | (Blokhuis et al. 2009a), (Blokhuis et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW09 | Mamu-KIR3DSW09*005 | mmKIR3DH-1 | FN424249 | (Kruse et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DSW09 | Mamu-KIR3DSW09*006 | KIR3DH-8 | GU564162 | (Chaichompoo et al. 2010) |
| Mamu-KIR3DLX1 | Mamu-KIR3DLX1*001 | KIR3DL0 | DQ157756 | (Sambrook et al. 2006) |
Table 5.
Allele designations and their previous names
| Gene | Allele designation | Previous designations | Accession number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patr-KIR2DL4 | Patr-KIR2DL4*001 | None | HM068617 | (Abi-Rached et al. 2010) |
| Patr-KIR2DL4 | Patr-KIR2DL4*002 | None | AC155174, AF258804 | (Khakoo et al. 2000) |
| Patr-KIR2DL4 | Patr-KIR2DL4*003 | None | BX842589 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Patr-KIR2DL5 | Patr-KIR2DL5*001 | None | HM068617 | (Abi-Rached et al. 2010) |
| Patr-KIR2DL5 | Patr-KIR2DL5*002 | None | AF274005 | (Rajalingam et al. 2001) |
| Patr-KIR2DL5 | Patr-KIR2DL5*003 | None | AC155174 | |
| Patr-KIR2DL5 | Patr-KIR2DL5*004 | None | BX842589 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Patr-KIR2DL5 | Patr-KIR2DL5*005 | None | AF258805 | (Khakoo et al. 2000) |
| Patr-KIR2DL6 | Patr-KIR2DL6*001 | None | BX842589, AM292662 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Patr-KIR2DL6 | Patr-KIR2DL6*002 | None | AF258806 | |
| Patr-KIR2DL6 | Patr-KIR2DL6*003 | None | AM292661 | |
| Patr-KIR2DL7 | Patr-KIR2DL7*001 | None | HM068617 | (Abi-Rached et al. 2010) |
| Patr-KIR2DL8 | Patr-KIR2DL8*001 | None | HM068617 | (Abi-Rached et al. 2010) |
| Patr-KIR2DL8 | Patr-KIR2DL8*002 | None | AC155174, AM279149 | Biassoni, unpublished |
| Patr-KIR2DL8 | Patr-KIR2DL8*003 | None | BX842589 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Patr-KIR2DL9 | Patr-KIR2DL9*001 | None | AC155174 | |
| Patr-KIR2DL9 | Patr-KIR2DL9*002 | None | AM292657 | Biassoni, unpublished |
| Patr-KIR2DL9 | Patr-KIR2DL9*003 | None | AM400233 | Biassoni, unpublished |
| Patr-KIR2DS4 | Patr-KIR2DS4*001 | None | HM068617 | |
| Patr-KIR2DS4 | Patr-KIR2DS4*002 | None | AF258807 | |
| Patr-KIR3DL1 | Patr-KIR3DL1*001:01 | None | AC155174 | |
| Patr-KIR3DL1 | Patr-KIR3DL1*001:02 | None | AF266729 | (Rajalingam et al. 2001) |
| Patr-KIR3DL1 | Patr-KIR3DL1*002 | None | BX842589, AF258798 | (Sambrook et al. 2005) |
| Patr-KIR3DL1 | Patr-KIR3DL1*003 | None | AF266730 | (Rajalingam et al. 2001) |
| Patr-KIR3DL1 | Patr-KIR3DL1*004 | None | AF258799 | |
| Patr-KIR3DL1 | Patr-KIR3DL1*005 | None | HM068617 | |
| Patr-KIR3DL3 | Patr-KIR3DL3*001 | None | HM068617 | |
| Patr-KIR3DL3 | Patr-KIR3DL3*002 | None | BX842589 | |
| Patr-KIR3DL3 | Patr-KIR3DL3*003 | None | AC155174 | |
| Patr-KIR3DL3 | Patr-KIR3DL3*004 | None | AY327500 | |
| Patr-KIR3DL4 | Patr-KIR3DL4*001:01 | None | AM400232 | Biassoni, unpublished |
| Patr-KIR3DL4 | Patr-KIR3DL4*001:02 | None | AF258800 | (Khakoo et al. 2000) |
| Patr-KIR3DL4 | Patr-KIR3DL4*002 | None | HM068617 | (Abi-Rached et al. 2010) |
| Patr-KIR3DL5 | Patr-KIR3DL5*001 | None | AM400235 | Biassoni, unpublished |
| Patr-KIR3DL5 | Patr-KIR3DL5*003:01 | None | AF258801 | (Khakoo et al. 2000) |
| Patr-KIR3DL5 | Patr-KIR3DL5*004 | None | AC155174, AM292659 | Biassoni, unpublished |
| Patr-KIR3DS2 | Patr-KIR3DS2*001 | None | AC155174 | |
| Patr-KIR3DS2 | Patr-KIR3DS2*002 | None | AF258803 | |
| Patr-KIR3DS6 | Patr-KIR3DS6*001 | None | AM396937 | Biassoni, unpublished |
Table 6.
