Fig. 5.
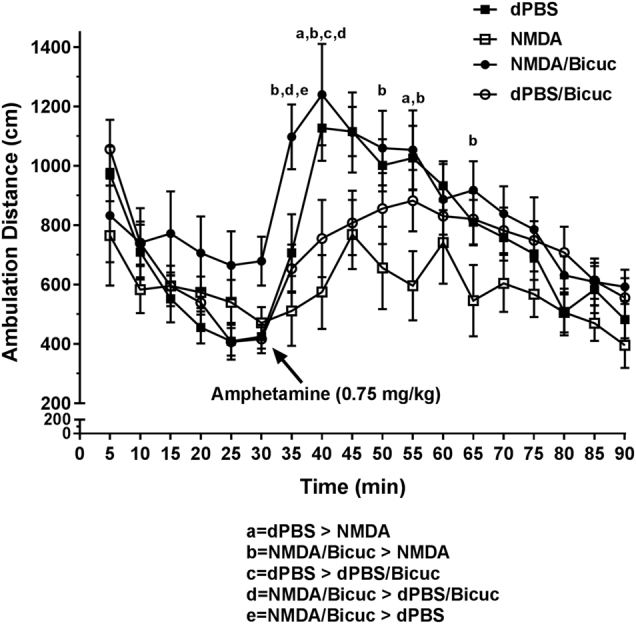
MS activation decreases amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion via GABAergic inputs to vSub. NMDA (0.75 µg in 0.2 µL) activation of the MS had no effect on basal locomotor behavior, but reduced locomotion following amphetamine injection (0.75 mg/kg; a = Bonferroni test P < 0.05). Bicuculline (Bicuc; 12.5 ng in 0.5 µL) infusion into the vSub just prior to MS activation prevented the decrease in amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion, restoring locomotor behavior back up to and beyond vehicle (dPBS) levels (b–e = Bonferroni test P < 0.05).
