Figure 1.
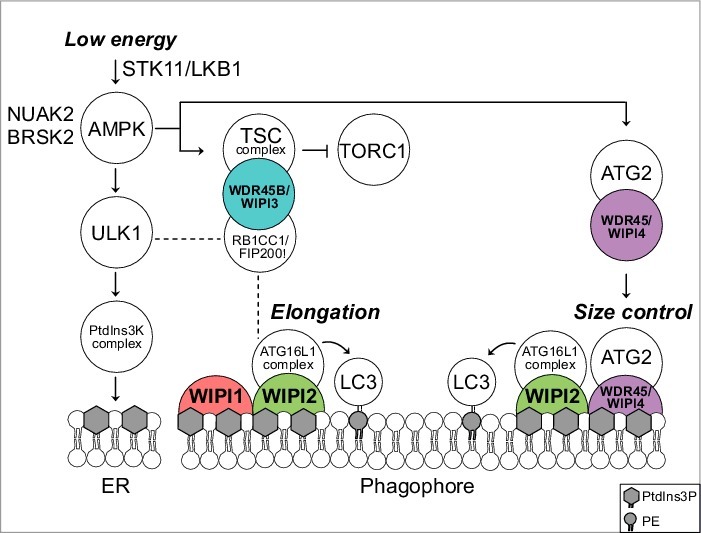
Predicted model for a functional WIPI scaffold circuit at the nascent autophagosome under the control of AMPK. Low energy stimulates the STK11/LKB1-AMPK axis to initiate catabolic pathways, thereby activating autophagy through ULK1. Downstream, the class III PtdIns3K, PIK3C3VPS34, a member of the PtdIns3K complex, produces PtdIns3P at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). This stimulates the formation of omegasomes (not shown) and phagophores (template membranes that elongate and close to form the autophagosome) through an as yet unidentified mechanism. Phagophore elongation is achieved through the PtdIns3P effector activity of WIPI2, that recruits the ATG16L1 complex for subsequent LC3 lipidation. WIPI1 assists WIPI2 in this function. Phagophore expansion is size controlled by WDR45/WIPI4-ATG2 that dissociates from AMPK-ULK1 upon AMPK activation. TORC1 inhibition is achieved through AMPK-mediated phosphorylation of TSC2 that in complex with WDR45B/WIPI3 (and RB1CC1/FIP200) displaces TORC1 from the lysosomal surface. Both AMPK-related kinases NUAK2 and BRSK2 produce a direct signal to WDR45/WIPI4 but the details are unknown. Dashed lines indicate known interactions that have not been addressed in the study described. PE, phosphatidylethanolamine.