Allele designations and their previous names
| Gene | Allele designation | Previous designations | Accession number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poab-KIR2DL10 | Poab-KIR2DL10*001 | 2DLA | AF470358 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR2DL11 | Poab-KIR2DL11*001 | 2DLB | EF014479 | (Guethlein et al. 2007b) |
| Poab-KIR2DL12 | Poab-KIR2DL12*001 | 2DLC | AC200148 | |
| Poab-KIR2DL5 | Poab-KIR2DL5*001 | 2DL5 | AC200148 | |
| Poab-KIR2DS10 | Poab-KIR2DS10*001 | None | AF470364 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR2DS13 | Poab-KIR2DS13*001 | 2DSC1/2DSB | AF470362 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR2DS14 | Poab-KIR2DS14*001 | 2DSB/2DSD2 | AF470361 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR2DS14 | Poab-KIR2DS14*002 | 2DSA/2DSD1 | AF470360 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Poab-KIR3DL1*001:01 | 3DLH | AF470373 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Poab-KIR3DL1*001:02 | None | AC200148 | |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Poab-KIR3DL1*002 | 3DLC | AF470367 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Poab-KIR3DL1*003 | None | AF470372 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Poab-KIR3DL1*004:01 | 3DLD2 | AF470369 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Poab-KIR3DL1*004:02 | 3DLD1 | EF014479 | (Guethlein et al. 2007b) |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Poab-KIR3DL1*005 | 3DLA | AF470365 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Poab-KIR3DL1*006 | 3DLI | AF470374 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR3DL1 | Poab-KIR3DL1*007 | 3DLB | AF470366 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIR3DL3 | Poab-KIR3DL3*001 | 3DL3 | AC200148 | |
| Poab-KIR3DS1 | Poab-KIR3DS1*001 | 3DS1 | AF470375 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Poab-KIRDP | Poab-KIRDP*001 | DP | AC200148 | |
| Popy-KIR2DS10 | Popy-KIR2DS10*001 | 2DSD/2DSA | AF470364 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Popy-KIR2DS13 | Popy-KIR2DS13*001 | 2DSC2/2DSB | AF470363 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Popy-KIR3DL1 | Popy-KIR3DL1*001 | 3DLF | AF470372 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Popy-KIR3DL1 | Popy-KIR3DL1*002:01 | 3DLE2 | AF470371 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
| Popy-KIR3DL1 | Popy-KIR3DL1*002:02 | 3DLE1 | AF470370 | (Guethlein et al. 2002) |
Table 7.
