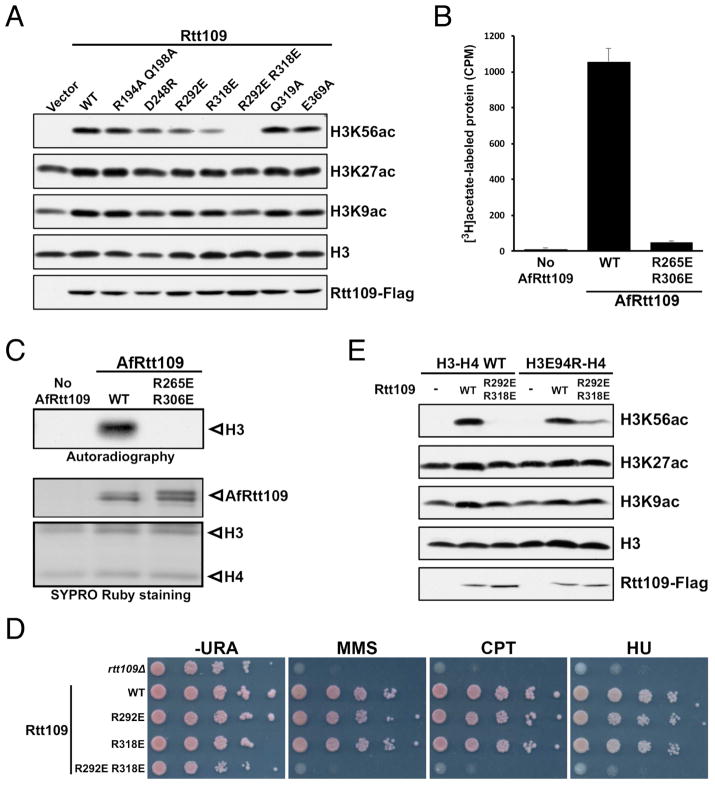
Figure 7. Rtt109 residues important for H3K56 acetylation.
(A) Western blot analysis of H3K56, H3K27 and H3K9 acetylation in budding yeast cells expressing the indicated Rtt109 mutants. (B) In vitro HAT activity assay of the corresponding AfRtt109 mutants detected by autoradiography. (C) Quantitation of the in vitro HAT activities of the WT and mutant AfRtt109 proteins using the AfAsf1-H3-H4 complex as the substrate. (D) Budding yeast cells expressing the R292E R318E mutant of ScRtt109 are sensitive to DNA-damaging agents like rtt1093Δ cells. (E) Partial rescue of H3K56ac in yeast cells by co-expressing indicated charge-swap mutants of ScRtt109 and H3. See also Figure S7; Tables S2, S3.