Allele designations and their previous names
| Gene | Allele designation | Previous designations | Accession number | Breed | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bota-KIR2DL1 | Bota-KIR2DL1*001 | KIR2DL1 | AY075102,AF490399 | UnknownHolstein | (McQueen et al. 2002; Storset et al. 2003; Zimin et al. 2009) |
| Bota-KIR2DL1 | Bota-KIR2DL1*002 | None | JX848327 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR2DS1 | Bota-KIR2DS1*001N | KIR2DS1 | JX848328 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR2DS2 | Bota-KIR2DS2*001N | None | JX848329 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR2DS3 | Bota-KIR2DS3*001N | None | JX848330 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR2DXS1 | Bota-KIR2DXS1*001 | None | AF490400 | Holstein | (Storset et al. 2003) |
| Bota-KIR2DXP1 | Bota-KIR2DXP1*001 | None | JX848331 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR2DXP2 | Bota-KIR2DXP2*001 | None | JX848332 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL1 | Bota-KIR3DXL1*001 | KIR3DL1 | AF490402 | Holstein | (Storset et al. 2003; Zimin et al. 2009) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL1 | Bota-KIR3DXL1*002 | None | JX848333 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL2 | Bota-KIR3DXL2*001 | None | JX848334 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL3 | Bota-KIR3DXL3*001 | None | JX848335 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL4 | Bota-KIR3DXL4*001 | KIR3DL2–001 | EF197118 | Holstein-Freisian | (Dobromylskyj and Ellis 2007; Zimin et al. 2009) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL4 | Bota-KIR3DXL4*002 | None | JX848336 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL5 | Bota-KIR3DXL5*001 | None | JX848337 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL6 | Bota-KIR3DXL6*001N | KIR3DL1P | AY075103JX848338 | UnknownHolstein-Freisian | (McQueen et al. 2002) (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL6 | Bota-KIR3DXL6*002 | KIR3DL3 | EF197119 | Holstein-Freisian | (Dobromylskyj and Ellis 2007; Zimin et al. 2009) |
| Bota-KIR3DXL7 | Bota-KIR3DXL7*001 | None | JX848339 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXS1 | Bota-KIR3DXS1*001 | KIR3DS1 | AF490401 | Holstein | (Storset et al. 2003; Zimin et al. 2009) |
| Bota-KIR3DXS1 | Bota-KIR3DXS1*002 | KIR3DS1–002 | EF197120 | Holstein-Freisian | (Dobromylskyj and Ellis 2007) |
| Bota-KIR3DXS1 | Bota-KIR3DXS1*003 | None | JX848340 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXS2 | Bota-KIR3DXS2*001N | None | JX848341 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
| Bota-KIR3DXS3 | Bota-KIR3DXS3*001N | None | JX848342 | Holstein-Freisian | (Sanderson et al. 2014) |
Each KIR allele name includes a unique number corresponding to up to three sets of digits separated by colons. All alleles are given a three-digit name, which corresponds to the first set of digits; longer names are assigned only when necessary.
The digits placed before the first colon describe the alleles that differ at non-synonymous substitutions (also called coding substitutions). Alleles that differ only by synonymous nucleotide substitutions (also called silent or non-coding substitutions) but are within the coding sequence are distinguished by their second sets of digits. Alleles that only differ by sequence polymorphisms in the introns, or in the 5′ or 3′ untranslated regions that flank the exons and introns, are distinguished by their third sets of digits.
In addition to the unique allele number, optional suffixes can be added to an allele name to indicate the expression status of the gene and/or its encoded protein. Alleles known not to be expressed—so called “Null” alleles—have been given the suffix “N.” Alleles that have been shown to be alternatively expressed may have the suffix “L,” “S,” “C,” “A,” or “Q.”
The suffix “L” is used to indicate an allele that has been shown to have “Low” cell surface expression when compared to normal levels. The “S” suffix is used to denote an allele specifying a protein which is expressed as a soluble, “Secreted” molecule and is not present on the cell surface. The “C” suffix is assigned to alleles producing proteins that are present in the “Cytoplasm” and not on the cell surface. An “A” suffix indicates an “Aberrant” expression, where there is doubt as to whether a protein is actually expressed. A “Q” suffix is used when the expression of an allele is “Questionable,” given that the mutation seen in the allele has been shown to affect normal expression levels in other alleles and other KIR genes.
As of May 2018, no alleles have been named with the “C,” “A,” “Q,” or “S” suffixes.
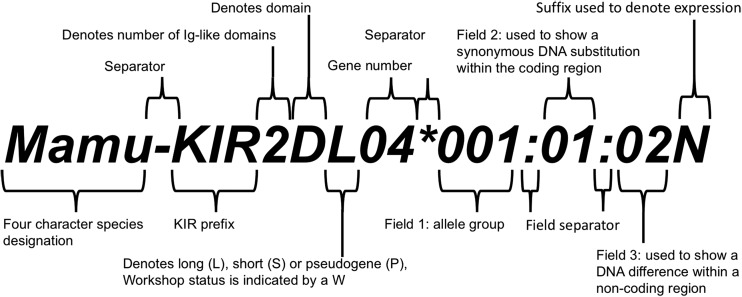
A schematic representation of the syntax for the non-human KIR allele designation is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Non-human KIR nomenclature.
Details the syntax and structure of a non-human KIR allele designation
Species-specific guidelines
Naming rhesus macaque KIR genes
The Mamu-KIR sequences fall into a number of distinct lineages based on phylogenetic analysis. Most sequences correspond to lineage II KIR and are further divided into those encoding KIR that have long cytoplamic tails or short cytoplasmic tails. The genes have been numbered sequentially and where possible the gene name has the same the same number as the first reported allele for that gene. For example, the Mamu-KIR3DL1 gene (Hershberger et al. 2001) was renamed Mamu-KIR3DL01*001.
The nomenclature uses a two-digit numbering of individual genes for the macaque sequences as seen with the naming of Mamu-KIR3DL01*001. This renaming aims to avoid confusion with previous sequence names. Subsequent analysis has shown that some of the proposed sequences of different genes are actually allelic variants of the same gene. Rather than skipping numbers to avoid confusion, it was thought better to introduce the two-digit numbering system.
Recombinant alleles are named according to the locus, which provide the majority of the sequence. For example, the sequence originally named Mamu-KIR3DL5 (Hershberger et al. 2001) is a recombinant of Mamu-KIR3DL01 and Mamu-KIR3DL07. As such, it has been renamed as an allele of Mamu-KIR3DL01, Mamu-KIR3DL01*005. This principal has also been applied to recombinant alleles in other species.
Along with the lineage II KIR genes, rhesus macaques have KIR genes for lineage I, III, and V KIR. The lineage I KIR gene in rhesus macaques is orthologous to other primate lineage 1 KIR, referred to as 2DL4 and has been named Mamu-KIR2DL04. A single lineage III KIR is also present on some Mamu-KIR haplotypes and in all cases appears to be expressed as a one Ig domain KIR. It has been named Mamu-KIR1D. Finally, there is a lineage V KIR gene that is expressed as either a two Ig or three Ig domain KIR. The published genomic sequence shows the gene to contain three Ig domain encoding exons; however, due to splicing out of exon 4, also two Ig domain KIR variants are expressed. The majority of the rhesus macaque gene sequence appears orthologous to hominoid KIR3DL3 sequences, the exception being exon 3 [encoding the D0 domain] which appears more like the hominoid KIR2DL5 sequences. This sequence relationship coupled with the presence of splice variants that lacked exon 4 led to the naming of some of these sequences as Mamu-KIR2DL5. The presence of the intact gene as evidenced by the published genomic sequence, as well as the existence of full-length [three Ig domain containing] sequences has led us to propose naming this gene as Mamu-KIR3DL20. This distinguishes this gene from the remaining Mamu-KIR3DL as well as retaining the name of one of the first mRNA sequences that included all three Ig domain encoding exons, see Table 1 for further details. A full list of Mamu-KIR sequences is described in Table 4.
The identification of sequences in other Macaque species will follow the same rules, and use the species prefix (Mafa-KIR, Mane-KIR), and that genes would be named to match the closest rhesus gene.
Naming chimpanzee KIR genes
Three studies (Abi-Rached et al. 2010; Khakoo et al. 2000; Sambrook et al. 2005) have described complete sequences of three chimpanzee haplotypes. In addition, the analysis of chimpanzee KIR genotypes has inferred the organization of genes infers the existence of another 17 chimpanzee KIR haplotypes. These analyses have defined 13 different Patr-KIR genes.
In all chimpanzee KIR haplotypes, the framework gene at the telomeric end is a lineage II KIR gene. Formerly, two variants, now known to occupy this position, were named Pt-KIR3DL1/2 and Pt-KIR3DL3. The name Pt-KIR3DL1/2 was given to reflect its close relationship to both human KIR3DL1 and KIR3DL2. Although segregation analysis showed that Pt-KIR3DL3 and KIR3DL1/2 were never present on the same haplotype, Pt-KIR3DL3 was given a different name because it has a distinctive sequence. We are renaming the Pt-KIRDl1/2 and Pt-KIR3DL3 as allelic variants of Patr-KIR3DL1, the new name for the framework gene at the telomeric end of the chimpanzee KIR locus. This will allow the Patr-KIR3DL3 name to be given to the gene previously known as Patr-KIRC1, and which is orthologous to human KIR3DL3, the framework gene at the centromeric end of the KIR locus. See Table 2 for further details. A full list of Patr-KIR sequences is described in Table 5.
Naming orangutan KIR genes
In the initial description of orangutan KIR cDNA (Guethlein et al. 2002), the sequences were given letter designations because their relationships, either alleles or genes, were uncertain. Subsequent studies (Guethlein et al. 2007a; Guethlein et al. 2017; Locke et al. 2011; Mager et al. 2001) have provided complete sequences of three orangutan KIR haplotypes, as well as genotyping data that has allowed the structures of two additional KIR haplotypes to be inferred. These genomic data, in combination with the cDNA sequences, defined 11 KIR genes and 1 KIR pseudogene in the orangutan. At first, all orangutan KIR were named as “Popy” (Guethlein et al. 2007b). The orangutan KIR is now divided into two series corresponding to the two species of orangutan: Popy for Pongo pygmaeus and Poab for Pongo abelii depending on species of origin. Some KIR alleles are present in both orangutan species. These alleles shared have been given a different name in each species (Guethlein et al. 2017; Guethlein et al. 2015), see Table 3: for further details. A full list of Popy-KIR and Poab-KIR sequences is given in Table 6.
Naming cattle KIR genes
Assembly of the first cattle KIR haplotype allowed previously known cDNA sequences to be assigned to particular genes and allelic relationships to be defined (Dobromylskyj and Ellis 2007; Guethlein et al. 2007a; Hammond et al. 2016; Mager et al. 2001; Sanderson et al. 2014). This presents the opportunity to adopt an accurate and logical nomenclature system. Cattle KIR cDNA sequences were previously named using the established convention of Ig domain number and tail length. However, these alleles were annotated prior to the discovery of a second deeply divergent KIR lineage, the KIR3DX lineage (Guethlein et al. 2007a). The majority of the expanded cattle KIR belong to this second lineage. In developing a nomenclature system for the cattle KIR, we have incorporate their lineage ancestry within the name. Cattle KIR have been prefixed with a four-letter species designation “Bota” (Bos taurus) in line with non-human primates. Where possible previously named Bota-KIR has retained the same name with only the addition of an “X” after the domain number if from the KIR3DX lineage. There are three exceptions; Bota-KIR3DL1P and Bota-KIR3DL3, which are allelic, and Bota-KIR3DL2. These previously described cDNA sequences are all members of the KIR3DX lineage. Based on their position in the cattle haplotype and their relationships to other genes, Bota-KIR3DL1P was renamed Bota-KIR3DXL6*001N, Bota-KIR3DL3 was renamed Bota-KIR3DXL6*002, and Bota-KIR3DL2 was renamed Bota-KIR3DXL4. We have identified 16 cattle KIR genes. The proposed nomenclature for cattle KIR is given in Table 7.
Future guidelines
The sequences described in this report will be included in the Immuno Polymorphism Database (IPD) (Robinson et al. 2013). They will be maintained as a component of the IPD and be accessible at https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ipd/nhkir/. New sequences for any of the above species can be submitted using the current submission tool. As with the other databases, there are requirements that should be met before formal names can be given and the submitted KIR are included in the database. First, submission of full-length sequences is encouraged and for some species like rhesus macaque is already mandatory. Second, novel sequences must be confirmed, either through their replication in multiple individuals or at a minimum by coming from multiple independent PCR/cloning experiments. Full guidelines for submission of non-human KIR sequences to IPD can be found at https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ipd/nhkir/submission/help.
As KIR sequence data from other species reaches the level of the species included in this report, those species can be included in the database. The inclusion of a species will be at the discretion of the Nomenclature Committee and IPD and will be based on the number of sequences available as well as evidence of identified genes and haplotype structure.
Funding
JAH and NDS were supported by the United Kingdom Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) through projects BBS/E/I/00001410 and BBS/E/I/00001710.
References
- Abi-Rached L, Moesta AK, Rajalingam R, Guethlein LA, Parham P. Human-specific evolution and adaptation led to major qualitative differences in the variable receptors of human and chimpanzee natural killer cells. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1001192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen H, Rossio JL, Coalter V, Poore B, Martin MP, Carrington M, Lifson JD. Characterization of rhesus macaque natural killer activity against a rhesus-derived target cell line at the single-cell level. Cell Immunol. 2004;231:85–95. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2004.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson DA, Cavanaugh M, Clark K, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Sayers EW. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D37–D42. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blokhuis JH, Doxiadis GG, Bontrop RE. A splice site mutation converts an inhibitory killer cell Ig-like receptor into an activating one. Mol Immunol. 2009;46:640–648. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.08.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blokhuis JH, van der Wiel MK, Doxiadis GG, Bontrop RE. Evidence for balancing selection acting on KIR2DL4 genotypes in rhesus macaques of Indian origin. Immunogenetics. 2009;61:503–512. doi: 10.1007/s00251-009-0379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blokhuis JH, van der Wiel MK, Doxiadis GG, Bontrop RE. The mosaic of KIR haplotypes in rhesus macaques. Immunogenetics. 2010;62:295–306. doi: 10.1007/s00251-010-0434-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostik P, Kobkitjaroen J, Tang W, Villinger F, Pereira LE, Little DM, Stephenson ST, Bouzyk M, Ansari AA. Decreased NK cell frequency and function is associated with increased risk of KIR3DL allele polymorphism in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques with high viral loads. J Immunol. 2009;182:3638–3649. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaichompoo P, Bostik P, Stephenson S, Udompunturuk S, Kobkitjaroen J, Pattanapanyasat K, Ansari AA. Multiple KIR gene polymorphisms are associated with plasma viral loads in SIV-infected rhesus macaques. Cell Immunol. 2010;263:176–187. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2010.03.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chojnacki S, Cowley A, Lee J, Foix A, Lopez R. Programmatic access to bioinformatics tools from EMBL-EBI update: 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:W550–W553. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantonio AD, Bimber BN, Neidermyer WJ, Jr, Reeves RK, Alter G, Altfeld M, Johnson RP, Carrington M, O'Connor DH, Evans DT. KIR polymorphisms modulate peptide-dependent binding to an MHC class I ligand with a Bw6 motif. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1001316. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot NG, Otting N, Robinson J, Blancher A, Lafont BA, Marsh SGE, O'Connor DH, Shiina T, Walter L, Watkins DI, Bontrop RE. Nomenclature report on the major histocompatibility complex genes and alleles of great ape, old and new world monkey species. Immunogenetics. 2012;64:615–631. doi: 10.1007/s00251-012-0617-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobromylskyj M, Ellis S. Complexity in cattle KIR genes: transcription and genome analysis. Immunogenetics. 2007;59:463–472. doi: 10.1007/s00251-007-0215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis SA, Bontrop RE, Antczak DF, Ballingall K, Davies CJ, Kaufman J, Kennedy LJ, Robinson J, Smith DM, Stear MJ, Stet RJ, Waller MJ, Walter L, Marsh SGE, Committee II-VCMN. ISAG/IUIS-VIC comparative MHC nomenclature committee report, 2005. Immunogenetics. 2006;57:953–958. doi: 10.1007/s00251-005-0071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grendell RL, Hughes AL, Golos TG. Cloning of rhesus monkey killer-cell Ig-like receptors (KIRs) from early pregnancy decidua. Tissue Antigens. 2001;58:329–334. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2001.580507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guethlein LA, Abi-Rached L, Hammond JA, Parham P. The expanded cattle KIR genes are orthologous to the conserved single-copy KIR3DX1 gene of primates. Immunogenetics. 2007;59:517–522. doi: 10.1007/s00251-007-0214-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guethlein LA, Flodin LR, Adams EJ, Parham P. NK cell receptors of the orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus): a pivotal species for tracking the coevolution of killer cell Ig-like receptors with MHC-C. J Immunol. 2002;169:220–229. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.1.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guethlein LA, Norman PJ, Heijmans CM, de Groot NG, Hilton HG, Babrzadeh F, Abi-Rached L, Bontrop RE, Parham P. Two orangutan species have evolved different KIR alleles and haplotypes. J Immunol. 2017;198:3157–3169. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1602163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guethlein LA, Norman PJ, Hilton HG, Parham P. Co-evolution of MHC class I and variable NK cell receptors in placental mammals. Immunol Rev. 2015;267:259–282. doi: 10.1111/imr.12326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guethlein LA, Older Aguilar AM, Abi-Rached L, Parham P. Evolution of killer cell Ig-like receptor (KIR) genes: definition of an orangutan KIR haplotype reveals expansion of lineage III KIR associated with the emergence of MHC-C. J Immunol. 2007;179:491–504. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond JA, Carrington M, Khakoo SI. A vision of KIR variation at super resolution. Immunology. 2016;148:249–252. doi: 10.1111/imm.12606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellmann I, Lim SY, Gelman RS, Letvin NL. Association of activating KIR copy number variation of NK cells with containment of SIV replication in rhesus monkeys. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002436. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershberger K, Shyam R, Miura A, Letvin N. Diversity of the killer cell Ig-like receptors of rhesus monkeys. J Immunol. 2001;166:4380–4390. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.7.4380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakoo SI, Rajalingam R, Shum BP, Weidenbach K, Flodin L, Muir DG, Canavez F, Cooper SL, Valiante NM, Lanier LL, Parham P. Rapid evolution of NK cell receptor systems demonstrated by comparison of chimpanzees and humans. Immunity. 2000;12:687–698. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J, Bontrop RE, Dawkins RL, Erlich HA, Gyllensten UB, Heise ER, Jones PP, Parham P, Wakeland EK, Watkins DI. Nomenclature for the major histocompatibility complexes of different species: a proposal. Immunogenetics. 1990;31:217–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00204890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse PH, Rosner C, Walter L. Characterization of rhesus macaque KIR genotypes and haplotypes. Immunogenetics. 2010;62:281–293. doi: 10.1007/s00251-010-0433-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke DP, Hillier LW, Warren WC, Worley KC, Nazareth LV, Muzny DM, Yang SP, Wang Z, Chinwalla AT, Minx P, Mitreva M, Cook L, Delehaunty KD, Fronick C, Schmidt H, Fulton LA, Fulton RS, Nelson JO, Magrini V, Pohl C, Graves TA, Markovic C, Cree A, Dinh HH, Hume J, Kovar CL, Fowler GR, Lunter G, Meader S, Heger A, Ponting CP, Marques-Bonet T, Alkan C, Chen L, Cheng Z, Kidd JM, Eichler EE, White S, Searle S, Vilella AJ, Chen Y, Flicek P, Ma J, Raney B, Suh B, Burhans R, Herrero J, Haussler D, Faria R, Fernando O, Darre F, Farre D, Gazave E, Oliva M, Navarro A, Roberto R, Capozzi O, Archidiacono N, Della Valle G, Purgato S, Rocchi M, Konkel MK, Walker JA, Ullmer B, Batzer MA, Smit AF, Hubley R, Casola C, Schrider DR, Hahn MW, Quesada V, Puente XS, Ordonez GR, Lopez-Otin C, Vinar T, Brejova B, Ratan A, Harris RS, Miller W, Kosiol C, Lawson HA, Taliwal V, Martins AL, Siepel A, Roychoudhury A, Ma X, Degenhardt J, Bustamante CD, Gutenkunst RN, Mailund T, Dutheil JY, Hobolth A, Schierup MH, Ryder OA, Yoshinaga Y, de Jong PJ, Weinstock GM, Rogers J, Mardis ER, Gibbs RA, et al. Comparative and demographic analysis of orang-utan genomes. Nature. 2011;469:529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature09687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maccari G, Robinson J, Ballingall K, Guethlein LA, Grimholt U, Kaufman J, Ho CS, de Groot NG, Flicek P, Bontrop RE, Hammond JA, Marsh SGE. IPD-MHC 2.0: an improved inter-species database for the study of the major histocompatibility complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D860–D864. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager DL, McQueen KL, Wee V, Freeman JD. Evolution of natural killer cell receptors: coexistence of functional Ly49 and KIR genes in baboons. Curr Biol. 2001;11:626–630. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh SGE, Parham P, Dupont B, Geraghty D, Trowsdale J, Middleton D, Vilches C, Carrington M, Witt C, Guethlein L, Shilling H, Garcia C, Hsu K, Wain H. Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) nomenclature report, 2002. Tissue Antigens. 2003;62:79–86. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashima J, Kodama Y, Fujisawa T, Katayama T, Okuda Y, Kaminuma E, Ogasawara O, Okubo K, Nakamura Y, Takagi T. DNA data bank of Japan. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D25–D31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen KL, Wilhelm BT, Harden KD, Mager DL. Evolution of NK receptors: a single Ly49 and multiple KIR genes in the cow. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:810–817. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200203)32:3<810::AID-IMMU810>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland AJ, Guethlein LA, Reeves RK, Broman KW, Johnson RP, Parham P, O'Connor DH, Bimber BN. Characterization of killer immunoglobulin-like receptor genetics and comprehensive genotyping by pyrosequencing in rhesus macaques. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:295. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor diversity: balancing signals in the natural killer cell response. Immunol Lett. 2004;92:11–13. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2003.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajalingam R, Hong M, Adams EJ, Shum BP, Guethlein LA, Parham P. Short KIR haplotypes in pygmy chimpanzee (Bonobo) resemble the conserved framework of diverse human KIR haplotypes. J Exp Med. 2001;193:135–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J, Halliwell JA, McWilliam H, Lopez R, Marsh SGE. IPD—the Immuno polymorphism database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D1234–D1240. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J, Bashirova A, Palmer S, Sims S, Trowsdale J, Abi-Rached L, Parham P, Carrington M, Beck S. Single haplotype analysis demonstrates rapid evolution of the killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) loci in primates. Genome Res. 2005;15:25–35. doi: 10.1101/gr.2381205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook JG, Bashirova A, Andersen H, Piatak M, Vernikos GS, Coggill P, Lifson JD, Carrington M, Beck S. Identification of the ancestral killer immunoglobulin-like receptor gene in primates. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:209. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson ND, Norman PJ, Guethlein LA, Ellis SA, Williams C, Breen M, Park SD, Magee DA, Babrzadeh F, Warry A, Watson M, Bradley DG, MacHugh DE, Parham P, Hammond JA. Definition of the cattle killer cell Ig-like receptor gene family: comparison with aurochs and human counterparts. J Immunol. 2014;193:6016–6030. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storset AK, Slettedal IO, Williams JL, Law A, Dissen E. Natural killer cell receptors in cattle: a bovine killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor multigene family contains members with divergent signaling motifs. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:980–990. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimin AV, Delcher AL, Florea L, Kelley DR, Schatz MC, Puiu D, Hanrahan F, Pertea G, Van Tassell CP, Sonstegard TS, Marcais G, Roberts M, Subramanian P, Yorke JA, Salzberg SL. A whole-genome assembly of the domestic cow, Bos taurus. Genome Biol. 2009;10:R42. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-4-r42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]